A computed tomograph is a device based on x-rays. He takes pictures from different angles using x-rays. A CT machine is a modernized X-ray, so it does no more harm than a regular X-ray. A tomograph is indispensable for conducting research - it provides more information than radiography, since it is possible to examine the organs being examined from different angles and at different depths.
Is CT scanning harmful?
Computed tomography is, first and foremost, a medical instrument. It is not the device itself that is considered dangerous, since a modern medical tomograph is useful for doctors and patients with its capabilities. The danger lies in X-ray radiation, which affects the composition of the blood, changes it, which can lead to the development of pathologies if the radiation dose exceeds acceptable standards for humans.
Examining a person once a year with a tomograph will not harm the body. If it is possible to use a safer method with the same effective diagnosis, then the doctor will stick to it. For example, if an X-ray can be replaced by taking tests and undergoing an ultrasound, then the doctor will limit himself to this without exposing the patient to the risk of radiation.
Frequency of tomography of other organs
How often can a CT scan of the abdomen and other organs be done? To answer this question, the doctor must carefully review the patient's medical history. The frequency of the examination directly depends on the complexity of the disease, the effectiveness of therapeutic treatment and other factors.
To minimize the likelihood of developing negative reactions and consequences dangerous to health, it is advisable to carry out diagnostics no more often than once every six months. If there are medical indications, the frequency of examinations can be reduced to 8 weeks. However, in this case, the risk of negative reactions increases several times.
What problems can arise from CT radiation?
If the dose of radiation is exceeded, an adult may experience:
- leukemia – a decrease in the number of white blood cells, which leads to a decrease in immunity;
- thrombocytopenia – decreased platelet count, deterioration of blood clotting;
- hemolytic changes - breakdown of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood;
- erythrocytopenia – breakdown of red blood cells, resulting in tissue hypoxia and oxygen starvation.
Such changes occur with an increased dose of radiation. With minor short-term exposure to CT, X-ray or fluorography, blood changes are insignificant and reversible within 1-2 days after the test procedure.
Medical equipment is relatively harmless, as it uses a special short-term and low-energy range of radiation, which increases the risk of developing pathology by only 0.001%.
Consequences
All negative consequences of CT are associated with radiation and the body’s reaction to contrast.
For the average person, the radiation exposure received from a CT scan is not dangerous. Although it is much greater than with radiography, it is not capable of reaching those values beyond which radiation sickness occurs (3 Sv or more).
Of course, ionizing radiation can accumulate in the body and increase the likelihood of developing cancerous tumors, but that is why it is used in medicine only according to strict indications and in cases where the benefits of it outweigh all possible risks .
A special category of patients are pregnant women and children under 14 years of age. The first study is strictly contraindicated. Research is carried out for children, but if it really cannot be done . special pediatric regimes are used with a reduction in all study parameters to a level at which the radiation dose corresponds to the size of the child’s body. You can read more about CT scans for children here.
As a rule, contrast agents used for enhanced CT are well tolerated by patients. But some patients experience an individual reaction in the form of side effects in response to their administration. Consequences may appear 20-60 minutes after administration of the drug . These include:
- nausea, vomiting;
- bronchospasm (spastic cough, suffocation)
- swelling of the larynx;
- urticaria (an itchy, urticarial rash on the body);
- diffuse erythema (redness of the skin);
- drop in blood pressure;
- feeling of heat;
- anaphylactic shock.
Less commonly, subjects develop late side effects (after several hours or even days):
- skin reactions (rash, itching, swelling);
- cardiac arrhythmia;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- influenza-like syndromes (fever, chills);
- hand pain.
These consequences are based on anaphylactoid reactions (reminiscent of an allergy, but are not caused by the interaction of an antigen with an antibody, but with other substances that activate the release of biologically active substances) or direct irritation of the wall of the vessel into which the contrast is injected. Their frequency depends:
- on the type of contrast;
- its concentration;
- volume and rate of administration;
- individual characteristics of the body (allergies, previous reactions to contrast, bronchial asthma, kidney and liver diseases).
In patients with any kidney pathology, CT scanning with contrast increases the risk of developing nephropathy.
In most cases, mild and short-term side effects are observed. They resolve quickly without medical intervention or with supportive care.
Important: Severe reactions are extremely rare, but we should not forget about them. After all, they pose a threat to life and require immediate assistance.
Therefore, after the end of the study, even if a person feels well, it is advisable that he be under the supervision of medical personnel or relatives for several hours. He is advised not to travel, especially while driving a vehicle.
Differences between CT and MRI
CT and X-rays are radiation that will be ionized during operation and thereby harm the body. Although CT scans are less harmful, many people imply that they should be replaced by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
MRI creates a magnetic field, the negative effects of which on the body have not yet been noticed. Diagnostics by X-ray, MRI and CT differ in the areas of research and their capabilities, so they are interchangeable in rare cases. A patient can receive an appointment for an MRI and an X-ray at the same time. Since MRI specializes in soft tissues, it perfectly shows the structure and volumes, distinguishes pathologically altered tissue structure from healthy ones, but X-rays will show the skeleton, bones and metal foreign bodies, changes in dense bone layers, or kidney stones.
The maximum permissible dose of radiation for preventive purposes (fluorography) is 1 mSv per year, for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes there is no limit. The radiation dose during a brain CT examination will be no more than 2 mSv.
Progress of the procedure
During a CT scan, the patient lies motionless on a special mobile table.
The most accurate image can be obtained by periodically holding your breath, which the radiologist warns the patient about during the procedure via speakerphone, observing the subject through the viewing window. The tomograph ring moves along the patient’s body, while X-rays illuminate the required area. Computed tomography is characterized by high scanning speed and low x-ray load on the body. High quality images ensure the detection of pathologies at the earliest stages of their development.
Make an appointment
Natural background radiation
High levels of radiation may be present in natural environments. It depends on the region of residence of a person. It is the natural background radiation that influences a person’s adaptation to a new place of residence. Moving to another region, changing climate and natural background radiation can have a significant impact on the health of sensitive people and children. In this case, it is better to postpone the dangerous move until the child is fully grown up or choose another region to live.
Limitations of CT Examination
Computed tomography is dangerous for a certain group of patients:
- Pregnancy;
- The patient's age is under 18 years (only with parental consent and under strict indications);
- Nursing women (in this case, the woman cannot feed the baby after the procedure; she must express milk at least 3 times within 3-4 hours after the x-ray examination).
Test intervals and protection of other organs
Radiation from CT increases with the duration of the examination, but the diagnosis itself rarely lasts long, and the intervals between examinations can reach 6 months or a year, which will not allow the permissible radiation exposure to be exceeded. The effect of X-rays ends immediately after the device is turned off.
When examined using X-rays, all other parts of the body are protected with a lead screen, “blanket” or special plates that must be held with hands, or they are placed on the body with the patient in a horizontal position.
Radiation protective clothing
Diagnostics using CT scans in terms of benefit to the patient exceeds the harm from radiation, and the resulting radiation dose is so low that a CT scan can be performed more than once a year if there are no other restrictions. A modern device has partial examination functions, when only the necessary part of the body is exposed to irradiation.
A disease or pathology using CT can be detected at an early stage, which will allow doctors to prescribe early and effective treatment or correct an existing one.
How does a CT scanner work?
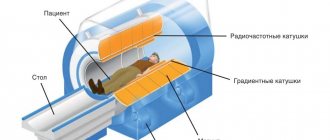
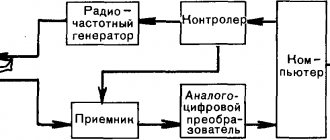
The question of whether computed tomography is dangerous should be addressed from the CT machine. The operating principle of the device is simple; its components are a gantry (ring-shaped installation) and a diagnostic table inside the gantry.
The ring-shaped installation is the basis of the device; on its outer side there is a beam tube and return signal sensors. Sensors catch the return signal and record changes, transmitting them to an analyzer in a computer. Next, the information is deciphered, and based on it, scanning images are produced in increments of 1 to 5 millimeters of the organ under study. CT makes it possible to examine the organ from all sides and at different depths.
Computer tomograph device
Use of contrast agent
The question of using contrast should be raised by a doctor. The contrast agent consists of iodine preparations, so if a person is intolerant to iodine or iodine preparations, then contrast cannot be administered to him - this can lead to an instant allergic reaction. A contrast agent is not administered for diseases of the heart, liver and kidneys, as it puts a strain on these organs.
An image obtained as a result of a computed tomography scan with contrast
The contrast agent itself may be administered intravenously or inhaled. Contrast makes the equipment more sensitive and helps to see the smallest vessels, which is very convenient for making a diagnosis, and an accurate prognosis helps to adjust treatment on time.
A modern computed tomograph is, first of all, an opportunity for doctors and patients, and then a harm. The risks resulting from radiation from the device are commensurate with the benefits.
Advantages of SCT and MSCT
Today, innovative types of computer diagnostics are widely used - these are spiral CT and multislice or multislice CT. Since these techniques are more modern and progressive, many people are interested in the question, how often can CT scans of the lungs, heart and other organs be done? These diagnostic methods can indeed be used more often than traditional CT.
This is due to a number of obvious advantages, which include:
- The research requires a minimal amount of time (just a few minutes instead of half an hour).
- Higher quality and clearer contrast resolution of images, making it possible to diagnose the most minor pathologies and changes.
- Minimum amount of radiation exposure to the human body.
- The number of foreign objects that appear in photographs is reduced to a minimum.
- Examinations with a contrast agent are carried out with the introduction of a much smaller amount, which reduces the possible burden on the human body.