When is the procedure performed?
This safe examination method is prescribed for adults and children. Used to detect brain diseases and injuries. Echoencephalography is performed for the following complaints:
- frequent headaches;
- nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief and is not associated with food intake;
- dizziness;
- periodic loss of consciousness;
- disturbance in movements, gait like that of a drunk;
This procedure is performed on people who hit their heads hard after accidents. Using the diagnostic method, doctors look at the condition of the brain, find hemorrhages, crushes and bruises. And then they decide on treatment methods.
Diseases for which ECHO EG is performed: focal accumulation of pus, abscess, brain tumor, hemorrhage in the nervous system and inside the skull, swelling and enlargement of the brain, foci of tuberculosis, dropsy, cerebral infarction, inflammation, to assess the effectiveness of treatment procedures.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for the procedure are a combination of alarming symptoms, which indicates disorders of the brain:
- Recurrent or chronic headache. Cephalgia, not relieved by analgesics.
- General cerebral signs: dizziness, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, sleep disturbance, chronic fatigue.
- Suspicion of a tumor, increased intracranial pressure.
- Traumatic brain injuries: skull fractures, brain contusions, fracture-dislocations of the cervical spine.
- Vascular accidents: subarachnoid hemorrhage, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
- Congenital malformations in children.
- Mental retardation, hydrocephalus, cerebral palsy.
- Inflammatory and purulent diseases of the brain, for example, encephalitis, meningitis or tuberculosis.
- Neurotic and mental disorders: schizophrenia, obsessional syndrome.
- Syndromes accompanied by behavioral disorders in children: hyperactivity, excitability, autism.
- Decreased memory, concentration, thinking: forgetfulness, absent-mindedness.
Child examination
This examination method is safe; children have thin bones through which ultrasound passes better; echo-EG equipment is widely used in pediatrics. With the help of echoencephalography, the doctor receives more data than when used in adults .
Carrying out the procedure:
- The sensor of this device is pressed in turn on the sides of the child’s head, the result is assessed by the time during which the ultrasound wave from the device travels to the organs, is reflected from them, and an image of this organ appears on the screen.
- It is done in one-dimensional M-mode, when a graph appears on the screen in which doctors determine the places where brain tissue is normal. And in two-dimensional ultrasound scanning, the image is displayed on the screen.
- In this study, the doctor looks to see if the echo ripple curve increases. The larger the range of fluctuations, the faster the curve increases. This shows that intracranial pressure is increased.
M-echo is more informative . This is the process of reflection of ultrasonic waves from the conditional midline, which divides the head into the right and left parts. If this strip is displaced, then the midline structures of the brain are deformed. This indicates its asymmetrical position.
If it is in the center, then everything is in order. Normally, this displacement is up to 1 mm.
In addition to the above-described median complex, the ventricular index has diagnostic significance. Its norm is 1.8-1.9. It shows how severe the dropsy of the brain is.
Advantages and disadvantages of this study
Like any study, echoEG has advantages and disadvantages. This method appeared a long time ago, therefore, according to some doctors, it is somewhat outdated. This is due to the large number of new devices for studying the brain, which give a clearer picture of pathological processes. For example, magnetic resonance imaging allows you to see tissue layer by layer and identify the slightest formations. Nevertheless, echoencephalography remains a common diagnostic method, as it has its advantages. First of all, this method is safe. Therefore, it is often prescribed to children and pregnant women. It also does not require large expenses, special training and time. Ultrasound examination can exclude many brain diseases.
What does the procedure diagnose?
Often using this method, finding tumors and the location where they are located. Also hydrocephalus, inflammation, hemorrhage and brain injury. Determined using the same median complex. Since the M-echo must be in the center, the distance to it is measured from both sides of the brain. In adults it is 65-80 mm, the same on both sides with a difference of up to 2 mm.
When formed in the brain, the gap to the median complex increases on the affected side and decreases on the normal side.
On the line of the median complex there is the third ventricle and the pineal body. This means that with a volumetric formation in one of the halves of the brain, these structures shift towards the healthy hemisphere. If the displacement is pronounced, doctors think about malignant formations .
Displacement also occurs with hemorrhages. If it is more than 4-8 mm and gradually increases, a neurosurgical operation is performed. When the displacement is about 3 mm, this indicates the most likely swelling of the brain after a bruise.
This disorder goes away on its own within a few days and does not require surgical intervention. To clarify the diagnosis, electroencephalography can be performed together with ECHO EG.
Pros and cons of EEG
The electroencephalography technique occupies a leading place in the list of methods for assessing the work of the brain. The procedure is available in almost any outpatient clinic, is low-cost compared to magnetic resonance and computed tomography, and takes no more than 15-20 minutes.
EEG allows us to identify the very initial stages of pathological processes in brain tissue. The method is safe, harmless, has no effect on ability to work, and does not require special preparation for the study.
Another positive aspect of the technique is the possibility of performing it on patients in a coma or in serious condition. The procedure is painless, EEG can be performed on both adults and children, even infants.
A relative disadvantage of EEG is the need to remain motionless during the study, but this requirement is generally applicable to many studies in neurology.
When you contact a neurologist with complaints of epileptic seizures, and after performing an EEG, you may not find signs of epilepsy on the encephalogram. Indicators that appear on the encephalogram are not observed in all patients, but only during convulsive seizures. There are cases when signs of epilepsy can be noted on the encephalogram without clinical signs - in the complete absence of seizures. In these cases, it is necessary to further examine the patient using other methods.
Hemorrhage inside the brain
If there have been no head injuries, the cause of hemorrhage can be arterial hypertension, which is when perforating arteries in the head rupture. There may be other reasons: atherosclerosis, inflammation of blood vessels, various blood diseases, and more.
In case of intracerebral hemorrhage, it is necessary to do a computed tomography of the brain. Ecoencephalography can also help; under its influence, an active shift in the M-echo is observed. In the damaged hemisphere, significant echo signals can be heard.
Additional diagnostic methods
We list additional ways to recognize various brain diseases:
- X-ray
Doctors usually send the patient for an x-ray to confirm or refute the diagnosis. If the disease affects the child, then craniography is performed, while the body receives minimal radiation exposure, because of this the negative impact on the body is minimized.
But in order to send a child for an x-ray, there must be important reasons for this. This will allow us to identify various pathologies, microcephaly, possible injuries during childbirth, concussions, and more.
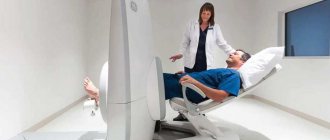
- CT scan
Includes instrumental examination of various parts of the body, the brain; computed tomography is based on examination using x-rays. Patients are prescribed a CT scan when there is a suspicion of a tumor in the brain, with increased intracranial pressure, head injuries, etc. At the same time, the level of radiation is minimal, so this method is safe for the child’s body.
There are contraindications: impaired kidney function and allergy to iodine. CT scans are performed on children under general anesthesia; this is necessary to ensure that the child is completely immobilized.
- Magnetic resonance imaging
This method works from a magnetic field. This is precisely the difference between an X-ray and an MRI, when in the first case the body receives radiation, while in an MRI it does not. This is a completely safe and painless method that is suitable even for babies.
Magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed for the following: sleep disturbance, severe headaches, abnormal behavior, developmental delay, speech impairment. In rare cases. To make an accurate diagnosis, an additional contrast agent may be administered.
- Duplex scanning
In this case, the arteries of the brain are examined, blood pressure and the condition of the blood vessels are determined. Duplex scanning can be prescribed for: developmental problems, speech disorders, injuries during childbirth, etc. In addition, in some cases, neurosonography is prescribed along with duplex scanning.
- Neurosonogram
In this case, a study is carried out using ultrasonic waves that cannot be felt by humans. A neurosonogram is performed through a fontanel that has not yet healed; usually the head is in this state in children under one year of age. When the bones become stronger, ultrasound will not be able to penetrate the brain.
This study is prescribed if hypoxia occurs during birth due to head injuries and suspected infection. This procedure differs from the studies described above; it is always possible to determine the patient’s condition and note the dynamics. A neurosonogram is absolutely safe and painless, and can be performed on small children even several times .
Several specialists can refer a child for examination: a neurologist, a traumatologist, a neurosurgeon.
Features of ECHO brain
The interpretation of the results largely depends on the experience of the doctor interpreting the data obtained. Often the opinion of the diagnostician and the opinion of the treating neurologist are strikingly different. This is the peculiarity of the ECHO head.
- After receiving the results, the patient should be examined by a neurologist and prescribed appropriate treatment. In some cases, the neurologist himself performs an echo on patients.
- With a properly configured device, skillful regulation of the length and frequency of ultrasound waves, echoencephalography reveals any damage and injury to the brain.
Procedure modes
Transmission
Two U3 sensors are installed on your head on the same axis so that they are on the same line. The first sensor scatters the signal, and the second sensor’s task is to catch the reflected impulses. In this way you can recognize the “midline of the head.” It is approximately located near the anatomical midline.
If you have damaged the soft tissues of your head, suffered bruises or other injuries, this may be an accumulation of blood under the periosteum or in the skull area, this will not be a problem.
Emission mode
This time, only one sensor is needed; it is placed on special places on the head, these places are easily penetrated for ultrasound. It happens that you have to move it a little, thereby you can adjust the sensor signal and produce the best image.
Double echoencephalography can only be obtained if you smoothly move the sensor over a person’s head. At this moment, the doctor can see on the monitor a clear horizontal slice of the brain as the sensor advances; it allows the brain to be scanned.
This method is not very accurate, since moving the U3 sensor contributes to the appearance of artifacts. If you need an accurate image for subtle brain disorders, you don’t need to go to U3, it’s better to do an MRI to get a good result.
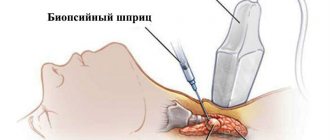
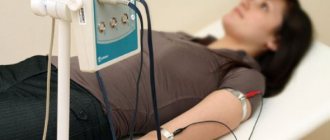
How is ECHO-EG of the brain performed?
Echoencephaloscopy of the brain is performed mainly with the patient in a horizontal position. During the examination, the head is motionless, so when conducting an examination in young children, parental assistance is required.
During the procedure, a contact gel is applied to the scalp, which increases the accuracy of the study, after which plates are installed.
Depending on the type of diagnosis, the doctor smoothly moves the sensors over the head. The whole procedure lasts no more than 10-15 minutes.
In M mode
Echoencephalography in M-mode or one-dimensional is one of the quick and accessible ways to obtain the necessary information about the state of the brain and identify possible diseases and abnormalities.
Using this method, the state of intracranial pressure is assessed, the size of tumors and the degree of displacement of structures are determined.
When conducting a one-dimensional Echo EG, sensors are installed above the external auditory canal, at the temple above the brow arch, 4-5 cm behind the ear vertical.
What does the diagnostic result look like? In the form of a graph of signals received from the inside of the head.
The one-dimensional method does not allow reliably diagnosing pathological processes. Often after Echo EG in M-mode, CT or MRI is prescribed.
Two-dimensional echoencephalography method
The 2D method, or ultrasound scan, uses a single transducer that is placed in an area that allows ultrasound waves to easily penetrate the bones of the skull.
To produce a clear image, the sensor is moved in different directions during the procedure. As a result, a flat picture appears on the monitor.
One of the varieties of two-dimensional echo EG is neurosonography - an ultrasound examination of the brain in children through the fontanel.
Meningoencephalitis
This disease can be contracted if you are exposed to a virus, bacteria or protozoan organism. When a patient is diagnosed with such a pathology, the protective membranes and substance in the center of the nervous system become inflamed.
A person experiences symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, severe headache, chills, and the body temperature rises and the person begins to become delirious.
Patients who are infected with this infection experience severe inflammation of the M-echo. If the inflamed area exceeds 7-8 millimeters, this is a direct indicator of a brain abscess. The acute form is characterized by the accumulation of a large amount of pus in the central nervous system.
Indications for echoencephalography
This study is quite informative, as it allows us to identify a wide range of neurological pathologies. Echoencephalography of the brain is one of the imaging methods based on the ability to perceive ultrasonic waves. Both neurologists and general practitioners can prescribe this study. Indications for an EchoEG are patient complaints that may indicate brain pathologies. The most common reason for undergoing the procedure is headache. In some cases, this symptom rarely bothers the patient and appears only during mental stress or changes in weather conditions. In others, pain haunts a person constantly, preventing him from working and resting. In both cases, an echoEG should be performed, since even the rare appearance of symptoms sometimes indicates severe brain pathology. Other indications for ultrasound examination of the head are sleep disturbances, memory disturbances, tinnitus, and head contusions.
Dropsy (hydrocephalus)
This disease begins due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull. Why does it accumulate:
- cerebrospinal fluid is produced too quickly;
- fluid circulation is impaired;
- absorption deteriorates.
What symptoms appear in newborns:
- the head grows too quickly;
- eyes go down;
- the fontanel swells greatly;
- on the head, where the bones have not yet fused, there are pulsating, round-shaped swellings.
If you check the center of the nervous system during this illness, then the M-echo breaks into 2 parts. The distance level will be approximately 5-6 millimeters.
If you check the echogram, you will notice a bunch of other signals that have high amplitude; they are located at a distance between the initial, middle and final complexes.
Decoding the results
The encephalogram is recorded in children according to a similar principle with adults. In order to be able to understand the specialist’s calculations, you need to find out the answers to specific questions.
If we divide echoencephalography into main signals, then there are only 3 of them:
- Starting signal . The first impulse that reaches the sensor fixed on the skin.
- The middle signal collides with brain structures that are located between the hemispheres.
- End signal . This is an impulse that comes from the opposite side of the sensor, from the dura mater of the brain, from the skull.
Echoencephalography displays 3 main additional signals that can be seen on the specialist’s screen.
Data decryption
EchoEG is based on three complexes (or bursts):
- The initial complex is formed by sound waves reflected from the dense bone tissue of the skull, skin and superficial brain structures from the side located next to the sensor.
- The average complex is obtained when ultrasound waves collide with brain structures located between the hemispheres.
- The final complex is obtained from the soft tissue and dura mater on the opposite side of the sensor.
ECHO of the head connects these signals and, based on the received impulses, reflects them on the monitor in the form of a graphic diagram. Decoding begins with data analysis:
- M-echo is a signal with the highest amplitude, occupying an average position between the two complexes. Displacement up to 5 mm is allowed. In neurological disorders, a displacement of more than 6 mm is an alarming factor requiring additional diagnostics.
- A dilated or disrupted signal received from the third ventricle indicates high intracranial pressure.
- The ripple of M-echo signals should not exceed 30-40%. If the indicators are at the level of 50-70%, then this is a clear sign of hydrocephalic syndrome.
- The SI or average sellar index is within the range of 3.9-4.1. If it is low, then this indicates high intracranial pressure. This indicator is not assessed in children.