Hysteroresectoscopy of a polyp: postoperative management
As is known, there is a division into the early and late postoperative period, and depending on this, the tactics of its management also differ.
When hysteroresectoscopy has already been completed, recovery after surgery during this period does not take long, since this period lasts only until discharge.
Services table
| Service name | Price |
| Initial consultation with a gynecologist | 2,300 rub. |
| Ultrasound gynecological expert | RUB 3,080 |
| Insertion of an intrauterine contraceptive device | 4,500 rub. |
| Hysteroscopy | RUB 22,550 |
| Repeated consultation with a gynecologist | 1,900 rub. |
| Taking a smear (scraping) for cytological examination | 500 rub. |
| Laparoscopy (difficulty category 1) | 61,000 rub. |
| Program "Women's Health after 40" | RUB 31,770 |
| Treatment of the cervix (medication) in 1 procedure | 800 rub. |
| Diagnostic curettage | 12,000 rub. |
Specifics of the procedure
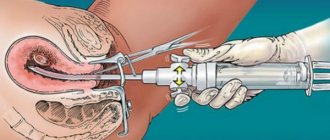
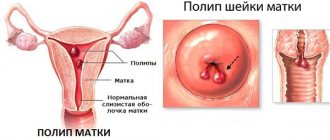
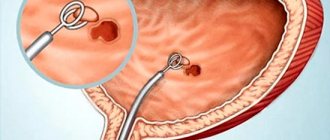
Hysteroresectoscopy is performed using a special camera (hysteroscope), which moves from the vagina into the uterine cavity. Thanks to this, the doctor can obtain the most accurate clinical picture of the condition of the tissues and the location of polypous formations. This makes it possible to adjust your actions during surgery.
The polyp is removed using instruments and requires careful scraping of the affected area of the endometrium. Then the walls of the uterus are treated with special means to eliminate relapse and the appearance of an inflammatory process.
The method has a lot of positive aspects. It is painless, does not require long-term recovery, and does not threaten the patient’s reproductive function.
Does the endometrium grow quickly after hysteroscopy surgery?
The surgical intervention is carried out in the operating room, the patient first undergoes tests and prepares for the procedure. The operation is performed by a qualified gynecologist in the presence of an anesthesiologist, assistant and nursing staff.
The patient is given an anesthetic intravenously or mask anesthesia is used. In exceptional cases, paracervical anesthesia may be used - anesthesia of the tissues of the cervical area. After anesthesia, the doctor expands the cervical canal, inserts a hysteroscope and fills the cavity with gas or solution for better visualization.
The techniques for performing gas and liquid hysteroscopy differ. Let's look at them separately.
With gas
A portion of carbon dioxide is injected into the uterine cavity, expanding the space. The doctor monitors gas pressure and the filling level of the uterus. If the gas is supplied without violating the rules, the patient does not experience complications. If gas supply rules are violated, heart failure and even death can occur.
The gas technique is not used if there are traces of bloody discharge in the cavity - this interferes with clear visualization. Also, gas is not used during surgical interventions.
Using solutions
Hysteroscopy using solutions to enlarge the uterine cavity is the most popular procedure. Saline solution, glucose, glycine or simply distilled water are used as the basis for solutions. Can there be complications after the administration of liquid solutions?
Complications are possible with any examination technique. In this case, there is a risk of postoperative infectious tissue damage. However, hysteroscopy of the uterus using solutions is considered the most gentle compared to gas.
The advantage of therapeutic hysteroresectoscopy is the ability to preserve the integrity of the uterine body while eliminating neoplasms from it. A simple operation on the uterus does not require preliminary preparation and can be performed in a gynecologist’s office. We are talking about polyps and small processes, the elimination of which is not difficult.
During a simple operation, fragments of the fertilized egg or an ingrown intrauterine device can be removed. Foreign bodies and a thin intrauterine septum are also removed in the office.
Carrying out complex operations involves a large amount of work; they are carried out using special equipment and in appropriate conditions. Sometimes preparation for a complex operation requires a course of hormone therapy. It is also practiced to combine hysteroscopy with laparoscopy.
It is very difficult to forcibly restore the original state of the endometrium, since the ability of this type of uterine cavity tissue to divide and regenerate is influenced by several factors:
- hormonal background;
- immunity;
- intake of basic nutrients and biologically active substances into the body.
In most women with standard health indicators, restoration of the endometrial layer occurs after 1-2 menstrual cycles.
Experts say that restoration of the endometrium after hysteroscopy is a purely intimate and unique matter for each patient. They prefer to intervene in the process if, a month after the intervention, ultrasound reveals insufficiently rapid tissue regeneration. This most often occurs during treatment after hysteroscopy of an endometrial polyp that is large in size and has a wide base. In this case, the wound surface is extensive and requires the use of additional measures:
- taking medications to balance hormonal levels;
- taking medications to stimulate the immune system and regenerative abilities of the body;
- taking antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent infection of postoperative wounds;
- carrying out physiotherapy, massage and so on.
A good stimulating effect is achieved by following proper nutrition and moderate physical activity. As a rule, the efforts pay off quite quickly - after 2-3 weeks the endometrium begins to recover more intensively.
Note! It is impossible to use stimulating drugs without consulting a doctor, since there is a possibility that instead of normal endometrial tissue, connective or scar tissue will grow at the site of the postoperative wound.
Better than other methods
Hysteroresectoscopy is a modern method of combating formations, significantly reducing the possibility of repeated growths and the development of infected lesions. The use of the device allows the doctor during the operation to carefully observe his actions performed on the site of the emerging formations. The ability to see everything clearly makes it easier to completely remove pathological particles and eliminates the possibility of their regrowth.
The peculiarity of the technique is the simultaneous removal of the polyp and cauterization of the source of its growth. This minimizes the risk of infection growing on the existing scar and the surrounding endometrial layer. The method is especially valuable when eliminating numerous formations. This allows you to get rid of pathologies without injuring or damaging other areas on the walls of the uterus. Hysteroresectoscopy is also prescribed for single formations. It is most effective in removing pedunculated polyps.
The operation is not abdominal and does not require a traditional incision in the peritoneum. This allows you to reduce injury to the organ, reduce the pain of the procedure and shorten the rehabilitation period. The postoperative stage takes place without additional therapeutic measures. It is enough to prescribe supportive measures to the patient.
Using the method, it is excluded:
- the appearance of adhesions;
- manifestations of severe postoperative pain;
- difficulties conceiving a child;
- development of infertility.
The method is the most gentle, preserving all reproductive functions and painless. Some painful sensations occur and discomfort is possible, but all phenomena are short-lived.
Does the endometrium grow quickly after hysteroscopy surgery?
This examination is one of the main ones for female diseases, and sometimes the only one possible. Hysteroscopy of the uterus is performed using an endoscopic instrument, which consists of the following parts:
- housings;
- telescopic camera;
- channel for inserting medical instruments;
- holes for input/output of working solution.
A hysteroscope for diagnostic examination is smaller in size compared to a surgical one. When performing surgery, the doctor may use additional medical instruments such as forceps, catheters and other devices.
An innovation in operative gynecology is the creation of an electrosurgical hysteroresectoscope. This new generation instrument performs a whole range of gynecological operations on the uterus. The monopolar hysteroresectoscope was replaced by a more advanced bipolar one.
The hysteroresectoscope consists of two parts - a telescope and a working body with a set of tools. The advantages of this device are that diagnostic hysteroscopy of the uterus can turn into surgical hysteroscopy at any time. The appearance of a resectoscope gives the right to talk about the development of such a branch in gynecology as intrauterine surgery.
With the help of new equipment, hysteroscopy may well replace laparoscopy and even hysterectomy. This is important because reducing the volume of surgical procedures may be important for patients with poor health or the elderly.
Hysteroscopy is generally very safe, but like any procedure there is a small risk of complications. The risk is higher in women who undergo treatment during hysteroscopy.
Some of the main risks associated with hysteroscopy are as follows:
- Accidental injury to the uterus - this is very rare, but may require treatment with antibiotics in hospital or, in rare cases, other surgery to repair it.
- Accidental injury to the cervix is a rare complication and the injury can usually be easily repaired.
- Excessive bleeding during or after surgery – this may occur if the treatment was carried out under general anesthesia; very rarely, the uterus may need to be removed (hysterectomy)
- Uterine infection – can cause smelly vaginal discharge, fever and heavy bleeding; it is usually treated with a short course of antibiotics.
- Feeling weak – affects 1 in every 200 women who have a hysteroscopy, done without anesthesia or with local anesthesia only.
Bleeding or infection can occur after any surgery. Sometimes the surgeon cannot complete the procedure safely due to excessive bleeding, fluid absorption, or the size of the fibroid. Complications common with hysteroscopy include uterine perforation and disproportionate fluid retention.
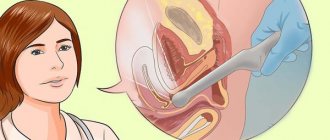
This procedure is prescribed both for diagnosing the uterine cavity and for performing surgical interventions. Diagnosis using a hysteroscope is carried out in a gynecologist’s office (diagnostic hysteroscopy). This takes a little time - no more than 25 minutes.
Anesthesia is not required for examination with a hysteroscope, but local anesthesia may sometimes be used.
Surgical hysteroscopy of the uterus is performed with a violation of the tissue layer, as it involves excision of tumors in the cavity. The surgery is performed using a hysteroresectoscope under general anesthesia in the presence of medical personnel in an equipped operating room.
Indications
In what cases is a referral for examination with a hysteroscope issued?
For diagnostic purposes, the examination is carried out to identify the following conditions:
- the presence of overgrown mucosal tissue - endometriosis;
- checking for the presence of a tumor;
- the presence of placental remains after childbirth;
- menstrual irregularities;
- uterine bleeding of unknown etiology;
- monitoring the condition of the uterus after taking hormones or surgery;
- postpartum complications;
- causes of infertility;
- habitual miscarriage.
A hysteroscope can also be used to examine the structure of the internal genital organs and identify pathological abnormalities.
Surgical hysteroscopy is prescribed in the following cases:
- fertility preservation;
- elimination of growths on the endometrium;
- ablation (destruction) of the endometrium;
- elimination of intrauterine septa or adhesions;
- removal of ingrown contraceptive coils;
- elimination of fibroids.
The examination is carried out between the fifth and seventh day of the menstrual cycle, when the cervical canal is as open as possible. It is also during this period that blood loss is minimal. Sometimes manipulation is prescribed 3-5 days before the start of menstruation, if the subject of the study is pathology of the uterine mucosa.
Contraindications
Examination with a hysteroscope is not carried out for pregnant women and for severe cancer of the reproductive organs. The ban on the procedure also applies to patients:
- with an extensive focus of inflammatory nature of the pelvic organs;
- with an acute form of a cold or infectious disease;
- with uncontrolled uterine bleeding;
- with narrowing of the uterus (stenosis);
- with impaired blood clotting function;
- with other severe pathologies of organs and systems.
The examination is also prohibited in case of severe obesity, localized inguinal hernia and the presence of postoperative adhesions.
Complete bowel cleansing is performed by patients at home or in the hospital, depending on the type of procedure. You can prepare for office hysteroscopy at home, but the procedure with elements of surgical intervention requires short-term hospitalization, and therefore cleansing is carried out in a hospital setting.
To completely empty the intestines of contents, you can use a laxative (Fortrans, Lavacol). They begin to be taken the evening before the procedure according to the instructions. In the morning, 2-3 hours before the start of hysteroscopy, you can use a microenema, for example, Microlax.
If the patient is intolerant to the active ingredients of microenemas or laxatives, use a regular cleansing enema, but provided that the woman does not have signs of intestinal obstruction. It is placed the night before and, if necessary, repeated early in the morning on the day of hysteroscopy.
At the moment, this is the most progressive method for removing uterine cavity tumors. The surgeon can monitor the progress of the resection on the monitor and control his actions. This makes it possible to completely remove the polyp without leaving a single fragment. Fragmentary particles cause the growth of a new polyp at the site of the removed one, so visual control allows you to monitor the quality of the resection performed.
Another advantage of resectoscopy is the simultaneous cauterization of the polyp site after its removal. This ensures the preservation of the injured area from the development of the inflammatory process, especially in the presence of multiple polypous formations. Also, resection and simultaneous cauterization of the pathological area preserves the adjacent unaffected endometrial tissue from infection or injury.
Resectoscopy is many times more effective than polypectomy, in particular in terms of eliminating pedunculated polypous formations. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure eliminates cutting into the abdominal cavity and organs adjacent to the uterus. This ensures a quick recovery period and minimal trauma during surgery.
The recovery period after resectoscopy is short and does not require additional therapy, as after abdominal operations. All that is required is restorative and strengthening manipulations.
Flaws
These include, first of all, possible complications:
- infection during surgery;
- injury to organs adjacent to the uterus;
- poor-quality removal of pathological tissue;
- heavy bleeding.
However, complications are largely the body's reaction to surgical procedures. This cannot be avoided with any gentle method of surgical correction.
Despite these complications, hysteroresectoscopy is considered the most progressive method of cleansing the uterine cavity from tumors.
When performing an office hysteroscopy, a woman will not need any personal items, except for a loose shirt, which she will wear during the operation. You are also allowed to bring a robe with you for this procedure. In addition, you should have a sanitary pad with you, since after hysteroscopy some spotting appears.
When undergoing hysteroresectoscopy, the woman is in a hospital, so for a comfortable stay there she will need much more things. The list of what you need to take to the department includes:
- a cotton shirt, and if preliminary hospitalization is necessary, then two;
- bathrobe and slippers;
- personal hygiene products;
- several sanitary pads.
In addition, it is important not to forget at home the medications that your doctor has prescribed to take regularly. It will not be possible to take them before hysteroscopy with anesthesia, but after the patient comes to her senses, you should take the pills as quickly as possible.
After general anesthesia (this procedure can also be done in a doctor's office with local anesthesia, but is usually limited to diagnostic purposes only), the hysteroscope is inserted into the uterus using a saline solution (NaCL) or a sugar solution (sorbitol) to stretch the uterus and provide visualization of the uterine cavity.
A local anesthetic cervical block is often performed first to provide local anesthesia. Once the examination of the uterine cavity is complete, several different instruments can be inserted through the hysteroscope to treat uterine fibroids, heavy menstrual bleeding (periods), and polyps.
Hysteroscopy will only be performed if the benefits are considered to outweigh the risks.
The uterus can also be examined using:
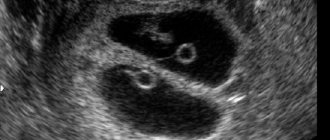
- pelvic ultrasound – where a small probe is inserted into the vagina and uses sound waves to create an image of the inside of the uterus;
- endometrial biopsy – where a narrow tube is passed through the cervix into the uterus, with suction used to remove a sample of uterine tissue.
Flaws
To understand what it is, what capabilities hysteroresectoscopy has, and in what cases it is recommended for patients, you should better understand the consequences and possible complications after its use.
The postoperative period may be characterized by the following deviations from the norm:
- the development of infections in the uterine cavity (can be caused by instruments);
- injury to organs located near the uterus;
- unsuccessful elimination of polypous formations;
- bleeding, to eliminate which abdominal surgery is used.
According to experts, almost all deviations are not associated with a violation of the technique, but are a consequence of forced intervention in the body and its vital processes. Even despite possible adverse consequences, hysteroresectoscopy is considered the safest and most harmless method for removing polyps and has many significant advantages. However, each specific case has its own nuances and, therefore, the need to perform the procedure is determined only by a specialist. He is responsible for the qualified and successful course of the operation and postoperative period.
Possible complications
After hysteroresectoscopy, a woman may experience certain complications - despite all the relative safety and the use of modern instruments and equipment, this is still a surgical intervention in the integrity of the reproductive system.
Doctors include possible complications:
- injury to the uterine cavity and cervical canal;
- infection due to non-compliance with hygiene and sanitation standards, which in turn provokes inflammation and sepsis;
- severe bleeding due to penetrating injuries of the uterine cavity and cervical canal.
If signs of bleeding and signs of infection appear - discharge with an unpleasant odor and interspersed with pus, increased body temperature and pain in the lower abdomen, chills, you should immediately visit a doctor and undergo a course of diagnosis and treatment.
Indications for use
Before operating on a patient, a set of measures, tests and examinations is provided that the doctor will need to familiarize himself with the clinical picture and condition of the patient in each specific case.
Polyps can cause severe pain and heavy bleeding in women. In cases where, when they are detected, the pain increases significantly, then there is a possibility that the patient has an additional and serious gynecological pathology. The operation is carried out only after a serious examination. It will be necessary to use all possible research methods and identify the cause of this symptom, and based on the final data, make a decision on performing hysteroresectoscopy.
Hysteroscopy and hysteroresectoscopy differences
Both of these procedures are procedures performed for the comprehensive diagnosis and complete treatment of many diseases that affect the reproductive system of a woman. What is the difference between hysteroscopy and hysteroresectoscopy? In the first case, the goal is a full and comprehensive diagnosis carried out using an endoscope, in the second case it combines both diagnosis and treatment. Hysteroresectoscopy, as we see, has more capabilities and requires special training and the use of anesthesia. Hysteroscopy takes less time, but also involves the use of local anesthesia.
About the advantages of hysteroresectoscopy on video:
Contraindications
The hysteroresectoscopy method is not recommended for everyone. The operation should be postponed if diagnosed:
- inflammation caused by infections of the reproductive system;
- inflammation detected in the uterine cavity, ovaries, tubes or vagina;
- infections not related to the reproductive system (influenza, ARVI, pneumonia);
- severe pain;
- seemingly unreasonable, intense bleeding.
An exacerbation of certain chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver or kidneys can become a serious obstacle to the operation. Exacerbation of existing pathologies is considered individually and in each specific case the decision is made by the doctor.
Polyps cause discharge, but if they are excessive in nature, then removal will not solve the problem. It is not recommended in the presence of an adenomatous neoplasm during menopause. In this case, it is advised to amputate the uterus, since this type of polyp is a harbinger of cancer and is fraught with relapse. The feasibility of the operation is determined by the gynecologist.
What not to eat before hysteroscopy
An important part of preparing for hysteroscopy of the uterus is following a slag-free diet. It helps empty the intestines of food debris and solid contents. Such measures are necessary to ensure that intestinal loops do not compress the uterus during examinations and therapeutic procedures.
The list of what not to eat before surgery includes:
- legumes;
- all types of cabbage;
- cereals with a high content of indigestible particles;
- dark varieties of bread and bread with bran and whole grains;
- marinades, pickles, smoked meats, sausages and semi-finished products.
What equipment is used
The surgery is performed using a hysteroresectoscope (mono- or bipolar). This is a complex electronic device consisting of several systems:
- optics allows you to control and monitor the progress of the operation. This is possible because a microscopic video camera moves through the cavity and is connected to a monitor. It displays an image that helps the doctor examine the uterine cavity as accurately as possible, identify pathologies, and monitor the process of eliminating polyps;
- medical instrument - a set of electrosurgical electrodes, with the help of which removal, dissection, grinding, cauterization, and elimination of fragments of polyps from the walls of the uterus are performed. There are special attachments for laser, cryo and microwave surgery.
Methods of pain relief during hysteroresectoscopy
Hysteroresectoscopy is a full-fledged operation that requires high-quality anesthesia. Only after diagnosing the disease and the amount of work expected is one of the types of anesthesia determined:
- epidural (the patient is conscious, but there is no sensation in the lower extremities);
- general – sound sleep caused by drugs;
- intravenous (provides pain relief for 1 hour);
- endotracheal - drugs are introduced into the respiratory system. This allows the patient to get deep sleep. Used in cases where a lengthy operation is required.
Hysteroresectoscopy (where it is done)
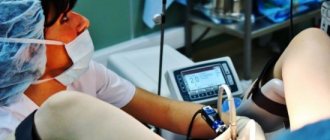
Since we have figured out what hysteroresectoscopy is in gynecology, now we will decide on the location. Since hysteroresectoscopy is a surgical intervention, it is performed in a gynecological hospital, under the supervision of medical personnel, although the patient’s stay there is not long. It is the operation itself that is performed only in an operating room.
If we talk about where to do hysteroresectoscopy, then this is a personal matter for each patient. Many factors come into play here. The choice of a gynecological clinic can be made based on the conditions of the hospital, the equipment of the department, the competence of specialists, and also, not unimportant, is the financial side of the issue.
Dates
The procedure is prescribed as planned or for urgent reasons. The planned date is determined taking into account female physiology. During menstruation, the endometrium is shed, which renews over time. During the follicular phase, the layer is thin, so the uterine cavity is perfectly visible. This occurs 7-9 days from the start of menstruation.
Emergency surgery is necessary in the presence of serious indicators, which are determined by the attending physician and prescribed on any day of the cycle. Menstruation is a reason for delay, since heavy bleeding distorts information.
Preparation
Before the operation, measures are prescribed to assess the condition and exclude the development of complications in the patient. The operation is performed strictly on an empty stomach. The patient is given an enema and the urine is removed. A list of diagnostic procedures is proposed that must be completed a week or 10 days before surgery and done:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- vaginal smear to determine the level of cleanliness;
- blood clotting test;
- fluorography;
- biochemistry analysis;
- blood group and Rh factor;
- sugar level analysis;
- analysis for sexually transmitted diseases;
- analysis for the presence of antibodies and HIV;
- colposcopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs;
- ECG.
The diagnostic results will help eliminate the possibility of complications and determine the presence of contraindications for surgery. Strict adherence to medical prescriptions that involve blocking sex hormones with hormonal drugs will be required.
It is necessary to perform hygiene measures one week before the operation. In this regard, vaginal suppositories are prescribed to sanitize the genital tract. These are combined drugs that eliminate fungi, protozoa and bacteria.
How it is carried out - stages
The procedure is simple for the woman because the patient is exposed to minimal risks. The doctor will need experience, knowledge and qualifications to work with complex equipment. As a rule, hysteroresectoscopy takes place within 20-40 minutes and involves the following steps:
- administration of anesthesia;
- expansion of the cervical canal with liquid or gas;
- insertion of a flexible tube with a video camera into the uterine cavity;
- insertion of a resectoscope - an instrument for disconnecting the polyp and healthy tissues;
- using a surgical loop or hook, the removed polyp is brought out;
- fluid or gas is removed from the uterus;
- the patient is sent to the ward;
- remote formation requires histological analysis in a special laboratory to possibly detect malignant changes.
Reviews
Despite the fact that the doctor is ready to explain to the patient in detail what hysteroscopy is and how the procedure is carried out, for greater reliability, women are looking for real reviews from those who have already decided to undergo such a manipulation.
Svetlana, 29 years old: During preparation for IVF, I was prescribed to undergo diagnostic hysteroscopy. They did it for me without anesthesia. It was a bit painful, but tolerable. But my roommate had to undergo a mini-operation, so she was first given intravenous anesthesia. It’s scary, but I’ve been through more unpleasant procedures.
Ksenia, 36 years old: I believe that for polyps, hyperplasia and severe pain during menstruation, this is simply an irreplaceable procedure. No, you, of course, can try to make the polyp fall off on its own (if it is small) with the help of drugs, but I don’t want to take that risk. Girls, don't be afraid to do hystera. It will help avoid serious complications in the future.
Alina, 28 years old: During a routine ultrasound, I was diagnosed with an endometrial polyp and was prescribed a hysteroscopy. As expected, I was terribly worried. But as it turned out, it was in vain. The operation itself is done in 10–15 minutes. Well, then you need to recover a little more after the anesthesia. They didn’t keep me in the hospital longer than I was supposed to and they sent me home the same day.
Diagnostic and therapeutic hysteroscopy is an effective procedure performed with minimal risk to the patient, which is widely used and considered the “gold standard” in gynecological practice.
What to Expect
Despite the apparent simplicity of the operation, devices that enter the uterine cavity can cause minor damage. During the first day, bleeding may appear after hysteroresectoscopy, which differ in quantity, depending on the purpose of the procedure. So during diagnosis, there is less blood, and during surgery, the discharge is more abundant and prolonged. After the operation, hemostatic drugs are prescribed.
When diagnosed, the menstrual cycle is not disrupted, whereas during surgery, the first day of menstruation is considered to be the date of the operation. To exclude negative consequences and complications during hysteroscopy, careful monitoring of the processes occurring in the body will be required. If the discharge does not stop or cease to be intense, and is accompanied by pain, then a doctor’s consultation is necessary. After surgery to remove a polyp, temporary rest from sexual activity is required. You should pay attention to the sensations during menstruation, the first after hysteroscopy.
Rehabilitation period
The patient is discharged on the second day after hysteroresectoscopy, and the recovery period continues for another 2 weeks. Do not be surprised if during this period you are bothered by pain in the uterus and scanty bleeding from the vagina. It is important to give up sexual contact for a whole month. Other restrictions are presented below:
- it is important to avoid excessive physical activity;
- it is necessary to exclude hypothermia of the body;
- you cannot take hot baths, visit the sauna, bathhouse (avoid overheating);
- Douching is prohibited;
- Visiting the pool and open water bodies is prohibited.
The patient is recommended to observe the rules of personal hygiene, replace the bath with a shower, and, if necessary, undergo a full course of drug therapy to accelerate the restoration of injured uterine tissue. Taking hormonal drugs is not excluded. Recommendations from specialists regarding the recovery period are presented below:
- you need to apply cold to the uterine area for 20 minutes three times a day;
- take a shower once a day, perform toileting of the genitals twice a day;
- use medications as prescribed by a doctor.
If hysteroresectoscopy is performed, it is important to avoid acute infections, otherwise the woman’s general condition will deteriorate sharply. Among the potential complications, doctors identify the following dangerous diseases:
- gas embolism of the uterine vessels;
- hematometra (uterine spasms with bleeding);
- perforation of the uterine wall, which urgently needs timely resuscitation measures;
- diagnosed infertility;
- infectious diseases.
Taking medications after hysteroresectoscopy
The patient is observed by the attending physician for two weeks after the operation, and the use of medication is possible. Representatives of the following pharmacological groups participate in the complex therapy scheme:
- Oral contraceptives. In 3-4 months of completing the course, endometrial tissue is restored, the disrupted menstrual cycle is normalized, and protection from unwanted pregnancy is achieved until the reproductive system organ is completely restored (Yarina, Danazol, Regulon, Premarin).
- Antibiotics. Provide prevention of bacterial infection in the postoperative period. Particularly effective in a given direction are representatives of the pharmacological group of cephalosporins with a full course of 5-7 days, for example, Ceftriaxone, Cefuroxime, Cephalexime.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drugs provide anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects in the body and act systemically. Doctors recommend Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, which should be taken for a course of 7-14 days.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs for external use are prescribed to completely destroy pathogenic microorganisms in the vagina. For example, you can use Terzhinan and Betadine at night for 5 days.
- Multivitamins. Representatives of this pharmacological group restore disturbed hormonal balance, restore injured uterine tissue, and strengthen local immunity. It is advisable to focus on multivitamin complexes containing vitamins A, E and group B.
Positive dynamics are observed at the very beginning of the treatment course. It is recommended to place special emphasis on the following medications:
- Diclofenac. This is a representative of the pharmacological group of NSAIDs, which is available in tablet form. The drug is prescribed from the first day of rehabilitation in the recommended dosage of 1 tablet no more than 3 times per day. From day 3 you should reduce the dose to 1 tablet at night. The duration of treatment is determined individually by the attending physician. One should not exclude the “addictive effect” to the medicine.
- Ibuprofen. Another representative of NSAIDs, which relieves pain, inflammation, high temperature in a state of fever. Recommended dosages – up to 3-5 tablets up to 4 daily approaches. Individual course of treatment. The instructions indicate contraindications; doctors do not rule out side effects; if there is no positive dynamics after 2 days, the medication should be replaced with an analogue.
- Regulon. These are oral contraceptives for replacing missing female hormones, as an important component of replacement therapy. It takes 3 to 6 months to take the tablets, with the daily dose determined according to a special scheme. You need to take 1 tablet per day, every day at the same time without breaks. If side effects occur, this oral contraceptive is replaced with Yarina, Zhanin.
- Danazol. These are antigonadotropins that prevent the growth of the endometrium. The drug is available in capsule form and is intended for oral administration over several weeks without interruption. The maximum daily dose for adult patients is 800 mg; for more detailed information, please consult a specialist. The action in the body is systemic, the drug is prescribed for many female diseases.
- Premarin. This is a medical drug that increases the concentration of estrogen in the body. It is necessary to take the tablets for 4 weeks, since they promote rapid healing of the wound after surgery. The recommended dosage is 625 mcg - 1.25 mg per day, alternating oral administration for 3 weeks with a break of 7 days. The doctor may increase the daily dose. The course of treatment is several weeks.
Pregnancy after hysteroresectoscopy does not occur immediately, but by completing the full course of medication and following all medical recommendations, the patient’s chances of experiencing the joy of motherhood increase significantly. When conservative treatment ends, re-diagnosis is necessary. Only after this the doctor gives valuable recommendations regarding further pregnancy planning.