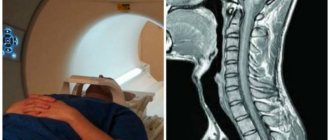
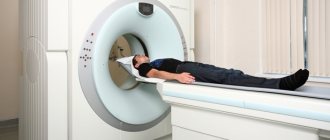
MRI of the cervical spine and MR angiography of neck vessels
Tomograph Siemens, Philips 1.5 T
Study time up to 25 minutes
Qualified written opinion in 20 minutes.
Cost without contrast is 6000 rubles.
6000 RUB
MRI of the cervical spine and MR angiography of neck vessels at the ICLINIC MRI center. We use expert-level tomographs with a magnetic field strength of 1.5 T
The cervical spine experiences enormous physical stress every day. For this reason, the anatomical region is in a vulnerable zone: a person can feel severe pain and discomfort in the neck at any time. If complaints from the neck occur, the doctor recommends undergoing a comprehensive examination, including an MRI of the cervical spine. This diagnostic method allows you to visualize both bone structures and soft tissues, cartilage structures, the spinal cord and nerves.
What is angiography?
Angiography allows you to determine what is happening to the vessels of the neck. Using this technique, the doctor sees the veins, arteries, and capillaries that are responsible for saturating the brain with oxygen. Depending on the device, the image may be in two or three dimensions. For examination, the patient is injected with a contrast agent. At the same time, it can be seen whether there are neoplasms in the cervical spine.
Depending on the volume, angiography of neck vessels is divided into three types:
- when the general state of the brain is determined, a special substance is injected through the aorta;
- superselective determines the activity of small vessels;
- a selective method is required to determine pathologies; a contrast liquid is injected into cerebral vessels.
Angiography comes in two types:
- CT angiography uses x-rays;
- MRI angiography detects changes using a magnetic field.
The key difference is the operating principle
The difference between the two methods lies in the physical principles of visualization. Ultrasound (or sonography) is based on the unequal ability of biological tissues to reflect ultrasound. For better contact with the patient’s body, a special gel is applied to the skin and an ultrasonic sensor is passed over it, which emits pulses of inaudible high-frequency waves and directs them to the desired area of the body. It also receives signals reflected from internal organs, fluids and tissues, and registers the slightest difference in intensity. The echoes are measured by a machine that creates a real-time image on a monitor.
Indications for examination
To undergo an angiography examination of the vessels of the neck, a doctor’s referral is required. A therapist or neurologist can prescribe a diagnosis based on the patient’s complaints and if abnormalities are suspected. There are a number of cases in which it is advisable to undergo examination:
- after operations performed in order to identify deviations;
- before surgery related to brain activity;
- if you suspect insufficient brain activity;
- after head injuries, bruises, extensive hematomas;
- for epilepsy;
- if you suspect a tumor in the head;
- after a stroke or mini-stroke;
- if there are congenital brain pathologies;
- hearing impairment;
- with atherosclerosis;
- to exclude vascular pathologies or thrombosis;
- with ringing in the ears, nausea, vomiting;
- with constant pain in the neck;
- frequent headaches;
- severe pain or loss of consciousness.
Indications for MRI of neck vessels
Pathologies of extracranial arteries and veins lead to circulatory disorders in the brain and deterioration of the trophism of its tissues. Such conditions have various manifestations. Indications for MRI of neck vessels are:
- dizziness;
- nausea, morning vomiting;
- fainting;
- sudden attacks of weakness;
- blood pressure surges;
- headache;
- discomfort in the neck;
- speech and swallowing disorders;
- hearing loss;
- blurred vision;
- memory disorders;
- sleep disorders;
- noise in ears;
- poor coordination of movements;
- impaired sensitivity of the skin of the hands, etc.
The method is used in planning operations, as well as for assessing brachiocephalic circulation a certain time after injury. It is necessary to monitor the condition of important vessels in some systemic diseases, for which MRI of the arteries and veins of the neck is prescribed, namely:
- multiple sclerosis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- atherosclerosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- hypertension.
Most often, MR angiography is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis when duplex scanning has low information content.
Contraindications
When performing angiography of neck vessels, it is almost impossible to harm the patient’s health. But, like any procedure, this method has contraindications. This type of diagnosis is not recommended for women carrying a child and breastfeeding. The fact is that no research has been conducted in this area. The procedure is not performed on young children. In case of increased sensitivity to the components included in the contrast agent, diagnostics should be abandoned. The study should be used with caution in persons with mental disorders.
Absolute contraindications for this procedure are:
- thyroid diseases;
- obesity with complications;
- some heart diseases;
- a person being in a coma;
- bleeding disorders;
- failure of the kidneys and liver;
- for infectious diseases in acute form;
- diabetes;
- the presence of metal implants;
- thrombophlebitis.
What is better to choose
Ultrasound diagnostics of the brain or MRI? In conclusion, it makes sense to provide information about the advantageous and unattractive aspects of each method. Experts were able to identify the following pros and cons of MRI diagnostics:
| Benefits of MRI | Disadvantages of MRI |
| — obtaining a clear result in three-dimensional form — no radiation exposure to the body — obtaining images of areas inaccessible during ultrasound — designation of the nature of the tumor without a biopsy | - long diagnostic period - the need for the patient to remain immobile - the need to administer anesthesia in the case of children - the impossibility of diagnosing pregnant women in the 1st trimester - restrictions on the examination for persons with metal objects and devices built into the body - high price |
The table below shows a similar characteristic of an alternative procedure - ultrasound:
| Advantages of ultrasound | Disadvantages of Ultrasound |
| — complete absence of contraindications — carried out during pregnancy — use of various techniques — small, compact equipment for diagnostics — short study period — affordable price | — the impossibility of demonstrating bone tissue pathologies — the need for preparatory measures (when examining the abdominal organs, genitourinary system) — the effect of the patient’s obesity on image quality — the dependence of the diagnostic result on the experience of the specialist and the quality of the equipment used |
Ultrasound of the head
It is impossible to say specifically what is more accurate and better. Both methods are highly informative in their area of specialization, however, they are not interchangeable.
MRI and ultrasound are hardware techniques that are equally successfully used in medical practice.
An ultrasound examination is prescribed if it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis and obtain a general “picture” of the condition of the examined organs.
If it is necessary to obtain detailed information, diagnose the lesion (tumor or cyst), its characteristics and extent of prevalence, MRI will be preferable.
How is the examination carried out?
CT and MRI angiography of neck vessels with contrast is done upon the doctor’s direction. The nurse will tell the patient what to do, but it is better to know in advance how the procedure goes:
- The patient lies down on the couch.
- The place where the special solution is planned to be injected is treated with an antiseptic drug.
- A puncture is made in the vessel through which a probe is inserted into the artery.
- A catheter is inserted through the probe and entered into a vein or artery.
- Next, a colored liquid is injected into the catheter.
- The liquid is required to ensure that the visual image is as clear as possible, so with the help of a catheter, the contrast liquid is brought to the desired location.
- The device takes a series of pictures.
- The catheter and probe are removed, the puncture site is treated and sealed.
The entire procedure takes from 15 minutes to an hour, depending on the method. Most often it takes up to 40 minutes. The probe may cause discomfort to the patient. It is important to lie still during the procedure.
The diagnosis has a high degree of reliability. Detects the following deviations:
- consequences of stroke;
- predisposition to stroke;
- presence of a tumor;
- consequences of head injuries;
- atherosclerosis;
- presence of blood clots;
- blockage of blood vessels;
- vasoconstriction;
- consequences of surgery.
How is MRI of the cervical spine with angiography performed?
MRI of the cervical spine and MRA of neck vessels are performed according to a generally accepted protocol. No preparation is required before the procedure, so the patient can lead a normal lifestyle.
Immediately before scanning, the patient must remove any items or products that contain metal. It is also necessary to leave electronic gadgets, watches, pens, removable dentures and hearing aids outside the manipulation room.
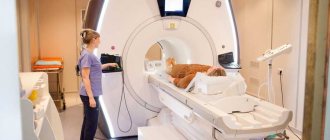
Next, the radiologist assistant guides the patient into the treatment room, where the patient lies on his back on the retractable tomograph table. A specialized neck coil is worn. Patients suffering from psychomotor disorders and claustrophobia may be prescribed sedatives. After this, the table moves into the MRI tunnel.
The device starts working, taking cross-sectional images in different projections. After obtaining the initial images, if indicated, the patient is injected with a contrast solution. An additional series of images is taken, which will allow the diagnostician to identify the most minimal deviations from the norm.
Important! Contrast-enhanced MRI of the cervical spine uses a gadolinium-based solution, which does not cause an allergic reaction. The component is completely eliminated from the body naturally within 24 hours.
How to prepare for diagnosis?
When preparing for diagnosis, CT or MRI angiography of neck vessels requires consultation with a therapist. In case of contraindications, the procedure is postponed or cancelled.
During diagnosis, there is a risk of vessel damage, so before the examination it is necessary to visit a neurologist. Take blood and urine tests, a blood clotting test. Kidney function is checked and an ECG is performed.
You should refrain from eating 12 hours before the procedure. Avoid alcohol for a few days. It is better to refuse water 2 hours before the procedure. The solution injected into the blood may cause nausea. Jewelry must be removed and clothing should not restrict movement.
A few hours before the procedure, a contrast sensitivity test is performed. 2 ml of solution is injected into a vein and the patient’s condition is monitored. If a reaction is detected, the procedure is carried out without liquid.
There are classic diagnostic methods, magnetic resonance angiography of neck vessels and computed tomographic angiography.
Features of the MRI procedure of the cervical arteries
The procedure for scanning neck vessels does not differ significantly from MRI of other areas of the body - the patient is placed on the tomograph table on his back in a horizontal position, a special coil is put on the area under study, after which the machine table with the patient is moved inside the scanning equipment.
The main condition of the procedure is complete immobility of the body during the examination in order to avoid image defects.
Diagnostics are carried out using open (low-field) and tunnel (high-field) devices, but the former cannot provide the highest quality image.
The duration of MRI of neck vessels ranges from 15-25 minutes; if contrast enhancement is necessary, the duration increases by 10 minutes.
Angiography CT of vessels
CT angiography of neck vessels is considered the most modern and highly accurate method for diagnosing pathologies. The colored liquid is injected using a catheter. The puncture method is not used. Using a tomograph, the image is superimposed layer by layer. In order to translate it into a form convenient for perception, an angioprogram is used. In the picture produced by the device, the vessels and capillaries of the cervical spine are visible quite clearly.
This method determines blood flow disturbances and changes in blood vessels. When using a three-dimensional image, nuances are visible that cannot be seen with an ultrasound examination.
When using a tomograph you can see some advantages:
- high accuracy of the information received;
- minimal x-ray exposure;
- the least number of complications due to the absence of a puncture method when administering the solution.
MSCT is a more accurate method of CT angiography of neck vessels.
Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels and MRI – which is better?
None of these procedures is mandatory, therefore, without a justified need, the doctor will not prescribe an ultrasound scan or MRI of the vessels of the head. With lower sensitivity, MRI seems to be the most acceptable method for examining the brain, but ultrasound examinations are much cheaper and more accessible. Doppler ultrasound of the brain is more informative than conventional ultrasound. In this regard, it is often prescribed after an ultrasound. An absolute indication for MRI is already diagnosed brain pathologies.
Angiography MR
To determine the condition of the walls of blood vessels, the MRI method is used. In this case, X-ray irradiation is completely absent. It is based on electromagnetic radiation.
What does MR angiography of the neck vessels show?
- The appearance or growth of neoplasms into the walls of blood vessels. Reliability will not depend on the benignity of the tumor.
- Neck injuries and their consequences.
- Condition of veins and arteries, their integrity.
This method will not be informative enough for traumatic brain injury. The condition of bone tissue or brain fluid cannot be examined. The method is used only for diagnosing the vascular system of the body.
A contrast agent is not always necessary for the study. The degree of visualization is quite high. This allows the study to be carried out for those patients who are allergic to the composition of the contrast agent.
MRI angiography of the neck vessels is often used in conjunction with MRI of the head. This allows the doctor to get the most informative picture about the patient’s condition.
MRI is used more often than CT. A computed tomography scan is necessary if the MRI does not show something.
MRI of the neck arteries: what does this study show?
Diagnostics allows you to successfully identify:
- atherosclerotic plaques;
- blood clots;
- damage to the vascular wall;
- pathological tortuosity, arteriovenous malformations, aneurysms, kinking syndrome and other vascular malformations;
- areas of vasoconstriction, thrombosis;
- inflammation of the vessel, for example, vasculitis, Takayasu's disease;
- anomalies in the size and location of the veins and arteries of the neck;
- thrombophlebitis;
- vein fusion;
- compression of blood vessels by scar tissue;
- changes in blood vessels due to the influence of neoplasms of neighboring organs and tissues - compression of blood vessels, invasion of tumors into blood vessels.
MRI of the carotid artery may be indicated if dissection of the wall of this vessel is suspected.
MRI of the veins of the neck, as well as diagnostics of the arteries in this area, allows you to assess the features of the anatomical and functional state of the veins, identify developmental anomalies, and also determine the nature of blood flow in these vessels.
Based on the data obtained, it is possible to plan angioplasty and stenting - MRI of the neck arteries is successfully used in preparing the patient for surgery to assess the relative position of the neck organs and blood vessels, as well as to monitor the results of the prescribed treatment.
Angiography in children
To identify vascular lesions, angiography of neck vessels is used in children. Reviews about the procedure are positive. The method makes it possible to detect vascular aneurysms in the early stages. Clearly determines the degree of damage, shape, location. This allows the use of neurosurgical intervention. Using a puncture, an iodine-based contrast agent is injected into the carotid artery. The volume injected into the blood depends on the age and weight of the child. A sensitivity test to iodine is performed first.
The fluid is injected under pressure and a series of images are taken. This allows you to quickly take clear pictures. The procedure is easier for children to tolerate than for adults. Before the puncture is performed, the child is given anesthesia.
Indications for diagnosing a child are:
- suspicion of hemorrhage;
- aneurysms;
- vascular lesions;
- hematomas and brain contusions;
- brain tumors;
- epilepsy;
- cyst, brain abscess;
- hydrocephalus.
In babies who have been injured during childbirth, cerebral circulation disorders and prolonged removal of the contrast agent are detected.
Comparison of diagnostic value
Both brain ultrasound and MRI are used to evaluate the condition of the blood vessels supplying the brain. The structure of the carotid arteries and the inner layer of blood vessels are examined in order to detect calcification and atherosclerotic plaques in time and begin treatment. To examine the brain itself, neurosonography (in infants) and transcranial sonography are used.
Neurosonography
An ultrasound examination of the head provides images of the brain and cerebrospinal fluid. Because waves do not travel well through bone, this method is usually used to detect early pathologies in infants whose skulls are not yet fully formed. Acoustic windows in newborns are the fontanelles, that is, soft, non-ossified areas. The doctor places the sensor, for example, on the anterior fontanel and moves it right and left, forward and backward, in order to visualize the brain structures as accurately as possible.
Ultrasound has long been used to evaluate babies born prematurely. The procedure is done to check for bleeding or damage to the brain tissue. The need for subsequent sessions depends on the results of the study.
In infants, sonography can diagnose almost all brain diseases. Scientists from Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore have proven that for young patients this is a more gentle and cheaper alternative to tomography. But only if doctors use high-tech devices that create two- and three-dimensional images. Much depends on the qualifications of the specialist.
In adults, doctors use an ultrasound scan of the head to locate and evaluate the size of the tumor during surgery to facilitate its safe removal.
Transcranial sonography
Transcranial Doppler examination (TDI) is to assess the speed of blood flow through the vessels inside the cranium. Used to assess the risk of stroke in adults and children with sickle cell disease and to identify pathologies affecting cerebral circulation, such as stenosis or vasospasm. According to scientists, TDI is suitable for diagnosing Parkinson's disease.
The main disadvantage of the method is that the possibility of its use depends on the quality of the ultrasonic windows, that is, the places on the skull through which the waves penetrate. Some people don't have them at all. In addition, to obtain a high-quality image, you need an expert-class device.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI has more possibilities than ultrasound. The images of the brain obtained with its help reveal the smallest details. You can diagnose:
- tumor,
- inflammation of the meninges (meningitis),
- hemorrhage,
- changes in blood vessels (narrowing, protrusion)
- Parkinson's disease,
- dementia.
- Korsakoff-Wernicke syndrome.
Using this method, focusing on characteristic details, doctors also determine whether it is an autoimmune or inflammatory disease, a malignant or benign tumor. Sometimes the procedure is done after a stroke, but the number one choice here is a CT scan.
The method is not suitable for examining infants, since they cannot lie still. The use of sedatives and anesthesia is not recommended, as complications may occur in rare cases.
Combining methods
If necessary, ultrasound and MRI can be done on the same day. Brazilian scientists have gone even further. They developed a new method for identifying pathologies in unborn children: using tomograph images and ultrasound data, specialists created a three-dimensional model of the fetus, which requires special glasses to view. Perhaps in the future it will be used to diagnose head diseases.
What can be seen in the photographs?
Images obtained as a result of magnetic resonance angiography of the neck vessels allow the doctor to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. The main direction for diagnosis is the identification of disorders in the vascular system. You can see where the disorder is localized and at what stage of development it is. The examination will help to identify and prevent circulatory disorders in time.
Deformation of blood vessels will tell the doctor that the patient has developed atherosclerosis. If blood flow is reduced, this indicates hypertension. Enlargement of the vessel walls allows the diagnosis of aneurysms to be made. Displacement of blood vessels indicates a tumor.
Complications
During diagnosis, complications may arise:
- entry of the contrast agent outside the blood vessel;
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart;
- failure of the kidneys;
- discomfort when inserting the catheter;
- swelling of tissues due to incorrect puncture;
- the appearance of an allergy to contrast liquid;
- in rare cases, stroke.
Within 2 days, all complications and discomfort disappear. In order to avoid unforeseen situations, you must adhere to the following rules on the first day:
- do not remove the bandage;
- rest;
- exclude physical activity;
- do not carry out water procedures;
- drink enough liquid.
Review of contraindications
Both methods are non-invasive and safe for the body, so the number of sessions is not limited. However, the disadvantage of magnetic resonance imaging is the presence of absolute and relative contraindications, including:
- the presence in the body of fragments of magnetically susceptible metals or implants made from them;
- having a pacemaker, defibrillator, cochlear implant or other medical device;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- claustrophobia;
- mental illness.
Another disadvantage of MRI is the need to use contrast agents, to which allergies and intolerances occur.
Ultrasound has no side effects and is well tolerated by most patients. Some experience only unpleasant sensations associated with the pressure of the sensor on the skin, the application of cool gel, or pulsating sounds.