What does a fertilized egg look like?
Having learned about their pregnancy, many curious expectant mothers begin to ask the doctor questions about how and at what stage the fertilized egg is visible and what it looks like. We will try to answer them.
The fertilized egg, the diameter of which is very small in the first days of pregnancy, can be seen within two to three weeks after a missed period. The formed structure in most cases is located in the upper part of the uterine cavity, has a dark (gray) tint and a round or oval shape. The embryo at this time is still microscopic in size, so it is not detected by ultrasound.
When to do an ultrasound for pregnancy
Ideally, early pregnancy is confirmed by a positive test, examination by a gynecologist and a high level of human chorionic gonadotropin in the peripheral blood. At the same time, the first ultrasound to determine pregnancy, or rather, to clarify its duration and diagnose the condition of the fetus, is carried out only at the 11-13th week (first screening).
Common indications for early ultrasonography:
- The test shows pregnancy if there is a history of ectopic localization of the embryo. It is possible to see an ectopic pregnancy using the transvaginal ultrasound diagnostic method only in the fifth week, and when using the transabdominal method - no earlier than the 7-8th week.
- The presence of a long delay in menstruation and a negative pregnancy test.
- When a doctor confirms pregnancy during an examination and using the hCG level, and a woman has a history of illnesses such as uterine fibroids, an ovarian cyst, or other serious pathology of the reproductive system. In this case, diagnostics are carried out not only to confirm the presence of a fertilized egg, but also to determine the severity of the disease.
- An ultrasound is also performed in the early stages to confirm pregnancy after IVF. Usually the procedure is scheduled on the 21st day after embryo transfer.
Development and structure
The growth of the fertilized egg begins from the moment of conception. The fertilized egg begins to move through the fallopian tube, during which cell fragmentation occurs. Making its way to the uterus, the fertilized, crushed egg needs nutrients and oxygen, so after a week a chorion begins to form on top, which subsequently transforms into the placenta.
The surface of the chorion has villi, which help the formation to attach to the uterus. In the future, these villi are contained only at the site of implantation of the formation into the uterine wall. The rest of the structure loses lint and remains smooth. The chorion provides the fetus with all vital functions, one of which is protection against infections.
Twenty days after menstruation, during a hardware examination, you can see the yolk sac, which is designed to provide the fetus with nutrients. The presence of a yolk sac in the fertilized egg does not guarantee a normal pregnancy, but if it is absent, this indicates pathology. Inside the membrane surrounding the embryo there is an amnion - a hollow sac that produces the optimal environment and amniotic fluid for the development of the child.
Often, during an examination, an ultrasound specialist may detect a second fertilized sac. In this case, the woman can be congratulated, as she will have twins. Such a pregnancy develops when two eggs are simultaneously fertilized or two zygotes develop from the same egg.
If a woman is expecting twins, the fertilized egg may form one or two placentas at the time of division.
If the moment of attachment of the egg to the uterus occurs after 8-13 days from the day of fertilization, then 2 fetuses and one placenta are formed for two. This means that both fetuses will develop in the same amniotic sac. If division occurs earlier than this period, then each embryo will develop in its own fertilized egg.
How is ultrasound performed?
During such a pregnancy, ultrasound scanning can also be performed in two main ways:
- transabdominal;
- transvaginal.
Both methods are allowed for IVF, since they do not pose any danger to the fetus and the expectant mother.
Transabdominal method
The study consists of installing a sensor that converts ultrasound waves on the skin of the abdomen in its lower parts. Therefore, the procedure is completely non-invasive and painless.
Preparation for the examination consists of following a certain diet to reduce gas formation in the intestines and filling the bladder for better visualization of the uterus. Approximately 2-3 days before the test, a woman should not eat foods that could potentially cause flatulence.
These include:
- all legumes;
- fresh vegetables;
- confectionery and bakery products;
- carbonated drinks and fast food products.
To fill the bladder cavity, you should drink about a liter of clean still water an hour and a half before the appointed time. As soon as the urge to go to the toilet appears, the procedure can begin.
The doctor does a study in several planes, after which all the results and his conclusions are recorded in the protocol.
Transvaginal method
In this case, the ultrasound sensor is directly inserted into the vaginal cavity, thereby achieving maximum proximity to the uterus and ovaries. This technique gives a more accurate and reliable picture compared to the previous method.
- In preparation, you only need to make sure that the intestines are not filled with gases, so for a couple of days it is recommended not to eat foods that contribute to flatulence.
- If a woman suffers from increased gas formation, then an hour before the examination it is necessary to drink several capsules of Espumisan or a bag of Smecta.
The ultrasound doctor puts a special disposable condom on the sensor and inserts it with gentle movements into the vaginal cavity about 5-6 cm. As a rule, the procedure is painless, and the woman may only feel some discomfort. Such proximity of the transducer to the organs being examined allows even a small embryo to be seen. Therefore, the first ultrasound during IVF pregnancy should be performed transvaginally.
Sizes of fertilized egg by week
A table will help you find out the size of the fertilized egg by week of pregnancy, according to which the obstetrician-gynecologist compares the size of the fetus with the norms for the expected period. The parameters indicated in this table are the most important indicators of the formation of pregnancy, therefore, when the fertilized egg is already visible, the doctor is obliged to determine them.
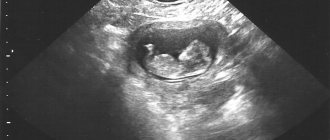
Ultrasound of the fetal egg at 4 weeks determines the size of only 1 mm. A woman at this time may not even know about the birth of a new life, but a hardware study will already reveal and even show what the fertilized egg looks like at 4 weeks. At this time, the cells of all future organs of the baby are formed.
The size of the fertilized egg increases daily by about 1 mm. When the egg reaches a size of 3 mm, it already has a yolk sac, which provides hematopoietic function and nutrition to the embryo. All elements of the fertilized egg within the fourth week make it possible to confidently establish the presence of pregnancy. It is already possible to examine the embryo during this period. It happens that at a given size the structure of the embryo is not visible. There is no need to panic, since in individual cases the embryo may still be forming at this time.
The question of when an embryo appears in the fertilized egg interests many expectant mothers. Normally, around the fifth week of gestation, the embryo is already visualized on the ultrasound monitor and even a heartbeat is recorded. To clarify the progression of pregnancy, hCG levels are additionally monitored.
A value less than 7 mm indicates the middle of the fifth week. This is one of the most important periods when active formation of blood vessels, heart and nervous system occurs. The size of the embryo is usually 2 mm.
When an ultrasound shows a fertilized egg measuring 10 mm, this indicates that the heart and blood vessels are already fully formed and the embryo has a neural tube with a slight thickening at the end (the future brain).
6 obstetric week visualizes a value of 12 mm. At the 6th obstetric week, the fertilized egg is 12 mm in size, has a spherical shape, the embryo looks like a white stripe about 5-6 mm long. At this point, the heart rate is 110-130 per minute. If any abnormality is detected during the sixth week, a repeat examination a week later is recommended.
During the first two days of the 7th week, the value is determined to be 19-20 mm. During this period, the baby’s brain and genitals are forming; on the ultrasound monitor you can see arms, legs, mouth and nostrils.
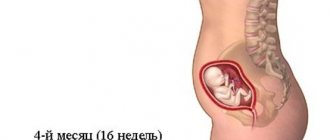
Structure dimensions of 21-22 mm indicate the middle of the seventh week. At this time, the development of the brain and face continues. From this period, the child cannot be considered an embryo, since it is already a full-fledged fetus measuring about 10-13 mm.
Location
An egg that is fertilized and attached to the uterine cavity can be located in various parts of the reproductive organ:
- If the fetus is at the bottom of the uterus, this indicates that it has assumed the most comfortable position. Located at the bottom, the baby will calmly grow and develop, nothing will fit him. This arrangement is considered correct and does not indicate a threat of miscarriage or increased tone of the organ. If the fertilized egg is located in the fundus of the uterus from the moment the pregnancy begins, then as the baby develops and grows, it may change position, but this will no longer be considered a pathology or its sign.
- If the fertilized egg is located in the corner of the uterus, this indicates that it is attached close to the fallopian tube, from which the fertilized egg emerged. In gynecology, this location is not considered a pathology, since the fetus will no longer be able to return to the fallopian tube. Being in a corner, he has the opportunity to change location, and this kind of “migration” is often accompanied by the appearance of bloody discharge, which is not abundant and is not capable of causing a miscarriage.
- If the fertilized egg is in the lower third of the uterus, there is a chance of miscarriage. It is too close to the throat, which is fraught with consequences. If the fertilized egg is located in the lower third of the uterine cavity, then under unfavorable circumstances: in case of stress or nervous strain, a spontaneous miscarriage may begin. In this case, the woman will experience pain in the lower abdomen and bloody discharge will begin.
Disorders and pathologies
If the fertilized egg develops incorrectly, a specialist will notice deviations from the norm on an ultrasound.
Deviations from parameters
The growth and size of the fertilized egg and embryo must correspond to the duration of pregnancy. If the fetus is less than 2 mm in size at 5 weeks, a developmental disorder can be stated. Fetal size less than 4 mm at seven weeks so
also indicates a violation. With these parameters, you need to make sure that the set deadline is correct.
A large fertilized egg with a small embryo often indicates a frozen pregnancy. But re-examination is necessary to confirm. A frozen pregnancy can also be indicated by a too small fertilized egg. However, again we need to observe the dynamics of development.
Irregular shape
We can also talk about a violation when the structure surrounding the embryo has a non-standard shape. If the angles of the membrane are uneven, then the specialist may suspect increased uterine tone. In many cases, this condition is harmless, however, if there is pain, dark vaginal discharge, or dilatation of the cervix, then there is a possibility of miscarriage.
To correct the situation, doctors remove the tone of the uterus, after which the egg takes the correct shape. What the fertilized egg looks like during a miscarriage depends on the gestation period. At 1-2 weeks, a miscarriage may look like menstrual bleeding. At later stages, the formation looks like a blood clot. If a miscarriage occurs at 7-9 weeks, the woman may find pieces of fetal tissue.
If the structure is oval and at the same time flat, this may also indicate a frozen pregnancy. However, in the absence of pain and other ailments, it makes sense to continue monitoring the pregnancy. A repeated examination will allow the doctor to draw the correct conclusion.
Wrong location
A low gestational sac does not indicate a serious pathology, but requires more careful monitoring throughout pregnancy. If the formation is very close to the cervix, then cervical pregnancy may occur, which can lead to removal of the uterus.
Empty fertilized egg
With an ectopic pregnancy, you can find an empty ovum when the cavity contains only fluid or a blood clot.
Why doesn't an ultrasound show pregnancy?
Many women are concerned about whether an ultrasound may not show pregnancy. There are a number of reasons for the “absence” of the fertilized egg in the uterus:
- The embryo is too small. A large number of women have irregular menstrual cycles, so they do not know exactly the day of ovulation. In this case, it is difficult to calculate the duration of the expected pregnancy.
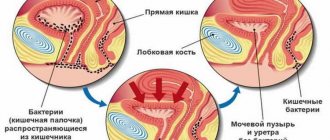
- Also, an ultrasound does not show pregnancy if the fertilized egg is implanted in the fallopian tube, in the cervix or on the bladder. The uterus itself will be enlarged, but the thickness of the endometrium will remain almost unchanged, which will indicate the absence of the embryo in the right place.
- The type and sensitivity of the ultrasound machine plays an important role, since not every one of them is able to see a small ovum. Don’t forget about the doctor’s experience, which can help you “miss” pregnancy at an early stage.
- Sometimes ultrasound diagnostics do not show the fetal egg due to abnormalities in the structure of the uterus or due to the location of the embryo on its posterior wall. There may be errors in diagnosis due to inflammation of the endometrium.
Types of ultrasound. What are SVD and KTR?
To determine the parameters of the ovum, various types of ultrasound are performed:
- Transabdominal - examination occurs through the outer abdominal wall.
- Transvaginal – examination is carried out through the vagina.
With a TA examination, a clear identification of the formation is possible starting from the 5th obstetric week. At this time, the fertilized egg is 5-8 mm in size. Using the second research method, you can determine the size of the fertilized egg on the 3-6th day of missed menstruation, which is 4-5 weeks of gestation.
Read more about the first ultrasound during pregnancy →
The embryo is visualized starting from the 5th week of pregnancy during a TV examination, and during TA - from the 6th week in the form of a linear formation.
To assess the size and growth of the formation and embryo, the following indicators are used:
- SVD is the average internal diameter of the fertilized egg.
- KTP – coccygeal-parietal size of the embryo/fetus.
SVD shows the size of the fertilized egg by week and is measured in millimeters. Thus, the indicator of the size of the fertilized egg constantly varies over the weeks of pregnancy; the CTE indicator is more accurate for determining the reliable gestation period.
In this study, the error may be three days up or down. Basically, the study is carried out up to 12 weeks of gestation.
The size of the fertilized egg helps to quickly determine how far along the pregnancy is and how the fetus develops in the womb.
The first three months of development are the most important, because it is during this time that all the organs and systems of the future baby are actively developing. Accordingly, it is important to undergo a scheduled ultrasound on time, which helps to identify possible deviations and carry out optimal correction of the current situation.
Author: Lyudmila Morozova, especially for Mama66.ru
Twelfth week
Conclusion of the most important and dangerous period of fetal formation. It is already possible to make a full assessment of the condition of the unborn baby and whether the important organs that develop during this period were formed correctly. At this stage, you can determine with precision down to the day which week you are pregnant. An experienced specialist can already name the gender of the baby.
When undergoing the procedure, it is advisable to choose a trusted specialist with high-quality equipment. It is important at this stage not to overlook the beginning of the development of possible pathologies.
Causes of miscarriage
There are many reasons for termination of pregnancy, ranging from banal stress to serious endocrine disorders. In some cases, the cause of the miscarriage cannot be determined.
The main causes of miscarriages include:
Genetic (chromosomal) abnormalities of fetal development that are incompatible with life. As a result, the non-viable fetus dies and a miscarriage occurs; - hormonal disorders: lack of the hormone progesterone, hyperandrogenism, hyperprolactinemia, thyroid disease and diabetes; — sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, HPV, HSV, CMV) and TORCH infections (rubella, herpes, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus infection); - anatomical anomalies: malformations of the uterus (unicornuate, bicornuate and saddle uterus, the presence of an intrauterine septum); uterine fibroids with submucosal localization of the node, intrauterine synechiae; — isthmic-cervical insufficiency (insufficiency of the muscular layer of the cervix, leading to its dilatation); - Rh conflict between mother and fetus.
Other factors that can also trigger a miscarriage include: previous abortions, smoking, drinking alcohol, using drugs, stress, acute respiratory diseases, taking analgesics and hormonal contraceptives.
Why do an ultrasound after IVF?
An increasing level of hCG in the blood of a pregnant woman indicates pregnancy, but the result still requires confirmation. In addition, this analysis does not reveal all pathologies.
Already in the third week of gestation, using ultrasound, doctors can:
- confirm the fact of pregnancy;
- find out how viable the fetus is;
- identify fetal pathologies;
- eliminate the possibility of miscarriage;
- see in which area of the woman’s reproductive organs the fetus is located (uterus, ovaries or fallopian tubes);
- count the number of embryos;
- determine the condition of the ovaries.
Sometimes, to confirm the information obtained during the first examination, it is necessary to do a second ultrasound, which confirms the implantation of the embryo, if this was not yet noticeable during the first screening. It also reveals the nature of pregnancy, especially multiple pregnancy. Upon repeated examination, it will be possible to determine the heartbeat of the fetus. The heart rate of the fetus is used to judge its full development.
You should definitely go for your first ultrasound to rule out diseases such as:
- Down syndrome.
- Edwards syndrome.
- Patau syndrome.
Children with such pathologies already at the initial stage have heart rhythm disturbances, which leads to their developmental delay. Another indicator of such diseases, which can be detected with accuracy only by ultrasound screening, is a flat face.
An ultrasound examination after unsuccessful IVF will help the specialist to identify the cause of this failure and determine further actions for successful reconception. Therefore, even after negative fertilization, it is necessary to undergo ultrasound screening.
What to do at home
After being transferred home from the clinic, you should travel by taxi or your own car (not on foot, not by public transport, not by driving). There is no need to go somewhere on the way and be among people. It is better to spend the rest of the day in a supine position, but strict bed rest is not necessary. At home it is recommended:
- avoid stress and negative emotions. Fear or a stress reaction causes significant contractions of the myometrium, which may be the cause of unsuccessful implantation of the embryo;
- limit physical activity and active sports. Swimming, leisurely walks, light work, and simple fitness exercises under the supervision of a trainer are allowed and even beneficial. You should not constantly lie in bed or sit so that blood does not stagnate in the genitals, but you should not overload yourself;
- do not take hot baths, do not go to the sauna, bathhouse.
For the next 2 weeks after embryo transfer, it is recommended to alternate physical activity and rest, do not lift weights (more than two kg), and do not lean forward sharply. You can do your usual household chores, but during the day it is better to lie down for an hour or two. You should tune in to any result, since inflated expectations in case of failure can lead to depressive disorder. An unstable psycho-emotional background can negatively affect subsequent IVF attempts.
There are no strict rules of conduct after embryo transfer. But following medical advice will increase the chances of successful implantation, minimize the risks associated with embryo transfer, and avoid harm to the body.
You should not do tests in advance without the permission of your gynecologist. If you rush, you can get a false negative answer, which will have a bad effect on your emotional state. And if a woman turns out to be pregnant, then negative reactions can harm the implantation process. Working women are given sick leave after the embryo transfer procedure.