Open magnetic resonance imaging
The first tomographs without a restrictive tunnel were designed for the needs of veterinary clinics: the veterinarian often needs to hold the animal in place while simultaneously performing therapeutic manipulations. A few years later, the innovation was actively introduced into the diagnosis of serious diseases, solving the problem of patients with claustrophobia.
An open-type MRI tomograph repeats classical models in many characteristics, second only to the frequency level of the electromagnetic field: it fluctuates between 0.4–0.5 tesla. The device is a table parallel to which powerful magnetic coils and highly sensitive sensors are located. The small structure has no sides, so the patient has a clear view of the diagnostic room.
Among the advantages of such open-type equipment:
- recommended for examining children who require parental presence during the procedure;
- low level of noise effects;
- the ability to scan a patient with severe spinal fractures that require careful transportation;
- Suitable for obese people weighing over 120 kg.
Modern open-type devices often have small dimensions and easily fit in a standard room.
Preparing for the study
No special preparation is required before performing a dental CT scan. If it is performed without the use of contrast, the patient must refrain from eating before the procedure for 4 to 5 hours.
Upon arrival for the examination, the patient must remove all metal objects: braces, belts, accessories, jewelry. This is required to ensure that the research results are without errors.
If contrast will be used, a little preparation is necessary before the study. A few days before the procedure, blood is taken from the patient to identify contrast allergens, as well as to determine the urinary function of the kidneys.
Main advantages of an open tomograph
Open type tomographs have appeared on the medical services market relatively recently. The high price limits their purchase for small diagnostic centers. But they have a number of advantages over standard models:
- allow scanning of a patient weighing up to 180 kg;
- the doctor can be next to the patient, monitor his condition and well-being;
- During the scan, drugs can be administered, and a person can be examined under a drip;
- do not provoke panic attacks in people suffering from claustrophobia or other nervous disorders;
- the structure of the open apparatus makes it easy to examine a victim with severe ruptures and fractures;
- noise and light effects during sensor operation are minimized;
- Open MRI allows you to obtain high-quality images if the patient moves slightly;
- recommended for examining children without the use of anesthesia;
- facilitates scanning the body of an immobilized patient after a stroke.
With the development of open MRI, doctors have a unique opportunity to perform complex operations under the control of the device. It can be used to install a cardiac bypass, remove a blood clot from an artery, or replace coronary arteries. In real time, the surgeon monitors the conductivity of the veins and aorta and cleaves the brain aneurysm. This significantly reduced the number of complications and deaths, and reduced the time of surgical intervention for stenting.
What is the difference between CT and MRI - contraindications
Like any examination method, MRI and CT have their own number of contraindications that prohibit the procedure.
When is it better to refuse magnetic resonance therapy:
If you need to undergo a CT examination, not a single doctor will refuse you, because the technique has no contraindications. It is prohibited only in rare, purely individual cases.
The second difference is the difference in contraindications or their complete absence for CT (except for pregnancy and allergies to contrast).
Features of closed type devices
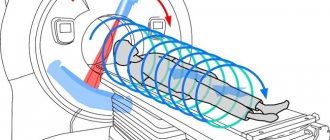
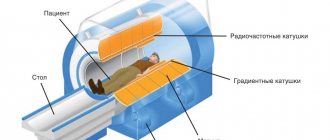
Classic devices for magnetic resonance imaging are of a tunnel type design. The large chamber includes a mobile table on which the patient is placed in a supine position. Magnetic and computer sensors work around the patient, creating a high frequency electromagnetic field: from 1.5 to 3 Tesla.
The closed-type MRI machine has impressive dimensions, reaching 1.6–2 m in height and 60 cm in width. While the sensors are operating, the patient may be disturbed by blinking or extraneous noise, which often creates psychological discomfort. On average, the scanner operates for at least 30 minutes. Being in a closed chamber is painless, but patients with unstable mental health may show anxiety: this negatively affects the quality of the images, leads to inaccuracies and misdiagnosis.
CT is more informative for
- Diagnosis of circulatory disorders, brain tumors;
- Lesions of the teeth, facial skeleton, thyroid and parathyroid glands, as well as jaws;
- Injuries to the bones of the skull, brain and intracranial hematomas;
- Lesions of the temporal bones, paranasal sinuses and bones of the base of the skull;
- Diagnosis of otitis, sinusitis and pyramids of the temporal bones;
- For almost all pathologies in the abdomen;
- Atherosclerotic lesions of blood vessels and aneurysms;
- Research on tuberculosis, lung cancer, pneumonia and other chest pathologies;
- Diseases of the spine (disc herniation, osteoporosis, scoliosis, etc.);
- Observations on metal implants, damaged bones and their diseases.
Before identifying the difference between MRI and CT, it is necessary to understand what these two types of diagnostics are.
CT (computed tomography) is a sequential scan of both individual areas of the body and the entire body (general scan) using X-ray irradiation. There are two types of scanning - with a substance (contrast) and ordinary, without the use of additional substances and equipment. The procedure is carried out using a capsule, spiral tomograph; the number of spirals (4, 8, 16, 64) directly affects the diagnostic object (heart, intestines, brain).
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Scan) is the best diagnostic method for monitoring the condition of soft tissue. The description of the diagnostic method immediately contains the answer to the first question: “What is the difference?” — X-rays are not used, a picture of the state of the body is obtained through the magnetic field and the position of radio frequencies. During the procedure, the person is placed in a special capsule, closed tunnel, in which he is scanned.
What is the difference between CT and MRI:
Comparison of disadvantages of MRI equipment
Compared to open-type MRI machines, tunnel tomographs have a number of significant disadvantages:
- a high level of noise that irritates the patient and interferes with relaxation;
- the need to maintain a static body position for a long time;
- During the examination, the doctor is in the adjacent room, the patient is left alone with the scanner;
- young children and patients with claustrophobia can only be served after administration of sedatives;
- It is not recommended to scan a person with severe injuries, risk of cardiac arrest or hemorrhage;
- The mobile table and closed-type MRI tomograph camera are not designed for a weight exceeding 120 kg.
If there are any complaints or discomfort, doctors have to stop the examination so that the patient leaves the tunnel. Considering the high cost of such diagnostics, an unsuccessful attempt greatly impacts the patient’s pocket.
The main problem when using open MRI is the low level of electromagnetic radiation. During operation of the tomograph, part of the radiation is sprayed to the sides, scattered and loses power. Therefore, it is not recommended to use:
- If necessary, identify the smallest defects in blood vessels, search for metastases in bone tissue.
- When examining organs that move (human lungs, heart).
- When operating the tomograph, you should remain motionless and hold your breath at the radiologist’s command.
Carrying out CT and MRI procedures
During a visit to the office for diagnosis using MRI, you remove things that are harmful to the diagnosis, and perhaps undress to the waist. Lie down on the retractable table of the device and you are loaded into the tunnel.
The examination is quite long (25-40 minutes), there is little space inside, so it is better for those suffering from claustrophobia to refrain. The device has a built-in video transmitter and a special microphone for communication with a doctor. The results are ready in a day, you can pick them up yourself, or your doctor will have them. Sometimes an injection of a special solution (5-15 ml) is required to highlight the organ (MRI with contrast).
Before a CT scan there are no strict limits regarding implants and prostheses. The patient lies down on a mechanical couch, which is guided in different ways to the tomograph. There is plenty of space left, so attacks of claustrophobia are excluded. The duration of the procedure is maximum 10 minutes. Results are obtained almost immediately.
If we talk about the specifics of the techniques, the main differences between them are: the speed of the examination (CT takes less time), the speed of obtaining the result, the amount of free space (especially important for those suffering from claustrophobia) and the type of equipment.
Does the quality of the result depend on the power of the device?
If it is necessary to prescribe an MRI procedure, the doctor proceeds from the expected diagnosis: the higher the power of electromagnetic radiation, the smaller the defects and pathological foci the tomograph can detect. Therefore, in case of cancer, specialists prefer diagnostics using a tunnel scanner. It concentrates the field around the patient, which allows you to obtain three-dimensional images with unique detail.
Open MRI is suitable for diagnosing chronic diseases of internal organs and assessing the patient’s condition after surgery. But if it is necessary to clarify the type of tumor, it is recommended to use a device with a power of 1.5 Tesla. This is important when detailing blood flow, searching for the smallest punctures, cracks or deformations.
It should be noted that, regardless of the power of the tomograph, there is no dangerous effect on the human body. This makes magnetic resonance examination practically safe.
Operating principles and main differences between CT and MRI
To have a simple understanding of the main differences between MRI and CT, you first need to understand how they work.
When examining parts of the body using MRI, the patient is exposed to both pulsating constant magnetic fields and radio frequency radiation. They are formed by a special device - a tomograph. In a matter of seconds, the device sends a radiofrequency pulse to a certain area, which causes hydrogen atoms in the body's cells to sway and resonate. Next, special equipment collects the received signals, processes them and outputs a three-dimensional image with the chemical structure of the tissues of this area.
In the case of using the CT technique, the examined part of the patient is exposed layer by layer to a beam of X-ray radiation, which is sent from a special apparatus. Due to the different densities of the fabric, the rays are absorbed differently, which is recorded by special devices. They process the received data and then produce a layer-by-layer image of tissue sections, that is, their physical state.
Cost of the procedure
It is better to check the price for open or closed magnetic resonance imaging at the medical institution. It depends on several factors:
- Medical center pricing policy.
- Quality and technical characteristics of the tomograph.
- Level of training and qualifications of diagnostic doctors.
- Location of the hospital where the examination is carried out (capital, regional or district center).
As a rule, the cost of a standard MRI increases when a contrast agent is used, so an examination service using an open-type machine will be 1000–1500 rubles less.
Benefits of MRI
The main advantage of magnetic resonance imaging scanners is the high accuracy of the results. Some devices can examine every 2 centimeters of the body, which allows you to see a tumor, hernia or any other pathology in detail. By the way, only an MRI can show a tumor located under the bone tissue - X-rays, ultrasound and other devices cannot do this.
An important advantage of MRI is that a three-dimensional image is displayed on monitors. Any area of interest can be viewed from all sides. During the procedure, the patient does not receive radiation, so MRI is considered harmless.
Which procedure to choose
Closed and open MRI are practically the same in terms of accuracy and information content of the result. According to doctors, the detail of the images reaches 95–98%, while the number of errors is reduced to 2–5%. This allows you to use the procedures before preparing for a complex operation, when diagnosing chronic and acquired diseases.
Assessing the advantages and disadvantages of open and closed MRI, the doctor will choose what is best for the patient:
- The use of closed-type equipment is ideal for searching for neoplasms over 1 mm, tumors, and metastases. The results are always accurate and make it possible to construct a three-dimensional model of the affected organ. At the same time, some patients complain of discomfort from a long stay in a narrow tunnel, loud sounds, and experience fear.
- Modern open-type MRI scanners have many practical models. They scan the patient while sitting, standing or lying down. This is convenient for people with limited mobility. But the radiation power is not always enough for a serious examination of large areas of the body. It is not used when performing small-section analysis of a tumor, vascular angiography, or analysis of the intestinal condition. At the same time, the operating time increases if it is necessary to clarify the result.
Which MRI machine is better, open or closed, depends on the magnetic resonance imaging equipment. Old tunnel-type models do not have high power, which affects the results. Ultimately, the choice of technique should be entrusted to the attending physician, and a diagnostic center should be selected based on patient reviews.
The whole truth about MRI and computed tomography
Can bones be seen on an MRI?
Which is safer - MRI or computed tomography (CT)? Why can MRI be replaced by CT, but CT cannot be replaced by MRI?
Answers to these and many other questions are given by Anton Ivanovich Chugaev, chief physician of the MRI 24 network of diagnostic centers.
Radiologist Anton Ivanovich Chugaev.
What is MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern method for diagnosing diseases using nuclear magnetic resonance. The method is based on measuring the electromagnetic response of hydrogen atoms.
It sounds complicated, but in reality everything is much simpler. MRI shows the signal from tissues that contain hydrogen atoms. The more hydrogen atoms in tissue, the better they are visible on MR images.
And since water contains the most hydrogen atoms, the more water there is in the tissue, the brighter the signal on the MRI image. The less water, the weaker the signal.
What does magnetic resonance imaging show? What can be seen on an MRI and what cannot?
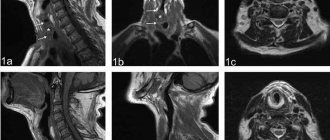
MRI photograph of the knee joint.
Tissues and media that contain water are best seen on MRI. Therefore, MRI shows the brain very well, because the brain is 75% water.
In addition to the brain, the following are very clearly visible on MRI:
- Tumors and cysts;
- Healthy and damaged muscles, ligaments and any other soft tissues;
- Ligaments, menisci of joints;
- Vertebral bodies and joints.
It is very convenient to use MRI to study bone pathology. The hard bone itself is not visible, but the adjacent bones of the joints, soaked in bone marrow, are clearly visible. Thanks to this, the doctor immediately notices bone problems.
Limitations of MRI
1. It is very difficult, and sometimes impossible, to distinguish between hard bodies such as skull bones and foreign bodies on MRI.
2. Lungs are not visible on MRI images. There is too much air in the lungs for this, and the MRI does not see air.
Who should not have an MRI?
MRI cannot be performed on patients whose body contains objects with iron parts: for example, implants, hearing aids, pacemakers, neurostimulators, ferromagnetic clips and other inclusions. This is a direct contraindication to MRI.
Before the examination, a patient with an implant* or prosthesis that does not contain ferromagnetic or electronic components must bring the doctor a special extract or conclusion from the attending physician.
The statement should describe what the implant is made of, and the doctor’s report may say whether an MRI can be done with this implant.
Under no circumstances should MRI be performed on patients who have electronic pacemakers or pacemakers. People with pacemakers should not even come close to the device.
*Cardiac bypass surgery is not a direct contraindication to MRI. Your doctor will usually allow magnetic resonance testing 1 to 3 months after bypass surgery.
How is an MRI performed? There is an opinion that during the procedure you need to lie motionless for a long time in a large apparatus. What happens if you move?
It is recommended to do MRI examinations in specialized centers using modern equipment.
To get good MRI images, exposure time is needed. This means that you will have to lie still in the device for some time. If you move, the outlines of the tissues will be blurred.
This implies another limitation. MRI cannot be done on people who are not fully conscious, who are in shock (for example, after being shot in the abdomen or after a stroke), or those who cannot obey commands or lie still.
Patients with severe pain will not be able to lie still and hold their breath at the doctor's command. When a person moves, the result is a fuzzy, blurry image that is useless to the doctor.
Patients who cannot lie still are referred for a computed tomography (CT) scan or an MRI under general anesthesia.
Are MRIs done for children?
Yes, MRIs are done for children. But children have an innate fear of closed spaces, which kids cannot consciously control. Therefore, young children are often given anesthesia before the procedure.
If the child is older, a parent may be nearby. If dad or mom holds the child's hand and calms him down, there is a chance that the child will not move, and a good result will be obtained.
In what cases is it necessary to do an MRI?
If the attending physician has referred you for the test, an MRI must be done. For example, magnetic resonance imaging is often ordered after surgery to remove a brain tumor.
Which doctor can refer you for an MRI? Can I come for an MRI on my own?
Any doctor can refer you for an MRI.
There is also nothing wrong with going to an MRI yourself. Many diagnostic clinics even have a comprehensive study that allows you to examine most body systems.
After the MRI, you will be given a report. But to understand what is written in the conclusion, you will have to consult your doctor.
You mentioned computed tomography. How does MRI differ from CT?
The MRI machine (left) looks very similar to the CT machine (right). But the operating principles of the devices are different.
The main difference is that MRI is not an x-ray method. This means that the person who came for an MRI does not receive a dose of radiation.
MRI is not harmful. If you schedule an MRI for yourself, nothing bad will happen. MRI can be done even for pregnant women, starting from the second trimester of pregnancy.
CT is a modern x-ray diagnostic method. Accordingly, the person who comes for this procedure receives a dose of radiation.
It is often impossible to do a CT scan, and neither is it possible to prescribe it for yourself. Only a doctor can refer you for a CT scan.
Advantages of CT over MRI
1. CT is less demanding on movements. Even a person in an inadequate and shock state can undergo a computed tomography scan.
2. On CT, foreign objects and hard tissues are clearly visible, which are not visible on MRI. For example, CT can accurately diagnose skull fractures.
3. Lungs are visible on CT scan.
4. CT scanning can be performed on people who have metal objects in their bodies. This is especially important if you need to urgently evaluate a person who has been involved in a car accident or anyone else who has received resuscitation measures.
Such patients are given subclavian catheters and oxygen equipment is connected. If you refuse all this during an MRI examination, the victim may die.
Are there any analogues for MRI? Can it be replaced by an x-ray examination?
CT machine from the diagnostic center MRI 24.
Although MRI and computed tomography are similar at first glance, they are very different diagnostic methods that do not replace, but complement each other.
As for the technical quality of the image, MRI images, in my opinion, are still better than CT images. But at the same time, CT is suitable for those people who cannot undergo MRI.
Therefore, when public hospitals have a choice of which device (CT or MRI) to purchase first, they always start with a CT machine.
Where is it better to do an MRI - in a large hospital or in a specialized center?
It is better to do an MRI where there is a good machine and a good specialist. Usually the best equipment and specialists are available in specialized centers.
For example, in clinics dealing with a specific pathology and having their own diagnostic department, or in specialized centers dealing with MRI and CT diagnostics.
Moreover, the examination can be done in any hospital where there is a modern MRI machine. A good modern MRI machine should have a power of at least 1.5 Tesla (Tesla).
How to prepare for an MRI?
As a rule, there is no need to prepare specifically for an MRI. But there are some tests before which you need, for example, to drink water or take special medications. You should be warned about such manipulations in advance when you sign up for the study.
For example, if a person is being examined for organs that are near the intestines, it is important not to eat before the examination so as not to increase intestinal motility. The more intense the intestinal peristalsis, the worse the MRI images of neighboring organs are obtained.
What should I do after I receive the MRI image and transcript?
It is difficult to understand the results of an MRI on your own. After they give you the image and transcript, you will need to contact the attending physician who referred you for an MRI.
Finally, I will say that there is no need to be afraid of MRI. This is a safe, modern and very informative study that helps make an accurate diagnosis.
Source: //zen.yandex.ru/media/id/59c4ede73c50f71d116106cb/5c1b9ea102117205163923c7
Which is more accurate: CT or MRI?
Both methods are highly informative. However, when studying certain pathologies and diseases, a specific diagnostic method can give a more accurate result.
MRI gives the most accurate results if you have:
- Malignant formations in the body.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Stroke.
- Pathologies of the spinal cord.
- Injury to tendons and muscles.
CT gives accurate results if:
- Injuries and internal hemorrhages.
- Diseases of the skeletal system.
- Pathologies of the respiratory system.
- Sinusitis and otitis.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland.
- Lesions of the facial skeleton.
Main differences
In order to get a detailed picture of the difference between the two diagnostic research methods under consideration, it is better to familiarize yourself with the following table:
| CT | MRI | |
| Application | Used to obtain a clinical picture when problems occur with the bones, lungs and chest. | Used to assess the functional state of internal organs and soft tissues. The method is widely used to detect tumors and pathologies of the spinal cord. |
| Principle of operation | X-rays | Magnetic field |
| Duration of the procedure | As a rule, does not exceed 5 minutes | On average, the diagnostic procedure lasts 30 minutes |
| Safety | The method is safe. However, long-term exposure to X-rays may result in body radiation exposure. | Completely safe for human health and well-being. |
| Restrictions | Patients weighing about 200 kg may not fit into the scanning machine. | The method is contraindicated for patients who have metal implants and electronic devices in the body. |
Differences between CT and MRI appointments
For a comparative analysis, it is important to know which diseases can be detected by each method.
Indications for computed tomography:
- Disorders of the musculoskeletal system and joint diseases. Helps identify arthrosis, arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, osteochondrosis and more. Despite the fact that it is impossible to completely scan the spine. The technique remains one of the most accurate, the first to detect a violation of the bone apparatus.
- Tumors, growths, bone deformation.
- Injuries and damage to the human skeletal body - fractures, cracks in bones, dislocations, deviations that occurred due to mechanical impact - are identified after receiving the results.
- Changes in the structure and functioning of blood vessels at the atherosclerotic level.
- When examining the soft tissues of the respiratory apparatus, gastrointestinal tract and genital and urinary organs, a contrast study is performed.
When is magnetic resonance therapy needed:
- If tumors, cysts, growths of soft tissue (muscles, organs, adipose tissue) are suspected, the procedure is prescribed only after an initial examination and preliminary results of an ultrasound examination.
- To monitor the condition and quality of the brain (not only physical factors, but also mental ones). For example, people with schizophrenia have strong activity in the area of the brain responsible for hearing and vision - this indicates hallucinations.
- To detect spinal cord disorders.
- To identify pathologies of soft cartilage of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs.
This difference speaks to the exclusivity of each of the methods - they are very different and each of them is required for certain pathologies.