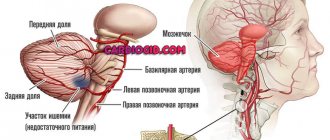
The information obtained through scanning provides an accurate diagnosis. The equipment allows us to identify various ailments at the earliest stages, when the symptoms are not yet clear and expressed.
Patients do not always know which examination method to give preference to. Which is better among modern diagnostic methods - MRI or CT of the brain? The choice of examining foci of pathology depends on the characteristics of the clinical picture.
What will a CT scan of the larynx and neck show?
Computed tomography of the neck and larynx allows you to take pictures of the internal organs of this anatomical region, examine in detail all layers of muscle bundles, and identify the presence of a foreign body in the lumen of the upper respiratory tract or esophagus.
CT scan of the larynx and neck can reveal pathological changes:
| Anatomical formations | What do the larynx and neck look like on a CT scan? | What is revealed |
| Thyroid | The gland should normally look like a homogeneous parenchymal organ, the lobes should be symmetrical. | Computed tomography of the neck will show the exact dimensions of the endocrine organ, boundaries, homogeneity, pathological nodes and cysts. It is better to do MSCT, since the study allows you to obtain thinner sections (scans layers in 0.5 mm increments) and reduces the radiation dose to the patient. |
| Parathyroid glands | Normally located near the thyroid gland. In most cases, you can find 4 pieces behind it, two on each side, of uniform consistency, separated from it by layers of capsules (their own and a nearby localized organ). | CT scan of the soft tissues of the neck allows you to determine the exact localization of organs, analyze the internal structure, confirm their dystopia (changes in the typical location) and the formation of glandular adenomas and cysts. |
| Larynx | A hollow organ belonging to the upper respiratory tract, in which the vocal cords are located, it is surrounded on the outside by cartilaginous structures. Well supplied with blood and innervated. | A CT scan of the larynx makes it possible to identify pathologies in the structure of structures, diseases of the vocal cords, and oncological growths. |
| Vocal cords | The glottis and ligamentous apparatus are visualized. | Computed tomography of the larynx and neck shows structural anomalies, tumors, papilomatous growths, polyps, granulomas, cysts of the vocal cords; examination is possible during phonation, when the patient is asked to say something at the time of diagnosis. It is better to do a multislice computed tomography. |
| Trachea | A CT scan of the larynx and neck visualizes the transition of the throat to the trachea; layer-by-layer sections allow you to examine in detail the cartilaginous semirings located in this anatomical area and identify pathological changes. The contents of the lumen of the hollow organ are clearly visible. | Layer-by-layer axial sections will show foreign bodies, inflammatory discharge, pathological thickening of cartilaginous structures, and the spread of the oncological process. |
| Esophagus | A CT scan of the neck reveals the upper esophagus. | The study shows the condition of the esophageal wall, the presence of ulcerations or tumor-like growths, foreign bodies, and diverticula. |
| Muscles | On a CT scan of the nasopharynx and larynx, there are 17 muscles, each of which is surrounded by its own membrane. | CT scan of soft tissues shows asymmetry of muscle bundles in congenital malformations and traumatic injuries. When the mediastinum is inflamed, exudate can penetrate into the interfascial spaces, which is clearly visible on the photographs. |
| Vessels | On a computed tomography scan of the neck, arteries and veins are visualized, and the analysis allows the diameter of the vessels to be calculated. | Computed tomography of the larynx and neck area with contrast allows you to identify disorders in the bloodstream: vascular aneurysms, aplasia and hypoplasia of the main arteries supplying blood to the brain, thyroid gland, larynx and other anatomical structures. |
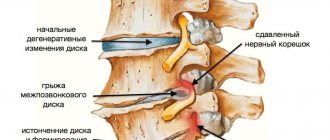
| Spine | A CT scan of the cervical spine clearly shows the structure of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. | Diagnostics shows signs of osteochondrosis, determines the presence of prolapsed or herniated discs when they penetrate the lumen of the spinal canal, and narrowing of the intervertebral space. |
| Regional lymph nodes | On a CT scan of the neck and larynx, all groups of lymph nodes are clearly visualized. With a SCT study, you can even examine the vessels that collect lymph from the organs of the neck, mediastinum, salivary glands, and nasopharynx. | With any inflammation, they increase in size and become inflamed, which will be visible on a CT scan of the soft tissues and organs of the neck. In chronic processes, lymph nodes can become sclerotic and calcified. |
The figure shows layer-by-layer axial sections of the neck during a CT study
How does a CT scan differ from an MRI of the brain?
MRI of the head differs from CT, as described in more detail in the table:
| CT | MRI | |
| Time spending | 5-10 minutes | 15-30 minutes |
| Irradiation | 2 mSv, or 0.2 BER (biological equivalent of x-rays) | No |
| Information content | More effective when studying dense tissues, larger pathologies, hematomas, injuries, atherosclerotic changes | Higher when studying small objects, blood flow, soft tissues, organ functionality |
| Contraindications | Pregnancy, many contraindications for CT with contrast | Presence of metal implants, tattoos, prostheses |
Comparison by indications and contraindications
Absolute contraindications to CT are pregnancy and the patient’s body weight is more than the maximum allowable for the tomograph to operate (for some devices this is 130 kg, for others – 150 kg).
Relative contraindications relate to the use of contrast:
- allergy to contrast agent;
- severe general condition of the patient;
- renal failure;
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes mellitus (severe forms);
- myeloma (oncological disease of the blood system);
- severe liver and heart failure.
Absolute contraindications to MRI:
- presence of a pacemaker;
- electronic or ferromagnetic middle ear implants;
- the presence of large metal implants, fragments;
- Ilizarov ferromagnetic implants.
Relative contraindications to MRI:
- pregnant women (first trimester);
- decompensated heart failure;
- heart valve prostheses;
- hemostatic clips;
- presence of an insulin pump;
- nerve stimulants;
- hearing aids without ferromagnetic metal;
- the presence of tattoos made using paint containing metal;
- dentures, braces.
MRI is considered safer. Damage to tissues from ionizing radiation accumulates, so the doctor always has to decide on an individual basis whether a diagnostic CT scan is necessary.
The difference in capabilities, indications, and contraindications between CT and MRI is significant. It helps the doctor decide on the research method: choose a safer MRI or CT, which is convenient in an emergency, or even resort to other forms of diagnosis. Information about broken large bones of the extremities is easier to obtain using an X-ray machine - widely available, available in every clinic, giving a low dose of radiation. Duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic (carotid, vertebral) arteries, ultrasound of blood vessels and lymph nodes of the neck, extremities, sinuses, eyes, abdominal cavity, and other areas is a cheap and accessible alternative method for obtaining data for diagnosis. To diagnose diseases of the urinary system, excretory urography is traditionally used - a reliable, simple way to obtain images that study urine excretion over time. To check the pelvic organs, there is often no need to do CT and MRI - you can get by with more conventional studies.
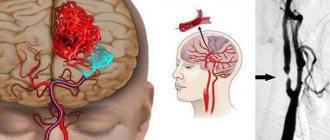
In general, CT is more informative for injuries and swelling of the brain, damage to the inner ear, skull bones, neoplasms, abscesses, hematomas, hemorrhagic strokes, thrombosis and atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels. Magnetic resonance imaging better identifies pathologies of the meninges, inflammatory diseases of the brain, ischemic strokes, multiple sclerosis, pathologies of the pituitary gland, nerve disorders, vascular thrombosis, and benign tumors. The MRI method is more accurate, which allows you to visualize smaller pathologies of the vessels of the head and soft tissues, but the scanning process takes longer.
Difference in preparation
Carrying out a tomography does not require any special preparatory steps. Before diagnosis, it is necessary to remove metal objects and electronic devices (watches, jewelry, mobile phones, hairpins, belts with buckles, etc.). When scanning the pelvic organs, the bladder should be full. If all contraindications are taken into account, then the difference between CT and MRI does not affect the preparation for the examination in any way.
What does a tomography image show?
The information obtained as a result of tomography is recorded, the data is entered into a computer, processed, and a three-dimensional model of the body part being studied is visualized. Further information is provided in the form of layer-by-layer sections of the studied area with small steps. There are a lot of pictures, you can get images of projections in different axes, which allows you to examine in detail all possible changes in the soft tissues and skeletal system.
MRI and CT, as tools for studying the state of the brain, differ only in the presence of indications and contraindications.
CT scan of the larynx and neck with contrast
Despite the fact that the price of a neck CT with contrast is more expensive than a conventional study, much more information can be obtained from such a diagnosis. Computed tomography, as an X-ray method, is designed to visualize bone structures; the introduction of a contrast agent allows you to improve the image of the soft tissues and organs of the neck in the image and identify vascular anomalies. It makes more sense to strengthen it.
The information content of CT of the larynx and neck with intravenous contrast is comparable to MRI. Only the price differs. The cost of a regular diagnostic CT is 2,450 rubles, a study with angiography is 6,100 rubles, while the price of contrast is included in the price (calculated for a person weighing up to 60 kg - 2 doses). If additional administration of Ultravist is necessary, it will be paid for separately. The time required for diagnosis also increases.
Diagnostic specialist doctors provide advisory services. After the examination, the patient will be able to find out comprehensive information from the specialist based on the diagnostic results, which are ready within 2 hours after the procedure. The applicant receives free electronic photographs recorded on disk or by e-mail. If the results are lost, you can request a duplicate, since all studies are stored in the device’s memory.
Who is the procedure contraindicated for?
There are a number of diseases and limitations for CT scanning. Among them:
- The patient is overweight. The table can be designed for a patient weighing up to 120 kg, 200 kg.
- Acute renal or heart failure. CT scanning is contraindicated in such patients.
- Diabetes. Diabetics taking medications to regulate glucose levels (Metformin, Glucophage) must notify their doctor about the disease in order to calculate how long to stop taking the medication.
- Asthma . People with asthma should also tell their doctor about their condition.
- Multiple myeloma.
- Pacemaker, insulin pump, other metal elements.
- Allergy to iodine. Contrast computed tomography is not performed on such patients. It is possible to replace the contrast agent with one that does not cause allergic reactions in the patient
- Children under seven years of age. And also in the event that the child cannot calmly stay in a confined space for a long period of time.
- Pregnancy and lactation period. A breastfeeding woman can undergo a CT scan, but if a contrast agent is used, it is recommended that she express milk and not feed the baby for a certain period of time. The time of abstinence depends on the characteristics of the procedure performed and can range from 7 hours to two days.
Considering what a CT scan of the brain is, it is imperative to inform the doctor about all your diseases before the procedure.
CT scan of soft tissues of the neck and larynx
A CT scan of the larynx and neck must be done not only to diagnose pathology and confirm the diagnosis, but also to determine the patient’s treatment tactics and prognosis for life and health. A detailed analysis of the obtained CT images of soft tissues and organs of the neck is carried out to identify anatomical defects and pathological substrates.
With multislice computed tomography, a three-dimensional image can be obtained when, using programs, a 3D image of all anatomical structures is reconstructed. This procedure is done in preparation for surgery in a given anatomical area. Contrast enhancement makes it possible to highlight all vascular collaterals - their location and quantity are individual for each patient. Since the vascular network is very dense, there is a high risk of possible damage during surgery and the development of uncontrolled bleeding.
Comparison of indications for referral for examination
Computed tomography of the brain is prescribed:
- for head injuries;
- for frequent headaches and dizziness;
- with noise in the ears and spots before the eyes;
- with hearing and vision impairment (auditory hallucinations, loss of visual fields);
- with high intracranial pressure;
- with frequent pre-fainting conditions and fainting;
- to control the treatment of already identified pathologies.
MRI of the brain is done in the following cases:
- the patient will suffer a traumatic brain injury;
- a cancerous tumor or metastasis is suspected;
- a cerebral infarction or stroke occurred;
- it is necessary to differentiate multiple sclerosis from other diseases with similar symptoms;
- diagnosis of demyelinating or degenerative pathologies of brain tissue is necessary;
- to check the effectiveness of the chosen treatment method or evaluate the effectiveness of the operation.
Sometimes two procedures are required to make an accurate diagnosis.
Indications for CT examination of the larynx and neck
It is necessary to carry out CT diagnostics when the following patient conditions are present:
- enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter);
- visual asymmetry of structures in the neck area;
- clinical signs of thyroid dysfunction;
- neoplasms of the upper respiratory tract (larynx, trachea);
- inflammatory pathology of the nasopharynx, larynx;
- lymphadenopathy, lymphogranulomatosis or other oncopathologies of lymphoid tissue;
- inflammatory diseases in the neck (edema formation, possible abscess formation)
- neoplasms of the esophagus;
- thyroid tumors;
- cysts in the neck area;
- clinical manifestations of dysfunction of the parathyroid glands (manifestations of hypo- or hypercalcemia);
- pathology of the vessels of the neck (hypoplasia and aplasia of the main arteries, veins, aneurysms, atherosclerotic lesions);
- traumatic damage to the anatomical structures of the larynx and neck;
- stridor breathing (noisy, loud, the main reason for the formation of which is obstruction in the glottis or upper respiratory tract);
- hoarseness or aphonia;
- foreign bodies in the esophagus or trachea.
Information content of methods
The question of what is more informative, CT or MRI, cannot be answered unambiguously, since they are used for different purposes. CT is used to obtain a clinical picture of pathologies of the skeletal system and chest organs (usually the lungs). MRI is prescribed for a targeted study of the functional capacity of organs and tissues: studying the brain and spinal cord, their vessels, identifying tumors. What is more accurate, MRI or CT? To study hollow organs, skeletal system and lungs - CT. To study nervous and muscle tissue, tendons, blood vessels, cartilage and tumors - MRI.
Which is better than MRI or CT of the larynx and neck?
CT and MRI are two similar studies, while CT is aimed at identifying bone pathology, MRI is better at visualizing soft tissues and internal organs. An important aspect when choosing techniques is the goals and indications for diagnostics, as well as the cost of the study, since CT of the larynx and neck is actually half the price of MRI of the same anatomical area. Unlike MRI, CT is not contraindicated in patients with metal prostheses and metal heart rate stimulators.
CT is strongly recommended not to be prescribed to pregnant women, due to the fact that ionizing X-ray radiation is used, despite its negative impact on actively dividing tissues, and can cause mutations in the fetus.
How are the results deciphered?
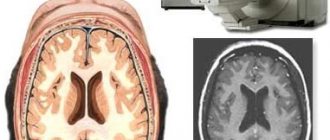
Pictures that are recorded on a computer are not informative in the raw version. They are processed through a special program (producing mathematical modeling). The photos are black and white; when using a computer program, the doctor can create a three-dimensional image. In this case, the specialist receives data on the state of all brain tissues; all areas are available for examination at any depth. In addition, you can record both a draft version of the images and finished processed data on digital media.
The advantages of this type of study are that you can get a complete picture of the development of the disease, which is shown by a CT scan of the brain. In addition, you can see the state of the brain tissue at the time of the study. It is possible to compare finished images with those that were taken earlier, to obtain data on the development of pathology or the patient’s recovery over time. The decoding is carried out by a doctor, sometimes obtaining the result and making a diagnosis can take a long time (sometimes up to an hour).