According to statistics, arthrosis of the knee joint is given one of the leading places among all types of arthrosis. In numbers this is more than 20%. Of all the diseases that affect the knee joint, the incidence of gonarthrosis is 53%.
If you have knee pain, you need to get a diagnosis early.
The danger of gonarthrosis, like most arthrosis, lies in late diagnosis.
What methods of diagnosing arthrosis of the knee joint exist in modern medicine?
Should X-rays be discounted?
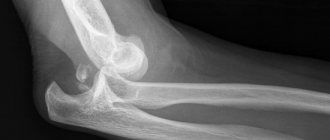
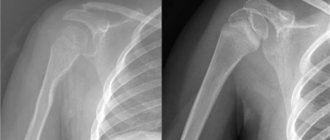
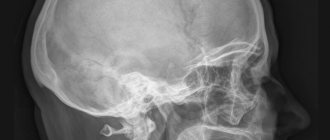
The standard for diagnosing arthrosis of the knee joint has always been an x-ray examination. The method is based on recording the residual energy of X-rays absorbed by the object under study. Bone tissue has the maximum absorption coefficient. Therefore, it is not difficult to figure out what an x-ray of the knee joint will show. All bone changes will be clearly visible.
In addition to bone pathology, this method will also monitor the pathology of intra-articular cartilage.
The standard for diagnosing arthrosis of the knee joint has always been x-ray examination.
X-rays of the knee joint are simple to perform and, for an objective assessment of the condition of the knee, are performed in 4 projections:
- Straight;
- Side;
- Transcondylar;
- Tangential.
Despite the growth of advances in medical technologies and their widespread introduction to the masses, radiography of the knee joint does not lose its importance today.
The digital processing of X-ray images available today minimizes the radiation dose received during the examination and improves the quality of the images, which has a positive effect on the accuracy of diagnosis.
What is the difference between ultrasound and x-ray?
The main difference between the techniques lies in the nature of the radiation that is used to form an image on a monitor screen, photographic film or paper.
X-ray medical imaging is based on the ability of bones, soft tissues, hollow and parenchymal organs to absorb ionizing radiation differently. Soft tissues allow x-rays to pass through, causing slight deflection, but bones and cartilage absorb them completely. X-ray images of organs are black and white due to differences in radiation absorption by biological tissues. The doctor can easily make a diagnosis from the X-rays obtained.
For ultrasound, high-frequency sound waves (1-22 MHz) are used, which is the difference with the previous method. These sounds are not perceived by the human ear. They are converted into rays and used to study the body. Living tissues conduct ultrasound differently: some completely reflect, others scatter. The reflected echoes are captured by the sensor, amplified, and a balanced image is formed on the device’s screen.
What are the indications and contraindications for each method?
The choice of diagnostic method depends on the attending physician. When prescribed correctly, both medical imaging modalities carry minimal risk to the patient's health.
X-rays are prescribed to study the musculoskeletal system during injuries and surgical interventions, also in pulmonology and gastroenterology. Ultrasound is preferred when examining the abdominal organs, thyroid and mammary glands, cardiovascular system, in obstetrics and gynecology.
Ultrasound scanning is a safe and accessible research method at any age and for all diseases. Over 40 years, millions of people, including pregnant women, were examined, and there was not a single side effect.
The negative effects of X-ray radiation include increased ionization load. X-rays are contraindicated in pregnant women and infants because electromagnetic and alpha rays affect growing tissue.
How the procedures are carried out and what is shown
X-rays are performed in a specially equipped room. To protect the patient from excessive radiation, aprons and caps made of leaded rubber are used. The duration of the procedure depends on the type of examination and averages up to 10 minutes.
Ultrasound scanning requires no preparation and can be performed directly at the patient's bedside. A gel is applied to the ultrasound probe and the skin at the test site, which increases the conductivity of sound waves.
Advantages and disadvantages of each method
The main advantage of radiography is its clear examination protocols, which minimizes human error. Disadvantages include radiation exposure and the cumbersome nature of the technology.
The positive aspects of ultrasound scanning include safety, the ability to repeatedly study the patient’s condition in a short period of time, and examination of almost all organs and systems. Disadvantage: the accuracy of diagnosis depends on the skill of the ultrasound physician.
Compare prices
The cost of an ultrasound examination and an x-ray are equivalent. Despite this, X-ray equipment is more expensive and more expensive to maintain than an ultrasound scanner.
However, radiology is actively supported by targeted government programs, and the examination can be done at any district clinic. Ultrasound examination services are offered by private centers, where prices are often inflated.
Advances in Ultrasound Research
The second most frequently prescribed additional examination was knee ultrasound. The method is based on recording ultrasonic waves reflected from the object under study. Depending on the density of the substance, the intensity of the reflected beam changes.
Having one informative research method available (x-ray), it will be interesting to know what an ultrasound of the knee joint shows, why it is prescribed more and more often, and how it differs from the results of an x-ray examination.
The capabilities of the first ultrasound devices were limited and making a correct conclusion from an ultrasound examination required great skill from the doctor. Today, almost all medical centers have ultrasound devices - the latest generation devices with three-dimensional visualization, which allow you to perform ultrasound of the knee joint and soft tissues. In addition to examining the dense bone and cartilaginous components of the knee (which X-rays can do well), ultrasound can visualize the ligaments, tendons, and surrounding periarticular tissue. Ultrasound diagnostics of the knee joint makes it possible to assess the amount of synovial fluid and localize its maximum accumulation in the inversions of the joint capsule. Such precise visualization is necessary for performing surgical procedures.
Ultrasound allows you to see the ligaments, tendons and surrounding periarticular tissues
But it should be understood that modern ultrasound machines only provide a high-quality image of the structures, and the doctor performing the study is responsible for interpreting the ultrasound of the knee joints.
The specialist who gives an opinion on an ultrasound examination is called a functional diagnostics doctor. A specialist certificate is issued either after completing a residency in a given specialization, or after a retraining course for a doctor of any other profile.
What is ultrasound of joints?
An ultrasonography machine records ultrasound waves that are reflected from a given organ.
Thanks to innovative achievements, the latest equipment allows you to display on the monitor in three-dimensional images:
- Condition of the ligaments.
- State of blood flow.
- Identification of pathologies of joints, tendons, and soft tissues.
Ultrasound of joints
In most cases, ultrasound of joints is prescribed in the presence of the following symptoms:
- Swelling.
- Painful sensations.
- Crunching in the joints.
Knee pain
To obtain a three-dimensional image of any joint, the patient is placed on a couch, the area to be examined is lubricated with gel, and the condition of the organ is recorded from different angles using a sensor. During the diagnosis, the doctor receives detailed information about the condition of the soft tissues, ligaments, muscles, bone mass of the hip joint or knee. The results of the examination are recorded in paper and electronic format.
Diagnostic choice between radiography and ultrasound, in whose favor?
Of course, in addition to a good professional base of medical training, experience in the chosen field plays an important role in the correct interpretation of the results of an ultrasound examination.
Therefore, when choosing where to have an ultrasound of the knee joints, you need to focus on the status of the medical institution.
Not a single medical institution that values its name will recruit medical personnel with an insufficient professional level. Regarding medical professionalism, when asking the question: “What can an ultrasound of the knee joint show?”, one can answer: “What the doctor sees.” And this will not depend on the public or private status of the medical institution.
Any patient suffering from pathology of the knee joint, after visiting a doctor, will be faced with a choice: “What is better: ultrasound or x-ray of the knee joint?” It is difficult to answer this question unequivocally. To diagnose diseases/damages of the knee, x-ray examinations have always been sufficient. This should be taken into account in case of predominant destructive damage to bone and/or cartilage tissue.
If tendons, muscles, ligaments, and joint capsule are involved in the process, then preference should be given to ultrasound examination.
Not the least factor in the patient’s final decision is the cost of the study. There is always a pressing question: “How much does an ultrasound of the knee joint cost?” Approximately, the cost of an ultrasound scan of the knee ranges from 700 to 1000 rubles. This will depend on the region of residence and the level of the medical institution providing the service.
Which method should you choose?
Which diagnostic method to choose is the decision of the attending physician, but the patient would do well to familiarize himself with the remarkable features.
For example, ultrasound diagnostics will not be effective enough when examining bone tissue and will be completely ineffective when diagnosing the condition of organs that are filled with air (lungs, stomach, intestines), since the air completely reflects high-frequency waves and does not give any echographic image.
And X-ray radiation has limitations on the frequency of use. It should not be performed on pregnant women, so as not to harm the baby. Also, a number of problems can be diagnosed exclusively using ultrasound (transvaginal, transrectal and transurethral diagnostic methods, in which a sensor is inserted into the vagina, rectum and urethra, respectively, thus providing an overview of the organs of the genitourinary system).
In addition, devices for ultrasound diagnostics are more portable, which allows, if necessary, an appointment at home. To undergo an x-ray or fluorography, you must visit a special room in the clinic.
Computed tomography – a whim or a necessity?
Relatively recently, the arsenal of instrumental research has been expanded with computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. What makes these studies unique? They allow you to see tissue layer by layer, with a given slice thickness.
A CT scan of the knee joint, like any other instrumental study, can be prescribed for any disease of the knee.
But CT will have a diagnostic meaning only if it is necessary to determine the exact localization of a particular pathological process. This will be relevant for injuries and neoplasms.
In this video, the doctor will explain in detail the difference between MRI and CT.
When deciding whether MRI or CT of the knee joint is better, it is important to know the area of diagnostic interest.
If the pathological process affects bone and/or cartilage tissue, then CT should be chosen. If the process is most localized in soft tissues, then it makes sense to opt for MRI.
MRI of the knee is a rather complex physical process to understand, based on the registration of electromagnetic waves emitted from the tissues of the object under study after exposure to a constant high-intensity magnetic field.
Invention by V.K. X-ray
After Roentgen discovered the X-ray tube, a new era in diagnostics began. Most often, X-rays are used to examine the lungs, bone structures, kidneys, and digestive tract.
An X-ray tube is a glass vessel with a hole for the beam to exit. Has 2 poles: cathode and anode . At the cathode, when a low voltage is applied, electrons are emitted and an electron cloud is formed. When high voltage is applied, electrons fly to the anode, generating radiation. At the anode plate they brake sharply. Therefore, radiation is also called bremsstrahlung.
Advantages of x-ray examination:
- Good visualization of bone tissue . This is the main and most informative method for diagnosing fractures, neoplasms, and inflammatory changes in bone tissue. For better visualization, studies are performed in several projections. For a comprehensive examination, layer-by-layer study of bone structures, computed tomography is performed.
- The main method for studying the lungs . Lung tissue contains air, which improves its visualization with X-rays. For mass examination, fluorography is used. For patients with pathology, X-ray examination or, if necessary, computed tomography is used.
- Quick examination . The examination takes a few minutes.
- Possibility of creating an image archive . This helps track the course of the disease over several years.
The essence and diagnostic need of magnetic resonance imaging
To understand what an MRI of the knee joint shows, it is important to know that this physical process is aimed at tissues with a high content of hydrogen atoms, that is, tissues with a low water content will appear poorly on an MRI. MRI examination of the knee joints allows visualization of soft tissues with a resolution step of 0.3 - 0.5 cm.
The procedure is quite expensive, practically safe, and highly informative.
Therefore, taking into account medical recommendations regarding the nature of the pathological process, the patient decides whether or not to perform an MRI of the knee joint.
MRI examination of the knee joints allows visualization of soft tissues with a resolution step of 0.3 - 0.5 cm
The diagnosis of arthritis or arthrosis, gout or rheumatoid arthritis, bursitis or effusion synovitis can be established using cheaper methods.
MRI for diseases of the knee joint, without the importance of establishing the extent of the pathological process, the accuracy of its localization, and determining the degree of vascularization, does not become a diagnostic advantage.
Therefore, deciding whether ultrasound or MRI of the knee joint is better depends on the process. If there is, for example, gonarthrosis with secondary synovitis, ultrasound will answer the same questions as MRI, but for a lower cost.
When answering the question: “Where can I get an MRI of the knee joint?”, it should be noted that not every clinic can afford an MRI examination. This is expensive, massive equipment that requires certain conditions for its placement.
Therefore, MRI examinations can only be performed in large medical centers, often ordered by the state.
An MRI machine is an expensive, massive piece of equipment that requires certain conditions for its placement.
Regardless of the area being examined, MRI of the knee is the same as MRI of any other organ. To specify the answer to the question: “How does an MRI of the knee joint work?”, it is enough to know that the scanning procedure takes place in a closed tube, and the induction coils that generate the magnetic field are located at the level of the knee joint being examined. No preliminary preparation is required before the MRI.
The main contraindications are:
- Pregnancy;
- Mental disorders;
- The presence of metal objects in the body.
Pathology of the knee joint on MRI scans
Pathological changes in the knee are diagnosed by CT, X-ray or MRI according to the purpose of the examination.
What does a knee X-ray show:
- Degenerative-dystrophic processes (osteoarthrosis);
- Joint dislocations, fractures;
- Children's chondropathy.
CT complements radiographic diagnosis with nosologies detected by transverse scanning through 1 mm. The scan determines the relationship between individual anatomical formations, the accumulation of inflammatory foci, and areas of edema.
X-ray or CT should be chosen if bone pathology is suspected. If verification of soft tissue changes is required, MRI is performed. The examination visualizes significant bone defects.
What does an MRI of the knee reveal?
- Exudative synovitis;
- Periarticular lesions (around the joint cavity);
- Joint deformities;
- Erosion of articular surfaces;
- Changes in the shape and size of bones;
- Length of articular cartilage lesions;
- Overgrowth of fibrous tissue;
- Deformation of the epiphyses, severe marginal growths;
- Destruction of the menisci.
The list of nosologies can be continued. Innovative technologies for the development of methods are improved every year.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the knee menisci
Knee menisci are diagnosed better by MRI than by ultrasound. The method is characterized by an accuracy of over 95%.
Features of diagnosing meniscal destruction on MRI:
- Increased signal intensity of the central part (weak degeneration);
- A wide area of amplified signal of linear extent without penetration into the joint cavity (widespread degeneration);
- Penetration of the central part of the contents into the joint with displacement or separation of part of the meniscus, destruction of the peripheral contour (rupture).
What ligament injuries does MRI show:
- Complete or partial rupture of ligamentous elements;
- Rupture of tendon fibers;
- Abnormal arrangement of ligaments (horizontal course);
- Expansion, thickening of the cruciate, collateral, lateral ligaments;
- Isolated fiber arrangement.
The inflammatory process inside the knee is accompanied by infiltration of bone, fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial membranes. An irreversible joint condition is rheumatoid arthritis.
What an MRI reveals for knee inflammation:
- Exudative fluid;
- Popliteal fossa (Baker) cyst;
- Hypertrophic growths of the synovial surface;
- Overgrowth of connective tissue along areas of degeneration of the knee surfaces;
- Meniscal degeneration;
- Thinning of cartilage;
- Joint effusion.
The advantage of magnetic resonance imaging of joint changes is the identification of minor changes (marginal lesions, local osteoporosis (low concentration of bone calcium), small cysts, epiphyseal deformities, tenosynovitis).
Proliferative changes in arthrosis are visualized on magnetic resonance imaging - thinning of the ligaments, degeneration of the menisci, multiple defects, defects of the intra-articular space, subchondral and intra-epiphyseal cysts.
Modern types of MRI of the knee joint reveal not only soft tissue, but also bone changes.
Coronal projection complements the list of information:
- Detection of fibrosis;
- Marginal growths of intra-articular surfaces;
- Subchondral osteosclerosis of the epiphyses.
MRI diagnostics allows for differential diagnosis between infiltrative and expansive processes.
Detection of infiltration indicates an aggressive course of the process. Inflammatory processes inside the medullary canal, along the bone beams, are accompanied by gradual destruction of the bone. The pathology must be treated with intensive long courses of antibiotic therapy.
Tumors (benign) are characterized by expansive growth. The lesions are separated by a zone of ossification from the medullary canal. Massive infiltration or expansion of the knee bones on tomograms requires immediate treatment.
It should be noted that there is concomitant contrast tracking of vascular pathology during MR scanning of the knee joint. Diagnostics is important for obese people with varicose veins, as it allows you to detect blood clots (vascular clots).
How long does a knee MRI take?
An MRI of the knee joint lasts on average 20-25 minutes if the procedure is without contrast. Injection of gadolinium salts into a vein improves the visibility of blood vessels. Performed after native scanning. Requires the exclusion of allergic reactions to the paramagnetic.
The duration of the procedure is about 10 minutes. The manipulation involves the injection of small doses of gadolinium drugs. The patient's condition is observed for several minutes. No change allows contrast. Skin rashes, breathing problems, increased heart rate, and other negative manifestations require exclusion of the procedure.
You can roughly estimate how long an MRI takes to complete. In the absence of unusual situations, the duration of tomography with contrast will be approximately 40-45 minutes. The patient must remain motionless throughout. Performing manipulation on a child involves the use of anesthesia.
Diagnostics in Astana
It’s good that our citizens take care of their own health, improve medical literacy, lead a healthy lifestyle, etc. If there is a need for quality medical care, then contact us, Medar Clinic.
We have all the necessary equipment for high-quality diagnostics and treatment. More than ten years of experience, unique techniques, cozy rooms, friendly medical staff. We also help with rehabilitation after severe injuries or operations. Our patients are always satisfied with the results.
In our methods, we use psychological support for the patient, special diets, traditional medicine, physical therapy and the most advanced healing methods.