Calcium is one of the main intracellular cations, which is found mainly in bone tissue. If we take the percentage ratio of a person’s body weight and calcium in his body, then there is quite a lot of the latter in him and its amount is about two percent. Moreover, this amount is mainly concentrated in bone tissue, and partly in the blood. That is why the presence of calcium in the urine, and especially in large quantities, indicates some deviation in the functioning of the body, which must be understood and measures taken to eliminate it
What determines the excretion of calcium by the kidneys?
Normally, calcium ions are in the blood; when passing through the kidneys, a process of reabsorption occurs, that is, they remain in the bloodstream. A small amount of the mineral is excreted from the body. If there is an excess of salts in the blood, then the kidney tubules do not try to retain them, and the amount of calcium in the urine increases.
The concentration of a microelement is influenced by:
- food supply;
- absorption from the intestine;
- the rate of destruction of old bone tissue and the construction of new one;
- urine filtration by the kidneys;
- the level of phosphates that bind the mineral (as they increase, calcium decreases);
- intake of vitamin D through the skin and food (helps absorb the trace element from food and retain it in the kidneys).
Regulation of the content of calcium salts in the body depends on the functioning of the thyroid and parathyroid glands. The first releases calcitonin. It helps calcium to be incorporated into bones, and its concentration in the blood and urine decreases. The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone, which helps increase the level of the mineral in biological fluids.
We recommend reading the article about blood tests for osteoporosis. From it you will learn who is recommended to take a blood test for osteoporosis, what tests need to be taken for osteoporosis.
And here is more information about calcium supplements for osteoporosis.
Interpretation:
- Primary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism, malignant tumors, polycythemia vera, pheochromocytoma (combined with parathyroid hyperplasia), sarcoidosis, vitamin D intoxication, Paget's disease, thyrotoxicosis, acromegaly, diuretic phase of acute tubular necrosis, dehydration, familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia, iatrogenic hypercalcemia.
- Hypoparathyroidism, pseudohypoparathyroidism, alcoholism, liver cirrhosis, hypoalbuminemia, magnesium deficiency, vitamin D; Chronic renal failure, long-term therapy with anticonvulsants, acute pancreatitis, hyperphosphatemia, massive blood transfusions, hypofunction of the anterior lobe
Sample result (PDF)
Who needs to donate calcium in daily urine
Your doctor may order a test for calcium excretion through the kidneys in the following situations:
- determining the sufficiency of intake from food and medicines;
- study of the level of absorption in the intestine;
- determining the cause of low bone mineral density (osteopenia, osteoporosis), the need to evaluate the results of treatment;
- suspicion of urolithiasis - pain and cramping when urinating, attacks of severe pain in the lumbar region, bleeding in the urine;
- detected increase or decrease in the function of the thyroid and parathyroid glands;
- diseases of the small intestine with insufficient absorption - nonspecific ulcerative colitis, consequences of removal of part of the intestine, cystic fibrosis.
Stages of bone density destruction
Indications for use
1. Diagnosis and monitoring of osteoporosis. 2. Assessment of the condition of the parathyroid glands (including after thyroidectomy), diseases of the pituitary gland and thyroid gland.3. Diagnosis and control of rickets therapy. 4. Bone diseases, bone pain. 5. Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. 6. Muscle hypotonia, convulsive syndrome, paresthesia. 7. Cardiovascular pathology (rhythm and vascular tone disturbances). 8. Malignant neoplasms (breast cancer, lung cancer). 9. Urolithiasis (X-ray-positive stones) and other kidney diseases, polyuria.
When the analysis does not provide the necessary information
Determination of calcium in urine is a fairly reliable, economical and simple method for diagnosing metabolic disorders. However, there are limitations to the purpose of the analysis.
Distortion of indicators can occur in the following conditions:
- prolonged immobility of the patient;
- extensive injuries;
- increased phosphorus levels in the blood and urine;
- exposure to the open sun during the summer holidays, sunbathing in a solarium;
- the patient did not take into account the preparation requirements or collected urine incorrectly.
Treatment of abnormalities
Urine calcium testing is widely used in clinical practice. It is used to assess the functioning of the kidneys and parathyroid glands, nutrient absorption, and identify the causes of osteoporosis. If the results do not correspond to the norm, you should seek treatment from the doctor who referred you for the study - therapist, nephrologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, traumatologist. Minor deviations caused by physiological reasons can be corrected through dietary changes. With a reduced level of calcium in the urine, it is necessary to introduce more sources of this trace element and vitamin D into the diet - milk, cheese, eggs, fish, vegetable oils. In addition, it is worth remembering that oxalic acid, contained in many vegetables (sorrel, berries, tomatoes), reduces the absorption of calcium.
How to collect material
10 days before the test, the patient should discuss with the doctor the possibility of using medications, vitamin complexes and nutritional supplements; catheters can affect the result. For two days, diuretics and herbs with this effect, alcohol and dark-colored vegetables, fruits, berries (beets, carrots, blueberries, blackberries, citrus fruits) are discontinued.
You need to collect urine in a container that is pre-sterilized. Its volume must be at least 3 liters. If a glass jar is used for this, then it is thoroughly washed with soda and doused with boiling water twice. The lid is processed in the same way. On the morning of the test day, the first portion of urine is not collected. The patient should pour all the rest into a prepared container, kept closed in the refrigerator.
The next morning, the first void is added to the collected urine and the entire volume is measured. Approximately 100 ml should be poured into a standard urine collection container and taken to the laboratory. The accompanying note indicates the daily amount of urine and medications taken, if they could not be canceled.
Patient preparation rules
Random urine without preservativeStandard conditions:
Biological material is accepted during the working day of the departments of ML "DILA".
Any portion of urine, regardless of the time of day. The material is collected after toileting the external genitalia. Daily urine Standard conditions:
Biological material is accepted during the working hours of the departments of the medical clinic "DILA". Add the resulting amount of preservative (hydrochloric acid) to the container for collecting urine.
• do the first morning urination in the toilet. • collect all subsequent urine, including the morning portion of the next day, in a container with a preservative. • during the entire collection period, store biological material in a cool, dark place. • after collection is completed, measure the daily volume of collected urine, mix , pour 30-40 ml into a container with a preservative, deliver to the “DILA” ML department within 1-1.5 hours. Important:
Consult with your doctor about taking diuretics, which may affect the results.
Possible:
To collect daily urine, the patient is asked to purchase a 2-liter container at the price price (the cost of the container is not included in the cost of the test).
You can add this study to your cart on this page
Decoding indicators
The obtained results are compared with the reference ones. This is what the average normal values are called. The predominant research method is colorimetric, based on the change in the color of the solution when a reagent is added. Different laboratories may use different reagents and methods, so the normal value is always indicated next to the patient’s data.
Norm of calcium in daily urine
The dependence of normal values of calcium in urine on the age of the subject can be traced.
| Age, years | Calcium in urine per day, mmol/l |
| Up to 1 | Not higher than 1.85 |
| From 1 to 4 | 1,9 — 2,55 |
| From 4 to 5 | 2,3 — 3,5 |
| From 5 to 7 | 2,8 — 4,55 |
| From 7 to 12 | 2,5 — 6,9 |
| From 12 and adults | 2,5 — 7,5 |
Periods of accelerated growth, pregnancy and lactation are accompanied by increased consumption of the microelement, so its slight decrease is noted. If the patient's diet is dominated by dairy products and fatty fish, then the calcium content increases slightly. Such conditions do not require treatment and are regulated by nutrition.
Increased mineral
Excess calcium in urine may be associated with the following diseases:
- stones in the kidneys and urinary tract;
- hereditary diseases with damage to the renal tubules;
- sarcoidosis;
- increased function of the parathyroid glands, thyroid dysfunction;
- tumor processes, bone metastases;
- tuberculosis;
- gangrene;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- extensive inflammation of the peritoneum;
- fractures with prolonged immobilization (forced immobility due to a plaster cast, fixation of the limb);
- paralysis, the need for strict bed rest after surgery;
- taking vitamin D, anticonvulsants, Diacarb, Furosemide, Veroshpiron.
Low calcium
Low mineral concentrations may be due to:
- increased loss of protein and phosphorus in the urine due to nephritis, renal failure;
- low function of the parathyroid glands;
- intestinal diseases with malabsorption;
- liver damage;
- the use of drugs and their analogues: Prednisolone, Hypothiazide, birth control pills, female sex hormones, Methindol, vitamin K, A, ascorbic acid, lithium;
- lack of sun exposure, insufficient consumption of milk, cheese, fish.
A calcium test in urine is prescribed for changes in bone density, function of the endocrine glands, kidneys, and also to evaluate the treatment performed. Not informative in cases of forced immobility or the use of medications that alter calcium metabolism.
We recommend reading the article about the drug calcimine. From it you will learn about the features of the drug Kalcemin, how to take it for osteoporosis, as well as when it is better to drink Kalcemin Advance and Kalcemin Silver.
And here is more information about the causes of osteoporosis in men.
To obtain an accurate result, it is important to follow the rules for collecting daily urine. The obtained data are compared with age-specific norms. Small deviations require nutritional correction. In case of pronounced disorders, it is necessary to search for the cause - study of hormonal levels, kidney function, and intestines.
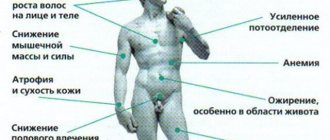
Increased calcitonin in the blood
An increase in calcitonin in the blood above normal is a serious sign of a developed pathology. At a concentration of more than 100 pg/ml, we can speak with complete confidence about the presence of a neoplasm in the thyroid gland.
Calcitonin is a tumor marker, that is, a characteristic indicator of medullary thyroid cancer. This disease is inherited, so if it is present in relatives, everyone should be tested.
There is an unfavorable prognosis for medullary thyroid cancer. If it is confirmed, the patient is scheduled for surgery to remove it. The sooner this is done, the less likely it is for metastases to spread throughout the body.
If you detect high levels of calcitonin, you should consult a doctor immediately, if this has not already been done. A competent specialist will prescribe additional clarifying research methods and, based on their results, prescribe treatment.
In addition to malignancy, there may be other reasons for increased calcitonin:
- an increase in the number (hyperplasia) of parafollicular cells;
- Ellison-Zollinger syndrome (pancreatic tumor that produces gastrin);
- liver cirrhosis caused by alcohol damage;
- pernicious anemia (resulting from vitamin B12 deficiency);
- benign tumors;
- inflammation of the thyroid gland;
- taking calcium supplements;
- third trimester of pregnancy;
- chronic renal failure.
Vitamin D role in a woman’s body
In the early 20th century, calciferol (vitamin D) was isolated from fish oil. It is a fat-soluble vitamin as well as a hormone. In ordinary life, it is called the “sun vitamin”, since it is synthesized under the influence of ultraviolet rays in the skin. Does not change its properties during storage and heat treatment.
There are 2 active types of vitamin D: cholecalciferol and ergocalciferol. The first form (D3) enters the human body with food, and can also be synthesized under the influence of UV rays. The second (D2) is a synthetic plant vitamin that is used to enrich foods and add them to dietary supplements.
All these compounds are active metabolites of stable biological substances supplied with food and sunlight.
Vitamins represented by group D perform important functions:
- participation in hormonal synthesis;
- regulation of calcium metabolism in the body;
- increasing immunity;
- transporting calcium, phosphorus and ensuring their absorption into the intestines.
Women need a regular supply of D vitamins to their bodies. They are responsible for the exchange of phosphorus and calcium, without which normal functioning of the heart and nervous system is impossible.
Calcium is involved in blood clotting, metabolism, strengthens bones and supports joints. If it is deficient, the likelihood of serious injuries and fractures increases.
Redness and peeling may appear on the skin. The more vitamin D you have in your body, the better these vital minerals are absorbed.
Indications for analysis
The process of building bone tissue begins during the formation of the fetal skeleton. An increased need for calcium occurs in newborns, and subsequently maintaining normal calcium levels is critical to the child's health. Therefore, urine analysis using the Sulkowicz method is a mandatory procedure prescribed for newborns and infants.
The study is also used to determine the required daily dose of vitamin D. Vitamin D deficiency leads to improper formation of the skeleton, the development of rickets and other diseases. Rickets often develops in children who do not receive a prophylactic dose of vitamin D due to lack of sunlight.
A urine test according to Sulkovich is prescribed as part of annual preventive examinations of patients at risk, with symptoms of excess or lack of calcium in the body.
Detection of abnormalities based on the results of the analysis does not allow making an accurate diagnosis; additional research is required for the diagnosis and selection of effective treatment tactics for the attending physician.
The Sulkowicz test is performed if the following diseases are suspected:
- rickets;
- vitamin D hypervitaminosis;
- hyper- or hypothyroidism;
- hypo- and hyperparathyroidism;
- pancreatitis;
- kidney stone disease;
- chronic renal failure;
- sarcoidosis;
- Wilson-Konovalov disease (disorder of copper metabolism in the body);
- tuberculosis of bones, kidneys, lungs;
- calcitonin-producing tumors.
Norms for the average concentration of hb in erythrocytes
The normal average hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes depends on the age and gender of the patient.
READ ALSO: normal hemoglobin levels in children by age
To calculate the MSHC, data on hemoglobin and hematocrit (volume of red blood cells) is required (we recommend reading: increased hematocrit in a child: causes). The unit of measurement is grams per liter.
Standard indicators of the average concentration of hb in erythrocytes in the blood of children by age are presented in the table.
INTERESTING: table with platelet levels in the blood of children of different ages
| Age | Indicator, g/l | |
| Boys | Girls | |
| 0-2 weeks | 280-350 | 280-350 |
| 2 weeks-1 month | 280-360 | 280-360 |
| 1-2 months | 280-350 | 280-350 |
| 2-4 months | 290-370 | 290-370 |
| 4-12 months | 320-370 | 320-370 |
| 1-3 years | 320-380 | 320-380 |
| 3-12 years | 320-370 | 320-370 |
| 12-15 years | 320-370 | 320-360 |
| 15-18 years old | 320-380 | 320-370 |
What does protein mean in a child’s urine test?
Ideally, there should be no protein in a urine test. But in a newborn, a small amount is considered normal, and in children under 6 months it can be a signal of overfeeding.
In children, a low concentration of up to 0.036 g/l should not cause concern and can be the result of many reasons:
- Allergies
- Fatigue
- Stress
- Significant physical activity
Monitor the health of your children, undergo timely examinations and tests to have an idea of the baby’s health status. Do not neglect the health of your child, because children are the most important thing in the life of each of us.
Specific gravity of urine
| Newborns (up to 10 days old) | 1008-1018 | g/l |
| Children aged 2-3 years | 1010-1017 | g/l |
| Children aged 4-12 years | 1012 – 1020 | g/l |
| Children over 12 years of age and adults | 1010 – 1022 | g/l |
- Diabetes
- Glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome
- Use of high doses of drugs excreted in urine (antibiotics, diuretics)
- Low fluid intake
- Excessive fluid loss (vomiting, diarrhea, profuse sweating)
- Toxicosis of pregnant women
- Infectious process in the kidneys and urinary tract (pyelonephritis, cystitis)
How to take vitamin D - dangers of excess
Vitamin D intake should be agreed with a specialist. Only an experienced doctor can say, based on the woman’s condition, in what form and form it is best to consume the nutrient. Mono-supplements with high concentrations of calciferol (from 2,000 to 10,000 IU) can be harmful if the patient does not have a significant deficiency of the vitamin.
A lack of D3 and D2 is very dangerous for the female body, but an excess can lead to serious consequences. This is blockage of blood vessels, demineralization of bones, as well as the appearance of calcium deposits in various internal organs. Long-term overdose can lead to a dangerous condition - hypercalcemia.
Excess is determined by the following early symptoms:
- high blood pressure;
- excessive thirst;
- constipation and increased urine production;
- loss of appetite, nausea.
Quite often, an overabundance is diagnosed in young children when mothers, without consulting a specialist, exceed the recommended doses. Therefore, before taking the vitamin, strict adherence to the prescribed dosage is required.
Information to note:
What is gluten? Benefits and harm to the body
Read further:
Testosterone in women - normal indicator by age, reasons for increased and decreased hormone levels
Reduced or increased creatinine in the child’s blood: reasons for changes in indicators and the norm
Prolactin in men - the norm by age, causes of increased and decreased hormone levels, treatment
FSH in men - norm by age, reasons for increase and decrease in the indicator
Norm of ESR in children by age with a table, reasons for increased and decreased levels in the blood
Atypical mononuclear cells in the blood of a child - the norm and reasons for increased levels
Norms of indicator in urine in boys and girls of different ages
The norm of leukocytes in the urine of children will differ for different ages (for more details, see the article: the norm of leukocytes in the urine of infants). The gender of the child has no less influence on quantitative indicators. As a rule, girls have slightly more white cells than boys.
How many leukocytes should there be in the urine of a healthy baby? Ideally, they are absent, but even if their number in children is from 7 to 10 pieces per 1 μl, this will be considered a variant of the norm. The table with the normal number of leukocytes shows that on average in children aged 2-3 years the figure should not exceed 5 units of leukocytes per μl.
| Type of urine test | Norma (boys) | Norma (girls) |
| General | 0-3 | 0-5 |
| According to Nechiporenko | ||
| According to Kakovsky-Addis | ||
| According to Amburge |
At birth, a child’s kidneys do not function fully, so a larger number of leukocytes are present in the urine - up to 10 units. You need to sound the alarm if the quantitative indicator has not changed over time, or the leukocyte count has increased. The norm for a one-year-old child is up to 8 units per 1 μl. Sometimes due to excess intake of protein and vitamin C, the white blood cell count becomes low and test results may be false negative.
READ ALSO: what to do if the leukocytes in a child’s blood are low?
Sometimes an increase in white blood cells is observed after an illness or due to teething. If the results obtained make parents suspicious, then they should consult a doctor. If the fears are not unfounded and there are too many white cells, the pediatrician will refer you to specialists for additional diagnostics.
What do increased urine levels mean in a baby?
Elevated urine levels in infants are rare. In most cases, deviations from the norm in the content of red blood cells in urine indicate the development of a cold or microtrauma of the penis in boys. It should be taken into account that the normal level of red blood cells in the urine of a newborn and a child of the first year of life is much higher than in older children.
Shortly before birth, the process of producing red blood cells is activated in the child’s body. He returns to normal in the first months of life. However, up to one year of age, jaundice and loss of salts from the kidneys may be observed. Usually we are talking about physiological phenomena, however, to exclude pathology, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician or neonatologist.