Despite the fact that today there are such diagnostic methods as computer and magnetic resonance imaging, radiography also does not lose its relevance. Several years ago, an improved examination method was created - digital x-ray. This diagnostic method also projects images of bone fibers and organs using X-rays.
In this case, the image is processed not in a classical way, but digitally, due to which it is clearer and allows you to view the tissues being examined in detail. Not only does digital radiography offer multiple benefits, but it also allows images to be stored on a computer for long periods of time.
What is the essence of x-rays?
The use of digital equipment increased the quality and information content of the study. The technology saves diagnostic results on any digital medium or sends them by email in DICOM, HL7 format, which eliminates the loss of the X-ray report.
Another convenience is the ability to keep a photo in perfect condition for a long time. A standard image on film loses quality over time, fades and becomes scratched, unlike its digital counterpart.
Film X-ray takes an image that cannot be duplicated. A modern diagnostic option will allow you to take any number of images.
Chest X-ray
X-ray of the chest organs (chest organs) is the most common examination method, which allows us to identify pathologies of the respiratory, as well as cardiovascular systems, ribs, and thoracic spine that arise from various injuries and diseases.
How do X-rays work? As they pass through the body and organs, they are absorbed in different ways. The result is an x-ray image. Tissues with a denser structure look white on it, those that are softer look dark. After development and drying, the radiologist evaluates the resulting picture. An X-ray of the lungs will show all pathologies, if any, and indicate possible diseases.
Modern digital devices simplify the procedure, while the radiation dose is significantly reduced. There is also mobile equipment that allows you to examine bedridden patients.
Positive aspects of diagnosis
Digital radiology and its first advantage is the ability to document the examination results. Thus, during a standard examination, the image is, in fact, the only “document” confirming the completion of the diagnosis, when digital radiography allows data to be archived and stored in a single database.
In addition, the study allows access to images at any time, remotely, which helps resolve many issues.
The main point is radiation exposure; this indicator is primarily assessed when prescribing a particular diagnostic measure.
Digital examination differs from film examination in lower radiation exposure - radiation is 10 times less. The dose is 0.02-0.3 mZV depending on the type of diagnosis (fluorography, mammography, etc.), the weight of the person, the organ being examined and its density.
Example: when undergoing fluorography on a scanning machine (Proscan), the dose will be 0.02-0.05 mSV, in the film version 0.1-0.3 mSV.
The next positive side is the technical capability, namely the availability of options that increase image contrast, sharpness, and size. This helps the doctor to effectively assess the situation, determine diagnosis and treatment.
Digital X-ray equipment allows images to be flipped, rotated, or cropped. If necessary, comments on pictures are saved on a personal computer.
Against the background of the listed positive aspects, it is worth noting the diagnostic pricing policy. It does not require the use of expensive film and special reagents, which makes it affordable.
What is the research procedure like?
When performing radiography, there are no special features in preparation for the study. The digital method is organized in the same way as the analogue one.
First you need to understand where you can get tested. The installations for performing this diagnostic method can be located in a clinic, in a hospital, or in a tuberculosis dispensary. In order to sign up and then undergo the procedure, you must first consult with your doctor. He will explain whether there are indications, what shortcomings this examination has, and will suggest what specific options will be necessary for a more accurate and rational use of the results.
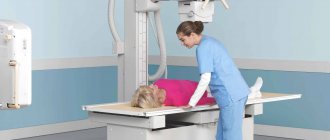
X-ray technician conducting a study
The procedure itself has no special requirements. In order to get the most out of the test, you need to listen carefully to the medical staff. If necessary, all jewelry, metal bracelets, and earrings must be removed, especially when performing a hand scan when the bones are small.
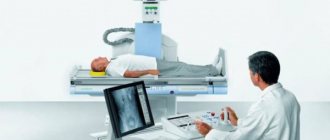
The result is assessed without the participation of the patient. A board-certified imaging physician or radiologist carefully reads the image at his desk. Digital radiography allows you to do this even with remote access, remotely. You can see the results the very next day. It makes no sense to draw any conclusions from the image yourself. Except, of course, when the patient has a medical education.
The study results do not contain a specific diagnosis.
They only reflect the specialist’s vision of a shadow picture of a particular area of the body. The diagnosis and treatment tactics must be determined by a clinician: therapist, pulmonologist, gastroenterologist, urologist, surgeon, traumatologist.
The final diagnosis is made by the attending physician, analyzing images and clinical data
In what cases is the study contraindicated?
The most harmful diagnostic method
Digital radiography has no contraindications; if necessary, it is performed during pregnancy and in young children.
Diagnostics clearly indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the lungs, the initial stages of tuberculosis and atypical formations.
Considering the lower concentration of radiation compared to film research, this does not give the patient the right to prescribe a study without consulting a doctor. Diagnosis is determined by a specialist after a physical examination, history taking and preliminary laboratory tests.
Some modern devices, using an exposure meter, can determine the permissible radiation exposure to the patient’s body.
The concept of the method and its essence
Radiography, both digital and analogue, has the same fundamentals. X-rays pass through the object being studied - the chest, pelvic organs, skull bones, limbs. The source of radiation is a so-called X-ray tube. In the analog version of the study, film is a storage place, as well as a place where this research result can be seen. If it is lost, it will be impossible to restore the X-ray picture.
When using this method, radiation from tissues that are capable of differently blocking the rays from the tube forms a picture on the monitor screen, and not on film.
This is achieved using an electronic sensor: the result, which should be realized on film, is converted into a digital signal using computer programs. And only then a copy of the result can be made by recording to disk or hard film.
Digital radiography is not carried out simultaneously, but in stages. This is its main difference from the analog method. What are the stages?
- Detection (search) of the resulting image.
- Setting it up and trying to handle stiffness, as well as other parameters.
- Directly recording the result.
- Evaluation of the resulting x-ray picture.
- Saving and archiving the image.
The examination time will not exceed 15 minutes (with X-ray of the lungs and pelvis). When the organs of the gastrointestinal tract or urinary tract are examined, the digital method is carried out no longer than the usual analogue one.
X-ray myth
Digital image of the hand
Patients are sure that radiation accumulates in the body, adversely affecting its condition. This statement is unjustified and is a myth.
In X-rays, the radiation carrier is electromagnetic waves, which disappear immediately after the equipment is turned off. They do not accumulate in the body, unlike the radioactive form of iodine. For this reason, there is no need to be afraid of diagnostics when prescribed by a doctor.
Advantages of portable X-ray machines - how do they differ from conventional stationary ones?
The type of diagnostic equipment in question first made its presence known during the First World War. The founder of portable devices is the French experimental scientist Marie Curie . Her invention made it possible to save many lives, thanks to an adequate diagnosis right on the battlefield.
Since then, these devices have been improved: they have significantly decreased in size and become more productive in terms of the resulting images.
How to choose the right X-ray machine - main types and applications in medicine
Modern portable X-ray machines have a number of positive aspects:
- Low radiation load. This characteristic is the basis for the structure of a portable X-ray device (exposure time on average does not exceed two seconds), as well as the presence of internal protection in it. However, this does not exclude the fact that the patient and operator must wear special protective clothing during the examination.
- Light weight, thanks to which the device can be easily transported. This is relevant when it is necessary to conduct a routine inspection at enterprises, or in the case of examining a patient at home. The weight of dental portable X-ray machines is so small that during use it can be held in one hand.
- Saving time spent on shooting, which is ensured by the presence of built-in memory.
- Good quality of the resulting X-ray images. These devices have a function that allows you to change shooting modes. In addition, the focal reflection of the X-ray tube is tiny. During such diagnostics, images are obtained that are not inferior in quality to images obtained using stationary X-ray machines.
- Possibility to take pictures during surgery. In this case, the patient should not go to a specially equipped room: the event is carried out directly in the chair/on the couch.
- Operation from a regular network or from a battery, which holds a charge for a long time.
What can a digital x-ray detect?
Brain diagnostics can visualize subdural and epidural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, strokes and metastases. Pathologies of the respiratory tract: pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer, pneumonia, bronchitis.
X-ray examinations are carried out in the abdominal area and will show: local tumors, metastases, foci of inflammation, abscesses, structural changes and more.
An X-ray of the spine is performed if local damage, spinal disc herniation, infection, or oncology are suspected.
However, this is not all the diagnostic capabilities of digital radiography; the study is carried out to confirm or exclude diseases and pathological disorders.
Indications for CT and X-ray
Radiography is indicated for diagnosis in the following situations:
- vascular examination;
- manipulations in dentistry;
- bruises, injuries of various origins and severity;
- suspected fracture or sprain;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- pathologies of the heart and kidneys;
- lung diseases.
A chest x-ray allows you to assess the condition of the organs located in it, namely:
- ribs;
- spine in the thoracic region;
- hearts;
- vessels;
- lungs;
- pleura;
- bronchi;
- trachea;
- other soft tissues.
Symptoms such as shortness of breath, prolonged dry cough, chest pain and fever of unknown origin are indications for an X-ray examination.
Indications for CT scanning are slightly different from those listed for radiography. The doctor will prescribe this procedure for research:
- lungs;
- hearts;
- brain;
- bones and joints;
- endocrine glands;
- hollow and parenchymal internal organs.
Due to its speed and high information content, CT is often used in dentistry.
Contraindications and restrictions for CT and X-rays
Both procedures have a number of limitations. In this case, their implementation is possible only if the benefit of the diagnosis outweighs the possible risks of complications. X-rays and CT scans are not prescribed unless necessary:
- patients under 14 years of age;
- pregnant and nursing mothers;
- persons in serious condition;
- patients with extensive hemorrhage or open pneumothorax.
In addition, a CT scan is not performed if the patient has increased emotional arousal, because during the scan it is necessary to remain motionless for a long time, which is not easy in this condition.
Stages of the diagnostic procedure
Diagnostics does not require preparatory procedures. Before manipulation, you need to remove metal jewelry and things with metal elements. The study does not take much time, it takes place within one minute. The radiologist's report is received on the same day or a day later.
It is worth noting that the results do not imply the presence of a specific diagnosis. The specialist describes what he saw on the x-ray and issues a conclusion. The diagnosis is made by a specialized specialist.
Modern radiography methods help to obtain highly accurate and informative results, which makes the study indispensable in medical practice. You can take digital x-rays in private clinics; ask the x-ray technician for information about the type of device and doses.
Advantages of radiography
This method is considered one of the most accurate and informative.
- The doctor gets the opportunity to examine in detail the state of the child’s internal organs and detect abnormalities that can cause serious illness.
- Such an examination is indispensable for fractures, injuries and bruises, since an external examination does not allow drawing conclusions about the extent and nature of the damage.
- Timely X-ray of the lungs makes it possible to avoid the development of serious diseases, including tuberculosis.