X-ray properties
The following properties of X-rays have been used in medical practice:
- Huge penetrating power. X-rays successfully pass through various tissues of the human body.
- X-rays cause light reflection of individual chemical elements. This property underlies fluoroscopy.
- Photochemical exposure to ionizing rays makes it possible to create informative images from a diagnostic point of view.
- X-ray radiation has an ionizing effect.
During an x-ray scan, various organs, tissues and structures are targeted by x-rays. During a minor radioactive load, metabolism may be disrupted, and with prolonged exposure to radiation, acute or chronic radiation sickness may occur.
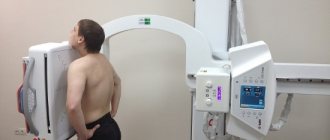
X-ray machine
X-ray machines are devices that are used not only for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in medicine, but also in various fields of industry (flaw detectors), as well as in other areas of human life.
X-ray machine design:
- emitter tubes (lamp) - one or more pieces;
- a power supply device that supplies the device with electricity and regulates radiation parameters;
- tripods that make it easier to control the device;
- X-ray to visible image converters.
X-ray machines are divided into several groups depending on how they are designed and where they are used:
- stationary – they are usually equipped in rooms in radiology departments and clinics;
- mobile – intended for use in surgery and traumatology departments, in intensive care wards and on an outpatient basis;
- portable, dental (used by dentists).
As X-rays pass through the human body, they are projected onto film. However, the angle of reflection of the waves may be different and this affects the image quality. The bones are best visible in the photographs - bright white. This is because calcium absorbs X-rays the most.
Types of diagnostics
In medical practice, X-rays have found application in the following diagnostic methods:
- Fluoroscopy is an examination method in which, in the past, the organs being examined were projected onto a screen coated with a fluorescent compound. In the process, it was possible to study the organ from different angles in dynamics. And thanks to modern digital processing, the finished video image is immediately obtained on the monitor or displayed on paper.
- Radiography is the main type of research. The patient is given a film with a fixed image of the examined organ or part of the body.
- X-ray and fluoroscopy with contrast. This type of diagnosis is indispensable when examining hollow organs and soft tissues.
- Fluorography is an examination with small-format X-ray images, which allow it to be used en masse during preventive examinations of the lungs.
- Computed tomography (CT) is a diagnostic method that allows a detailed study of the human body through a combination of X-rays and digital processing. Computer reconstruction of layer-by-layer X-ray images takes place. Of all the methods of radiation diagnostics, this is the most informative.
X-rays are used not only for diagnosis, but also for therapy. Radiation therapy is widely used in the treatment of cancer patients.
In case of emergency care, a plain radiography is initially performed on the patient.
The following types of X-ray examination are distinguished:
- spine and peripheral parts of the skeleton;
- chest;
- abdominal cavity;
- a detailed image of all teeth with jaws, adjacent parts of the facial skeleton;
- checking the patency of the fallopian tubes using x-rays;
- X-ray examination of the breast with a low dose of radiation;
- X-ray contrast examination of the stomach and duodenum;
- diagnosis of the gallbladder and ducts using contrast;
- examination of the colon with retrograde injection of a radiocontrast agent into it.
Abdominal x-rays are divided into plain x-rays and procedures performed with contrast. Fluoroscopy has been widely used to determine pathologies in the lung. X-ray examination of the spine, joints and other parts of the skeleton is a very popular diagnostic method.
Neurologists, traumatologists and orthopedists cannot give their patients an accurate diagnosis without using this type of examination. X-ray shows spinal hernia, scoliosis, various microtraumas, disorders of the osseous-ligamentous apparatus (pathologies of a healthy foot), fractures (of the wrist joint) and much more.
Results
Fluoroscopy, despite the emergence of innovative examination methods, continues to remain a relevant diagnostic method in modern medical practice. This is due, first of all, to its lower cost compared to ultrasound, CT, MRI, as well as accessibility (most medical institutions are provided with X-ray machines). The images obtained during X-ray examination clearly visualize the main types of pathological changes, which allows doctors to detect diseases of internal organs at different stages of their development.
Preparation
Most diagnostic procedures involving the use of X-rays do not require special training, but there are exceptions. If an examination of the stomach, intestines or lumbosacral spine is planned, then 2-3 days before the x-ray you need to follow a special diet that reduces flatulence and fermentation processes.
X-ray for children
When examining the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to do cleansing enemas in the classical way using an Esmarch mug on the eve of diagnosis and directly on the day of the examination or to cleanse the intestines using pharmaceutical laxatives (oral medications or microenemas).
When examining the abdominal organs, you should not eat, drink, or smoke at least 3 hours before the procedure. Before going for a mammogram, you should visit a gynecologist. An X-ray examination of the breast should be performed at the beginning of the menstrual cycle after the end of menstruation. If a woman who is planning a breast examination has implants, then she must inform the radiologist about this.
How are radiographic results interpreted?
After radiography is performed, it is necessary to correctly interpret its results. To do this, the doctor evaluates:
- Location of internal organs.
- Integrity of bone structures.
- The location of the roots of the lungs and their contrast.
- How different are the main and small bronchi?
- Transparency of the lung tissue, presence of shadows.
If an x-ray of the skull was performed, it is necessary to identify:
- Presence of fractures.
- Severe intracranial hypertension with brain enlargement.
- Pathology of the “sella turcica”, which appears as a result of increased intracranial pressure.
- Presence of brain tumors.
To make a correct diagnosis, the results of an X-ray examination must be compared with other tests and functional tests.
Carrying out
Upon entering the X-ray room, he must remove items of clothing or jewelry that contain metal, and also leave his mobile phone outside the room. Typically, the patient is asked to undress to the waist if the chest or peritoneum is being examined. If it is necessary to perform an x-ray of the extremities, the patient can remain in clothes. All parts of the body that are not subject to diagnosis must be covered with a protective lead apron.
Pictures can be taken in various positions. But most often the patient stands or lies down. If a series of images from different angles is needed, the radiologist gives commands to the patient to change body position. If an x-ray of the stomach is performed, the patient will need to take the Trendelenburg position.
This is a special pose in which the pelvic organs are slightly above the head. As a result of the manipulations, negatives are obtained, which show light areas of denser structures and dark areas indicating the presence of soft tissues. Deciphering and analysis of each area of the body is performed according to certain rules.
Children often have x-rays taken to check for hip dysplasia.
Chest Exam Options
X-ray of the chest organs (chest organs) is usually performed in a direct projection, as it allows one to accurately determine the pathology. However, in some cases, a different type may be required - the rear one.
When performing direct diagnostics, the patient stands facing the film or detector. And during posterior diagnostics, the device is brought to the patient’s back. There is also a lateral R-graph of the chest, which is necessary to clarify the pathology detected during a classic examination.
The most common recommendation for performing a lateral procedure is to examine the spine to identify any bends or distortions. In this case, all diagnostic methods are usually performed. If tuberculosis is suspected, an oblique projection may be required. If pleurisy is suspected, a chest x-ray is performed in a supine position.
There is another diagnostic method - fluoroscopy, characterized by the ability to visualize organs in real time. Using this method, doctors take a series of pictures and record the process on video.
Digital and analog X-ray
Digital chest radiography
The procedure is divided into digital and analogue according to the type of device on which the diagnostics are performed:
- the film or analog version is carried out on outdated equipment with an increased radiation dose, and also provides less important information;
- Digital chest radiography allows you to change the quality of shooting and the parameters of the resulting image, and is also customized for a specific patient, taking into account diagnostic purposes.
The result of the digital examination is recorded on a medium and given to the patient for further interpretation by the doctor.
When choosing a digital or analogue examination method, it is better to give preference to the first option. Its cost differs insignificantly, but the quality will be many times better.
Frequency
The maximum permissible effective dose of radiation is 15 mSv per year. As a rule, only people who need regular X-ray monitoring (after severe injuries) receive this dose of radiation. If during the year the patient only undergoes fluorography, mammography and x-rays at the dentist, then he can be completely calm, since his radiation exposure will not exceed 1.5 mSv.
Acute radiation sickness can only occur if a person receives a single dose of 1000 mSv. But if this is not a liquidator at a nuclear power plant, then in order to receive such a radiation dose, the patient must take 25 thousand fluorographs and a thousand x-rays of the spine in one day. And this is nonsense.
The same radiation doses that a person receives during standard examinations, even if they are increased in quantity, are not capable of having a noticeable negative effect on the body. Therefore, x-rays can be taken as often as medical indications require. However, this principle does not apply to pregnant women.
X-rays are contraindicated for them at any stage, especially in the first trimester, when the formation of all organs and systems in the fetus occurs. If circumstances force a woman to have an X-ray while carrying a child (serious injuries during an accident), then they try to use maximum protective measures for the abdomen and pelvic organs. During breastfeeding, women are allowed to have both x-rays and fluorography.
Moreover, according to many experts, she does not even need to express milk. Fluorography is not performed on young children. This procedure is permissible from the age of 15. As for x-ray diagnostics in pediatrics, they resort to it, but take into account that children have increased radiosensitivity to ionizing radiation (on average 2–3 times higher than adults), which creates a high risk for them of both somatic and genetic radiation effects.
X-ray examination of the spine
X-rays of the spine are performed quite often; the indications for their performance are:
- Pain in the back or limbs, a feeling of numbness.
- Detection of degenerative changes in intervertebral discs.
- The need to identify spinal injuries.
- Diagnosis of inflammatory diseases of the spinal column.
- Detection of spinal curvatures.
- If there is a need to recognize congenital anomalies of the spine.
- Diagnosis of changes after surgery.
An X-ray procedure of the spine is performed in a lying position; first you need to remove all jewelry and undress to the waist.
The doctor usually warns that you should not move during the examination so that the pictures do not turn out blurred. The procedure does not take more than 15 minutes and does not cause any inconvenience to the patient.
There are contraindications for radiography of the spine:
- Pregnancy.
- If an X-ray using a barium compound was taken within the last 4 hours. In this case, the pictures will not be of high quality.
- Obesity also makes it difficult to obtain informative images.
In all other cases, this research method has no contraindications.
Contraindications
Fluoroscopy and radiography of organs and structures of the human body have not only many indications, but also a number of contraindications:
- active tuberculosis;
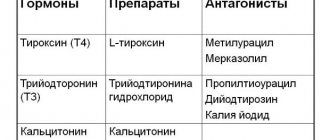
- endocrine pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- general serious condition of the patient;
- carrying a child at any stage;
- for radiography using contrast – lactation period;
- serious disturbances in the functioning of the heart and kidneys;
- internal bleeding;
- individual intolerance to contrast agents.
Nowadays, X-rays can be taken in many medical centers. If radiographic or fluoroscopic examination is done on digital complexes, then the patient can count on a lower radiation dose. But even digital X-rays can be considered safe only if the permissible frequency of the procedure is not exceeded.
What can you accurately see on an x-ray?
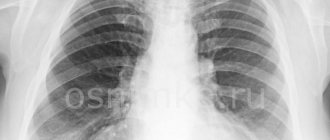
Pneumonia on x-ray
The diagnostic procedure is most effective when detecting the following pathologies:
- foci of inflammation in the lungs;
- expansion of the heart shadow as a symptom of ventricular or atrium hypertrophy;
- displacement of organs as a signal of pneumothorax or pleurisy;
- widened mediastinum due to pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- diagnosis of cancer and tuberculosis.
Experienced doctors are able to examine the signs of benign tumors in the images, but to clarify the diagnosis in this case, additional examination methods are most often required.