Postpartum complications most often occur in the first days after childbirth. Manual obstetric examination does not always give a complete picture of a woman’s condition. Therefore, in maternity hospitals they resort to the method of ultrasound examination of the postpartum woman before discharge. Ultrasound helps to timely diagnose various pathologies of the postpartum period.
Read about how an ultrasound is performed after childbirth and what problems the procedure reveals in this article.
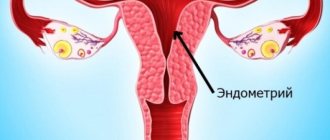
What happens to the uterus?
During pregnancy, the uterus increases in volume and size many times – 500 times or more, gaining weight from 50 grams to a kilogram. Under pressure from the baby's body weight, as well as with the development of the placenta, the uterus changes its shape and stretches. And immediately after childbirth, it begins to contract back, most intensely in the first days.
Simultaneously with the change in shape, the uterus returns to its anatomically correct place in the woman’s pelvis, because in the last stages of pregnancy it occupied all the space in the abdominal cavity.
And on a pelvic ultrasound immediately after childbirth, it is necessary to evaluate the weight of the uterus: it is decreasing. The shape gradually changes from round to pear-shaped, as it was before pregnancy and the birth process itself.
Involution of the reproductive organs
During the postpartum period, the female body experiences a process of involution (reverse development) of all systems and organs that have changed during pregnancy. This change begins from the moment the placenta falls away. It will take about 6 weeks. After the birth of the baby, contractions of the uterus are observed under the influence of postpartum contractions.
After the birth of the baby, the size of the uterus decreases, the bottom of which is located at the level of the navel. The bottom is sinking lower every day. So by the second day it is located slightly below the navel, by the 4th day - between the womb, navel, by the 8th - 9th day - slightly above the womb. After some time, it will take its place, which corresponds to the norm.
By this time, the shape of the uterus should change. It normally takes the following forms:
- Ball-shaped – by the 3rd day;
- Oval - by the 5th day;
- Pear-shaped - by the 7th day.
Also observed during this period is discharge from the genital tract, which is called lochia. They change color starting from the first day after birth:
- Bright red – on days 2–3;
- Pale – from the 3rd day;
- Yellowish – from the 5th day.
After a week, the discharge becomes the same as before before pregnancy.
How an ultrasound examination is performed after childbirth
After labor ends, there is no more amniotic fluid left in the uterus. Therefore, before the ultrasound, which is performed in the maternity hospital, the doctor recommends filling the bladder properly in order to slightly elevate the uterus and improve visualization of the organ for a more accurate assessment by a specialist. To sufficiently fill the bladder, you need to drink about one and a half to two liters of warm water. If there is a reason for an urgent examination, and there is no way to wait, the bladder will be filled with fluid through a special catheter.
Ultrasound examination in the immediate postpartum period is carried out by installing a sensor on the abdominal wall: the uterus is still very large, transvaginal ultrasound (accessed through the vagina) will not show an objective and accurate picture.
The examination procedure takes about thirty minutes. The woman lies on her back.
How is ultrasound performed?
To check for scar tissue after a cesarean section, ultrasound is done in two ways. In most cases, the condition of the uterus is checked through the lower abdomen (abdominal).
How the clinic diagnoses the uterus with ultrasound:
- The patient covers the couch with a towel. She lies on her back, exposing her stomach.
- A special gel is applied to the lower abdomen.
- The doctor moves the sensor over the skin and looks at the image that appears on the screen.
- After the procedure, the woman removes the remaining gel from her stomach.
Sometimes the uterus is examined through the vagina (transvaginally). In this case, a condom is put on the device.
To watch a video review from the chief physician of the medical center, Dr. Nikolaev, on the topic:
What will an ultrasound of the uterus show after childbirth?
Diagnosis of the condition of the uterus, as well as the pelvic organs, after childbirth is performed to detect possible disorders that can lead to complications. The doctor analyzes and studies the woman’s health status according to several parameters:
- the size of the uterus, how it contracts, where and how it is located at the time of examination;
- whether there are any formations or fragments in the cavity inside the uterus (for example, blood clots, parts of the fetal membrane or remaining placenta may be found);
- what is the volume of fluid in the uterus, is it excessive;
- assessment of the endometrium: is there any development of inflammatory phenomena;
- assessment of the suture at the surgical site (if the birth took place by cesarean section);
- general condition of all pelvic organs.
Changes in the uterus during the postpartum period
After natural delivery, with a short time interval, the placenta with the membranes of the fetus (afterbirth) is “born”, the uterus begins to contract vigorously. These contractions cause sharp pain in the lower abdomen. The organ works in active mode, on days 5–7 the uterus contracts three times, by the 10th day – ten times, that is, it takes on the size corresponding to the state before pregnancy. At the same time, the uterus shifts to its anatomical location. The shape of the reproductive organ (spherical uterus) changed during pregnancy returns to its natural pear-shaped shape within a week.
The contractile process time increases in the following cases:
- performing an operation for artificial delivery (caesarean section);
- multiple embryonic pregnancy;
- artificial feeding (the woman does not release the hormone oxytocin, which stimulates contractile activity);
- excess amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios);
- injury during childbirth;
- coagulation disorders (poor blood clotting).
These reasons require increased attention from the gynecologist. Low contractile activity of the uterus can lead to serious postpartum complications, in particular: inflammation of the intrauterine mucosa (endometritis), uterine bleeding, impaired outflow of postpartum discharge (lochia), kinking of the reproductive organ, formation of a barrier in the vagina due to the accumulation of postpartum clots. The task of doctors is to prevent unwanted complications, or to record them at the initial stage, which is why they do an ultrasound after childbirth.
Normal transformation of the uterus after childbirth
Ultrasound results after natural childbirth
After the child is born through the natural birth canal, diagnostics of the pelvic condition by ultrasound is prescribed from the second to the fourth day. If the birth was complicated or there is concern that there is a rupture of the uterine wall, an ultrasound will be performed as an emergency. Visually, normally the uterus will have a certain shape, close to spherical. Immediately after childbirth, it will be located in the middle pelvic region. If a woman has had two or more children, or if she has one large baby, the uterus will move slightly toward the lower part of the pelvis.
If you conduct the study several times over a short period of time in the postpartum period, it is possible to monitor how the weight of the contracting uterus decreases and how it narrows. The reduction of the organ and its displacement to the location that was before the birth occurs little by little. The norm for changes is a shift of 1–2 cm every day. In terms of weight, the uterus loses approximately half (about 450–550 g) in the first few days (up to a week). Subsequently, weight loss becomes smoother and more gradual: about 100 g per week, to the standard 95-100 g that was before childbirth.
Violations
The process of restoration of the uterus and cervix does not always follow a clear algorithm. Complications often appear during this period; a woman may hear the following conclusions from a gynecologist:
- Large or enlarged uterus after childbirth. A woman can hear this conclusion 1-2 years after giving birth based on ultrasound results. In this case, the changes affect only the uterine cavity, the cervical canal is not deformed. In this case, we can talk about endometriosis of the uterine body, namely adenomyosis. The disease has a favorable prognosis, but its danger cannot be underestimated.
- Soft uterus. This change is diagnosed in the first week after birth. A violation may indicate that particles of rejected endometrium and membranes remain in the cavity. It is impossible to underestimate and ignore the pathology; the problem is that there is a risk of developing hematometra. With this pathology, blood accumulates in the uterine cavity, increasing the risk of infection.
- Inversion of the uterus. An equally dangerous condition that manifests itself in the early postpartum period or directly during childbirth. The mucous membrane of the uterus is on the outside. The preconditions for the development of the problem are created when the obstetrician-gynecologist provides improper care to the woman. Another reason is the abuse of relaxing drugs in the postpartum period, under their influence the uterus can turn out.
- Lichiometra. This term refers to blockage of the cervical canal. The reason for its development is the abrupt, rough removal of the child from the mother’s birth canal. The natural outflow of blood is disrupted due to spasm of the internal pharynx.
- Omission. The most common complication, experienced by about 50% of women. The risk of its development increases with multiple pregnancies and repeated births.
If detected in a timely manner, such disorders do not pose a danger to the woman’s body and can be successfully eliminated with the help of medications and simple operations. The main risk lies in the late detection of the problem, since the prolapse can progress for a long time, and its full treatment is possible only in the early stages.
The process of restoration of the uterus and its cervical canal after childbirth takes about 2 months, but the changes occur unnoticed by the woman herself and do not interfere with her enjoyment of motherhood. The fundus of the uterus returns to its natural position within the first 2 days, the size of the uterus (its weight, width and height) returns to normal within 2 months. The cervix remains deformed, its canal becomes slit-like.
The intensity of the recovery process largely depends on the current factors. For example, with complications during childbirth, the regeneration process takes longer. This feature is typical for patients with hypertension and multiple pregnancies. Repeated births are often easier than the first if you ignore the mother’s recovery process. Very often the uterus cannot contract on its own.
Involution always proceeds differently, so you should not ignore the need for constant medical monitoring. If detected early, the doctor can eliminate the problem without harming the mother's health. The quality of recovery must be monitored 2 months after birth and 3 months after cesarean surgery. The given deadlines are relative, so you should not worry about minor deviations.
7 minutes Author: Irina Bredikhina 586
During the perinatal period, a woman's reproductive system undergoes a certain biological transformation. The return of internal organs to an adequate state takes an average of one and a half months. To control this process, a mandatory ultrasound procedure is provided after childbirth. The greatest number of complications is recorded in the first postpartum week. Ultrasound examination is the only highly informative and accessible method for diagnosing distorted manifestations of the reproductive system during the recovery period of a woman after childbirth.
Ultrasound results after cesarean section
After a birth performed by cesarean section, the restoration of the reproductive organs takes a long time due to the fact that the mass and overall size of the uterus, taking into account surgical intervention, expands and adds mass by about 40% when compared with natural childbirth. During ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor can see small hematomas, which are foci of hemorrhage in the area of the scar formed at the site of the operation. Such lesions are not dangerous, but they are quite capable of impairing the passage of ultrasound from the sensor to the organ and back. And if the scar swells, then this phenomenon may be a sign of the onset of inflammation in the uterine cavity and endometrium.
After delivery has been performed by cesarean section, the weight of the uterus decreases by approximately 200–250 g during the first postpartum week. The organ usually returns to its original weight values after two months. In terms of the shape of the organ: it acquires the appearance it had before birth no earlier than by the middle or end of the second week after the operation. Standard, basic measurement values (length, width, and anteroposterior dimension) are similarly delayed in parameters when compared with those for vaginal delivery. After the surgical delivery, the doctor will certainly conduct an extremely thorough ultrasound examination of the ovaries, veins and arteries of this area to be sure that their integrity has not been compromised.
Control procedure
A standard postpartum ultrasound examination is performed 2–4 days after the date of birth. In case of unnatural delivery (cesarean), the doctor prescribes the timing of the procedure on an individual basis. An urgent ultrasound should be done when a woman exhibits the following symptoms:
- copious separation of clots;
- intense outflow of blood from the vagina;
- febrile or pyretic body temperature (38–41 °C);
- unbearable pain in internal organs;
- pain, swelling, wetting of the postoperative suture (in case of cesarean section).
Based on the results of ultrasound diagnostics, conservative therapy or emergency surgery is prescribed to eliminate the complications that have arisen. A control ultrasound is performed in the maternity hospital and only after this the woman is discharged home. A re-examination should be done in a week.
Preparation and execution
Since the birth process is already over and there is no amniotic fluid, to visualize the uterus before the study, it is necessary to fill the bladder. The amount of liquid you drink should be at least two liters. In case of an urgent procedure, fluid is administered through a catheter, followed by the prescription of diuretic medications.
After childbirth, an ultrasound is usually performed abdominally, that is, externally. Transvaginal (internal) examination is informative only when examining the cervix. The organ itself is still too voluminous, so an intravaginal sensor will not give an objective result. The time interval of the procedure is from 20 to 40 minutes, depending on the health of the reproductive system.
Study parameters
Postpartum examination of the patient’s reproductive system is aimed at identifying possible pathologies leading to complications. The assessment is made according to the following parameters:
Ultrasound of the genitourinary system
- contractility, location and size of the uterus;
- the presence of organic formations (pieces of the “baby place”, blood clots, fragments of the fetal membrane);
- the presence of excess fluid in the uterine cavity;
- possible inflammatory processes of the endometrium;
- condition of the postoperative suture (if a caesarean section was performed);
- general condition of the pelvic organs.
The indicators obtained during ultrasound diagnostics are compared with average standards. If there is a discrepancy between the values, the patient is prescribed special treatment. In case of an uncomplicated postpartum period, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist after a month. At your appointment, the doctor will determine the need for ultrasound monitoring.
Changes in the uterus: immediately after delivery, a week later, after 5 weeks
What are the complications?
Conducting a pelvic ultrasound almost immediately after childbirth ensures the detection of some possible problems, which, if not eliminated in time, are quite capable of developing into serious complications requiring treatment. The most common abnormalities that a specialist can see during an ultrasound procedure include:
- the presence of residual blood clots that have coagulated in the uterine cavity, or fragments of the placenta. If enough such fragments have accumulated, they interfere with the outflow of normal postpartum secretions, which leads to inflammatory diseases or even bleeding from the uterus. In order to remove debris from the uterus, the doctor will usually prescribe vacuum aspiration (that is, removal) of the contents of the cavity;
- insufficient activity of uterine muscle contractions. The doctor will suspect this condition when the organ measurements do not correspond to standard values. Prescribing certain medications will help correct the situation;
- inflammatory phenomena of the mucous layer of the uterine cavity (so-called endometritis). The basis for the development of the disease, as a rule, is the addition of a bacterial infection. Pathological microorganisms enter the organ cavity from the genitals if shortly before birth the vaginal microflora was disturbed or its sanitation (cleansing) was not carried out.
Indications for ultrasound
When discharged from the maternity hospital, every woman in labor must undergo examination. Examination of internal organs is very important to exclude postpartum complications. Also, this examination may be prescribed some time after discharge. A referral for an ultrasound scan is issued by a specialist after examining the patient and familiarizing herself with her complaints.
Ultrasound diagnostics must be carried out urgently in the following cases:
- The occurrence of increased bleeding;
- Pain in the suture placed as a result of the operation;
- Temperature increase;
- Liquid leakage from the seam;
- The appearance of discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- Swelling, redness of the postoperative suture.
An indication for urgent ultrasound diagnostics is the appearance of blood discharge. Their presence may indicate the formation of a placental polyp in the uterine cavity. It is an outgrowth of placental tissue that forms on the wall of the uterus.
Ultrasound of the uterus after discharge from the hospital
The new mother must undergo a repeat or so-called control examination at her place of residence, in strict accordance with the doctor’s recommendations upon discharge. However, emergency testing may be required. Indications for it will be the following conditions and signs:
- a large amount of discharge with a sharp, sour or unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- sudden bleeding;
- pain, discomfort in the pelvic area;
- the occurrence of suppuration and/or swelling of the scar after cesarean section;
- prolonged fever not associated with a cold.
It is important to know that if an ultrasound examination was not performed while the woman was in the maternity ward, you should consult a doctor for consultation and conduct an ultrasound yourself, even if the alarming symptoms do not bother you.
Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy
Doppler ultrasound is done in the same way as a pelvic ultrasound, but it studies the movement of blood through the vessels. This method has been used to study pregnant women since 1977, primarily examining the blood that drains through the umbilical cord. Since the 1980s, this method has also been used to look at the blood flow between the uterus and placenta. Both tests are used to assess the functioning of the placenta and the well-being of the baby. Doppler flowmetry uses waves of higher intensities than abdominal and vaginal ultrasound of the uterus, and at the same time ensures continuity of wave delivery.
3D and 4D ultrasound during pregnancy
Ultrasound generally uses 2D (or two-dimensional) images. These images are made up of a series of thin "slice" images, visible at all times to create a "flat" picture. In the late 1990s, 3D or "three-dimensional" ultrasound (also known as "holography ultrasound") became available at some ultrasound centers. However, 3D ultrasound machines are very expensive and are not widely available.
From a medical point of view, 3D/4D ultrasounds are not essential and, as a rule, all information can be obtained by conventional 2D ultrasound. However, there are significant advantages to using 3D/4D examination.
With these methods, some parts of the child are visible more clearly and from any angle. For example, abnormalities such as heart defects, cleft lips, or neural tube defects such as spina bifida are better visualized. This can help manage pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. Sometimes you cannot do without an additional 3D ultrasound of the uterus. The photo will confirm or refute the anomalies that were detected during conventional 2D ultrasound.
These types of ultrasounds strengthen the bond between parents and their baby because the baby's drawing is more realistic and the baby's various movements (such as yawning, swallowing, opening and closing eyelids) are more clearly visible.