- Home /
- Branches /
- CT scan /
- CT scan of the pelvic organs
Computed tomography of the pelvic organs allows you to obtain a detailed layer-by-layer image of this area, assess the condition of internal organs, lymph nodes, soft tissues, blood vessels and bone structures.
In most cases, this procedure must be performed with intravenous contrast enhancement. Pelvic CT is used to diagnose tumor processes, inflammatory diseases and injuries. Often included in a comprehensive examination of the abdominal organs. It is an alternative imaging method in the presence of contraindications to MRI.
Pelvic CT is inferior in diagnostic value to MRI at the stage of early detection of pathological processes in the reproductive organs: ovaries, uterus, vagina (women); prostate gland, seminal vesicles (men).
Features of pelvic CT
Despite the radiation on which the computed tomography method is based, the dose a person receives is much less than with a conventional x-ray. Using highly sensitive sensors built into the tomograph, the reflected signals are sent to the computer.
There they are processed and displayed on the screen in the form of a graphic image. The minimum slice thickness is approximately 1 mm. In total there are almost 100 pictures. This makes it possible to detect many diseases in the initial stage, when there are no obvious symptoms yet. During a CT scan of the pelvis, the following will be examined:
- soft and hard tissues;
- rectum;
- nearby lymph nodes;
- coccyx;
- genitourinary system;
- sacrum;
- bone structure of the pelvis and its bottom;
- bladder.
More accurate visualization is provided by a contrast agent that is injected into the patient’s body in advance. It is given orally or intravenously. Iodine-based preparations (mainly Urografin) are used for examination.
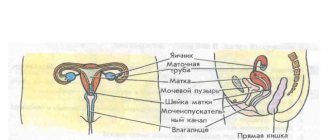
CT scan in women
With the help of CT scans in women, the urinary tract and lower part of the intestine are checked. At the same time, the fallopian cavities, ovaries, uterus (and the space behind it), and vagina are examined. In women, inflammation of the reproductive organs, prolapse or prolapse of the uterus, pregnancy (if the woman did not know about it before), accumulation of pus or blood in the fallopian tubes and their lumens may be detected.
CT scan in men
CT scans are performed less frequently on men than on women. In addition to the main parameters, the testicles and seminal ducts, prostate, and rectum are examined. In men, prostate adenoma, prostatitis, inflammation (orchitis, vesiculitis), as well as abnormal development of the genitourinary system can be detected.
Advantages of the method
A CT scan of the pelvis in both women and men provides comprehensive information about organs, bone structures, and blood vessels. It is possible to examine the intestinal lumen and mucosal features.
If necessary, pictures can be enlarged without losing image quality. Due to the fact that this diagnosis has virtually no contraindications, it becomes accessible to a large number of people.
CT scans of the pelvic organs are performed less frequently in men, but are still widely used to detect tumors and determine their size.
Radiation dose for MSCT
Although the radiation from a tomograph is not as strong as that of a regular X-ray, it cannot be said that it is completely safe for humans.
The radiation dose depends entirely on the diagnostic equipment, duration and location of the scan. It is worth considering that when introducing substances based on iodine and barium, the radiation exposure increases slightly. For this reason, doctors always find out about previously conducted studies in order to prevent exceeding the norm.
What does a CT scan show?
Regardless of gender, during a CT scan of the pelvic organs the following can be detected:
- benign or cancerous tumors;
- prolapse or prolapse of the intestine or bladder;
- urethral fistula;
- polyps;
- vascular insufficiency, venous lesions (for example, thrombophlebitis);
- sand and stones in the bladder or ureters;
- injury to organs and blood vessels in the pelvic area;
- cystic formations;
- deformation of the coccyx, sacrum, bone structures.
To identify diseases of the intestines or ureters, during a CT scan of the pelvic organs, organs located in the abdominal cavity are simultaneously examined. Such diagnostics are also done for serious indications.
What will a pelvic CT scan show?
During the study, a layer-by-layer scan of the pelvic organs treated with X-rays is carried out. The information obtained during the procedure is processed by a complex computer program, and the doctor receives clear images of the elements being examined. Based on these photographs, a 3D image is reconstructed. The doctor will record all examination materials on a DVD disc or other electronic media for saving photos and videos.
Layer-by-layer scanning helps to evaluate the structure and homogeneity of tissues, see changes in the shape and size of internal organs, and the presence of even small tumors and pathological changes in them. CT scan of the pelvic area allows you to evaluate the functioning of the circulatory system and the intensity of blood supply to the studied elements. A CT scan of the pelvic organs shows what is happening in the bladder, how the reproductive and urinary systems work, and reveals developmental features and pathological changes that indicate the presence of diseases. Differential diagnosis of diseases in this area is complicated by the presence of similar symptoms, so the ability to study in detail the condition of internal organs significantly increases the likelihood of determining a diagnosis.
Indications for examination
Computed tomography is prescribed to examine the pelvic bones and identify diseases in the lumbosacral region. Scans are done after operations to monitor treatment. General indications include:
- suspicion of bladder pathology;
- diseases and lesions of the rectum;
- injuries in the pelvic area, fractures and cracks of bones;
- cancerous tumors and suspicions of them;
- insufficient data after other diagnostic methods (X-ray, ultrasound, colonoscopy, etc.);
- inflammatory processes in the pelvic area;
- assessment of the spread of metastasis;
- constant pain in the sacrum, lumbar region;
- abnormal development of the genitourinary system;
- infertility for unknown reasons;
- assessment of neoplasms (malignant or benign), their size, exact location;
- abscesses.
CT scanning for men is performed for prostatitis. For women, computed tomography is prescribed for suspected vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology, ovarian apoplexy, or ruptured cysts. An examination is also prescribed to find out the reasons for the failure of menstruation.
Contraindications
Although CT has a minimum of harmful effects, there are a number of conditions in which CT scanning is dangerous and should not be performed. These are situations and pathologies such as:
- pregnancy (due to the possible negative impact of radiation on the formation of the fetus);
- when breastfeeding (the restriction is lifted if the woman can not breastfeed her child for at least 2 days after the administration of contrast);
- children under 14 years of age (due to rapid growth and formation of the body);
- allergy to iodine (when using CT with contrast);
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- serious pathology of the thyroid gland;
- multiple myeloma;
- an obese patient with a waist measurement of more than 120 cm (does not fit into the tomograph);
- the patient's condition requiring the use of life support equipment or medical procedures;
- chronic conditions of liver or kidney failure, when the use of a contrast agent is contraindicated;
- mental or neurological pathology with symptoms of hyperkinesis (inability to control one’s own motor activity): acceptable when using light medicated sleep;
- for claustrophobia (the need for light sedatives before manipulation or the use of open-type tomographs).
Contraindication is pregnancy in the first trimester.
Contraindications for diagnosis
Since X-rays are used during a CT scan of the pelvic organs, the scan is not performed on pregnant women, as it may disrupt the development of the embryo. Also, diagnosis is not recommended during breastfeeding, especially if a contrast agent was used. Other contraindications:
- the examination is not carried out for people weighing more than 150 kg;
- if the patient is unconscious, in a coma;
- is not given to people with mental disorders, as their behavior may be unpredictable;
- severe diabetes;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- chronic cardiac, renal and liver pathologies.
Since drugs containing iodine may be used during scanning, the diagnosis is not made if there is an allergy to this substance. CT scanning is not performed on children under 14 years of age, since during this period the body is still growing and actively developing. In such cases, computed tomography is used only in emergency cases, when the threat to the child’s life outweighs the possible risks from scanning or the diagnosis is replaced by magnetic resonance imaging.
Contraindications for examination
Apart from pregnancy and allergic reactions, there are no other serious contraindications for the use of computer diagnostics. Even women during lactation can undergo such a study if, after the procedure involving a contrast solution, they refrain from breastfeeding for 2-3 days.
Relative contraindications include:
- heart failure;
- renal failure;
- liver failure;
- mental disorders;
- comatose state;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- diabetes.
But all of the above refers to risks that are not an absolute obstacle to carrying out this diagnosis. This means that the examination may still be recommended if the benefits of the results obtained are greater than the possible harm.
Situations with patients suffering from obesity are considered separately. Typically, a contraindication for scanning involves a weight limit of 150 kilograms. But here everything depends on the specific model of the equipment itself. There are some variations where the weight limit is reduced to 120 kilograms.
Preparing to Scan
A referral for a CT scan is issued, depending on the expected pathology and symptoms (by a gastroenterologist, surgeon, urologist, etc.). Before performing a tomography, preliminary preparation is required - the intestines are cleared of gases, and the bladder is filled only 50 percent.
Three days before the tomography, foods and drinks that cause flatulence - cabbage, legumes, soda, etc. - are excluded from the diet. Foods that cause constipation are also excluded. Otherwise, the data may not be entirely reliable due to a full intestine. A couple of days before the CT scan, laxatives and sorbents are prescribed.
Since computed tomography of the pelvic organs is performed on an empty stomach, food and water intake is stopped 8 hours before the procedure. 60 minutes before the diagnosis you need to drink 500 ml of liquid. Before the examination, the patient must remove metal objects and implants. To avoid allergic reactions, a test is done to determine the body's absorption of iodine. If there is hyperkinesis, then the examination is done under short-term anesthesia.
How is the procedure done?
The examination procedure using a tomograph takes place in a special room where the device is located. Before sitting on the couch, the patient must remove all metal objects. During a pelvic CT scan, the patient should lie still while the machine takes pictures. The specialist will inform the patient that they should hold their breath and not move for approximately 10-15 seconds while the organs are being scanned. The entire procedure lasts 20 minutes, with the patient lying on a special table that slides into the ring of the device. Throughout the entire time, the laboratory assistant will be in the next room, but you can communicate with him via speakerphone.
CT scan of the pelvic organs with contrast
CT scan of the pelvic organs with contrast is prescribed for the diagnosis of cancer. Typically, the contrast agent is administered intravenously or orally. The drug is safe and is eliminated from the body within one and a half days. If a CT scan of the abdominal cavity and pelvis is performed with the introduction of contrast, it is possible to view the arteries and veins that lead to the organs. In addition, the use of contrast will allow specialists to detect inflammatory processes and other pathological changes. It is very important before conducting diagnostics with the introduction of a contrast agent to consult a doctor and determine possible individual intolerance to the drug.
Carrying out a CT scan
The patient is placed on the tomograph bed. After turning it on, the table slides into the tunnel of the device. A ring equipped with multiple sensors begins to rotate around the patient. They pick up signals reflected from tissues and send them to a computer. The tomograph is equipped with a microphone through which the patient communicates with the diagnostician.
He may ask you to hold your breath for a few seconds. The main rule is that the patient must lie still while the tomograph is operating, otherwise the images will be blurry and the procedure will need to be repeated. During the scan, the person does not feel any discomfort or pain. However, some people may find crackling and buzzing noises annoying. Duration of CT scan is up to 30 minutes.
Carrying out CT with contrast agents
With the use of dyes, the examination time increases to an hour. During this time, the circulatory system is additionally assessed, and, if necessary, pathological foci and tumors are studied in more detail. In general, CT scanning of the pelvic area does not differ from the standard method, only before scanning the patient is injected with an iodine-based substance.
It quickly spreads throughout the vascular system, which helps detect many pathologies at an early stage. In places of malignant tumors and metastases, contrast accumulates, which indicates cancer. The concentration of the dye occurs due to greater blood flow to the affected areas. CT scanning with contrast is prohibited for people whose kidneys cannot quickly remove the substance.
Indications and contraindications
The main advantage of choosing this method is the ability to quickly and accurately diagnose. With its use, it is possible to detect and identify most known pathologies at the initial stages of development, as well as clarify the boundaries of tumor formation, detect cancer at an early stage, which significantly increases the chances of saving the patient’s life.
A referral for MRI or MSCT of the pelvis is prescribed by a urologist, gynecologist, surgeon or oncologist. There are many indications for such procedures. The first method of research helps diagnose inflammatory and infectious processes in women, pathologies of the uterus, appendages and ovaries, and determine the causes of pain of unknown etiology. In men, confirm suspicions of a tumor of the pelvic bones and prostate gland.
MSCT is indicated for women in the following cases:
- diagnosing pelvic inflammation;
- clarification of the degree of damage in case of injuries;
- identification of pathological conditions of the urethral fistula;
- detection of tumors in the uterus and ovaries;
- determination of the stage of development of oncological processes.
MSCT of the pelvis is indicated for men if necessary:
- diagnosis of prostatitis and abscesses;
- visual assessment of the degree of organ damage due to injuries;
- clarification of pain of unknown etiology;
- detection of bone metastases;
- determining the stage of oncology;
- dynamic study of rectal cancer therapy.
The procedure is not performed during pregnancy, if the patient is in a serious condition requiring intensive care, or if there is severe pain that will not allow the patient to remain motionless for a long time during the scan. MSCT cannot be performed if a person weighs more than 120 kg. Examination with contrast is contraindicated for those who are allergic to iodine preparations or have kidney failure, since the contrast will not be able to be cleared from the body.
Side effects
Side effects from CT scans of the pelvis are extremely rare. Mostly negative sensations appear after the administration of contrast. There may be a slight itching and a salty or metallic taste. Some people experience nausea and dizziness during the scan as the scanner ring moves around the body.
During or after the procedure, an increase in blood pressure is sometimes observed. All of these side effects are normal and go away on their own within a day. To speed up the removal of contrast from the body, it is recommended to drink as much fluid as possible after the examination.
Carrying out MSCT
The patient is escorted to the diagnostic table and placed with his head facing the device. The doctor presses a button and sends the person inside the tomograph. There he must lie motionless during the entire procedure. It takes no more than fifteen minutes.
When scanning occurs, the tomograph ring rotates around the examination table and makes a slight noise. It can cause some discomfort, so the patient is first asked to put on headphones. The doctor is in the next room, but the patient can maintain contact with him and report changes in his health.
MSCT with contrast takes place in three stages:
- First, a regular native scan is performed. It helps to make a primary analysis of the clinical picture.
- Then a contrast agent is injected into the patient through a vein, and after 15-20 seconds a second scan is performed. It allows you to evaluate the vascularization of pathological organs.
- The third scan is taken another five minutes after the contrast is administered. At this time, iodine preparations are maximally absorbed by the tumor, so it is possible to better determine the boundaries of the tumor.
If necessary, MSCT is supplemented by ultrasound, colposcopy, ureterocystoscopy and hysteroscopy.
Decoding the results
The results are deciphered immediately and given to the patient within half an hour. The certificate is certified by the doctor’s signature and seal. When decoding, the normal parameters of all scanned organs and systems are taken into account. Particular attention is paid to accumulations of contrast material, the size and distribution of pathological foci.
The images clearly show tumors, polyps, cysts, and various damage to the walls of organs and blood vessels. When metastases are detected, it is checked whether they have spread to other organs. Using a CT scan, you can detect the causes of pelvic pain if other methods have not been able to determine this.
How do they do it?
During the examination, it is advisable to wear loose clothing that does not have metal parts. Before scanning begins, the patient is positioned on the rigid table of the tomograph. Since the procedure requires complete immobility, the body is secured with straps.
A contrast agent is injected into a vein using a catheter. This can be done either once or in doses throughout the examination.
During the procedure, staff watches the person through a window from an adjacent room. There is also a two-way speaker in the room for communication.
After activating the device, the person enters the scanning ring. When it rotates, X-rays are passed through the body. Children and everyone who wants to wear special headphones, as humming, clicking and crackling noises can be heard during the procedure.
The examination time ranges from 10 minutes to half an hour. It is completed after receiving clear images. If a person becomes unwell during the study, it will be suspended until his condition improves.
As a rule, MSCT of the pelvis does not cause any discomfort.
Cost of CT and its alternative
The cost of a pelvic computed tomography depends on the region, the chosen clinic, its location, the choice of scanning method, and equipment. For example, a simple CT scan in Moscow costs from 3,000 rubles, with contrast – up to 14,000 rubles. The price may be slightly higher if those in the abdominal cavity are examined simultaneously with the pelvic organs.
Alternative methods include ultrasound. However, such an examination cannot provide a complete picture, and the image is much lower in quality and information content. MRI is also an alternative method. Sometimes it can provide more information than a CT scan because the images are obtained from different angles. The best option is to conduct two diagnostics at once; they complement each other perfectly.
CT scan of the pelvis is a safe and highly informative procedure. However, despite the minimal radiation exposure received, frequent examinations are not recommended. The optimal interval between examinations is one year. If there is a need for a CT scan earlier, then a repeat tomography is prescribed after 6 months. Until this time, alternative diagnostic methods are used.
- Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages. How does it go and what will it show?
- Prostate MRI. How does the research work and what will it reveal?
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Ultrasound of the prostate gland. Features of the procedure…
- MRI of the lumbosacral spine
Research results
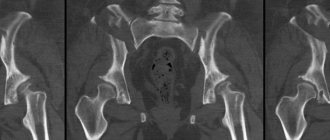
MSCT image - metastases in the pelvis
With proper preparation, the decoding of the received data will be as reliable as possible. The patient is given multi-slice photographs showing internal organs and bone joints. On them you can examine the contours of the rectum, bladder, assess the condition of the prostate gland in men, and the uterus and appendages in women. If there are inflammatory processes, mechanical damage, neoplasms, MSCT will display them.
At the patient’s request, the examination results can be presented in the form of images printed on large format film or in electronic form. The information in this case is recorded on a flash drive or disk.
For a fee, specialists can make a three-dimensional model of the pelvis. The conclusion is issued a few hours after the procedure. It will also highlight recommendations to help you understand which doctor you should see for treatment.
Angiography of pelvic vessels in women
Computed tomography with angiography of the pelvic vessels in women in the vast majority of cases is performed in connection with diseases of the reproductive system. The resulting images contain information about the characteristics of the blood supply to the ovaries, tubes, uterus and its cervix. In addition, the condition of the arteries of the rectum and bladder, and iliac vessels is assessed. The procedure is an extremely important point in diagnosing the causes of infertility and recurrent miscarriages.
Uterine arteries on CT angiography
Thanks to angiography, it becomes possible to indirectly judge the benign or malignant nature of neoplasms if they are detected. Assessing the degree of vascularization of a tumor is an important criterion for choosing tactics for its treatment and can significantly influence whether all internal female genital organs will be removed, only part of them, or whether they will be preserved.
Preparation
There is such a thing as preparation for a pelvic CT scan: the results of the study depend on how the basic rules and recommendations were followed.
The examination is best done on an empty stomach. Women need to undergo a CT scan with a full bladder, for which it is recommended to drink 0.5-0.8 liters of liquid before the examination.
Since gases in the intestines impair visualization, two days (minimum) before the examination it is necessary to exclude foods from the diet that are rich in fiber and contribute to increased gas formation - brown bread, cabbage, fried and fatty foods, legumes, raw fruits and vegetables. If necessary, you can take anti-bloating agents - espumisan or another drug in this category.
Meaning of the results
Immediately after a CT scan of the arteries, a radiologist will examine the resulting image in detail. Based on these results, he will draw up a description and conclusion; he should not make any decisions regarding treatment. The patient receives the results of the study on electronic media, and this data can also be sent to him by e-mail. With this conclusion, he turns to the treating doctor to establish a further treatment strategy or refute the diagnosis.
Complications after CT
Some people do not agree to the tomography procedure because it is harmful. But you need to know that:
- A pelvic CT scan is considered a safe procedure, although it does involve x-ray training. The radiation dose with this method is microscopic and not dangerous, so it allows the CT procedure to be performed repeatedly. To prevent unnecessary radiation exposure, doctors recommend (if possible) spacing repeat scans at 3-4 weeks.
- Complications after tomography are unknown. The only point of danger may be an allergy to iodine. However, to prevent this problem, the doctor collects information about all allergic manifestations of the patient. And minor discomfort (nausea, metallic taste in the mouth, high blood pressure) goes away quite quickly and does not pose any threat.
Computed tomography is becoming an increasingly popular research method. For many women, it was CT that really helped to identify the changes that had begun in the pelvic organs. Early diagnosis of even the most serious disease gives a chance to overcome it, giving a woman a long and happy life.
CT venography of the pelvis
Special attention is paid to such a study of the pelvic area as venography. Pelvic venography is a study of the veins of the pelvis using a computer scan. This method differs from previous ones in its invasiveness and the use of a contrast agent. In this case, contrast is injected into the thigh area, femoral, dorsal veins, penile vein, inguinal vein, or intraosseous into the bone marrow. The substance is administered through a special catheter under local anesthesia. The most important indication for the use of this research method is venous congestion in the pelvic area and all the negative consequences associated with this - varicose veins in this area, thrombus formation, etc. This procedure does not pose a danger to the human body even 3-4 hours after After the examination is completed, the patient is sent home.
CT angiography images of the pelvis
The vessels of the pelvic organs on contrast-enhanced CT images appear as branching structures with clear contours. If pathologies are present, they may have local narrowings, additional branches, or, conversely, the necessary branches of the arteries will not be visualized.
Stenoses in the pelvic arteries identified by CT (indicated by arrows)
At the MAGNIT medical center, CT angiography of the pelvis is performed using modern equipment by highly qualified specialists. To make an appointment, leave a request on the website or call +7 (812) 407-32-31.