14.04.2017
Last modified: July 27th, 2020 at 03:48 pm
Angiodystonia (otherwise called vascular dystonia, vegetative-vascular dystonia, VSD) is a clinical syndrome manifested by a complex of symptoms associated with disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels.
It is not a disease according to the international classification. The syndrome is characterized by pathology of vascular tone. The syndrome can be focal (has a specific localization) or systemic (affect the entire vascular system). Violations of tone are observed, for the most part, in medium-sized vessels.
What controls vascular tone
The name of the syndrome contains part of the answer to your question. Vascular tone is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. In addition, it also ensures the activity of internal organs, innervation of glands, trophic innervation of skeletal muscles and receptors. Consequently, when the autonomic nervous system is damaged, disturbances in the functioning of various organs are observed. Doctors count about 170 symptoms that are manifestations of VSD.
Where did it come from and in whom does it manifest?
A single cause causing VSD has not been established.
Common reasons include:
- frequent stressful situations
- unstable nervous system
- emotional overstrain
- puberty
- depression
- hypotension (lack of physical activity)
- hormonal disorders
- overweight
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse, excessive consumption of coffee and other substances that affect systemic blood pressure)
Symptoms of VSD, to one degree or another, appear in almost the entire working population. More often observed in those whose work is associated with constant stressful situations, violations of the daily routine, violations of the work and rest schedule, when spending most of the time at the computer or computing machines. Angiodystonia syndrome is often detected in adolescents. This is due to an excessive reaction to external stimuli, instability of the nervous system, which entails “jumps” in pressure.
In many cases, VSD is a concomitant syndrome of another pathology. For example, pathologies of the endocrine system (diseases of the ovaries, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland), diseases of some internal organs (pancreatitis, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis), chronic infections and allergies.
Signs of angiodystonia
Characteristic and most common symptoms that suggest the presence of dystonia:
- unexplained pressure changes
- chronic feeling of fatigue
- dizziness
- loss of consciousness
- sleep disorders
- causeless headaches of various types (dull, aching, shooting)
- tinnitus (often when changing body position)
- numbness in the legs and/or arms
If you observe one or more of the above symptoms in yourself or your loved ones, you should consult a doctor.
Cerebral angiodystonia: consequences of the development of the disorder
Cerebral angiodystonia can develop both as a result of various disorders in the body (internal factors) and due to the influence of external factors (for example, stressful situations, eating heavy foods).
Cerebral angiodystonia requires careful diagnosis. In cases of lack of adequate treatment against the background of angiodystonia, encephalopathy, a non-inflammatory brain disease, may develop. Encephalopathy against the background of cerebral angiodystonia is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Chronic depression;
- Frequent headaches due to stress, fatigue;
- Disorders of consciousness, memory;
- Dizziness;
- Lack of initiative.
Concomitant symptoms may also include increased fatigue, mood swings, heaviness in the head, sleep disturbance and other signs inherent in angiodystonia.
Angiodystonia of the brain
As the name suggests, this pathology develops in the vessels of the brain. Otherwise it is called cerebral angiodystonia. “Alarm bells” are noises in the head, headaches of various localizations, tinnitus, dizziness and fatigue that does not correspond to physical activity.
Important Information: Heart Health Score
Cerebral angiodystonia is classified according to its location, cause of occurrence, presence of concomitant pathologies, and blood pressure indicators. The adequate choice of diagnosis and further treatment depends on these and many other factors. It must be remembered that one cannot “delay” with such a “harmless”, at first glance, syndrome. The longer you have symptoms, the more likely you are to develop encephalopathy. Encephalopathy is a non-inflammatory disease of the brain, however, its treatment is relatively more complicated than the treatment and prevention of VSD.
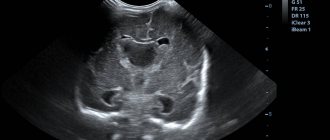
Often the diagnosis of cerebral angiodystonia is made in childhood based on the results of ultrasound of the neck vessels. If a violation of the location of the vessels is detected or their tortuosity is greater than normal. Because of this pathology, blood cannot flow normally to the brain and supply it with oxygen. Against this background, symptoms appear that indicate angiodystonia.
In many cases, cerebral angiodystonia is caused not only by concomitant pathologies, but also by an unhealthy lifestyle. Eating fatty foods, alcohol, large amounts of caffeine and smoking affects the blood vessels of the brain. Often, lifestyle changes can alleviate or completely eliminate the symptoms of VSD.
In what cases is it prescribed?
Normal blood supply to the brain allows a person to feel in a normal state - both physically and emotionally. However, if any disturbance occurs in this area, the brain immediately gives signals about it. A person begins to feel weakness throughout the body, his memory, mental and physical abilities deteriorate significantly.
In addition, he begins to feel severe headaches, which literally force him to see a doctor for a diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The REG procedure is precisely one of the diagnostic measures that allows us to find out the cause of such disorders.
As a rule, REG is prescribed for the following purposes:
- For diagnostic purposes, i.e. clarification of the diagnosis or cause that influenced the occurrence of the pathological process.
- For prevention purposes. Can be prescribed to children and the elderly to assess the condition of the blood vessels in the brain. It often acts as a primary diagnosis in infants, allowing to assess the elasticity and patency of cerebral vessels.
- To assess the effectiveness of previous treatment.
This procedure is prescribed not only for diagnosing angiodystonia, but also for identifying other diseases:
- For traumatic brain injuries.
- Migraines and weather dependence.
- To determine predisposition to coronary heart disease.
- Vascular atherosclerosis.
- Previous myocardial infarction and stroke.
Many people compare REG with MRI, because the data obtained from both studies are quite comparable. However, the advantage of rheoencephalography is the fact that this procedure is more affordable financially. In addition, an MRI study places certain requirements on the patient’s build - his weight should not exceed 120 kilograms, and his waist circumference should be no more than 70 cm. Patients who suffer from claustrophobia also cannot be examined using magnetic resonance therapy.
As for REG, the requirements are not so strict, so almost all categories of patients, including pregnant women, can be examined. The presence of wounds and abrasions in the head area may be considered a relative contraindication, but even in this case the doctor may decide to perform the procedure.
Angiodystonia of the retina
This syndrome develops due to pathology of the retinal vessels. Due to disturbances in the tone of the arteries and veins, the activity of the retina is disrupted - timely narrowing and expansion becomes impossible. This pathology is often one of the first to occur and is an important diagnostic sign for making a diagnosis.
Causes
Can be divided into two large groups:
| Associated with vascular pathology | Associated with pathology of other organs and systems |
| Atherosclerosis | Diseases of the nervous system, injuries of the cervical and thoracic spine |
| Hypertension | Severe forms of diabetes mellitus |
| Increased intracranial pressure | The influence of radioactive radiation, toxic substances |
| Congenital pathologies of the circulatory system | Some autoimmune diseases |
| Thrombosis of arteries of various sizes | Pregnancy (increases the load on blood vessels) |
How to recognize
The first signs, of course, will be a decrease in visual acuity and limited visual fields. In addition, there may be a veil before the eyes, flies or fog. Color vision disturbances are possible. It becomes significantly more difficult to recognize objects located at a considerable distance from you. The appearance of spots on the sclera of the eyes from yellow to red is characteristic. The appearance of red spots indicates the presence of hemorrhages from the retinal vessels.
In addition to the main manifestations, nosebleeds, leg pain and hematuria (the appearance of blood in the urine) may also be observed.
According to the reasons for the occurrence of VSD syndrome, it can be divided into several types:
- Traumatic - occurs when there is a sharp increase in pressure in the vessels of the eye. Occurs when the eye itself is injured, the body is compressed in the neck or chest - hemorrhage occurs in the eye and vision loss occurs. However, if the case is isolated, then vision is restored.
- Hypertensive – associated with the presence of hypertension or traumatic brain injury. In such cases, the uniform narrowing of the retinal arteries is disrupted, intracranial pressure increases, which increases the load on the visual apparatus. With timely initiation of treatment, it is possible to completely restore vision.
- Hypotonic – develops as a result of arterial hypotension. Due to a decrease in pressure in the bloodstream, the retinal arteries dilate, thereby preventing the venous blood flow from functioning normally. With this type of VSD, the patient feels pulsation in the vessels of the neck and dizziness.
- Diabetic – occurs in severe forms of diabetes. In this case, the key role is not in increasing systemic blood pressure, but in reducing the elasticity of the vessel walls. The vessels become brittle and lose their tone. Frequent hemorrhages occur in the retina.
Important information: What can you do to avoid problems with blood pressure?
Angiodystonic type reg what is it
Rheoencephalography is considered one of the most effective methods for diagnosing vascular dystonia. The angiodystonic type of REG, which is revealed by the results of the study, allows you to confirm the diagnosis. Thanks to this method, pathology is detected at an early stage, and this facilitates treatment.
Changes that can be seen on the REG
The main sign of vegetative-vascular dystonia, which is detected during REG of the brain, is unstable, variable vascular tone, and there is also a predominance of hypotension.
This is the so-called angiodystonic type of REG.
At the same time, an important difference from the hypotonic type is precisely the lability of the vascular wall - the tone is very unstable, constantly changing, which leads to the development of a characteristic clinical picture.
Sometimes patients experience an angiodystonic type of REG, what is it? This is a very similar type of reaction, in which long-term disruption of vascular tone levels has led to their dysfunction, changes in elasticity and more severe dystonia.
In such patients, the disturbance of cerebral blood flow is more pronounced, however, these are still reversible changes, and if they are detected, treatment should be started immediately. If this condition is not treated for a long time, then irreversible changes occur in the vessels due to a violation of the neurohumoral regulation of their tone.
All this leads to the development of hypertension, decreased vascular elasticity and impaired blood supply to peripheral organs.
On REG, a peculiar hypertensive type of reaction is observed, in which increased vascular tone is combined with a discrepancy in venous outflow. Patients develop plethora and increased intracranial pressure due to obstruction of venous outflow.
REG is prescribed both for diagnosis and for assessing the effectiveness of therapy, as well as for prevention. For children and the elderly, the study is carried out to determine the condition of the cerebral vessels. It is also prescribed to infants - in this case, it is the primary diagnosis for assessing the elasticity and patency of blood vessels in the brain.
In addition to angiodystonia, REG allows you to diagnose:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- predisposition to cardiac ischemia;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- migraine;
- weather sensitivity.
The method is also prescribed to patients who have suffered strokes and myocardial infarctions to assess their condition.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The study has no absolute contraindications. A rheoencephalogram is performed with caution in the following cases:
- damage to the skin on the head - abrasions, wounds, burns;
- implants in the skull (you need to inform a specialist about them);
- childhood.
REH is not dangerous for children, but you need to lie down quietly. Therefore, it all depends on the parents - whether they will be able to persuade the child to put on electrons and not fidget on the couch.
Risks associated with vegetative-vascular dystonia
Despite the fact that dystonia in the early stages is a process that is caused by reversible functional changes in the nervous regulation of vascular tone, it has adverse consequences.
Over time, dystonia can lead to the development of adverse consequences, the main of which is hypertension.
This means that irreversible organic changes in the vascular bed itself are observed in the body, which in the future will lead to the development of many unpleasant complications and diseases.
This needs to be understood, since many people, having heard that they have been diagnosed with a dystonic type of REG, think that this is only a temporary disorder and do not follow the recommendations of their doctor.
It should also be taken into account that angiodystonia is a more common occurrence in children than in adults. Therefore, vegetative-vascular dystonia detected in adult patients should be treated much more carefully.
It is necessary to pay attention to whether the angiodystonic type of vascular reaction has been identified or whether it has already become hypertensive.
Further actions if violations are detected on the REG
Based on the results of the REG in combination with complaints and other studies, the attending physician can make a diagnosis. In any case, if an abnormal rheoencephalogram is detected, the patient should be sent to the hospital, where the doctor will conduct a more detailed examination and history taking. The purpose of this is to find out how long the patient has had a violation of the nervous regulation of vascular tone, and what consequences this led to. After all, the approach to treatment and the necessary tactics for managing the patient depend on what stage the disease is at.
Source: https://baby-clinic-vozr.ru/narodnaya-medicina/angiodistonicheskij-tip-reg-chto-eto-takoe.html
Diagnosis of VSD
Successful diagnosis and further treatment, of course, depends on timely identification of symptoms. And, since the symptoms of angiodystonia often manifest themselves in a complex manner, diagnosis is not particularly difficult. The main diagnostic method is rheoencephalography. This method is based on the study of the resistance of brain tissue, which occurs under the influence of weak high-frequency electrical impulses. This is how data is obtained about the functioning of the brain vessels and their condition. For example, one can judge the elasticity of the vascular wall, its tone, the reactivity of the vessels and their pulse filling.
In addition, ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and cervical spine, ECG to detect changes in the heart, and electroencephalography are used. If the results of the study show evidence of a decrease in blood flow, a decrease in the diameter of the vessel and/or its lumen, a change in the position of the vessels or their tortuosity, then it is necessary to urgently begin therapy.
Dystonic type of REG: what is it, indications, advantages
Rheoencephalography (REG) is a high-frequency research method based on a mild electrical effect on the corresponding areas of the brain, using a special device - a rheograph. This diagnostic method allows you to carefully study the functionality, as well as identify diseases and pathological abnormalities in the blood vessels of the brain.
In essence, REG is a recording of waves that occur when certain areas of the brain are filled with blood and show the general reaction of the vascular system to this process.
A diagnostic specialist works with the data obtained, who studies the fluctuations of waves from normal values, their reaction to a test with a functional load, and then makes a conclusion about the state of the vessels responsible for cerebral circulation.
Classification
The disease is classified according to factors such as the origin of the pathology, the location of the lesion, the nature of the course and blood pressure.
They are due to the following characteristics:
- Origin . The disease can be primary (neurogenic) and secondary (symptomatic);
- Localization . Here angiodystonia is divided into localized vascular damage and damage to the entire system;
- The nature of the current . This division is caused by a temporary disturbance of vascular tone, or angiodystonic crisis (an acute disturbance of general or local circulation caused by increased pressure);
- Blood pressure indicator . This division is due to the blood pressure indicator at which angiodystonia progresses. There are hypertensive (high blood pressure), hypotensive (low blood pressure) and mixed types.
Angiocerebral dystonia has its own classification, depending on the course of the disease, which is as follows:
- Hypotonic type . This classification is due to vasodilation, leading to migraines and fainting. With the hypotonic type of cerebral angiodystonia, general weakness and inability to perform physical and intellectual work are noted. In some cases, memory loss is noted;
- Hypertensive type . It is observed during vascular spasms, causing sharp, severe pain in the head. With this type, angiodystonic syndrome is noted in pulsation in the temples, pain in the heart, the presence of a malfunction in the contractions of the heart muscle and increased blood pressure;
- Mixed type - characterized by manifestations of two of the above types at once. With this course, there may be loss of hearing, vision and decreased sensitivity to smells. There is an inability to understand new information and pain in the joints and back.
Blood flow in vessels
What do incomprehensible words mean: decoding REG
When a doctor begins to decipher the REG, he is first of all interested in the patient’s age, which must be taken into account to obtain adequate information.
Of course, the standards for tone and elasticity will be different for a young and an elderly person.
The essence of REG is to record waves that characterize the filling of certain areas of the brain with blood and the reaction of blood vessels to blood filling.
A brief description of the graphical representation of oscillations can be presented as follows:
- The ascending line of the wave (anacrotic) tends sharply, its top is slightly rounded;
- Descending (catacrota) goes down smoothly;
- An incisura located in the middle third, followed by a small dicrotic tooth, from where the descending wave descends and a new wave begins.
To decipher the REG, the doctor pays attention to:
- Are the waves regular?
- What is the top and how is it rounded;
- What the components look like (ascending and descending);
- Determines the location of the incisura, dicrotic tooth and the presence of additional waves.
Common types according to REG
After analyzing the rheoencephalography recording, the doctor records the deviation from the norm and makes a conclusion, which the patient strives to quickly read and interpret. The result of the study is to determine the type of vascular behavior:
- The dystonic type is characterized by a constant change in vascular tone, where hypotonicity with reduced pulse filling often predominates, which may be accompanied by difficulty in venous outflow;
- The angiodystonic type differs little from the dystonic type. It is also characterized by disturbances in vascular tone due to a defect in the structure of the vascular wall, leading to a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels and complicating blood circulation in a certain pool;
- The hypertensive type according to REG is somewhat different in this regard; here there is a persistent increase in the tone of the afferent vessels with obstructed venous outflow.
Types of REG cannot be classified as separate diseases, because they only accompany another pathology and serve as a diagnostic guide for determining it.
Reasons for the progression of angiodystonia
This disease is secondary and progresses against the background of the underlying pathological condition. The causes of arterial angiodystonia are a violation of the tone of the arteries, and venous angiodystonia progresses with changes in the tone of the veins.
Angiodystonic syndrome can progress against the background of the following pathological conditions:
- Impaired production of thyroid hormones;
- Diseases of infectious and inflammatory origin;
- Psycho-emotional stress, stressful situations;
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI);
- Sedentary lifestyle, low physical activity;
- Excessive body weight;
- Damage to the body by toxins;
- Atherosclerotic deposits on the walls of blood vessels;
- Pathological dilatation of veins (varicose veins);
- Emotional mood swings;
- Tuberculosis;
- Somatic pathologies;
- Syphilis;
- Vegetovascular dystonia;
- Herpes;
- Climax;
- Excessive consumption of alcohol, cigarettes, drugs;
- Osteochondrosis (damage to intervertebral discs and other tissues of the spine);
- Spondylosis (chronic disease of the human spine);
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Personal qualities of the patient (suspiciousness, aggressiveness, excessive worries).
The appearance of angiodystonia can be caused by one or several of the above factors.
Factors that provoke this disease in children are trauma during childbirth, maternal pathologies, prolonged labor and toxicosis during pregnancy.
The expansion and contraction of veins and arteries occurs under the control of neurohumoral regulation. Relaxation occurs after strong physical activity on muscle tissue, brain and internal organs, which promotes increased blood flow to them and the supply of more oxygen.
In a healthy state of the body, the venous system should supply waste blood to the lung cavity, where it will be saturated with oxygen.
The normal functioning of the autonomic system helps blood vessels respond normally to the influence of internal and external factors.
When body processes are disrupted, the arteries narrow, the tone of the veins increases, which leads to disturbances in blood circulation and its normal flow to the internal organs, progressing hypoxia (oxygen starvation of tissues).
Mechanism of vegetative-vascular dystonia
The diameter and tension of the blood vessel wall can vary widely under the influence of a whole system of regulatory factors. Moreover, both biologically active substances circulating in the blood itself and nerve impulses from the nervous system can act on the vessel.
This system is called neurohumoral regulation; it provides pressure variability and the ability to adjust the volume of blood flow to the changing needs of the body.
Indeed, thanks to this, the oxygen and nutrients they need are supplied to the peripheral tissues, and metabolic products are removed.
The need to increase blood flow can arise in different situations, most often during physical activity or stressful conditions, when the body works at an increased pace, which must be ensured by increased energy consumption. Many stimuli from the outside world can lead to this.
If the vascular system is not able to quickly and to the required extent respond to stimulation or an excessive change in vascular tone occurs unnecessarily, the person is said to have vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Risk factors for VSD
In this case, the patient may complain of extremely varied symptoms, for example:
- Various disturbances in the functioning of the heart - arrhythmias, extrasystoles, attacks of tachycardia.
- Asthenia, weakness, poor appetite and decreased performance.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system - constipation, diarrhea, frequent and sudden onset of heartburn, flatulence and a feeling of heaviness, poor food tolerance.
- Anxiety disorder, accompanied by a feeling of fear, sweating, and increasing anxiety.
- Neuroticism – the patient’s ability to concentrate decreases, he becomes inattentive, irritable, sleeps poorly and often loses his temper.
- Some people develop depression, depression, apathy and even panic attacks.
Unfortunately, dystonia does not have specific symptoms, which makes it difficult to differentiate it from other pathologies that may have a similar clinical picture. It is REG that is one of the best ways to make a correct diagnosis, since this study is non-invasive and relatively cheap.
Symptoms of angiodystonia
The manifested symptoms of the disease are quite varied.
Clinical symptoms of the pathological condition are due to the manifestation of the following signs:
- High or low blood pressure;
- Pain in the cervical region, back;
- Increase or decrease in the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle;
- Inability to concentrate on one task;
- Loss of sleep;
- Impaired attentiveness;
- Disturbances in the processes of memorization;
- Decreased vision, hearing, sensitivity to smells;
- Depression;
- Hard breath;
- Painful sensations in the heart area, which are characterized by pain, both at rest and during physical work;
- Numbness of the upper and/or lower extremities;
- Digestive disorders (heartburn, belching, bloating, etc.).
The main symptom of angiodystonia is angiodystonic headaches (also called cephalgia), which appears at any time, regardless of physical activity.
Diagnostics
At the patient’s first visit, the doctor listens to his complaints and performs an initial examination, as well as studying the medical history. Suspecting angiodystonia, the doctor may send the patient for examination to other specialists and additional hardware tests.
The most common diagnostic methods are:
- Ultrasound examination of blood vessels;
- Ultrasound examinations;
- Electroencephalography;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Ophthalmoscopy;
- Examination by a psychiatrist or neurologist;
- Rheoencephalography.
Diagnosis of angiodystonia
Treatment of angiodystonia
Therapy for this disease is complex and consists of drugs that are aimed at eliminating the disease that provokes angiodystonia. The course of therapy is selected individually, based on complaints, degree and location of vascular damage.
The most common medications prescribed for angiodystonia are:
- Pain-relieving drugs (Pentalgin, Ketonal);
- For low blood pressure – Captopril, Tenoric;
- For insomnia – Melaxen, Donormil;
- For disturbances in the rhythm of heart contractions - Verapamil, Diltiazem;
- For depression - Fluoxetine, Amitriptyline;
- For increased suspiciousness, fear and aggressiveness - Corvalol, Seduxen, Persen;
- For high blood pressure - Eufillin;
- For disorders of blood circulation in the brain - Piracetam, Pantogam, Vinpocetine;
- For eye damage - Taufon, eye vitamins (Anthocyanin Forte);
- Herbal medicines are various herbal preparations.
Treatment is carried out only after a complete examination of the body and the appointment of therapy by the attending physician.
Preventive actions
To prevent angiodystonia and speedy recovery after damage to the body, it is recommended to adhere to the following preventive actions:
- Maintain a daily routine with sufficient rest and sleep;
- Eat properly;
- Lose excess weight, if any;
- Exercise;
- Avoid psycho-emotional stress;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle;
- To walk;
- Get checked regularly;
- Regularly use herbal tinctures and decoctions that calm the nervous system.
Characteristic signs of angiodystonia
The main signs of angiodystonia are headaches of various types and etiologies, changes in blood pressure, dizziness, insomnia, numbness of the extremities, and systematic tinnitus.
A feeling of heaviness in the head develops. Some patients note memory impairment, impaired visual function, hearing, and sense of smell.
In some cases, signs of angiodystonia include pain in the limbs, neck, and back.
Source: https://diagnost-mk.ru/analizy/angiodistonicheskij-tip-reg-2.html
Treatment
Since VSD is not a disease, treatment is based on eliminating the root cause. If the syndrome was caused by a primary pathology of other organs, then treatment begins with the elimination of this pathology. In addition, part of the therapy is aimed at restoring and maintaining vascular tone. And, of course, symptomatic treatment, which includes normalization of the regime, proper alternation of work and rest cycles, giving up bad habits, gentle constant physical activity.
The doctor selects the exact treatment. If treatment of VSD symptoms is not combined with taking medications to eliminate the underlying pathology, then it is abandoned.
How does it differ from EEG and MRI analysis?
Most often, REG is confused with EEG, since both studies are carried out using electrodes.
What is the difference between REG and EEG:
- REG studies the state of blood vessels and blood flow;
- EEG determines the dynamics of neurons by measuring their activity in a specific area of the brain.
The question cannot be asked whether to choose REG or EEG. These are separate independent examinations, independent from each other.
If REG examines vascular problems, then EEG-electroencephalogram is usually prescribed to detect epilepsy, convulsive syndromes or similar diseases.
The procedure is completely different. An EEG takes much longer (sometimes several days) and is much more expensive.
Typically, EEG is accompanied by video monitoring with recording of the curve on electroencephalographs.
The situation is similar when they ask what is better: MRI or REG. Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to examine any human organ. The essence of the procedure is the ability to visualize the deep structures of the brain. MRI is highly informative and fully replaces REG.
However, due to the fact that the equipment used is expensive, the waiting list for examination can reach up to six months.
If it is necessary to urgently conduct a study, REG is prescribed, which is the most accessible and widespread.
REG can be used as an additional method, similar to echoencephalography - EchoEg.
An oscilloscope is used to conduct EchoEg. The result of the study is an oscillogram of the brain, which reflects the activity of its main structures.
Other research methods
According to WHO, for every 100 million people on the planet, there are 500 thousand strokes and cerebral vascular crises annually.
To avoid serious consequences or improve your health, you must promptly consult a doctor and undergo brain examinations.
Modern techniques
| Name | Description |
| Ultrasound Dopplerography (USDG) | Sets the speed of blood flow, narrowing in the lumens of blood vessels and atherosclerotic formations |
| Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) | Accurately determines the condition of the nerve trunks of blood vessels and medulla |
| Rheoencephalography (REG) | Evaluates blood circulation in the brain, vascular tone and blood supply status |
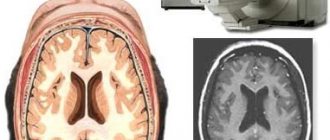
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | Allows you to see the brain in three dimensions |
| Computed tomography (CT) | Layer-by-layer “shows” the state of the necessary brain structures |
| Electroencephalography (EEG) | Examines brain activity, degree of functionality, carries out a comprehensive examination of the brain |
| Echoencephalography (EchoEg) – ultrasound examination of the brain | Provides information about the state of the vessels of the head, the performance of all parts of the brain |
| Neurosonography (NSG) | Allows you to determine the condition of the brain matter, soft tissues, brain vessels, the presence of aneurysms, tumors, and various pathologies |
| Positron emission tomography (PET) | The most modern diagnostic method, which is based on the use of radiopharmaceuticals. Creates a three-dimensional reconstruction of processes occurring in the brain. |
Prevention of VSD
As in most cases, the first thing you should do is try to lead a healthy lifestyle and spend more time in the fresh air. It is recommended to walk about 5 km at a moderate pace several times a week. However, if you have heart disease, then the pace should be slowed down. If you cannot eliminate the constant stressful situation in which you are, then herbal preparations are recommended for use. They are homeopathic, their effect appears within a month to a month and a half from the start of use, but they have significantly fewer side effects, unlike medications, and will help bring your nervous system back to normal.
REG and children
Rheoencephalography has no restrictions on the age of the patient. The difficulty is that when performing it you need to sit or lie quietly for several minutes. Not every child of primary school age is capable of this, not to mention preschoolers and infants. For this reason, it is better to conduct the examination in the presence of a parent.
Putting a hat or elastic band on your baby's head can also be difficult. Children under 3 years old will take it off. It’s better to practice putting on a pool cap or tying a ribbon around your head at home in advance. This way the child will get used to the discomfort and perhaps stop being afraid.
Before the examination, you need to pay attention to the fact that some children feel discomfort from the sticky cool gel applied to the skin. Electrodes can cause irritation or interest - it is better to remove them away from children's hands.
The best way to distract your child's attention is to tell him a fairy tale or read a book.
During the examination, the child is asked to sit or lie still, with his eyes closed. Since the study can last at least half an hour, this can be difficult for a restless child. In order to prepare your baby for the procedure, you need to try to tell him why it is necessary, explain how important it is. You can reach an agreement with your child in a playful format.
After all, here he sits or lies surrounded by adults. During the tomography he will have to be separated from everyone else, inside a machine that produces different sounds.