In what cases does low urine density occur?
For patients undergoing treatment for infectious diseases or gastrointestinal diseases, doctors recommend consuming liquid in large quantities to replenish the body's reserves.
This leads to the development of hyposthenuria - a decrease in the relative density of urine below normal. A factor such as drinking plenty of fluids, for example, in the hot season, is a physiological factor, so a decrease in the amount of dry residue is not a deviation. Such a deviation from the norm also occurs due to the use of natural or medicinal diuretics. In addition to physiological, there are pathological causes, which mainly take the form of diabetes insipidus of various origins:
- neurogenic character. In the absence of proper treatment, the patient experiences constant dehydration;
- nephrogenic character. With this type of disease, a disruption of the urinary system occurs due to a lack of response to the antidiuretic hormone;
- in pregnant women. This disease goes away after the birth of the child;
- due to nervousness. Develops due to nervous breakdowns. Prolonged depression and constant exposure to stressful situations are considered favorable conditions for the onset of the disease;
- the presence of problems in the functioning of the excretory system of a chronic nature. Due to such diseases, the processes of filtration and removal of urine from the body fail;
- pyelonephritis or other inflammatory kidney diseases.
Nervous breakdowns and prolonged depression cause low urine density.
If in tests the specific gravity of urine is low, that is, less than 1.015, specialists have every reason to talk about the presence of hyposthenuria. With this diagnosis, a thorough examination is required to establish the factors that provoke a decrease in the activity of the paired organ and their function in terms of the concentration of dry residue.
What do the tests say?
Functional abnormalities in the vital system are best identified by clinical laboratory tests . They help to find a malfunction in the body and identify the source of infection. And also, correctly diagnose the disease and start therapy in a timely manner.
That is why the doctor first of all writes out a referral for tests. They provide more than 60% of the information about the disease.
The most basic tests are blood, urine and stool. Without them, it is impossible to select a treatment regimen that is suitable for this particular patient.
A blood test detects a number of serious diseases of the immune system. Stool examination helps diagnose gastrointestinal diseases. And when checking urine, a number of diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary system are revealed.
Normal Specific Gravity Values
As mentioned above, this indicator determines the activity of the kidneys to dilute or concentrate urine. It depends on the amount drunk, spent and on the ambient temperature. There are even a number of factors that predispose to changes in specific gravity.
- The patient's consumption of salt, fatty and fried foods.
- Change in the amount you drink.
- Strong sweating due to various reasons.
- Separation of fluid during breathing.
Urine analysis, the specific gravity of which varies from 1.010 to 1.025, is normal for an adult. In children, the density differs somewhat from that in adults and is related to age. As soon as the child is born, its indicator has the lowest value and is 0.010. As the baby grows, the density of his urine increases. It is worth noting that the time of day is also reflected in the indicator. For example, in the morning the density is highest, since there is the greatest amount of dry sediment at the moment.
Increased density of urine: causes and what it means
When a patient contacts a specialist with any disease, first of all, a urine test is prescribed for research on various indicators. This is necessary for maximum information in diagnosing the disease; this analysis also indicates the state of various systems in the patient’s body.
Loading …
Urine is evaluated according to various parameters, transparency, color, impurities and other indicators. One of the most important values is the density of urine, which in the presence of diseases or pathologies can decrease or increase.
What does an increase in the density of human urine mean?
With an increase in the relative density of urine, specialists, during a general analysis in the laboratory, detect in the studied samples dissolved and insoluble substances that are part of the fluid excreted by a person.
The more of these components are present in urine, the higher its relative density.
If a general examination in a clinical laboratory reveals increased density of urine, in such cases patients are prescribed a number of additional diagnostic procedures.
The most common method for studying the relative density of urine is the Zimnitsky test, which allows, among other indicators, to evaluate kidney function, their concentration and urinary ability.
This diagnostic analysis technique allows you to determine the density of urine collected at a certain period of time during the day.
An increase in the density of the test sample is also indicated by the general analysis, which most often reveals a change in normal parameters.
The morning portion of the fluid excreted by the patient, which accumulated all night in his body, is not examined. The collection of biomaterial begins from the second urination after waking up and beyond.
It is necessary to collect fluid every 3 hours, starting at 9 a.m., so the patient collects 8 portions per day. Each of them is examined in the laboratory for certain indicators, including excess density and specific gravity.
When collecting liquid, a person must adhere to their usual diet and be sure to record the amount of liquid taken.
More on the topic: Why does the urine turn dark?
What do density indicators mean in tests?
Having received the results from the laboratory, people ask themselves the question: the relative density of urine is increased, what does this mean? If, after tests, an increased density of urine is revealed (above 1.035), a diagnosis of hypersthenuria is made. This phenomenon means that the permissible specific gravity of the released liquid is exceeded.
In clinical medicine there are normalizing indicators that depend on the patient’s age:
- in infants the first 10 days of life - from 1.008 to 1.018;
- in children under 3 years of age these figures range from 1.010 to 1.017;
- at the age of 4-5 years, the indicators vary from 1.012 to 1.020;
- for an adult, the normal value ranges from 1.010 to 1.025.
During the day, density indicators fluctuate. The reasons are physiological in nature - in the morning they are higher due to the lack of fresh fluid entering during the night and the concentration of urine in the body. During the daytime, the specific density is lowest, since the liquid is released in the largest volumes.
Why does urine density increase?
Several factors contribute to an increase in the density and specific gravity of urine, which differ for children, pregnant women and adults. Deviations can be either physiological or pathological.
Pathological causes are associated with the development of diseases in the body, and physiological ones depend on temporary factors of human life in the form of increased sweating, intake of a significant amount of fluid, and so on.
Hypersthenuria in pregnant women
A woman carrying a child experiences toxicosis, which is an acceptable indicator for this particular condition for her body. It is toxicosis that causes hypersthenuria, since fluid is retained in the vital systems, which specialists associate with gestosis. The presence of gestosis especially provokes an increase in urine density.
Hypersthenuria in children
In a child, the specific gravity of urine increases with kidney disease and changes in the kidney tissue. Quite often, intestinal infections appear in the child’s body or intoxication occurs due to prolonged vomiting or diarrhea.
More on the topic: What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
During these processes, severe dehydration of the child’s entire body occurs, which increases the density of urine. The specific gravity of urine is greatly increased in the first days of the baby, but doctors point to the physiological reasons for this deviation, and within 24 hours the tests come to acceptable levels.
Hypersthenuria in adults
In an adult patient, an increase in the density of the secreted fluid occurs due to a number of factors. Clinical practice has revealed the most common causes:
- Development of proteinuria and protein excretion in the urine;
- Elevated glucose levels, which often occurs with diabetes. This condition is called glucosuria by specialists;
- Kidney failure, glomerulonephritis, nephritis, cystitis and other infectious pathologies;
- A course of treatment with medications that are excreted by the body too intensively. These drugs include all antibiotics and diuretics.
- Dehydration and lack of fluid in the body, especially in cases where the patient takes very little water per day;
- Dehydration of a severe organic type, associated with being in a hot room, with severe sweating, vomiting and prolonged diarrhea.
By and large, the density of urine is the same for all patients, regardless of age and gender. To identify the root causes of the disorder, a Zimnitsky test should be analyzed, which will also indicate existing problems with the kidneys and examine their functionality.
With a strong decrease in the specific gravity of urine relative to acceptable values, hyposthenuria occurs when the lower limits of the specific gravity drop significantly relative to the lower limits of normal values.
This condition occurs in a patient who has begun to significantly increase the daily volume of fluid in any form - juices, water or tea. Males often abuse beer, which affects the density of urine.
Pathologies that are present in the body may also have an impact:
- diabetes;
- restoration of edema infiltrates after inflammation;
- low-calorie diet with a small amount of vitamins and enzymes, dystrophy;
- pyelonephritis in the chronic stage;
- interstitial nephritis, glomerulonephritis;
- exceeding the dosage of diuretics;
- excessive intake of liquids during the day.
More on the topic: What is the norm of red blood cells in urine?
Hypo- and hypersthenuria cause a lot of negative consequences for the body, which requires its timely detection and treatment. Diagnosis is carried out using the Zimnitsky method, as well as a general analysis.
Actions when urine density changes
Treatment is carried out in a hospital or on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a nephrologist or endocrinologist, as well as a pediatrician in case of illness in children. There are often cases when hypersthenuria accompanies diabetes mellitus, since high glucose in the blood provokes the consumption of large volumes of water, which disrupts the functioning of the kidneys and organs of the urinary system.
The patient with this disease must strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations so as not to cause complications and problems with treatment. Medicines prescribed by a doctor are aimed at effectively eliminating the cause of this disease with minimal impact on other body systems.
In cases of kidney failure, you must follow the diet recommended by your doctor and adhere to the basic rules of a healthy lifestyle. Spices and pickles, smoked meats and spicy foods, which irritate the organs and prevent the outflow of fluid, are excluded from the diet. In the chronic stage, it is necessary to donate blood and urine for analysis every 2-3 months.
responded with an error: The request cannot be completed because you have exceeded your quota. Rate this post: Loading...
Source: https://onefr.ru/organy/mochevoj-puzyr/chto-eto-znachit-kogda-povyshena-otnositelnaya-plotnost-mochi.html
Specific Gravity - Urine
The specific gravity of urine depends on the ratio of dry matter and water in it.
The specific gravity of urine normally ranges from 1010 to 1025, more often it is 1017 to 1020 and is closely related to the amount of urine excreted. Under various pathological conditions, the specific gravity of urine may change. A discrepancy between the specific gravity and the amount of urine is observed in diabetes mellitus, when, despite a large amount of urine, its specific gravity remains high.
If the specific gravity of urine is high, then a second type of urometer is used for testing. All determinations are usually carried out at a temperature of 15, since the urometer scale is mostly calibrated at this temperature. If the urine has a different temperature and for some reason it is difficult to bring it to 15, then for every 3 above this temperature you need to add, and for every 3 below, subtract 0.001 from the urometer scale reading.
The specific gravity of urine depends on the ratio between the amount of solid substances and water. During the day, dense substances are excreted in relatively constant quantities, but the amount of excreted water fluctuates widely and depends on the amount injected and excreted by the kidneys and skin. When drinking heavily, the specific gravity of a person's urine can drop to 1002; with moderate drinking and heavy sweating, it can rise to 1030 and higher.
The specific gravity of urine is measured. If the specific gravity is less than 1018, then 300 ml of urine is diluted to 50 ml in a volumetric flask with distilled water that does not contain ammonia. If the specific gravity is equal to or greater than 1018, then 300 ml of urine is diluted to 100 ml. After mixing, pipette 100 ml of diluted urine into a Pyrex glass tube measuring 25x200 mm.
Determination of the specific gravity of urine is of great diagnostic importance for diabetes mellitus, impaired renal function and a number of other diseases. The specific gravity of urine also depends on the amount of water consumed.
To determine the specific gravity of urine, special hydrometers called urometers are used. To determine the specific gravity, the test urine is poured into a cylinder and a urometer for low specific gravity urine is immersed in it. If the scale of this urometer is not immersed in urine at all, then the specific gravity is determined using a urometer for urine with a high specific gravity.
The specific gravity of urine is determined more accurately using a pycnometer.
The specific gravity of urine is determined in the cylinder using a hydrometer and, if it is above 1,030, the test urine is diluted 10 times, and if lower - 5 times.
Inextricably linked with the registration of diuresis is the determination of the specific gravity of urine, which characterizes the concentration ability of the kidneys. With good concentrating ability of the kidneys, impaired water excretion most often indicates the presence of extrarenal influences. The most important sign of renal failure is a violation of the concentrating ability of the kidneys, which is expressed in the phenomena of hyposthenuria or isosthenuria.
Inextricably linked with the registration of diuresis is the determination of the specific gravity of urine, which characterizes the concentration ability of the kidneys. With good concentrating ability of the kidneys, impaired water excretion most often indicates the presence of extrarenal influences. The most important sign of renal failure is a violation of the concentrating ability of the kidneys, which is expressed in the phenomena of hyposthenuria or isosthenuria.
B - 1), where B is the specific gravity of urine; 115 — conversion factor; D is the weight of daily urine in grams, determined by multiplying diuresis by specific gravity (B); m is body weight in kilograms.
In chronic nephritis, when the excretory function of the kidneys is impaired, the specific gravity of urine is reduced.
A floating urinometer is a simple hydrometer calibrated to determine the specific gravity of urine.
In addition to increased diuresis, there is an increased secretion of urea and uric acid, a decrease in the acidity and specific gravity of urine, and the appearance of protein is also noted. When lithium enters the body, the replacement of sodium ions with lithium ions is observed, similar to the replacement of chlorides with bromides, as a result of which there is an increased excretion of sodium and potassium from the body of animals.
The process of urine formation
In addition, it has been proven that the relative density of urine is considered an excellent assistant for assessing the functioning of the kidneys (to find out and evaluate their filtration function).
Few people know that the formation of urine in the body occurs through two stages. At the very beginning, primary urine is formed. It directly passes through the glomerulus, which has a large number of capillaries through which blood moves.
This process is carried out under the influence of high pressure, as a result of which blood cells and complex proteins are purified from water, nutrients or sugars.
The amount of primary urine in 1 day is 150 or 180 liters. Then it moves through the nephron tubules, which are considered the main structural and functional units of the kidneys. Here the urine will undergo reabsorption (the process of reabsorption of liquid), which means that, thanks to high pressure, water will begin to be reabsorbed into the tubules. And all the beneficial substances will be able to enter the body again.
The remaining liquid, where dissolved urea, ammonia and other substances will be present, is considered to be secondary urine. Regularly in the human body, it moves through the collecting ducts, then into the renal calyx systems (small and large), then through the renal pelvis and ureter. After passing through the ureter, the fluid accumulates in the bladder. The last stage of the movement of secondary urine is its removal from the body.
d8_8gKG9O0w
Urine color and density
The approximate density of urine can be determined independently: by color. They also pay attention to this indicator during analysis. Light yellow color is considered the norm. Therefore, if the liquid is almost transparent (the color of water), dark yellow, red and especially black, you should urgently consult a doctor to determine the cause. It should be noted that even urine that has a normal color can hide serious deviations in health (only special tests can reveal them).
Concepts such as urine color and density are closely related: the darker the color of the urine, the higher its relative density. Normally, urine should remain clear throughout the entire period of storage. However, you should not be alarmed right away, since a cloudy color occurs when the material is collected incorrectly, when mucus or cellular debris gets into the urine.
The following situations can cause cloudy urine in adults and children:
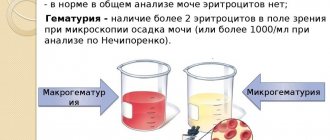
- The presence of red blood cells in the urine, which is observed in kidney disease, urolithiasis, bladder cancer, prostatitis.
- Leukocytes in the urine, which is a consequence of cystitis, pyelonephritis and some other diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Increased number of bacteria in the genitourinary system.
Also, cloudy urine can be due to a high number of epithelial cells, the appearance of which can be caused by the diseases mentioned above. A large number of precipitated salts - urates, oxalates, phosphates, is also the reason that the relative density of urine becomes higher than normal and is characterized by a cloudy color.
Average urine test results in children
1. Specific gravity of urine. Reference values for urine specific gravity vary depending on the age of the child. In a normal urine test in children, the specific gravity is:
- in newborns – 1018;
- up to two years – 1002–1004;
- from two to three – 1010–1017;
- from four to five – 1012–1020;
- from ten years of age – 1011–1025 (the same indicator is considered the norm for an adult).
If the specific gravity of urine exceeds the normal value, this indicates dehydration. If the specific gravity is below normal, this indicates an inflammatory process.
2. Complete transparency of urine is normal. If there is cloudiness, this indicates a urinary tract infection, the presence of leukocytes, red blood cells, salts, mucus, and blood in the urine.
3. The normal color of urine is from light yellow to amber. In newborns, the urine is colorless, and in infants it is lighter than in older children. If the child has toxicosis, hepatitis or another liver disease, the urine is dark in color. The color of urine is also affected by food, for example, when eating beets, the urine acquires a reddish tint. Taking certain medications can also change the normal color of urine.
4. When examining children's urine, the strong smell of ammonia indicates inflammation of the bladder, and the smell of rotten apples indicates the presence of ketone bodies.
5. The acidity (PH) of the urine of a healthy child depends on his diet and ranges from 4.8–7.5. If, when analyzing urine in children, the acidity level is higher than normal, this may indicate renal failure, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis of the bladder or lungs. With diarrhea, vomiting, pyelonephritis, an alkaline reaction of urine occurs.
6. When deciphering the results of a urine test, you should remember that there should be no protein in the urine of a healthy child. The presence of protein in the urine indicates inflammatory kidney disease or kidney failure.
7. The appearance of ketone bodies (acetone) in children's urine indicates diarrhea, anemia, elevated body temperature, nervous or physical fatigue.
8. Normally, there should be no glucose (sugar) in the urine. The maximum permissible value is 0.2%. If the value is higher, then this indicates diabetes mellitus or other diseases of the endocrine system.
9. Red blood cells should not be detected in the urine of a healthy child; normally, only single elements may be present. The detection of a large number of red blood cells in the urine indicates kidney disease, inflammation of the bladder, and tuberculosis.
10. Single leukocytes in the urine are normal. The presence of more than three leukocytes in the field of view indicates an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system.
11. Bilirubin in urine is determined in case of liver disease or difficulty in the outflow of bile. Normally it is absent.
12. When examining urine sediment, epithelial cells are almost always found. The acceptable limit is up to 10 cells in the field of view. The epithelium enters the urine from the reproductive system, bladder or kidneys. If the number of cells from the bladder is higher than normal, then this indicates possible inflammation of the bladder, neoplasms in the urinary tract, or urolithiasis. An increase in the number of kidney cells is detected during fever, intoxication, and infectious diseases.
13. A large amount of mucus in the urine sediment in children indicates an inflammatory process or improper preparation for taking urine for analysis.
14. Single crystals of salt may be present in the urine sediment of a healthy child. If salts are detected in the urine above normal, additional examination is necessary to determine the type of salt (calcium phosphate, calcium oxalate).
If the transcript of your child’s urine test shows results that differ from the norm, you should not immediately panic and suspect serious illnesses. It's better to retake the test again.
What is the density of urine?
Urine density testing measures the ability of the kidneys to increase and decrease the specific gravity of urine. This analysis is part of a general urinalysis, as well as a urine analysis according to Zimnitsky.
By the density of the urine of adults and children, one can judge the content or concentration of various dissolved substances in it. In most cases, density is determined using an instrument such as a refractometer. It allows you to find out the density of urine under a directed beam of light. This method is much more reliable than the float method, which measures density by the speed at which the liquid pushes the float to the surface.
The normal density of urine is 1005-1030 g/l. These figures are compared with the density of distilled water, which is 1000 g/l. Based on this, the relative density of urine can never be lower than a thousand grams per liter, since it is water with substances dissolved in it that increase its density.
The density of urine in children depends on age. The kidneys of young children are not yet capable of strongly concentrating urine, so their indicators are lower than those of adults, and are:
- in newborns: from 1001 to 1005 g/l;
- 6 months: from 1005 to 1015 g/l;
- up to 2 years: from 1004 to 1006 g/l;
- from 2 to 5 years: from 1012 to 1020 g/l;
- from 5 to 12 years: from 1011 to 1025 g/l;
- over 12 years old and adults: from 1010 to 1020 g/l.
During breastfeeding in babies, the specific gravity of urine may increase if the mother eats a lot of fatty and meaty foods. And, conversely, the specific gravity of urine in infants decreases if a woman consumes an increased amount of vegetables and fruits during lactation.
The specific gravity of urine in women is lower than in men. But during pregnancy, the specific gravity of urine in women fluctuates greatly and ranges from 1003 to 1035 g/l.
These fluctuations depend on many factors, which can even include the weather and time of year, as well as what phase of pregnancy the woman is in. In the first half of pregnancy, if a woman has toxicosis, the density of urine is greatly reduced. This indicator will also be lower than normal if a pregnant woman has high protein levels in her blood or has diabetes.
How is urine analysis performed?
Urinary excretions are products of metabolic processes.
They are formed from blood filtered by the kidneys. An aqueous solution of electrolytes (92-99% water) contains organic particles. It has many components. Every day, kidney filters remove urea and salts from the body. A urine test diagnoses the functionality of the kidneys and the whole body. It also helps to evaluate the effectiveness of already prescribed therapy. Why? Because metabolic processes affecting the specific gravity of urine go through several stages:
- The constituent elements of the blood are filtered, so primary urine is similar to plasma, but contains macroparticles (glycogen, protein, fat).
- Reabsorption occurs in the tubules. That is, beneficial substances are absorbed back into the bloodstream.
- The residual fluid forms secondary urine. It is just eliminated by urination.
To determine the weight of urine output in adults or children, a urometer is used. But to assess kidney function, tests are performed:
Zimnitsky;
The analysis checks the activity of renal function in men/women who do not change their drinking regime. Collect secretions every 3 hours. So in a day you should collect 8 samples of urine. Using a urometer, the average value of the indicators is determined. Normally, the amount of nighttime diuresis differs by 30% from daytime.
Concentration;
In this case, patients change their drinking regime, completely eliminating the consumption of any liquid during the day. To prevent hunger, they are given protein foods. If the patient cannot tolerate the regimen, then they are allowed to drink some water. Urine is collected after 4 hours. They look at the specific gravity data: if they are at the level of 1.015 or decrease to 1.010, then the kidney filters do not cope well with the concentration of secretions.
Values
If during the research it turned out that the density is slightly higher than normal, that is, it rises above 1.035, then they talk about hypersthenuria. This is the name given to the phenomenon in which the specific gravity of urine exceeds the norm.
Normal indicators according to age:
- Newborns in the first 10 days of life – 1.008-1.018;
- At 2-3 years – 1.010-1.017;
- 4-5 year olds – 1.012-1.020;
- 10-12 year olds – 1.011-1.025;
- In adults, the norm is considered to be urine density in the range of 1.010-1.025.
Fluctuations in daily urine output are considered normal. The morning portion, for example, will be more excessive, because the patient usually does not drink anything at night, so the urine is not diluted with anything. The specific gravity of urine during the daytime has the lowest density and is excreted in the largest volumes.
The process of urine formation
The specific gravity (density) of urine is an indicator that is used to assess the ability of the kidneys to concentrate substances. Also abbreviated SG on the analysis form. The process of urine formation takes place in several stages:
- Blood entering the glomeruli is filtered through a membrane. At this stage, the bulk of moisture and soluble chemical elements, both useful and harmful, are lost. The products formed during filtration (salt, glucose, water, toxins and others) enter a specific capsule and are called primary urine.
- Reabsorption is the movement of substances from the kidney tubules into the circulatory system (capillaries). At this stage, the beneficial elements that make up the primary urine enter back into the blood vessels.
- Tubular secretion is a process during which hydrogen and potassium ions, ammonia compounds and some medications are transported into primary urine. As a result of reabsorption and secretion of primary urine, secondary urine is formed. This stage is important in the process of maintaining the acid-base balance of the body. In adults, the normal volume of secondary urine per day ranges from 1.5 to 2 liters.
It doesn’t matter how much liquid a person drinks during the day, all metabolic products are eliminated by the kidneys. With reduced water consumption, urine is enriched with mineral compounds. That is, the specific gravity of urine is increased, this condition is called hypersthenuria. With abundant water consumption, the level of mineral compounds is reduced. In addition to metabolic products, urine excretes excess fluid. The urine concentration becomes low and this condition is called hyposthenuria.
Relative density of urine (specific gravity): norms for children and adults, interpretation
The fluid removed from the body is secondary urine. Unlike primary blood (similar in composition to blood plasma), it does not contain useful substances. It consists only of excess fluid and waste products (urea, acids, creatinine, urobilin and salts - chlorides, sulfates and phosphates).
Healthy kidneys must cope with the task of removing metabolic products when both small and significant amounts of fluid enter the body. In the first case, the urine should become denser, and in the second, diluted.
The specific gravity (density) of urine is a value that characterizes the ability of the kidneys to ensure a constant mass of excreted metabolic waste for any volume of secondary urine.
The relative density of urine is below normal - what might it indicate?
This test is carried out to determine the current functioning of the kidneys. These include samples of Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko .
The latter belong to the category of the most detailed laboratory studies, the results of which take into account the concentration of urea and salts.
If these substances are contained in quantities that differ from the norm to a lesser extent, then the patient clearly has reduced urine density - hyposthenuria .
Since the specific density of urine is an integral part of the functional indicators of kidney function, it can be diagnosed if there is a suspicion of:
- Kidney pathologies.
- Inflammatory processes in other structures of the genitourinary system.
- Somatic disorders.
Norms for adults and children
The total volume of fluid involved in metabolic processes is not a constant value. Factors such as:
- air temperature;
- drinking regime;
- current time of day;
- the presence of salty or spicy foods on the menu;
- the amount of fluid released by sweating and breathing.
However, normally in an adult, variations should fall within the range of 1.014-1.025 g/liter (normosthenuria).
During pregnancy, the range of daily values can be wider - 1.003-1.035. The reasons for this are partly toxicosis, nausea and vomiting, which causes dehydration.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LjxdK1et49c
If there is a deviation of the indicator (in the analysis form - SG), the following are distinguished:
- isosthenuria – SG fluctuations within limited limits – 1.010-1.012;
- hyposthenuria – decrease in SG less than 1.010 (1.008);
- hypersthenuria – increase in SG to 1.025 (1.030) and higher.
An increase in density can also be initiated by factors such as:
- presence of sugar in the blood – 1% per 0.004 g/liter;
- the presence of protein in urine - 3 g/liter of protein corresponds to an increase in SG by 0.001.
Normal specific gravity values for children can be summarized in the table:
| Child's age | Normal limits, g/liter |
| from 1 to 10 days | 1,008-1,018 |
| up to 6 months | 1,002-1,004 |
| up to 1 year | 1,006-1,016 |
| 2-3 years | 1,010-1,017 |
| 4-5 years | 1,012-1,020 |
| 7-8 years | 1,008-1,022 |
| 10-12 years | 1,010-1,025 |
In general, a specific gravity value of 1.020 g/liter is above the norm for children.
Reasons for the increase in specific gravity
All existing reasons for the urine density indicator to go beyond the normal range can be divided into physiological and pathological. The first factors independent of gender and age include:
- a feature of the drinking regime, expressed in insufficient fluid consumption during the day:
- taking in significant doses of drugs that are actively excreted in urine: diuretics (or rather, certain groups of diuretics that help increase the excretion of urea and other substances along with urine), as well as antibiotics;
- dehydration caused by frequent vomiting or diarrhea, as well as profuse sweating in hot weather or during intense physical exercise;
- burns of large areas of the body and injuries to the abdominal area - naturally, both of these conditions require therapy, but the mechanism for the appearance of hypersthenuria here is generally natural.
Among the diseases that can cause changes in the laboratory indicator SG are:
- heart failure, with accompanying edematous manifestations;
- diabetes mellitus, accompanied by a high concentration of sugar in urine;
- inflammatory diseases of the kidneys or lower urinary system;
- chronic glomerulonephritis or, on the contrary, the start of its acute stage;
- nephrotic syndrome (hypersthenuria is combined with oliguria - a decrease in the amount of urine);
- diseases accompanied by proteinuria (the presence of protein in the urine).
- endocrine pathologies.
Hypersthenuria in pregnant women
Laboratory indicators in women during pregnancy can differ significantly from the norm, both due to physiological and reasons requiring treatment. An increase in specific density may appear due to such phenomena as:
- toxicosis and accompanying dehydration, as well as disturbance of water-salt balance;
- gestosis (preeclampsia) - an increase in the specific gravity of urine occurs in conditions of extensive edema, a small volume of urine excreted and the presence of a large amount of protein in it.
In adults
In the adult population, pathological causes of low urine density are caused by conditions such as:
- Chronic kidney failure;
- Diabetes insipidus (nephrogenic, central or idiopathic);
- Chronic pyelonephritis;
- Chronic nephritis;
- Resorption of edematous areas and infiltrates of inflammatory origin, which is usually observed during the recovery period after any inflammation;
- Degeneration of healthy kidney cells into connective tissue structures, characteristic of nephrosclerosis;
- Interstitial type of nephritis;
- Nutritional dystrophy caused by lack of nutrients and starvation;
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Acute tubular lesions;
- Lack of antidiuretic pituitary hormone, in which there is no proper absorption of water, resulting in diluted urine with low density;
- Involuntary polydipsia, characteristic of persons prone to various kinds of neurotic disorders and having an unstable psyche (mainly in women);
- Drinking plenty of water or taking diuretics, etc.
A physiological decrease in the specific gravity of urine occurs against the background of alcohol abuse, but soon, if the patient stops drinking, the indicators return to normal.
In parallel with the decrease in density, patients may experience signs of kidney failure such as:
- Hyperswelling throughout the body;
- Chronic fatigue;
- Pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region;
- Changes in the color characteristics of urine (darkening or the appearance of bloody impurities);
- Decrease in the total volume of urine excreted.
Regardless of the reasons that caused urine density to be less than normal, the appearance of pathological signs requires a medical examination. Each of the factors, if left untreated, can cause complications and therefore requires mandatory treatment.
The relative density of urine is an important diagnostic indicator, according to which the pathological conditions of the patient are determined. Depending on the disease and the stage of its progression, urine can have completely different relative densities, including reduced ones.
Reasons for the decrease in specific gravity
A change in the indicator should not cause concern if the decrease occurred under the following conditions:
- abundant fluid intake into the body;
- taking short-term groups of diuretics (although this may require consulting a doctor);
- a diet lacking variety and characterized by insufficient protein intake. This also includes prolonged fasting and dystrophic conditions.
In the presence of a pathological process, urine becomes less dense in the absence of excessive (but not pathological) drinking regimen.
This can happen under the following conditions:
- involuntary polydipsia - excessive fluid consumption not caused by physiological needs. The disorder often accompanies mental disorders or diabetes insipidus;
- central or renal diabetes insipidus;
- diseases of the central nervous system – encephalitis, meningitis;
- chronic renal failure;
- amyloidosis.
Diagnostic methods
A general urine test cannot accurately determine specific gravity due to the fact that the concentration of substances dissolved in urine can vary significantly throughout the day. He is not able to differentiate the cause of the violation that has arisen. Therefore, the following types of functional studies are used:
- Zimnitsky urine test is a type of diagnosis that will determine the ability of the kidneys to excrete fluid, as well as concentrate and dilute urine. It is carried out without changing the drinking regime and consists of collecting 8 portions of urine per knock (after 3 hours). For each portion, the volume of urine and its specific gravity are measured. The result of the analysis will be the scatter of density figures per day and the difference between daytime and nighttime diuresis. Further tests are prescribed only if the result of the Zimnitsky test is questionable or if obvious deviations are detected;
- concentration test (with dry eating) – is carried out with the elimination of liquid foods and drinks from the patient’s diet. Collect several daily portions of urine from 9 to 21 pm and one at night. The test is not always advisable and has contraindications;
- dilution test - this tests the ability of the kidneys to dilute urine in case of excess fluid intake. To do this, the person being examined needs to drink a certain amount of water, calculated based on his body weight. There are groups of patients in whom the study is carried out with caution or is completely contraindicated.
The specific gravity of urine is an indicator in which the average person rarely shows increased interest. However, it can also be a source of information necessary for the doctor when assessing kidney function, and sometimes when diagnosing non-renal pathologies.
| In the article you will read what indicators are included in a general urine analysis, what are the reference intervals for these indicators, what is the norm of leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine, how much protein and sugar can be in the urine, what epithelial cells are found in the analysis. |
The information was prepared by doctors from CIR laboratories and clinics.
A general clinical examination of urine (general urinalysis, OAM) includes the determination of physical properties, chemical composition and microscopic examination of sediment.
Source: https://xn—-7sbbabkwnixgwr4a5a.xn--p1ai/uzi/plotnost-mochi-povyshena-prichiny.html
Reasons for decreased specific gravity of urine
As a rule, in case of infectious diseases or pathologies of the digestive tract, patients are advised to drink fluid in increased volumes. Increasing the drinking regime helps to quickly remove toxins from the body and replenish lost moisture. Often the change causes hyposthenuria, that is, a decrease in the specific gravity of urine.
Reasons for deviation of the specific gravity indicator downward, which do not require therapeutic intervention, also include the consumption of large volumes of liquid at high temperatures and treatment with certain medications (diuretics). Pathologies characterized by the development of hyposthenuria are: neurogenic and nephrogenic (renal) diabetes insipidus, diseases of the urinary system in chronic and acute forms, as well as diabetes insipidus of nervous etiology and pregnancy.
In neurogenic diabetes insipidus, there is a deviation in the production of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone). In the absence of adequate therapy, a person experiences stable dehydration. The progression of nephrogenic diabetes mellitus is accompanied by pathological disruption of the cellular structures of the distal segment of the nephron tubules. The deviation develops as a result of the fact that parts of the kidneys stop responding to vasopressin. A feature of diabetes insipidus during pregnancy is that it disappears on its own after childbirth.
Chronic diseases of the urinary system are accompanied by a violation of the correct performance of the filtration function of the kidneys and the removal of fluid from the body. In acute inflammatory processes, for example, pyelonephritis, a decrease in the specific gravity of urine occurs due to damage to the kidney tubules. The causes of diabetes insipidus of nervous etiology are prolonged depressive disorders and severe emotional distress. Most often, a decrease in the specific gravity of urine is caused by hormonal changes and pathologies of the urinary system.
If, when deciphering the results of a urine test, the doctor sees that the density indicator is lower or higher than normal, then hyposthenuria or hypersthenuria is diagnosed. Both conditions require detailed diagnostics to determine the cause of the abnormality and evaluate kidney function. In some cases, to stabilize the level of specific gravity, it is enough to normalize the diet and fluid intake. If the cause of the deviation is a pathological disorder, then therapeutic intervention is required, which is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
Hyposthenuria
With a strong decrease in the level of urine density, a state of hyposthenuria occurs. In this case, frequent urination, severe discoloration of urine, and possible swelling are noted. Too low specific gravity of urine is observed when the indicator is below normal at a value of 1 g/liter.
Causes of decreased density in adults
There are certain reasons for the occurrence of low urine density:
- drinking large amounts of liquid;
- taking diuretics;
- severe food restrictions, strict diets, fasting.
Reducing water consumption and normalizing nutrition help ensure that the specific gravity returns to normal without additional treatment.
The danger should be caused by hyposthenuria, which occurs against the background of pathologies:
- psychological diseases accompanied by a great feeling of thirst;
- diabetes insipidus;
- pathologies of the central nervous system (encephalitis, meningitis);
- renal failure;
- amyloidosis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- kidney tumors;
- infectious diseases.
In this case, hyposthenuria is a symptom of the underlying disease, and treatment should be aimed specifically at the main cause.
Why does a child’s density decrease?
After birth, children experience a decreased level of urine density. This is a normal occurrence during the first month of life. Subsequently, this indicator returns to normal.
If a low level of density is diagnosed in older children, then first the dynamics of the indicator are monitored over a certain period of time. In the case of persistently low density levels in a child, a thorough examination and identification of the cause is required. The most common cause of the condition is renal failure.
Factors reducing urine density in the elderly
It is not uncommon to see a decrease in the permissible specific gravity of urine in older people. Age-related changes affect all organs, including the urinary system. As a person ages, the immune system and the body's resistance to various diseases decrease.
Factors in the development of hyposthenuria can be:
- urinary tract infections;
- prostatitis;
- gout;
- diabetes;
- urolithiasis, etc.
Deviation from normal indicators
There are two types of changes in this indicator. 1. Specific gravity exceeds the norm. An increase in the concentration of urine is a consequence of certain processes of a pathological nature.
- Increasing edema occurs, which is caused by glomerulonephritis or insufficient renal function.
- Various pathologies of hormonal origin.
- Excessive loss of fluid from the body due to burns, vomiting, diarrhea, and blood loss.
- Damage to abdominal organs and intestinal obstruction.
- Vomiting in pregnant women.
- High doses of antibiotics.
- Kidney pathologies of an acute or chronic nature.
There are many factors that increase the density of urine. These may be metabolic disorders or diseases of the reproductive and urinary apparatus. This phenomenon can also be observed with physiological changes - increased sweating and thirst after eating salt. Oddly enough, the increased specific gravity of urine has its own clear manifestations
- The volume of urine is reduced.
- Urine has a darker color.
- The smell of urine is quite unpleasant.
- The appearance of edema is noted.
- The patient begins to experience swelling.
- The patient is weak, drowsy and prone to getting tired quickly.
- Pain in the lower back and abdomen is common.
In children, increased density may occur due to the presence of pathologies that are congenital or acquired. Very often, children are affected by intestinal infections due to weak immunity, and in case of poisoning, as is known, a lot of fluid is lost. You can separately consider diabetes mellitus, in which an increase in the weight of urine is based on the high content of sugars in it. Or if there is protein and breakdown products in the urine. Urine will be denser. To identify any such pathology, certain tests must be carried out.
2. Decrease in relative density Sometimes, after any illness, the doctor recommends that the patient consume more water and other drinks to quickly remove toxins and replenish fluid balance. Such replenishment will most likely reduce the concentration of dry sediment and dilute the urine; such dilution is physiological in nature. It is also considered normal for a decrease in urine concentration in the heat, when a person drinks a lot, or when taking diuretics. There are a number of reasons that cause pathological dilution.
- Neurogenic diabetes, characterized by a decrease in the synthesis of pituitary hormones.
- Nephrogenic diabetes, which occurs when nephron cells become tolerant to antidiuretic hormone.
- Diabetes that occurs during pregnancy.
- Nervous disorders due to stress and depression.
- Inflammation of the kidney tubules.
The condition of reduced density (hyposthenuria) requires diagnostic measures, as it can have quite serious causes. For further diagnosis, it is necessary to prescribe tests that determine exactly the functional component. Zimnitsky test, carried out in drinking mode and concentration test. It is worth remembering that if the change in night density is permanent, you need to urgently consult a doctor who will help you deal with the problem and find its cause.
Short link to the news: https://vladmedicina.ru/~1Yx7F
Hypersthenuria
When density increases above the maximum permissible values, a certain condition of the body occurs, which is called hypersthenuria. It is noted when the specific gravity of urine increases above normal already at a value of 1.04 g/liter.
Symptoms of hypersthenuria include the following:
- reducing the number and size of urine portions;
- darkening;
- the appearance of clots or sediment;
- the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen;
- weakness and increased fatigue;
- swelling of the whole body.
Causes in adults
All reasons contributing to the development of hypersthenuria can be divided into physiological and pathological. The first type includes:
- small amount of fluid consumed;
- taking medications (laxatives, antibiotics);
- excessive sweating in hot weather or during physical activity;
- dehydration as a result of poisoning, diarrhea, vomiting;
- severe body burns.
In these cases, it is necessary to replenish the fluid supply in the body, which will help reduce the relative density of substances in the urine.
Hypersthenuria can occur as a result of the development of certain pathologies. The second group of factors includes the following diseases:
- heart failure, which is accompanied by edema;
- diabetes mellitus, which is accompanied by a high concentration of glucose in the blood;
- the presence of inflammatory diseases in the urinary system and kidneys;
- acute or chronic form of glomerulonephritis;
- development of oliguria;
- pathologies that cause excess protein concentration in urine;
- disorders of the thyroid gland (for example, hypothyroidism).
In children
Many parents, having seen in the test results that the density of urine in children is increased, do not know what this means and what needs to be done. The phenomenon of hypersthenuria can be diagnosed even in children. Its symptoms are similar to those in adults. Among the reasons are:
- pathologies of congenital or acquired nature of the urinary tract;
- frequent cases of poisoning, diarrhea and vomiting;
- In very young infants, an increased level of density may occur due to an excess of fatty and protein foods in the mother's diet.
In the elderly
Hypersthenuria often occurs in older people due to decreased kidney function. As a result, the filtration capacity of glomerular filtration decreases and resistance in the vessels of the kidneys increases. All this leads to the fact that the saturation of urine in older people decreases.
Physiological process of urine formation
In the kidneys, the contents of the blood vessels are filtered as many as two times. When blood flows through the nephrons - the renal glomeruli, its plasma is filtered through the loose walls of the tubules and enters the glomerular capsule, as a result of which the so-called primary urine, containing all metabolic products, accumulates in it.
Then the plasma from the capsule again enters the bloodstream through the tubules, taking with it glucose and useful nutrients, and waste products (urea, uric acid salts, creatine, creatinine, potassium and sodium salts) are released from the capsules along with the remaining liquid in the form of final, secondary , urine.
Disruption of this process affects the density of the released liquid.
Carrying out analysis
Determination of density is carried out using a urometer apparatus. Urine along the wall is placed in a special cylinder; if the process is accompanied by the appearance of foam, then it must be removed. The entire cylinder is placed in the device. It should be noted that if the patient cannot go to the toilet himself, then urine must be collected with a catheter. The density is determined by the level of the underlying meniscus of the apparatus scale; therefore, the cylinder and the apparatus should not be in contact. There are situations when the volume of urine obtained is too small, then it is diluted with distilled water and all calculations are made taking into account the degree of dilution. And so, when diagnosing using this method, qualitative and quantitative indicators are taken into account. A mixture of chloroform and benzene is placed in a cylinder, and a drop of the test liquid is dropped into it. If she drowned, then the urine density is too high, if she floated, then it is low. By adding each of the components in parts, they ensure that the material under study is in the middle of the liquids. The density of the urine will be equal to the density of the resulting solution. It is worth remembering that the urometer was calibrated at 15 C, which means that it is necessary to make an adjustment for the ambient temperature. At high temperatures, a person always drinks more and loses more fluid, and at low temperatures, he consumes very little fluid. All this, of course, influences, and daily changes in density.
Specific gravity is higher than normal
Hypersthenuria, as this phenomenon is called, is expressed by a significant excess of the permissible density of urine. It is diagnosed at a high specific density - above 1030 grams per liter of liquid. The reasons causing it may be:
- Diabetes;
- Glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome;
- Dehydration due to diarrhea, vomiting, severe overheating, or not drinking enough fluids;
- Large doses of antibiotics and other medications;
- Toxicoses, including toxicosis during pregnancy;
- Inflammation of the genitourinary system.
Symptoms of hypersthenuria:
- A sharp decrease in single portions of excreted urine;
- Change in the shade of urine towards dark tones, often interspersed with clots;
- The occurrence of pain in the abdomen;
- Chronic weakness and apathy;
- General swelling without visible localization.
Reasons for deviation of urine test results from the norm
Color – normally it should be light yellow. If your urine is the color of strong tea or dark beer, you may have liver or gallbladder disease; Urine acquires a reddish tint due to glomerulonephritis; persistently colorless or slightly yellow urine is a symptom of advanced kidney disease; Specific gravity - the upper limit of this indicator of a general urine test in healthy people is 1.028 (in children under 4 years old - 1.025), the lower limit is 1.003-1.004. Specific gravity above normal is observed in oliguria (decreased urine output), toxicosis of pregnancy, taking certain medications, large loss or insufficient fluid intake, glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, liver disease and other diseases. This indicator may be below normal when taking diuretics, chronic renal failure, acute damage to the renal tubules, or drinking too much.
Protein in urine - in more detail about normal and increased protein in urine. Traces of protein and other deviations from the general analysis from the norm can be observed when collecting urine in containers that do not meet the requirements. Bilirubin – Normally there is practically no bilirubin in the urine. The reasons for the appearance of bilirubin in the urine may be increased breakdown of hemoglobin (hemolytic anemia, resorption of large hematomas), liver infections or dysfunction, the result of toxic substances (alcohol, infectious toxins) and others. Leukocytes - the norms of leukocytes and the reasons why they are elevated are described in this article; Red blood cells - the number of red blood cells in the urine is also considered an important indicator of health (about the norm and increased red blood cells in the urine); Ketone bodies are acetone, acetoacetic and beta-hydroxybutyric acids. The appearance of ketones in the urine can be caused by diabetes mellitus, acute pancreatitis, prolonged fasting, and weight loss diets. It is also observed with acetemic vomiting in young children (with infectious diseases, carbohydrate starvation, etc.), glycogen storage disease, thyrotoxicosis and other diseases. Sometimes the following may be observed in the urine:
- flakes – for inflammation of the urinary tract (urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis),
- foam - increased protein level, sperm has entered the urinary tract.
Test results are also affected by compliance with testing requirements. Check if you passed the general urine test correctly.
Helpful information