The effect of fibrinogen on pregnancy
Increased fibrinogen during pregnancy (hyperfibrinogenemia) is a normal reaction of the body of the expectant mother. This feature is associated with preparation for the upcoming birth. During the birth of a child, a woman always loses some amount of blood.
An increased concentration of fibrinogen prevents severe bleeding during the birth process. Due to its increase, a woman loses up to 500 milliliters of intravascular fluid, which is not accompanied by pathological symptoms. A few days after giving birth, the amount of protein in the blood returns to normal levels.
Excessively increased fibrinogen in pregnant women is a risk factor for oxygen starvation of the unborn child, premature placental abruption and fetal death. The protein activates thrombus formation in the body of the expectant mother. Blood clots can enter the blood vessels of the placenta, causing a lack of blood supply. In severe cases, death of the affected area of the organ and its detachment are possible.
Also, high levels of fibrinogen can cause general pathological conditions in the mother’s body. One of the most dangerous complications is pulmonary embolism. As a result of pathology, a person may die due to the lack of exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
A reduced amount of protein (hypofibrinogenemia) of the coagulation system is dangerous with the risk of bleeding. They can develop in any organ of the expectant mother. If uterine bleeding develops, there is a risk of miscarriage.
Causes of pathological increase
In general, the condition when fibrinogen protein gradually increases during pregnancy over the trimesters is considered quite common. But even such an increase has certain limits, beyond which there is a high probability of developing some pathology. To identify the causes, patients are usually prescribed a hemostasiogram.
- If the increase in fibrinogen protein levels occurs in the 1st trimester, then the reasons lie mainly in inflammatory processes. The patient is usually referred for additional laboratory tests. It is necessary to quickly identify the source of the disease, because in the early stages of gestation any inflammatory process can negatively affect the development of the fetus.
- An increase in fibrinogen in the 2nd trimester is usually observed against the background of the formation of blood clots in the bloodstream. This condition is extremely dangerous during pregnancy, since a formed blood clot can block blood vessels and disrupt normal nutrition and oxygen supply to the fetal tissues. And this has a very negative impact on the development and growth of the baby. Also, in the 2nd trimester, an excessively increased fibrinogen concentration can be caused by the presence of tumor processes of any nature, inflammatory pulmonary lesions or pneumonia, and functional disorders in the thyroid gland.
- Excessive levels of fibrinogen protein in the third trimester of gestation usually indicate the development of pulmonary pathologies. Such an excessive increase is dangerous due to pulmonary artery thrombosis or detachment of placental tissues, premature birth. Such conditions are dangerous for mother and fetus and are fatal.
- Thrombophilia can also provoke a pathological increase in fibrinogen, in which patients experience an increase in blood clotting rates. If pathology is not detected in a timely manner, dangerous consequences can be missed. Patients with thrombophilia should be monitored by a hematologist throughout the entire pregnancy period.
- Burns, injuries, diabetes or tuberculosis, pre-infarction or infarction conditions, nephrotic syndrome and rheumatism, hepatitis forms, etc. can also cause a surge in fibrinogen.
It is not at all necessary to look for causes of pathological origin, because the protein content can also be affected by living conditions, diet, daily routine of the pregnant woman, and sometimes stress conditions, depression, psycho-emotional experiences, etc.
Fibrinogen test
During a normal pregnancy, it is recommended to check fibrinogen levels three times - once in each trimester. If the expectant mother has aggravating factors (history of spontaneous abortion, previous myocardial infarction), the test is taken more often.
A referral for testing is issued by the obstetrician-gynecologist leading the pregnancy. Most often, the doctor recommends that a woman check not only the level of fibrinogen, but also other indicators - d-dimer, APTT, RFMC, antithrombin, hematocrit. A detailed coagulogram allows you to assess the state of the blood coagulation system in full.
A coagulogram is not a strictly mandatory analysis of the pregnancy period, but it is recommended for all expectant mothers. Diseases of the coagulation system are dangerous to the life and health of a woman and her child. Timely detection of pathology allows for competent treatment and prevention of serious complications.
The optimal timing for performing a coagulogram includes the following time intervals:
- 9-11 weeks;
- 22-24 weeks;
- 30-36 weeks.
Blood is taken for a coagulogram on an empty stomach; in the morning before the procedure, you are allowed to drink a small amount of clean water. A tourniquet is applied to the expectant mother's shoulder, then a specialist takes material from the ulnar vein. 10-20 milliliters of blood is enough for analysis. After the procedure, the expectant mother is allowed a normal diet.
What is the function of fibrinogen and how to determine its level
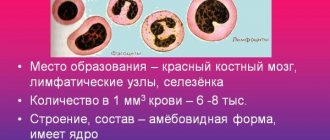
Fibrinogen is a protein produced by hepatocytes. It stimulates the production of hormones, bile acids, insulin and progesterone. During pregnancy, this blood clotting factor is considered one of the most important indicators of the hemostasiogram.
To enter the active state, the protein needs to go through a cascade of chain reactions: fibrinogen produces fibrin monomer, which, under the influence of factor 12, is converted into fibrin polymer.
In this case, the damaged vascular walls are strengthened with the formation of a blood clot, in which the substance acts as the basis of the thrombus. After some time, fibrin is broken down by fibrinolysin, and small substances appear that are gradually absorbed in the body.
Doctors monitor the content of the indicator throughout pregnancy, as it shows the degree of thrombus formation, which is especially important during childbirth. Blood clots reduce blood loss when the baby leaves the womb. At the same time, fibrinolysis during gestation is slowed down.
The fibrinogen content is determined using a hemostasiogram three times during the entire period of pregnancy (in the first, second and third trimesters), unless there are special indications that require a coagulogram more often.
To make the test more informative and help the doctor prevent possible complications, follow the necessary conditions:
- Donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. You cannot take the test after eating, and you cannot drink juices, tea or coffee an hour before the test. On the eve of the hemostasiogram, it is advisable to have a light dinner, excluding fatty foods 2 days before the test.
- Before a coagulogram, try not to do strenuous work or put stress on the body. Try to get a good night's sleep.
- If you are taking anticoagulants, you should warn your specialist about this.
- 1-2 hours before the test, drink 1 glass of clean water.
To determine the indicator, the pregnant woman comes to the treatment room, where venous blood is drawn. The specialist tightens the forearm with a tourniquet, after which, at the elbow bend, he inserts a needle into a vein, drawing blood into special tubes. After the procedure, the expectant mother squeezes the injection area, and the nurse turns the container with the material over several times to prevent the formation of blood clots in it.
To determine the content of the Clauss indicator, laboratory assistants do not use the manual method, since this does not ensure tight fixation of the formed blood clot. For this purpose, special coagulometers are used.
Increased fibrinogen
An increase in the amount of coagulation protein indicates the presence of pathology in the body of the expectant mother. Most often, an increased concentration of fibrinogen indicates an acute inflammatory process. An example of such diseases is viral respiratory infection (influenza), pneumonia, cystitis.
More rare causes of increased fibrinogen include the following conditions:
- Hormonal imbalance. Female estrogens are a factor activating the blood coagulation system. With an excessive increase in the amount of hormones, an increase in the concentration of fibrinogen is possible. Fibrinogen metabolism is also affected by the functioning of the thyroid gland. A deficiency of its hormones in the blood can cause activation of the coagulation system.
- Metabolic syndrome. The condition is characterized by a violation of metabolic processes in the body. With metabolic syndrome, a person experiences an increase in blood sugar and cholesterol, as well as obesity and increased blood pressure. Metabolic pathologies cause activation of the blood coagulation system.
- Liver diseases. Acute hepatitis caused by viruses or intoxication may contribute to increased fibrinogen synthesis.
- Kidney pathologies. When the condition of the organ's filtration system is disturbed, beneficial blood proteins are removed. In response to this, signals come from the brain about the need to synthesize new substances in the liver. This process stimulates the production of not only lost proteins, but also fibrinogen.
- Gestational arterial hypertension (late gestosis). The pathology is accompanied by impaired renal function.
- Gestational diabetes mellitus. When the disease occurs, there is an increase in blood glucose levels. An increase in sugar causes activation of the coagulation system.
- Neoplasms. In rare cases, the cause of an increase in fibrinogen is benign and malignant tumors.
Fibrinogen during pregnancy: violations of the norm, causes and methods of stabilization
Pregnancy is a special period in a woman’s life when the functioning of many systems and organs in the body changes. Doctors constantly monitor their work using various tests in order to monitor the child’s development and respond in time to the appearance of deviations. Fibrinogen is an indicator of blood condition that increases during pregnancy. A significant increase is a problem because it will affect the development of the fetus. The attending physician must assess the seriousness of the situation and determine further actions.
Decreased fibrinogen
Low fibrinogen levels can occur in early pregnancy as a result of severe toxicosis. Repeated vomiting causes beneficial blood proteins to be washed out of the body.
Also, a reduced concentration of coagulation protein is observed in endocrine pathologies. Male sex hormones are opposite to estrogens; their increase in the blood is accompanied by a decrease in fibrinogen synthesis. Sometimes activation of the blood anticoagulation system is a consequence of increased levels of thyroid hormones.
Attention! Low levels of fibrinogen can occur against the background of hereditary pathologies. They are usually detected in childhood, but mild forms do not appear for a long time. Pregnancy is a factor in the deterioration of a woman’s condition.
Chronic liver pathologies cause a decrease in fibrinogen in the blood. The destruction of organ cells is accompanied by a decrease in the synthesis of proteins, including fibrinogen.
Also, a decrease in fibrinogen is caused by vitamin B12 deficiency. It is involved in the process of hematopoiesis; with its deficiency, activation of the anticoagulant system is observed. In rare cases, a decrease in the amount of protein in the blood is the result of DIC syndrome.
What it is
Fibrinogen is a protein produced by the liver. It precedes the synthesis of fibrin, a substance that forms a clot during blood clotting.
The importance of this indicator is that deviations from the normal level can cause both fetal growth retardation and problems in the maternal body. There is a lot of blood loss during childbirth, and this important protein helps prevent heavy bleeding.
That is why a woman is prescribed a coagulogram and, if necessary, a hemostasiogram, with the help of which other serum parameters are determined
There is a lot of blood loss during childbirth, and this important protein helps prevent heavy bleeding. That is why a woman is prescribed a coagulogram and, if necessary, a hemostasiogram, with the help of which other serum parameters are determined.
Treatment of elevated fibrinogen
In order to reduce the amount of fibrinogen in the blood, the expectant mother is recommended to follow a special diet. A pregnant woman should avoid foods high in cholesterol. These include fatty meats, butter, eggs, liver, duck, goose. The expectant mother is recommended to take healthy fats contained in sea fish, avocados, and vegetable oils.
Non-drug measures to reduce the activity of the coagulation system also include reducing the amount of fast carbohydrates. It is recommended that the expectant mother exclude chocolate, confectionery and flour products, pasta, and white rice. A pregnant woman needs to walk more in the fresh air and do light exercises.
If indicated, the expectant mother is recommended to take medications. The main group of medications are antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants. Taking them reduces the activity of the blood coagulation system. Abciximab, Clopidogrel, and Pentoxifylline are allowed to be used during pregnancy.
Also, the expectant mother is prescribed complexes containing vitamins A, C and group B. They improve the microcirculation process and suppress the activity of the coagulation system.
How to get your numbers back to normal
Reducing elevated fibrinogen is achieved by prescribing a special nutrition system. What to do if fibrinogen is elevated during pregnancy in the third trimester?
Treatment of fibrinolysis is possible without medications. The diet excludes:
- fat meat;
- duck and goose meat;
- liver;
- egg;
- animal oils.
Healthy fats are a priority for hypofibrinolysis:
- sea fish;
- vegetable oils;
- avocado.
Refusal of fast carbohydrates:
- chocolate;
- confectionery products;
- baking;
- pasta;
- regular rice.
Eat more dishes with beets, seaweed, grape juice, seeds, tomatoes, cucumbers, etc.
How to reduce fibrinogen during pregnancy: a woman is recommended to go out into the fresh air more often and do light exercises. The doctor determines the indications for taking medications, this may be the prescription of an antiplatelet agent or an anticoagulant. When carrying a fetus, the use of Abciximab, Clopidogrel, Pentoxifylline is allowed to reduce fibrinogen. It is advisable to prescribe vitamins of groups A, B, C - they normalize microcirculation.
To increase the concentration of fibrinogen, the following diet is also prescribed:
- white meats;
- milk products;
- curds;
- dishes with nuts;
- spinach.
An obstetrician-gynecologist can prescribe herbal remedies: medicines with extracts of nettle leaves, yarrow or shepherd's purse herb, medicines with extracts of sandy knotweed, water pepper.
Note . Traditionally, vitamin B-12 and Tranexamic acid are prescribed.
Treatment of low fibrinogen
To increase the amount of fibrinogen in the blood of the expectant mother, it is recommended to follow a diet. The diet should include foods such as nuts, spinach, white meat, milk, and cottage cheese. A pregnant woman is also prescribed vitamin B12.
After consulting a doctor, the expectant mother may be recommended to take herbal preparations. Nettle leaves, shepherd's purse grass and yarrow help increase fibrinogen in the blood. Extracts of sandy knotweed and water pepper have a similar effect.
Among medications, a group of coagulants is widely used. They activate the blood coagulation system, reducing the risk of sudden bleeding. Pregnant women are most often prescribed Tranexamic acid.
Norms of values
Wise nature has provided everything for the unhindered development of a new life in the mother’s womb. Therefore, at the very beginning of pregnancy and throughout the first trimester, fibrinogen in the blood decreases so that the embryo can receive more useful substances, because blood fluidity increases.
During this period, the placenta is formed - and new vessels, including the vessels of the umbilical cord, need careful and gentle treatment. For this reason, maternal blood becomes more liquid.
In the second trimester, when the vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord become stronger and stronger, and the main formation of the child’s organs is completed, the mother’s body has a new task - to prepare for the upcoming birth. that the risk of blood loss during the birth of a child is inevitable, this is obvious. Therefore, the blood begins to “thicken”, the level of febrinogen increases, and consequently, the blood begins to clot faster.
The real danger during childbirth is the expulsion of the placenta. When a “baby spot” is born, it is always accompanied by bleeding. How heavy and controlled it will be depends on the time it takes for blood clots to begin to form.
This indicator is influenced by the amount of febrinogen. Therefore, in the third trimester, the level of this plasma protein is normally always higher.
Table of norms for fibrinogen concentration during pregnancy by week:
Obstetric period (weeks)
Fibrinogen concentration – minimum
Fibrinogen concentration – maximum
Prevention
To prevent pathologies of the blood coagulation system, the expectant mother should lead a healthy lifestyle. Her diet should include varied and healthy foods of plant and animal origin. A pregnant woman is advised to reduce her intake of unhealthy fats found in pork, eggs, duck, lamb, liver and other organ meats. Also, expectant mothers do not need to include large amounts of fast carbohydrates in their diet.
During pregnancy, the expectant mother should completely stop smoking cigarettes. Nicotine and other substances contained in tobacco cause activation of the blood coagulation system. It is also recommended that a pregnant woman engage in light sports and walk in the fresh air for at least 1 hour a day.
Fibrinogen levels in different trimesters: table by week of pregnancy
Fibrinogen levels change as pregnancy progresses. At the beginning it may be slightly lower than before pregnancy, but by the last months it increases noticeably. This will protect the woman from heavy blood loss during childbirth.
Normal fibrinogen levels for adults range from 1.8–3.5 g/L. But during pregnancy the following fluctuations may be observed:
Based on materials from in-waiting.ru