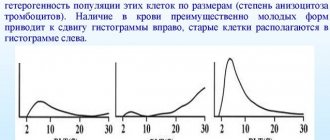
array(21) { ["catalog_code"]=> string(6) "100002" ["name"]=> string(158) "Prothrombin, International Normalized Ratio, INR" [ "period"]=> string(1) "1" ["period_max"]=> string(1) "0" ["period_unit_name"]=> string(6) "k.d." ["cito_period"]=> string(1) "3" ["cito_period_max"]=> string(1) "5" ["cito_period_unit_name"]=> string(3) "h." ["group_id"]=> string(5) "20202" ["id"]=> string(4) "1584" ["url"]=> string(106) "prothrombin-prothrombin—mezhdunarodnoje-normalizovannoje-otnoshenije- international-normalized-ratio_100002" ["podgotovka"]=> string(619) "Blood collection is carried out on an empty stomach (at least 8 and no more than 14 hours of fasting). You can drink water without gas. If the study is prescribed while taking medications that affect blood clotting, this must be noted in the referral.
Restrictions on taking biomaterial
" ["opisanie"]=> string(4732) "
Research method:
clotting (prothrombin according to Quick)
Prothrombin (according to Quick) is a test that reflects the state of the external coagulation pathway (activity of prothrombin complex factors). According to the international nomenclature, prothrombin is the II factor of the blood coagulation system, a precursor of thrombin. The test is based on the determination of prothrombin time.
The result of the study can be presented in various forms: prothrombin time, prothrombin according to Quick and INR. Presentation of the result in the form of INR (International Normalized Ratio) is currently recommended. The INR test is recommended by the WHO expert committee, the International Committee on Thrombosis and Hemostasis and the International Committee for Standardization in Hematology.
INR = POMICH
MICH - international thromboplastin sensitivity index (the value is indicated in the reagent data sheet); PO - prothrombin ratio (the ratio of the values of the prothrombin time of the subject and the prothrombin time of the control normal plasma).
What is prothrombin
Prothrombin - what is this indicator in blood tests and why monitor it
This is one of the plasma proteins involved in the blood clotting process and is called factor II. It got its main name thanks to thrombin, an enzyme of which it is a precursor.
When the volume of prothrombin corresponds to the physiological norm, dangerous blood clots do not form in the blood vessels, and minor bleeding stops naturally. The “factory” that produces this important protein is the liver, where its production is carried out with the direct participation of vitamin K.
In what tests can this protein be tracked?
The prothrombin level is assessed as part of a special blood test - a coagulogram, which is also called hemostasiography. It allows you to check the functionality of various elements of the hemostasis (coagulation) system, including the thrombin precursor. Information about the amount of this protein is indicated in the coagulogram (hemostasiogram) form by several points:
- PTI (prothrombin index). It is indicated as a percentage and means the ratio between the real clotting time of a particular blood sample and the standard indicator;
- PO (prothrombin ratio) - the reciprocal of PTI, also indicated as a percentage;
- INR (international normalized ratio), percentage;
- PTT (prothrombin time). Indicates the time period during which blood clotting occurs. The unit of measurement is seconds;
- prothrombin according to Quick, indicated as a percentage.
Doctors prescribe coagulation tests when required:
- check the functionality of the hemostatic system, including on the eve of pregnancy, childbirth or surgery;
- find out the cause of prolonged bleeding or pathological formation of blood clots;
- find out why the liver began to work worse;
- assess coagulability directly during treatment with blood thinning drugs, as well as after;
- clarify the cause of the development of antiphospholipid syndrome;
- identify diseases that cause vitamin K deficiency.
There are also indirect reasons to check prothrombin levels. One of these is changes in hormonal levels. It has been noted that the level of coagulation protein increases in women over 45 years of age, against the background of age-related hormonal changes.
In addition, coagulographic tests for prothrombin are included in the list of mandatory studies during pregnancy. Expectant mothers undergo such tests three times:
- when they become registered;
- at 22–24 weeks;
- at 30–36 weeks.
Unscheduled checks of hemostasis characteristics may be prescribed when:
- pregnancy was preceded by a long period of infertility;
- there have been miscarriages and premature births in the past;
- complications were identified (delays in fetal development, gestosis, etc.);
- signs of varicose veins are noticeable on the legs of the expectant mother;
- there is a tendency to bruises after minor injuries, as well as blood on the gums while brushing your teeth;
- pregnant woman smokes.
It is not only the gynecologist who prescribes a coagulogram. Depending on who the person contacted with symptoms of hemostasis impairment, this can be done by:
- therapist and pediatrician;
- traumatologist and cardiologist;
- pulmonologist and surgeon;
- other specialists.
Prothrombin tests can be performed in both public and private clinical laboratories that have the equipment to perform such an analysis. Coagulation takes less than an hour, but depending on the workload of the laboratory, the deadline for issuing results is sometimes postponed to the next day.
If PTI is higher than normal
An overestimated PTI indicator when interpreting the results of the study indicates an excessive rate of blood thickening. This deviation is also dangerous for health, as it indicates various diseases and pathologies.
In exceptional cases, deficiency syndrome of plasma constituent substances, which interferes with the normal process of blood clot formation, is genetically determined. In other cases, an increased level of PTI indicates the following conditions in the body:
- Increased platelet count in the blood.
- Thrombosis of the primary type, when blood clots block the deep veins of the extremities.
- Formation of malignant tumors.
- Side effects of certain medications, including steroid medications and oral contraceptives.
- Pathologies in the area of the heart and blood vessels. This is due to a slowdown in the blood circulation process, since thick blood cannot move quickly through the veins.
Prothrombin according to Quick, INR and other indicators: what do they mean
These coagulographic tests were mentioned above, but they deserve closer attention.
- Prothrombin according to Quick. The method provides information on the volume of this protein as a percentage relative to the physiologically acceptable amount. It has been noticed that the analysis is more accurate with low digital values.
- Prothrombin index. It coincides with the figure of the previous test, when the result is within the normal range. In general, it is believed that the result partly depends on the sensitivity of the plasma to the laboratory reagents used.
- Prothrombin time. It is determined after adding special reagents to the plasma. The result also depends on the age factor - in children, coagulation occurs a little slower than in adults.
- The international normalized ratio (INR) is considered complementary and is often used by physicians specifically to monitor the results of anticoagulant therapy.
A complete coagulogram also contains other indicators.
How fast is prothrombin time?
In order to determine prothrombin time, they use the very old, but reliable and simple Quick method, which was first proposed back in 1935. To do this, the patient’s blood plasma is taken and thromboplastin is added to it, which imitates platelet activity. This thromboplastin is generic, taken from 5 healthy donors with normal blood clotting.
After this, everything is heated in a water bath, and then calcium chloride is added and shaken. It is known that the presence of calcium is a very important factor in the reliable operation of the hemostasis system, and with its deficiency, blood coagulation significantly worsens. After shaking, the blood coagulates, and this process takes literally a few seconds. As a result, fibrin threads fall out. Accordingly, the faster they appear, the more active the prothrombin.
Decoding PTI in a biochemical blood test is very simple. In order to calculate the prothrombin index, the normal indicator of donor blood (in seconds) is put in the numerator of the fraction, and the clotting time of the blood being tested is put in the denominator. In a healthy person, the prothrombin time required to form a stable blood clot usually ranges from 12 to 15 seconds. And the prothrombin index in a healthy person, accordingly, can be from 78 to 142%.
You can find a more detailed description in our article Prothrombin time.
Since even an experienced laboratory technician sometimes finds it quite difficult to decipher prothrombin time indicators with an accuracy of up to a second, even with a chronometer in hand, modern laboratories use special analyzers that very accurately mark the moment of fibrin formation by changes in the spectrum and optical density at the moment of transition from solution to clot. Now everyone understands what PTI analysis is. What are the indications for this study?
How the analysis is carried out: requirements before passing, progress and interpretation of the results
Preparation for donating blood includes a standard set of rules:
- Do not have breakfast on the day of the test. The previous meal is allowed no earlier than 8–9 hours before the visit to the clinic.
- drinking is allowed, but only clean water;
- per day, fatty, spicy and salty foods, as well as alcohol, are excluded from the diet;
- one hour before the test you should not smoke;
- You should stop taking medications within two days, especially those that affect blood composition. If it is impossible to refuse some medications for health reasons, you must inform your doctor in advance.
What does an increased indicator mean?
Prothrombin - what is this indicator in blood tests and why monitor it? Elevated indicators require immediate treatment of identified pathologies or correction of previously prescribed drug therapy
Figures indicating an excess of prothrombin indicate a tendency to pathological formation of blood clots and can be explained by various reasons. One of them is a mutation in the prothrombin gene. Among the others:
- disseminated intravascular coagulation;
- oncological processes;
- polycythaemic disease is a benign change affecting the blood system;
- excess vitamin K, which is involved in the production of prothrombin;
- increasing angina pectoris;
- liver diseases;
- the presence of a blood clot;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- other conditions.
An increased amount of protein detected by the Quick method may indicate kidney disease, so it is recommended to undergo appropriate examination.
In addition to pathologies, the following factors can stimulate an increase in prothrombin complex values:
- uncontrolled use of laxatives and antibacterial drugs, anabolic steroids and hormonal contraceptives;
- transfusion of significant volumes of blood;
- last weeks of pregnancy;
- hyperglobulinemia or vasculitis;
- other.
How to reduce
First you need to figure out where the increase came from. If the problem is pathology, it is recommended to focus on its treatment. In this case, as after the end of pregnancy, prothrombin is normalized naturally.
Regarding medicinal causes, it is better to rely on your doctor's opinion. If he considers that discontinuation or regular use of the drug will normalize prothrombin levels, this will probably be the case. If anticoagulants are prescribed, they must be taken in strict accordance with the prescribed dosage.
In simple cases, prothrombin can be reduced using diet. To do this you will have to limit your consumption:
- fatty, fried and smoked meat;
- potatoes and bananas;
- sweets and baked goods;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks, as well as coffee.
What does a low score mean?
Prothrombin - what is this indicator in blood tests and why should it be monitored? A low indicator poses the greatest threat to pregnant women and those preparing for surgery
When immunity decreases due to diseases that occur with the development of antiphospholipid syndrome, various antibodies to prothrombin are detected in the blood. They, depending on the type, can increase or decrease prothrombin levels.
Other reasons for decreased protein levels include:
- liver failure;
- intestinal pathologies that make it difficult for vitamin K to enter the bloodstream;
- general deficiency of proteins in the blood, and in particular fibrinogen;
- decreased production of vitamin K due to problems with intestinal microflora.
Decreased prothrombin test results are no less a cause for concern than elevated ones. If in the second case the danger to life is expressed in the possible blockage of blood vessels, then in the first - in large-scale bleeding, for example, after childbirth or surgery.
Treatment of low prothrombin
As in the case of an increase, the cause pathology should be identified and treated. If coagulants are needed - drugs that increase blood clotting ability, the doctor will certainly prescribe them and tell you how to take them.
The easiest way to increase prothrombin is to enrich the diet:
- baked goods and fatty meats;
- pickles and smoked foods;
- legumes and greens.
However, you should not abuse such food, so as not to provoke the opposite violation of hemostasis.
Prothrombin plays an important role in ensuring hemostasis. Not only health, but also life depends on how well its level corresponds to the norm. To avoid any cause for concern, you should eat right, avoid stress, bad habits, and periodically donate blood for a coagulogram.
Diseases
There is an extensive list of diseases, a symptom of which may be a change in the prothrombin index. The following diseases lead to a reduction in blood clotting time :
- DIC syndrome;
- Hyperfunction of the spleen;
- Lack of water in the body;
- Consequences of radiation sickness;
- Acidosis (acidification);
- Metabolic disorders, especially carbohydrates.
To increase time:
- von Willebrand's disease;
- Hemophilia;
- Lack of folic acid;
- Lupus;
- Severe kidney disease.
- To accurately establish a diagnosis, sometimes it is necessary to conduct a number of studies, so you should not make a conclusion based on changes in PTI alone. Remember that a false diagnosis and treatment of a non-existent disease can cost not only time and money, but also life.