Why is calcium needed in the blood?
The amount of calcium in the blood is only 1% of the total concentration of this mineral in the body.
The bulk of calcium comes from bones and tooth enamel. The presence of calcium in the blood is necessary, since it is involved in many processes and can only be carried throughout the body through the bloodstream. Without this mineral, the following processes are impossible in the body:
- muscle contraction,
- activation of enzymes (enzymes),
- work of the endocrine glands,
- transmission of nerve impulses,
- regulation of cell membrane permeability,
- blood clotting,
- renewal of joint tissue,
- activation of hormones,
- normal functioning of the endocrine glands,
- cellular reception,
- dream.
The beneficial properties of the mineral in the body appear only if calcium in the blood is normal. When it is violated, pathological conditions develop that require mandatory therapy, without which many pathological processes will develop.
Lack of calcium in the body symptoms in women
Ca deficiency in the body, like any other pathological process, has its own manifestations. Symptoms of calcium deficiency are:
- general weakness and impairment of performance;
- increased irritability;
- dry skin and increased flaking;
- excessive sweating of the scalp;
- brittle nails;
- rapid tooth decay;
- numbness of the limbs and face;
- increased blood loss during menstruation;
- violation of bone integrity;
- abnormalities of the heart and blood vessels;
- decreased blood clotting ability;
- the occurrence of cataracts;
- disruption of the immune system;
- increased sensitivity to cold.
In the first few years of life, girls may experience developmental defects, such as abnormal formation of the skeleton and teeth.
Calcium level in blood
The level of calcium in the blood of women and men is the same and varies only with age. In total, 7 indicators of calcium in the blood were identified according to periods of life. The volume of calcium contained in the blood is indicated in mmol/l (this designation is accepted for all ages).
Table by age
| Newborns up to 10 days | from 1.90 to 2.60 mmol/l |
| Children's age from 10 days to 2 years | from 2.25 to 2.75 mmol/l |
| Children's age from 2 to 12 years | from 2.20 to 2.70 mmol/l |
| Adolescence from 12 to 18 years | from 2.10 to 2.50 mmol/l |
| Adults from 18 to 60 years old | from 2.15 to 2.50 mmol/l |
| Elderly people from 60 to 90 years old | from 2.20 to 2.55 mmol/l |
| Elderly people over 90 years old | from 2.05 to 2.40 mmol/l |
When a biochemical blood test for calcium is performed, a deviation from the norm, both greater and lesser, is considered pathology. The level of calcium contained in the blood of adults can sometimes deviate slightly from the optimal values without pathological reasons and soon recovers on its own. This phenomenon is not observed in children. The cause is still unknown to doctors. After decoding is carried out, the doctor determines whether there is a violation, and if it is present, he decides whether treatment is required, or whether a simple change in diet is sufficient.
Ways to level up
If calcium levels are low, they should be increased. To do this, you should take care of your diet by introducing foods rich in this element into your diet, and also taking vitamins that absorb calcium.
We are talking about vitamins C and D. The first helps to increase the body's protective functions against fungi such as candida. They prevent the body from fully absorbing calcium.
Vitamin D maintains the balance between phosphorus and calcium during bone mineralization. It also promotes their absorption by the intestine as a result of protein interaction.
Calcium is present in sufficient quantities in the following foods:
- Peas and beans.
- Milk, cheeses, yogurt.
- Broccoli, collard greens, turnips.
- Sardines, salmon, fish roe.
Products containing calcium
Advice! If possible, you should avoid consuming caffeine, as well as products that contain oxalic and phytic acids, which block the absorption of calcium. These include nuts, poppy seeds, chocolate, cocoa, beets, etc. Tablets that help increase calcium levels in the blood should be taken with caution due to the large number of side effects. They should be taken with magnesium and vitamins D and C.
Normal calcium levels in the blood are necessary for the proper functioning of a number of physiological processes. If there is an excess or deficiency of calcium, significant harm can be caused to human health. Therefore, if there are any deviations in this case, you must immediately contact a specialist for qualified help.
← Blood amylase levels: normal and causes of deviations
Causes of childhood hematuria →
We recommend studying similar materials:
- 1. Hemostasis system: why take a blood clotting test
- 2. How to choose a diet based on your blood type: losing weight together
- 3. Causes and dangers of increased basophil levels in children
- 4. Reasons for an increase or decrease in neutrophils in a blood test in children?
- 5. Functions and possible causes of pathologies of segmented neutrophils
- 6. Norms for the content of neutrophils in the blood and what functions they perform
- 7. What do elevated eosinophils mean in a blood test in adults?
How much calcium should you consume per day?
In order for calcium in the blood to be maintained at normal levels, it should be consumed daily in sufficient quantities. If the mineral enters the body in small quantities, the condition will begin to deteriorate, and children will experience impaired physical development. The recommended calcium intake per day by age is:
- Children up to six months of age – 200 mg.
- Children aged from six months to 1 year – 400 mg.
- Children aged 1 to 4 years – 600 mg.
- Children from 4 years to 11 years – 1000 mg.
- Adolescence from 11 to 17 years - 1200 mg.
- Adults from 17 to 50 years – 100 mg.
- Men aged 50 to 70 years – 1200 mg.
- Women aged 50 to 70 years – 1400 mg.
- Persons over 70 years old – 1300 mg.
The daily norm for women carrying a child and breastfeeding increases significantly and amounts to 1500 mg of calcium.
Reasons for the decreased
There is also an opposite pathological condition - a lack of mineral in the body, or hypocalcemia. It also results from various diseases:
- chronic renal failure;
- hypoparathyroidism;
- lack of vitamin D;
- pneumonia;
- poor nutrition;
- hypomagnesemia;
- pancreatitis;
- constant stress;
- hepatitis;
- hypoalbuminemia;
- low stomach acidity;
- peritonitis;
- passive lifestyle.
Excessive consumption of tea, coffee and alcoholic beverages also contribute to the leaching of calcium from the body. It is necessary to compensate for the deficiency of this element, because it can lead to serious consequences for the body. One of the most dangerous diseases caused by mineral deficiency is osteoporosis. It develops gradually. Due to the constant loss of calcium, it is washed out of the bones, causing them to become thin and brittle. This threatens complex and difficult to heal fractures, including those of the spine.
For treatment, medications are prescribed in combination with vitamin D. The optimal daily intake for osteoporosis is: from 1200 to 1500 mg of pure calcium + 800 IU of vitamin D3. These products include: Kalcemin Advance, Kalcemin Silver, Calcium-D3 Nycomed and others. Deviations from the norm can be noticed in time by specific symptoms.
When is a calcium level test necessary?
A blood calcium test is ordered by a doctor if there is a suspicion of hypercalcemia (excessive amounts) or hypocalcemia (insufficient amounts). It is necessary to take an analysis in the following cases:
- pain in the bones,
- muscle diseases,
- muscle cramps,
- loss of sensation in the limbs,
- insomnia,
- excessive urination,
- pathological nervous excitability,
- hyperthyroidism,
- urolithiasis disease,
- bone tuberculosis,
- general exhaustion of the body,
- liver failure,
- extensive injuries,
- extensive burns,
- systemic inflammatory diseases,
- carrying out hemodialysis,
- suspicion of osteoporosis,
- pathological changes in the state of the cardiovascular system,
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract,
- cancer diseases,
- general examination before surgery.
The level of calcium is detected in the blood serum by conducting a test for ionized calcium or total calcium. The first method is more complex, but also more accurate, although general analysis almost always gives a good result. Deciphering the analysis is not difficult for a doctor.
Diagnosis of the disease
If, after taking the medical history, the doctor suspects the presence of the disease, general and ionized blood tests are prescribed. Increased calcium - what does this mean? Such a symptom indicates a deviation of the mineral content from the norm. This may indicate serious health problems.
A blood test is one of the most common methods of clinical research and is highly informative. It allows you to identify many diseases associated with the skeleton, nervous system and internal organs at the earliest stages. Indications for its use are:
- malignant tumors of various etiologies;
- nervous disorders;
- pancreatitis;
- various bone diseases;
- renal and liver failure;
- heterogeneous structure of the thyroid gland;
- parathyroid disease;
- nutrient absorption problems;
- anomalies detected during electrocardiography.
In addition to confirming elevated calcium in the blood, a general analysis is used to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy in the treatment of many diseases. It shows how the body reacts to taking medications and what changes occur in it. It is also used to control side effects and reduce the risk of serious complications.
If there is a suspicion that calcium in the blood is elevated, general tests are done on an empty stomach. In addition, the patient must undergo preliminary preparation. For the most reliable results, the patient must tell the doctor about all medications taken. It is recommended that you refrain from eating and drinking before going to the hospital. The test may be delayed for some time if the person is taking the following medications:
- vitamin complexes;
- antacids;
- diuretics prescribed for hypertension;
- lithium, used to treat mental disorders.
All of these medications affect your blood chemistry, so your results may be incorrect. If a person consumes a lot of milk and dairy products, then he will also have abnormal Ca levels. When examining a patient, doctors take into account lifestyle and quality of nutrition. In addition, increased calcium in the blood of women during pregnancy is often observed. In the case of expectant mothers, additional laboratory tests and consultations with doctors of other specialties may be required.
What does high calcium mean?
If a person, after biochemistry has been carried out, is found to have an increased level of calcium in the blood, this indicates that one of the following pathological conditions is occurring:
- increased activity of the parathyroid glands,
- ovarian cancer,
- lungs' cancer,
- kidney cancer,
- excess vitamin D in the body,
- metastases of malignant tumors in the bones,
- lymphoma,
- leukemia,
- multiple myeloma,
- dehydration,
- Paget's disease,
- spinal tuberculosis,
- granulomatosis,
- hereditary hypercalcemia (asymptomatic and detected by chance),
- acute renal failure.
In order to accurately determine the reason why the level of calcium in the blood is increased, the doctor prescribes an examination using additional blood tests, tomography and x-rays.
A few words about nutrition
Maintaining a proper diet is one of the key success factors in treating hypercalcemia. For a while, you should avoid or at least reduce your consumption of the following foods:
- salt;
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks;
- black tea and coffee;
- confectionery.
To bring calcium levels back to normal, it is recommended to eat more healthy foods. These include:
- green vegetables;
- tofu;
- salmon and tuna;
- legumes;
- seaweed;
- eggs;
- mushrooms;
- cereal flakes;
- fresh or baked fruits;
- broccoli.
It is worth noting that it is very difficult to competently plan your daily diet on your own. Therefore, if you have detected increased ionizing calcium in your blood, you should consult with a qualified specialist.
What does low blood calcium level mean?
Calcium in the blood may be low, and this is evidence that a serious disease is developing in the human body. If the analysis shows calcium deficiency, then this is evidence that one of the following diseases is present:
- osteoporosis,
- pancreatitis,
- cachexia,
- rickets,
- osteomalacia,
- deficiency of thyroid function,
- liver failure,
- chronic renal failure,
- obstructive jaundice.
Calcium deficiency can also be caused by taking a number of medications to relieve seizures and fight tumors.
Causes of increased calcium
All causes of increased calcium in the blood fit into three pathogenetic mechanisms directly related to metabolism.
The first mechanism is high bone resorption, or its destruction. In this case, calcium directly penetrates into the blood and its concentration increases.
The second group of reasons is a violation of the renal mechanism of regulation of this electrolyte in the body. There are two possible mechanisms: high reabsorption or low excretion. In the first case, the substance is returned to the body in excess by the kidneys, and little of it is secreted into the final urine. In the second case, simply during primary filtration, calcium with great difficulty enters the ultrafiltrate, or primary urine.
Finally, the third mechanism for the formation of an excess of an element is increased absorption rates in the intestine. This phenomenon is called increased intestinal calcium absorption. Let's figure out which states are associated with this or that mechanism:
- Excessive destruction of bone tissue is possible with hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands, when excess parathyroid hormone is produced. This process is activated in case of malignant bone tumors, including bone metastases, with increased hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, with pheochromocytoma and with hypervitaminosis A. For example, with a fracture of long tubular bones, an increase in resorption also occurs. Immobilization, especially long-term (with a fracture of the pelvis or spine), can also cause an increase in calcium in the blood;
- The renal mechanisms of calcium accumulation in the blood plasma are usually realized in cases of necrosis of skeletal muscles, for example, in crush syndrome or long-term crush syndrome, in the use of thiazide diuretics, as well as in the case of so-called familial hypercalcemia. It was said above that an increased concentration of this substance in the blood plasma causes polyuria, or the release of large amounts of urine. As a result, dehydration occurs and the speed of the glomerular radio decreases. As a result, reabsorption rates also increase.
- High blood calcium can also be caused by alkalosis, or alkalization of the blood plasma. At the same time, the renal reabsorption of this element also increases. If a patient has signs of chronic renal failure, then calcium is difficult to filter into the urine.
- Increased calcium in the blood due to its excess absorption in the intestines. These are vitamin D hypervitaminosis, HIV infection in the AIDS stage, the presence of lymphatic neoplasms in the intestines, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, eosinophilic granuloma. There are also special occupational diseases in which absorption in the intestine increases. This is, for example, chronic beryllium poisoning.
How to lower calcium in the blood? What medications and therapeutic techniques exist that are aimed at reducing the concentration of this electrolyte?
Symptoms of high and low blood calcium levels
You can suspect that the level of calcium in the blood is not normal based on certain symptoms. The following symptoms indicate that the calcium level in the blood is exceeded:
- deterioration or complete loss of appetite,
- abdominal pain for no apparent reason,
- the appearance of constipation,
- nausea several times a day, sometimes with vomiting,
- frequent urge to urinate at night,
- headache,
- bone pain,
- persistent thirst
- intolerance to even minor physical activity,
- depression.
When deciding how to check the level of calcium in the body in such a situation, you should contact a therapist or surgeon. The specialist, having assessed the patient’s condition, will decide whether there is a need for a blood test or whether a disease can be accurately diagnosed during the initial examination without additional examinations.
A lack of calcium in the body, even before testing, can be noticed by the following symptoms:
- intestinal spasms
- tremor of the upper extremities,
- spasm of facial muscles,
- numbness around the lips,
- facial tingling,
- heart rhythm disturbances,
- hand cramps,
- foot cramps
In all these cases, if there is no clear cause for the pathological condition, it is necessary to donate blood for calcium. After the doctor deciphers the results of the study, the necessary therapy is prescribed.
Treatment methods
After undergoing diagnosis, depending on the severity of hypercalcemia, therapeutic therapy is prescribed aimed at reducing the level of the mineral and removing excess from the body.
If the value in the analysis results does not exceed 2.9 mmol/l, then plenty of fluids and diuretics are prescribed: Furosemide, Torsemide, Hypotheazid.
Potent diuretics can only be used in the absence of renal or heart failure. The mild course of the pathology responds well to therapy; calcium levels return to normal after a course of therapy.
Read: Therapeutic and preventive exercises for the intestines
Hypercalcemia in acute manifestations, when the amount of the element reaches 3.7 mmol/l, requires more serious treatment methods. The patient must be hospitalized and under constant medical supervision until the amount of the element in the blood decreases. In hospital mode, fluid (saline) is administered intravenously.
Diuretics are selected depending on kidney function
Diuretic drugs are selected depending on the performance of the kidneys. To preserve calcium in bone tissue, corticosteroids and bisphosphonates may be prescribed.
The use of calcitonin increases the excretion of the mineral in the urine. Drugs are selected depending on the functionality of internal organs and possible side effects.
In the most difficult cases, surgery is performed, during which the tissue of the parathyroid glands is removed. After surgery, the disease resolves in most patients. Hypercalcemia in cancer pathologies is difficult to treat.
If the tumor increases in size, then therapy aimed at reducing calcium levels does not give the desired result.
Drug therapy to reduce calcium levels in the blood is selected after establishing the causes of the disease and taking into account the severity of the disease.
How to prepare for a calcium test
In order to obtain the most reliable data after taking a blood calcium test, you should properly prepare for blood sampling.
The analysis is done on the basis of venous blood. 24 hours before taking blood, you should reduce physical activity as much as possible, since its high level affects calcium levels. It is also necessary to stop smoking, drinking alcohol and eating fatty and smoked foods the day before the test. 24 hours before blood sampling, you should not eat foods rich in calcium, as they will increase the amount of the mineral in the blood, which will distort the indicator.
The last time before donating blood for calcium, you can eat 8 hours before. You should only drink clean water, without any additives or gas, in an amount of no more than 2 glasses per hour. If you drink more liquid, the calcium in the body will be underestimated, as it will be excessively excreted by the kidneys.
Medicines can also affect the level of calcium in the body. For this reason, you should stop taking medications 7 days before blood sampling unless they are vital. When medications cannot be stopped, the specialist who determines blood counts must be informed about what medicine is being used and in what quantity. In this case, a special table is used, which allows you to determine which calcium norm will be as close as possible to the real one, undistorted by medications.
Blood is taken for analysis in the morning, when the content of total calcium in it is at its maximum. Ideally, material for analysis should be received before 11 am. The deadline is 12 days. Strict adherence to time is necessary, since it will be difficult to determine the lack of calcium or excess later due to the period of activity already quite long after the night, which leads to a distortion of the picture. Only morning blood shows accurate results.
Blood test for calcium: indications, interpretation
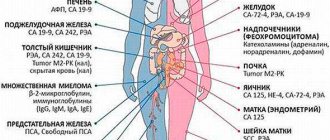
Calcium has a large number of functions in the human body: increasing the strength of tooth enamel and bones, controlling the process of transmitting nerve impulses to muscles, regulating blood clotting, improving iron metabolism. For this reason, there are many indications for testing calcium levels:
- oncology (during their treatment and primary diagnosis);
- kidney tumors;
- renal failure;
- multiple myeloma (plasma cell tumor);
- peptic ulcer of the intestines, stomach;
- hyperthyroidism (excessive production of thyroid hormones);
- arthralgia (joint pain);
- paresthesia (tingling in the limbs);
- osteoporosis;
- decreased muscle tone.
HypocalcemiaHypercalcemia
| frequent dizziness, headaches | constant feeling of thirst |
| lethargy, weakness, decreased performance | nausea, loss of appetite |
| deterioration of blood clotting | increased blood clotting |
| brittle nails, hair loss | shortness of breath even with light exertion |
| frequent seizures | frequent stomach upsets |
| irritability | problems with bowel movements (often constipation) |
| memory impairment | frequent urge to urinate at night |
| arrhythmia (irregular heart rhythm) | apathy |
Preparation
To exclude false results, you should stop taking medications 2 weeks before the test or notify your doctor before the procedure about what is being used and in what dosage. Additionally, you need to follow the general rules for preparing for blood donation:
- do not eat fatty, fried, salty foods (days before analysis);
- exclude alcohol, physical activity, stressful situations (24 hours before the test);
- donate blood on an empty stomach in the morning (at least 8 hours must pass since the last meal), but you can drink clean water (not mineral water);
- Do not undergo fluorography, radiography, or ultrasound diagnostics before analysis.
AgeCalcium (mmol/l) Ionized calcium (mmol/l) men women men women newborns 3-24 months 2-12 years 12-50 years 50 years
| 1,9–2,6 | 1,0–1,3 | ||
| 2,25–2,75 | 1,1–1,37 | ||
| 2,2–2,7 | 1,1–1,31 | ||
| 2,1–2,55 | 2,2–2,5 | 1,05–1,26 | 1,1–1,25 |
| 2,2–2,5 | 1,1–1,25 |
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
A calcium test may show non-compliance with standard indicators in 2 cases: under the influence of external factors or in the presence of pathologies caused by hyper- or hypocalcemia in the blood. False test results occur in patients:
- during pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- in childhood (a period of active growth associated with changes in tissues);
- taking hormonal drugs, vitamins A and D, diuretics, mood stabilizers - they increase the concentration of calcium;
- taking antibiotics, anticonvulsants, glucocorticosteroids, laxatives or antitumor drugs - reduce calcium levels.
HypocalcemiaHypercalcemia
| malignant neoplasms with metastasis | low-grade tumors (especially in the parathyroid glands) |
| physical inactivity | tuberculosis affecting the musculoskeletal system |
| Poor nutrition (deficiency of vitamin D, magnesium, dairy products) | disruption of the adrenal cortex and pituitary gland |
| chronic sepsis | sarcoidosis |
| liver dysfunction (cirrhosis, severe intoxication) | excess vitamin D |
| excess estrogen (in men) | blood pathologies (lymphomas, myelomas, leukemia) |
| chronic renal failure | kidney transplant |
| rickets in children | severe chronic enterocolitis |
| removal of parathyroid glands | dehydration |
| adrenal hyperplasia | hereditary hypocalciuric hypercalcemia |
| inflammation of the pancreas, malabsorption in the small intestine | long-term immobilization (immobility) in case of diseases or injuries of the musculoskeletal system |
Blood calcium test
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Biochemical blood test for calcium is a clinical test that determines the concentration of total calcium in the blood serum.
The concept of total calcium includes:
- Ionized calcium makes up 50% of all calcium in the blood.
- Calcium bound to proteins (mainly albumin) – 40%.
- Calcium, which is part of anionic complexes (associated with lactate, citrate, bicarbonate, phosphates) – 10%.
- Muscle contraction.
- The work of the endocrine glands.
- Blood coagulation, cell membrane permeability.
- Construction of the skeletal system and teeth.
- Transmission of nerve impulses, work of the nervous system.
- Enzyme activity, iron metabolism in the body.
- Normal heart rhythm, functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Ionized calcium is calcium that is not bound to any substances and circulates freely in the blood. It is the active form of calcium that is involved in all physiological processes. A blood test for ionized calcium will assess calcium metabolism in the body. This test must be given to patients in the following cases:
- Treatment after resuscitation, surgery, major trauma, burns.
- Diagnosis of cancer, hyperfunction of the parathyroid gland.
- Carrying out a hemodialysis procedure.
- Taking the following medications: bicarbonates, heparin, magnesium, calcium supplements.
A blood test for ionized calcium is carried out in conjunction with determining the level of total calcium and blood pH. The value of ionized calcium is inversely related to blood pH: the level of ionized calcium increases by 1.5 - 2.5% for each decrease in pH by 0.1 unit.
Indications for analysis
Indications for a biochemical blood test for calcium:
- Signs of hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia.
- Malignant neoplasms (breast cancer, lung cancer).
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
- Decreased albumin concentration.
- Preparation for surgery.
- Muscle hypotension.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Kidney diseases, urolithiasis.
- Bone pain.
- Cardiovascular pathology (impaired vascular tone, arrhythmia).
- Polyuria.
- Paresthesia.
- Convulsive syndrome.
- Diagnosis and screening of osteoporosis.
Symptoms of hypercalcemia: adynamia (immobility), asthenia, increased reflexes, impaired consciousness, disorientation, weakness, headache, vomiting, acute renal failure, heart failure, tachycardia, extrasystole, vascular calcification.
Symptoms of hypocalcemia: migraine-like headaches; dizziness, caries, osteoporosis, nail destruction, hair loss, dry skin, increased reflexes leading to tetanic convulsions, weakness, blood clotting disorders (extended clotting time), angina pectoris, tachycardia (increased heart rate - pulse).
Hypercalcemia is a pathological condition that occurs when the body becomes ill. Physiological hypercalcemia occurs - after eating and in newborns after the fourth day of life. Hypocalcemia is diagnosed much more often than excess calcium in the body.
- On the eve of the study, you should not drink alcohol, fried or fatty foods.
- The day before blood sampling, it is advisable to avoid heavy physical and emotional stress.
- Blood is donated on an empty stomach, 8-10 hours after the last meal. It is recommended to drink only still water.
- It is not recommended to donate blood immediately after fluorography, rectal examination, radiography, ultrasound examination or physiotherapeutic procedures.
Taking medications can affect the accuracy of the calcium blood test result. It is advisable to stop taking any medications 1-2 weeks before taking blood for testing.
If it is impossible to discontinue the drug, then in the referral for a biochemical blood test for calcium it is necessary to indicate which medications the patient is taking and in what doses.
The following medications affect calcium levels in the blood.
Increase calcium levels: vitamin A, vitamin D, testolactone, tamoxifen, parathyroid hormone, progesterone, lithium, isotretinoin, ergocalciferol, dihydrotachysterol, danazol, calusterone, Ca salts, androgens, regular use of diuretics.
Reduce calcium levels: sulfates, oxalates, fluorites, tetracycline, plicamycin, phenytoin, methicillin, magnesium salts, isoniazid, insulin, indapamide, glucose, glucagon, gastrin, fluorites, estrogens, ergocalciferol, corticosteroids, carboplatin, carbenoxolone, carbamazepine, calcitonin, asparaginase , aminoglycosides, alprostadil, albuterol.
The results of the study must be interpreted by a specialist with appropriate qualifications. Only a doctor will be able to properly assess the patient’s condition, the deviation from the normal blood test for calcium and make the correct diagnosis. And accordingly, prescribe adequate treatment in a timely manner.
Reference values for a blood test for total calcium:
- children under 1 year – 2.1-2.7 mmol/l;
- children from 1 to 14 years old – 2.2-2.7 mmol/l;
- children over 14 years old – adults – 2.2-2.65 mmol/l.
Increased values
Hypercalcemia indicates the following diseases:
- Acute renal failure.
- Sarcoidosis and other granulomatous diseases.
- Iatrogenic hypercalcemia.
- Hereditary hypocalciuric hypercalcemia.
- Williams syndrome (idiopathic hypercalcemia of newborns).
- Hypervitaminosis D.
- Milk-alkali syndrome.
- Hemoblastoses (leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma).
- Adrenal insufficiency.
- Immobilization hypercalcemia (for therapeutic purposes for injuries, congenital hip dislocation, Paget's disease, spinal tuberculosis).
- Malignant tumors
- Primary hyperparathyroidism (adenoma, hyperplasia or carcinoma of the parathyroid glands).
- Thyrotoxicosis.
Reduced values
What conditions can disrupt the calcium picture?
Whether there is enough or not enough calcium in the body cannot always be determined accurately, since the results of the analysis are significantly distorted under certain conditions. These include: pregnancy, breastfeeding and rapid growth of the child. Determining the calcium content is complicated by the fact that in these cases, changes are actively taking place in the tissues, due to which calcium consumption is constantly changing, as is its pattern in the blood. The serum value during such a period can vary significantly in the same person when blood is taken at short intervals. Most often, according to analyzes in such conditions, one may encounter a calcium deficiency, which in reality does not exist. With normal daily consumption of the mineral, the body has enough of it, but it is not always possible to determine this by taking tests.
Why calcium is not absorbed in the body reasons
There are many different factors that lead to impaired absorption of calcium by the body. The main ones are:
Improper functioning of the stomach.
As a result of poor nutrition and bad habits, insufficient production of hydrochloric acid and enzymes occurs in the stomach. Without these components, the body is not able to independently absorb various microelements, including Ca.
Fatty acids, in contact with calcium salts, turn into complex deposits that are not only not absorbed by the body, but are also difficult to remove from it.
Oxalic acid.
By consuming foods containing this substance, a person is unable to absorb calcium in the body. It, interacting with the acid in question, turns into difficultly soluble oxalate salts, which accumulate in the organs, leading to serious consequences.
Vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium. Without this component, Ca is not retained in the body and is excreted from it
Please note that for the absorption of vitamin D, it is necessary to enter the body with fatty acids contained in foods such as fatty fish, eggs and vegetable oils.
When the amount of estrogen (female sex hormone) in a woman’s body decreases, a disturbance in the conductivity of calcium in the tissue occurs. The production of female hormones slows down when the reproductive system, due to age, stops functioning.
Also, oral contraceptives, corticosteroids and pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract lead to impaired absorption of calcium. To exclude possible pathologies, you should undergo a preventive examination by specialists once a year.