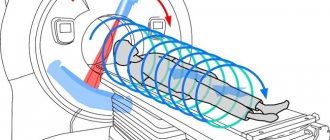
Some pathological conditions in the body are extremely difficult to diagnose. In this situation, in the absence of other ways to detect the disease, whole-body MRI is used. This is a highly accurate technique that allows you to evaluate the structural features in the tissues of the entire body.
Whole body MRI is a comprehensive study of the characteristics of structural damage in various tissues and organs using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. The study makes it possible to identify difficult-to-diagnose diseases at an early stage, which improves the prognosis for the prospects of the treatment process.
Since the diagnostic value of the manipulation is great, it is performed by the most highly qualified personnel of the institution. For research, only tomographs with a strong magnetic field should be used, preferably at least 1.5 Tesla. With low-field equipment, there is a high probability of simply not noticing small formations that can play a decisive role in the patient’s life.
Due to the complexity of data interpretation, the number of institutions performing the procedure is small, even in large metropolitan areas. The responsibility of a specialist conducting MRI of the whole body is extremely high, since often this diagnostic procedure is the last in a series of examinations. However, due to low competition and the use of expensive, powerful equipment, the price for MRI of the whole body is quite high. The cost depends on the qualifications of the specialist, the degree of high cost of the equipment, as well as the form of ownership of the medical institution. In public clinics, such examinations are carried out more often at a higher level due to the ability to interpret data jointly by several specialists. On average, a whole body MRI costs from 13 to 35 thousand rubles, depending on the region.
Benefits of MRI
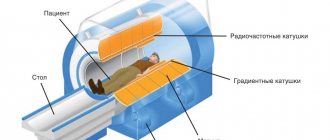
Magnetic tomography allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the areas under study in three projections. During the procedure, the device takes many slices, the thickness of which can be set individually and is usually 2-4 mm.
Images taken using a tomograph
Obtaining a large number of sections allows you to examine the entire organ and detect even the slightest abnormalities and pathologies.
Study of the upper sections
Duplex scanning of the neck vessels shows abnormalities in the nutrition of the brain. After all, it is through the blood arteries that nutrients and oxygen particles pass to the gray cells. The image is obtained using penetrating ultrasonic waves.
The upper sections are examined in the following ways:
- Duplex scanning is a common method for diagnosing blood vessels and blood flow through them. Diagnosis is made using the captured image in black and white.
- Dopplerography is a classic way to study the condition of the vessels of the neck, otherwise it is called “blind Doppler”. Analysis of blood flow is difficult, which is excluded with duplex examination. The method is abbreviated as ultrasound.
- Triplex scanning - coloring of the captured image is introduced, the type of blood flow and direction are diagnosed.
The vessels of the head are scanned in the same way. Violation of the structure of the walls, the formation of blockages leads to brain pathologies. Tumors are detected at the nascent stage and can be cured without surgery.
What types of tomographs are there?
Modern magnetic tomographs are available in various variations with a wide variety of characteristics.
All tomographic devices are divided into:
- open;
- closed.
Despite the fact that conducting a study in an open tomograph is usually considered more comfortable for the patient, closed devices have greater power and detail. If the patient does not have a strong fear of closed spaces and does not have weight restrictions, it is recommended to conduct the study in a closed-type apparatus.
Tomographs are also divided according to the strength of the magnetic field radiation, the unit of measurement of which is called Tesla. Magnetic tomographs can be:
- low-floor – power up to 1.0 T;
- high-field – radiation intensity above 1.0 T.
Low-field tomographs do not provide a clear and detailed picture. A study using a high-field tomograph will allow you to examine the diagnosed area with the highest accuracy.
Modern high-field tomograph
The DiMagnit clinic has a closed-type tomograph from Philips, whose power is 1.5 Tesla. Using the device, it is possible to obtain images of the highest quality and detail.
Should you be afraid of the procedure?
Some patients are worried before the test. But their fears are in vain - magnetic resonance imaging is absolutely painless, and the effect of magnetic radiation on the body is safe.
Unlike other types of radiation diagnostics, MRI does not use ionizing radiation. The magnetic field does not have a carcinogenic or mutagenic effect on the cells of the body. Magnetic resonance scanning can be performed as often as needed.
Patient reviews
The general impression of the procedure in the reviews of patients who underwent it is informative, but expensive.
Olga, 38 years old: We happened to encounter this procedure when multiple metastases in the brain were discovered during a CT scan of my mother’s head. After a comprehensive examination, doctors were unable to determine where the cancer itself was located, so they prescribed an MRI of the whole body. This procedure revealed some more problems in the mother’s general condition, but the source was never found. Although we were told that in 99% of cases primary oncopathology is always found, we ended up in that unfortunate 1%.
Christina, 29 years old: I’m probably too suspicious, but for preventive purposes I decided to do an MRI of the whole body. When deciphering the results, everything turned out to be in order. I heard that abroad, many people annually undergo an MRI to reassure themselves and, thus, check their bodies. I would probably do the same if this pleasure was not so expensive.
Whole body MRI is a valuable diagnostic tool for many diseases. It is especially appropriate in cases where the pathology is hidden or when it is necessary to exclude metastases. If, during magnetic resonance imaging of the whole body, morphological changes in a specific organ or area were detected, then it will be possible to conduct targeted additional examination.
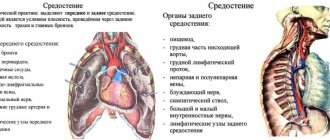
The difference between MRI and CT and ultrasound
Magnetic resonance diagnostics has a number of advantages compared to ultrasound and computed tomography.
Ultrasound examination allows you to obtain a two-dimensional image of the area under study, but does not allow you to see a three-dimensional image of soft structures.
Computed tomography can be compared to MRI in terms of image clarity, but has a number of serious contraindications. CT is more often used to visualize hollow organs and bone structures, while MRI is much more effective at visualizing soft tissue.
How to recognize a disease in an image
The images are interpreted by doctors who have undergone special training. They have an idea of the nature of layer-by-layer visualization of all organs and systems in normal conditions and in pathology. Tumors from different tissues, differing in degree of differentiation and stage, have their own characteristics. But it is possible to identify a number of general signs, the identification of which allows one to suspect cancer.
Borders of the neoplasm
Benign neoplasms grow without penetrating into surrounding tissues, but pushing them aside. Therefore, the images will show clear, smooth and even contours of the tumor. This growth of tumors is called expansive.
The malignant development of a tumor is manifested by its aggressive growth with penetration into nearby organs and tissues, damage to cells and blood vessels. Infiltrative growth in the picture has blurred boundaries, an unclear outline, and uneven outlines.
Tumor contents
A benign tumor consists of highly differentiated cells. In terms of activity, functions and metabolism, they are similar to other cells of the body, but their division control processes are disrupted. Excessive growth can be observed from cells of different tissues, for example, lipoma is formed from adipose tissue, fibroma is formed from connective tissue, and fibroids are formed from muscle tissue. In the photographs, such formations have contents of a predominantly homogeneous composition.
Malignant growth proceeds quickly, both in terms of penetration into the vessels and surrounding organs, and in terms of the processes taking place in the focus. Cancer cells lose control of both division and differentiation. In some tumors, the origin of the tissue cannot be determined. In the images, the cancer process will be characterized by the following signs:
- contents with a heterogeneous structure;
- foci of necrosis, calcification, hemorrhage and colloid degeneration are visible.
What does an MRI show?
Magnetic resonance imaging is successfully used to diagnose diseases:
- thyroid gland;
- liver;
- gallbladder and ducts;
- pancreas;
- kidney;
- spleen;
- joints;
- spinal cord;
- vessels of the head, neck, abdominal region;
- pelvic organs;
- soft tissues;
- etc.
All of the above anatomical structures are perfectly visualized on MRI images. The diagnostic results make it possible to accurately identify abnormalities in the functioning of the organs being examined.
Full MR Scan Process
The MRI procedure does not require special preliminary preparation, so before the examination you can eat and take the necessary medications as usual.
Clothing for diagnostics should not contain buttons, snaps, zippers or other metal parts. The patient can bring suitable clothing with them or use the gown provided at the clinic. Before diagnosis, you must make sure that there are no metal objects and accessories on the body (jewelry, piercings, hairpins, hairpins, buttons, buttons, etc.). Electronic devices, mobile gadgets, credit cards and other personal items should also not be left in the room with the CT scanner.
Best materials of the month
- Why you can't go on a diet on your own
- 21 tips on how to avoid buying stale food
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to curb your sweet cravings: 7 unexpected products
- Scientists say youth can be extended
During an MRI of the whole body, the table slides completely into the tunnel, and communication with the x-ray technician is carried out through a mini-headset. The patient is required to remain calm, breathe evenly and not move. The full body scan procedure takes approximately 90 minutes.
To prevent the clicks and taps of the tomograph from causing discomfort during diagnostics, it is recommended to use headphones or earplugs. For moral support of the patient, the presence of a loved one in the room is allowed, with the exception of women in the first trimester of pregnancy.
In what cases is MRI prescribed?
The wide capabilities of magnetic resonance diagnostics make its use indispensable in the following cases:
- the need for a primary diagnosis;
- conducting a comprehensive survey;
- preparation for surgery;
- monitoring the effectiveness of the therapy and treatment methods used.
In each individual case, the choice of diagnostic technique is made by the attending physician. Magnetic resonance imaging is more often used than other methods to detect diseases and injuries of soft tissues.
The MRI technique is indispensable for diagnosis:
- Neoplasms.
Magnetic resonance scanning can clearly identify the boundaries and size of the tumor and the extent of its invasion into soft tissue. No other radiation diagnostic technique is capable of providing such a clear and detailed picture of diseases.
MRI also makes it possible to determine the nature of the tumor with a high degree of probability. Malignant neoplasms have unclear boundaries and grow into surrounding tissues. Benign neoplasms, as a rule, are clearly differentiated from healthy tissues.
- Brain diseases.
The greater accuracy of magnetic resonance diagnostics makes it possible to visualize such small anatomical structures as the pituitary gland and the sella turcica. Also, MRI with contrast of the brain shows high efficiency for diagnosing demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, etc.), as it allows one to clearly see the structure of altered nerve tissues.
Brain images obtained with contrast-enhanced MRI of the brain are particularly clear because magnetic waves are difficult to image solid anatomical structures and there are no artifacts from the skull in the brain images.
- Diseases of the intervertebral discs.
MRI images of the spine
Magnetic resonance imaging is the only diagnostic method that allows you to see intervertebral discs. Even modern diagnostic methods, such as computed tomography, allow you to see only the space between the vertebrae, while MRI gives a complete picture of the condition of the discs, the possible presence of hernias and protrusions.
The use of MRI is not limited only to the above diseases, but is used when it is necessary to identify and monitor a wide range of pathologies, congenital developmental anomalies, consequences of injuries and previous surgical interventions.
Subject of examination
What organs can be checked by MRI? Resonance imaging is done to check all organs of the body. The following are examined:
- vessels of different parts of the body;
- brain and cervical spine;
- spinal column and skeletal system;
- cardiovascular system;
- hollow abdominal organs.
MRI shows all organs in a three-dimensional image, that is, it gives a three-dimensional picture. Unlike ultrasound diagnostics, resonance tomography can be used to check in which organs small neoplasms have appeared. Ultrasound cannot distinguish them.
Resonance tomography can distinguish even micro strokes and hemorrhages, which will provide prompt and timely therapy. The device detects vascular deformation, aneurysms, and multiple sclerosis that are invisible to other types of scanning.
When diagnosing the spinal column, a tomograph can detect a herniated disc that other scanning devices cannot detect. All this makes magnetic tomography irreplaceable and unique.
Let's consider what information about individual systems and organs can be obtained using MRI.
Brain scan
An appointment for tomography is given if the patient complains of frequent headaches of unknown origin, dizziness, or noise in the ears. The referral is prescribed for ischemia, vegetative-vascular dystonia and strokes. After the examination, you can obtain an objective clinical picture of the disease and prescribe a course of therapy adequate to the patient’s condition.
The tomograph shows the localization of blood clots, deformed vessel walls, hemorrhages, cholesterol plaques and other pathological abnormalities. Where can I get an MRI of the head? In any medical institution that has a tomograph.
Spine scan
This examination is prescribed for complaints of pain in the back and legs. What does the tomograph see? Using tomography you can detect:
- pathology of intervertebral discs;
- neoplasms of bone and nervous tissue;
- osteoporosis in the initial stage;
- deformation of the spinal canal;
- pathology of nerve fibers;
- infectious lesion.
The tomograph can also show the intensity of pressure of the intervertebral disc on the nerve processes, disruption of blood supply to any part of the spinal column, localization of metastases or tumors, and identify other pathological abnormalities.
The cervical spine is a complex interweaving of nerve endings and blood vessels with muscle fibers. The pathology of this part of the body leads to diseases of various body systems.
Diagnosis of the cervical spine is prescribed for complaints of osteochondrosis, after an injury, for congenital anomalies of the structure of the cervical spine, for pathology of cerebral circulation, before surgery and detection of metastases.
Pathological changes in the cervical spine provoke hearing/vision impairment, pressure instability, headaches, tinnitus and pain in the upper extremities. Vascular tomography allows you to find out the true causes of ailments.
Heart scan
Examination of the main organ of the body allows us to identify pathologies of the coronary system, atria, chambers, valves, myocardium, defects of any nature, and cholesterol deposits. The scan reveals disturbances in blood flow and arterial capacity. MRI is also used to monitor the condition of the heart and blood vessels in the postoperative period.
Since the heart muscle is in constant motion, scanning of the organ is carried out with a high-power tomograph and using contrast agents.
Peritoneal scanning
The peculiarity of an MR tomograph is that it qualitatively scans the soft tissues of organs. In this, no diagnostic device can surpass it. However, due to the high cost of the procedure, the diagnosis of abdominal organs is carried out using other methods, and MRI is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
Scanning of the knee joints and blood vessels of the extremities
Injuries to the knee joints can lead to a person's incapacitation. Invasive diagnostic methods are very painful; it is difficult for pediatric patients to undergo joint arthroscopy. Therefore, diagnostics using the resonance method is the only painless and safe examination method.
Diagnostic appointment:
- rupture and damage to the meniscus;
- ligament/tendon injury.
The tomograph shows not only the condition of the kneecap and meniscus, but also the changes occurring in the tissues.
Diagnosis of veins and vessels of the lower extremities is a popular procedure in modern times. An appointment for examination is given in case of venous insufficiency, thrombosis, aneurysms, damage to the walls of blood vessels and other pathologies.
When to Apply Contrast
Magnetic resonance diagnostics can provide a very high degree of clarity of the resulting images. In most cases, the use of contrast is not required.
But when it comes to diagnosing tumors and small anatomical structures, a contrast agent can still be used.
The staining agents are made from the rare earth metal gadolinium and are injected intravenously into the patient during an MRI.
MRI contrast agents are much better tolerated than CT contrast agents. This makes the use of the dye safe even for patients with kidney pathology and does not require a preliminary test for creatinine, which is necessary for CT diagnostics with contrast.
MRI with contrast is used in the following cases:
- suspicion of a neoplasm;
- the need for differential diagnosis of a malignant tumor;
- study of the pituitary gland;
- the need to diagnose demyelinating diseases.
The use of contrast allows one to obtain a comprehensive picture of the disease, its course and the effectiveness of the therapy used.
Alternative research methods
If an MRI is not possible, the patient is offered the following:
- Ultrasound - displays the abdominal organs, but the image is two-dimensional and there is no layer-by-layer imaging available.
- CT is an accurate method, but is not suitable for all types of diagnostics of abdominal pathologies. To obtain high-quality images, contrast is sometimes introduced.
MRI is suitable for examining the abdominal cavity - the images show in detail the organs of the digestive, biliary and urinary systems.
To improve the quality of the study, contrast is introduced. Preparation includes measures to reduce intestinal motility.
Contraindications for MRI
Despite the fact that magnetic resonance diagnostics is a safe technique, the study has a number of absolute contraindications, in the presence of which diagnostics are prohibited:
- presence of a pacemaker, neurostimulator, insulin pump;
- vascular clips on the arteries of the brain;
- the patient’s inability to maintain a stationary position for various reasons;
- early childhood up to 5 years;
- the patient’s weight is more than 130 kg and body girth is more than 150 cm;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
There are also a number of conditions in which MRI examination is carried out with caution:
- severe pain syndrome, in which it is difficult for patients to remain in a motionless position for a long time;
- fear of confined spaces;
- psychical deviations;
- second and third trimester of pregnancy.
The presence of various prostheses and implants in the patient's body may be a contraindication to MRI if they are made of metals sensitive to magnetic radiation. Modern medical devices are most often made of titanium and other materials that are inert to the effects of magnetic fields. Their presence in the body does not interfere with MRI.
When manipulation should not be carried out
Despite the complete safety and accuracy of the data obtained, MRI of the whole body has contraindications. These include:
- the presence of any magnetic devices built into the body, for example, a pacemaker;
- any metal fixed prostheses;
- artificial valve on a metal base;
- remaining metal fragments, for example from shells.
Built-in devices for supplying the body with insulin, as well as the reluctance to part with any metal object, make MRI impossible. A relative contraindication is claustrophobia. The patient will be in a completely enclosed space for 60 minutes. If claustrophobia is severe, then the patient is sedated.
How is an MRI performed?
Before the procedure, the radiologist questions the patient about the presence of contraindications to the study. The patient is asked to remove any metal accessories, including clothing with metal fittings, and lie down on a couch, which is then placed in the CT scanner tube.
During the diagnosis, it is strictly forbidden to move, as this may affect the clarity of the resulting images.
Scanning procedure
High-field tomographs produce a fairly high level of noise, which can cause some discomfort to patients. The medical department will provide you with headphones that will play pleasant music, drowning out the sounds of the operating device.
The tomograph scans the patient’s body in different projections and instantly transmits the images to the computer screen. The interpretation of the results by the research physician begins even before the procedure is completed.
How to prepare for the procedure
Preparing for whole-body diffusion MRI or other types of diagnostics involves preparing the internal organs (located mainly in the abdominal cavity). Since an examination of the intestines is required to recreate the full picture, you should switch to a special diet within 2-3 days so that fecal blockages do not form in it. You need to take a laxative 8-10 hours before the procedure, and give a cleansing enema 6 hours before it. To get the clearest images of the pelvic organs, it is advisable to empty your bladder no later than an hour before the examination.
Patients with kidney disease and claustrophobia require special preparation. In the first case, you will need a doctor's permission to perform the procedure. If you plan to administer contrast, you should discuss with your doctor in advance the possibility of adjusting the dosage of medications. As for people suffering from claustrophobia, they are advised to take a sedative an hour before the examination. If the patient continues to feel intense fear, the doctor may decide to put him into medicated sleep.
Important! All possible options for the development of events should be discussed with the radiation diagnostics doctor or the attending physician before the scheduled date of the examination!
Before starting the procedure, you must remove all metal objects, including jewelry, dentures, and other medical devices.
Getting Results
Scan results are available immediately after the end of the study. Many of the images obtained are carefully examined by a radiologist, and a detailed report is drawn up describing both the normal anatomy of the area under study and possible abnormalities and pathologies.
15-30 minutes after the procedure, the patient is given a written report and a computer disk with the resulting images.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern, safe type of radiation diagnostics that allows you to obtain accurate and quick results and thoroughly examine the area under study. MRI helps to identify many diseases and abnormalities even at the initial stages of their development.
| MRI of the rectum in Rostov-on-Don |
| MRI of the pancreas in Rostov-on-Don |
| MRI of the liver in Rostov-on-Don |
| How to do an MRI of the brain |
| MRI of the abdomen with contrast |
| MRI of the spine, what does it show? |
Indications sheet for examination
A complete MRI examination of the entire body is not available to everyone. This is explained by the high cost of the procedure. However, there are circumstances in which the described diagnostic procedure is the only reliable way to identify the disease. Among them:
- age-related pathological changes that can be asymptomatic, but worsen the patient’s well-being;
- tumor processes of stages 2, 3 with a high risk of metastases;
- numerous pathologies of internal organs that may be related to each other;
- serious injuries that cause extensive damage to several organ systems (in an accident, fire, etc.);
- patient complaints of unexplained malaise;
- predisposition to cancer. An annual examination of the whole body helps to identify pathological foci in time and take therapeutic measures.
Sometimes an MRI of the body is supplemented with other diagnostic techniques to confirm the suspected diagnosis.