Kidneys are vital organs, so even the most minor changes in their work can lead to a worsening of the condition of the body as a whole, as well as a deterioration in the quality of life.
Fortunately, today there are many ways to diagnose pathology in the early stages, which will allow you to begin proper treatment in time and prevent unpleasant consequences. And one of these methods is CT with contrast.
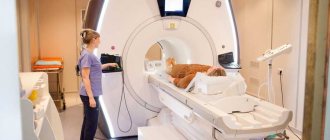
CT is one of the most modern diagnostic methods. The study is performed using a special device - a tomograph. During the procedure, the patient is inside the device. This is where the layer-by-layer scanning of the body takes place.
This diagnostic method was proposed back in 1927. Then Goldfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack proposed, therefore, to scan an object layer by layer without destroying it. For this they were awarded the Nobel Prize.
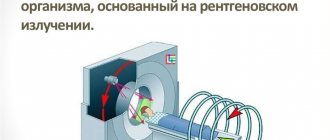
The diagnostic principle in this case is to lightly irradiate the body. During the study, the device records the difference between the radiation supplied and the radiation leaving the body.
The fact is that part of the radiation is absorbed. Dense tissue of the body absorbs rays in greater quantities and vice versa. At the end of the procedure, doctors will receive a three-dimensional image of the organ being examined. The doctor studies this image and if the patient has lumps in the body, it will be noticeable. These lumps are usually tumors.
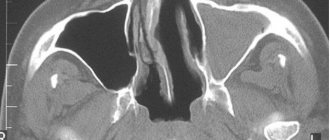
CT scan of the kidneys with contrast. Source: infomrt.ru
Not everyone knows what a CT scan of the kidney with contrast is, so after such a procedure is prescribed, the patient may experience a feeling of anxiety and concern. And in vain. There is nothing wrong with such research.
It is performed practically the same as a regular CT scan. The only difference is that with a CT scan with contrast, a special medication (contrast) is injected into the patient’s vein.
A contrast agent in a kidney CT scan is used to ensure that the resulting image of the organ being examined is as accurate as possible, and the doctor can examine everything in the smallest detail.
As a contrast, doctors usually use nonionic iodine-containing medications. These medications quickly spread throughout the patient’s body, and iodine increases the contrast of the resulting image.
The medication is administered during the procedure. The patient lies down on a table, which is subsequently pushed into the tomograph. A catheter is first inserted into his vein, through which contrast is supplied at a rate of 2-7 ml/s.
When tomography of different areas of the body, contrast can be supplied in different ways (including rectal, inhalation, etc.). However, for kidney studies, the medication is given intravenously.
During a CT scan of the kidney with contrast, the doctor controls the process of administering the medication, which helps obtain the most reliable images and helps to avoid complications.
Indications and contraindications
Computed tomography of the kidneys is a highly informative, painless, and most importantly, safe method of x-ray examination. During the scan, the patient receives a minimum dose of radiation – from 3 to 10 m3v.
If you have pain in the lumbar region and difficulty urinating, you should consult a nephrologist. He will issue a referral for a CT scan of the kidneys.
Indications for examination:
- kidney stones, renal colic;
- polycystic disease;
- chronic infectious kidney diseases, for example, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis;
- organ dysfunction, renal failure;
- congenital anomalies;
- open or closed kidney injury;
- hydronephrosis, nephroptosis;
- abscess;
- kidney infarction;
- abnormalities of the vascular system;
- thrombosis of the vessels supplying the kidneys;
- tumors.
As a rule, a CT examination of the kidneys is auxiliary after an ultrasound scan. It can be used to prepare for an upcoming operation, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of therapy or surgery.
Despite its safety, not everyone is allowed to examine their kidneys using computed tomography. Contraindications:
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- patient weight more than 200 kg;
- mental disorders;
- presence of a pacemaker, insulin pump or electronic devices in the body.
As for computed tomography of the kidneys with contrast, it is contraindicated in case of an allergy to the injected substance, as well as in case of renal failure.
There are relative limitations to performing CT:
- children under 14 years of age;
- diabetes;
- severe chronic diseases;
- severe pain that prevents the patient from lying still;
- lactation;
- recent CT or MRI scan;
- deterioration of health on the day of the examination, for example, increased body temperature, chills, nausea.
Computed tomography of the kidney with a contrast agent is questionable in cases of myeloma and thyroid pathologies.
In case of relative contraindications, the doctor assesses the risks and possible benefits for the patient, and then decides whether to give a referral for examination or not.
Indications for use
Computed tomography of the kidney is used if laboratory tests or previous hardware diagnostic methods - ultrasound, excretory urography - have given reason to think about pathological changes. Multislice tomography of the kidneys and adrenal glands is prescribed if suspicion falls on:
- urolithiasis;
- organ trauma;
- neoplasms (for example, cyst, cancer);
- abnormal development (adrenal hyperplasia);
- nephroptosis - prolapse of the kidney.
No contrast
Computed tomography of the kidneys is an informative way to confirm the diagnosis of diseases and determine the current state of the organ. The indications are:
- impaired renal function - impossibility of urine outflow, incontinence, increased frequency of urges;
- renal colic, pain in the groin, during urination;
- presence of flakes and/or blood in urine;
- prescribing kidney surgery, monitoring after it;
- probable stones in the urinary system;
- suspicion of organ rupture after injury.
With contrast
CT angiography (contrast tomography of the kidneys) is performed to diagnose vascular pathologies:
- aneurysm;
- arteriovenous fistula;
- kidney bleeding;
- arterial stenosis;
- thrombosis, thromboembolism.
For better visualization of arteries and veins, iodine-containing preparations are needed; they are very clearly visible in X-rays.
Why do you need a contrast agent?
A CT scan of the kidneys with contrast is necessary for better visualization. This is a more accurate examination method than conventional tomography, since scanning makes it possible to study not only tissue, but also blood vessels and arteries.
Kidney CT scan with contrast is used in the following cases:
- to identify vascular disorders, such as thrombosis;
- for better visualization of stones, assessment of their size and composition;
- to identify metastases and neoplasms;
- to assess urine output and glomerular filtration rate.
The contrast agent is iodine or gadolinium. It is administered intravenously or orally.
The essence of computed tomography of the kidneys and its varieties
Computed tomography is based on the use of X-rays and processing of the resulting scan data using modern computer technologies. Compared to conventional X-rays, a kidney CT scan is considered a more informative diagnostic method, since with its help the doctor receives a clear and reliable image. What happens during a CT scan? X-rays pass along the entire body, and a computer records changes in their energy. After this, the data is processed and a two-dimensional image of the scanned organs is displayed on the screen. CT scans are also sometimes done with a contrast agent. It is used to obtain a clearer image of the kidneys.
There are several types of CT:
Spiral computed tomography (SCT) - examines the structures of the body in layers within a few seconds. Multispiral computed tomography (MSCT) - differs from spiral in the number of detectors in the tomograph and the number of rotations of the X-ray tube during scanning of the human body. Return to contents
Preparation
Preparation is important for a CT scan of the kidneys. At the appointment, the doctor will give recommendations on nutrition, lifestyle, and taking medications. All requirements must be met.
Kidney CT scan with contrast
Early preparation for a CT scan of the kidneys with contrast looks like this:
- preliminary examination of the patient to identify contraindications, both absolute and relative, detection of allergies to the contrast agent;
- following a diet 2-3 days before the scan, which is aimed at reducing gas formation in the intestines;
- taking sorbents, for example, Smecta or Sorbex.
Dietary nutrition involves excluding alcohol, carbonated drinks, legumes, mushrooms, fermented milk products, fresh vegetables and fruits, and sweets from the diet.
The key to preparing for a kidney CT scan with contrast is a blood test for creatinine. It can be used to detect kidney failure.
Late preparation for a CT scan of the kidneys with contrast looks like this:
- 4–5 hours before the examination, stop eating and drinking liquids;
- Before entering the office, remove all metal jewelry.
During the examination, the patient's condition may worsen. This is due to the introduction of a contrast agent, so there is no need to worry. If a person feels a metallic taste in his mouth or has a headache, then this is normal.
CT scan of kidneys without contrast
Recommendations for preparing for a kidney examination using CT:
- take a urine and blood test;
- 2–3 days before the examination, avoid foods that increase gas formation;
- avoid stress and physical activity;
- 4–5 hours before the CT scan, do not eat or drink anything;
- remove all metal objects from yourself.
Under no circumstances should pregnancy or illness be hidden. This information is key in deciding whether to perform a CT scan.
Not only physical, but also psychological preparation for a computed tomography scan of the kidneys is important. If the patient is very nervous before the procedure, a sedative can be taken.
Progress of the procedure
The examination is carried out using a tomograph. The patient enters the office, removes all metal jewelry and lies down on a retractable table, which then slides into the CT machine.
It does not matter whether a CT scan of the left or right kidney is performed, the patient should lie on his back. The ring of the device rotates, so a three-dimensional image is obtained.
During the scan, the person must lie still and comply with all the specialist’s requirements, for example, hold their breath or exhale. The doctor is in the next office, from where he controls the CT machine. He looks at the monitor screen on which the image is displayed. Since the tomography unit has a built-in camera with a microphone, the doctor sees and hears the person.
A CT scan of the kidneys without contrast lasts up to 20–30 minutes. If it is necessary to introduce a contrast agent, then a pause is needed. An injection is given into the femoral vein, then scanning continues.
Computed tomography of the kidneys with contrast lasts up to 30–40 minutes. After the examination, it is possible to obtain a whole series of images.
Kinds
Computed tomography is represented by the following types:
- Standard . It is performed without additional injection of a special contrast agent.
- Multispiral . It is carried out on a multispiral apparatus. The equipment produces a 3D image of the organ. Diagnostics takes a short amount of time. The patient receives minimal radiation exposure.
- Spiral . Carried out using contrast. Over the course of several seconds, the structures of the organ are examined layer by layer.
What does a kidney CT scan show?
Photo from foodandhealth.ru
Kidney tomography allows you to see the following:
- any changes in the structure, shape or size of organs;
- congenital developmental anomalies;
- condition of the capsule and surrounding tissues, abscesses, phlegmon;
- malignant or benign formations, metastases;
- accumulated blood or fluid in the kidney calyces and pelvis;
- stones and cysts, urinary tract obstruction;
- abnormalities in kidney function, for example, changes in the rate of urine excretion, impaired glomerular filtration.
Thanks to CT, the anatomical condition and functioning of the kidneys can be assessed.
In what cases is it prescribed
This method can be used as an initial detection of the disease, in order to clarify the primary diagnosis, as well as to fully evaluate the course of treatment. The manipulation makes it possible to obtain detailed information about the condition of the organs, as well as check the adrenal glands and retroperitoneal space.
When executed:
- If you suspect the presence of stones.
- If there are injuries to the abdomen and spine.
- From time to time, this procedure is prescribed to patients with congenital anomalies.
- When determining inflammatory processes or in the presence of infections.
- In case of suspected oncology, to identify a neoplasm and assess its location.
- It is also used after organ amputation to monitor the condition of the renal bed.
Possible complications of the procedure
With a kidney tomogram, the risk of negative consequences is minimal. The procedure is well tolerated, there is no pain.
Complications are only possible with a CT scan of the kidneys with a contrast agent if the patient is allergic to the injected contrast or did not follow the preparation recommendations.
List of negative consequences:
- swelling of the lips;
- skin rash;
- redness of the skin at the site of injection of the contrast agent.
All these symptoms disappear after taking antihistamines.
Very rarely, more severe complications such as shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, hypertension and renal failure occur.
Possible risks
It is not uncommon for patients to experience anxiety about receiving radiation during a test. However, these fears are unfounded. The radiation exposure is very small and cannot harm the body. But undergoing such a procedure several times in a row over a short period of time can cause tumors to grow. This is why this procedure is re-prescribed only for certain indications or at intervals between examinations. If frequent examinations are necessary, it is better to undergo, for example, an MRI of the kidneys.
Patients with iodine intolerance are at risk of allergic reactions. Be sure to tell your doctor if you are allergic to iodine or seafood! The office also always has antihistamines for timely assistance to the patient. Some medications can also cause side effects in the patient.
In general, a kidney CT examination is painless and safe; in the absence of contraindications, it does not cause any side effects.
Decoding the results
The kidney CT scan is interpreted by the specialist who conducted the examination. He analyzes the pictures and makes a conclusion. After the scan, the patient should wait 1–1.5 hours for the results. They are handed out to them.
As a rule, the diagnosis is indicated in the conclusion. If it is absent, then you should contact a nephrologist with the results, who will decipher the data and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
As a rule, the conclusion should indicate the following:
- the kidneys are of normal size and location, with a clear outline;
- the renal pelvis is symmetrical, without stones, obstruction and growths inside, the passage of urine is not impaired;
- parenchyma of normal thickness and structure;
- there are no thickenings, inclusions and fluid in the perirenal and pararenal space;
- normal patency of blood vessels;
- no bleeding.
Normally, there should be no foreign bodies, tumors or inflammatory and infectious processes.
Using CT, you can identify the following pathologies:
- one or both organs do not correspond to normal sizes, there are deviations in location, which indicates inflammation, structural pathologies or injuries;
- signs of an infectious process;
- cysts or abscesses;
- stones in the kidneys;
- narrowing of the ureters;
- kidney tumor;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- obstruction of blood vessels.
When should a CT scan not be performed on a patient?
Computed tomography has a number of contraindications. Since the technique is based on the use of x-rays, it is not performed during pregnancy or in the presence of severe pathologies of internal organs.
Acute and chronic renal failure is a contraindication to the procedure.
CT examinations are not performed for endocrine system disorders: thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation.
Is it possible to do a CT scan of a child’s kidneys?
The radiation dose received during an examination is not as dangerous as an incompletely diagnosed disease. According to these considerations, CT scans are performed on children. But if this is possible, then preference is still given to MRI. This diagnostic method is safer for children.
For children under 3 years of age, a CT scan is performed under anesthesia, as it is difficult for them to lie still, they may be frightened by noise and begin to panic. Children over 5–6 years of age tolerate the examination more easily, so there is no need for anesthesia.
A child can have a CT scan with or without contrast. The contrast agent does not harm the baby's body, but it is important to rule out allergies.
Differences between CT and other kidney tests
If we talk about all the instrumental methods for diagnosing renal diseases, then CT and MRI are the most highly informative. They are accurate, but completely different in operating principle.
The procedure is identical. But MRI, unlike CT, is not based on x-ray radiation, but on the action of a magnetic field, so this method is safer.
The disadvantage of magnetic resonance imaging is its high cost. It is almost 2 times more expensive than CT.
Some kidney diseases are life-threatening, so accurate and timely diagnosis is more important than ever. Thanks to the development of modern technologies, it has become possible to identify the slightest deviations in kidney function.
Author: Oksana Belokur, doctor, especially for Nefrologiya.pro
Useful video about CT scan of the kidneys
List of sources:
- Karmazanovsky G. G. Clinical aspects of intravascular contrast in X-ray studies // Med. Visualization, 2003. – No. 1. – p. 131–137.
- Buylov V., Borisanov. A. Spiral computed tomography for kidney tumors. Practical medicine, 2009.
- Mukhin N.A., Tareeva I.B., Shilov B.M., Kozlovskaya L.V. Diagnosis and treatment of kidney diseases, 2011.
- Nephrology: a guide for doctors / ed. I. E. Tareeva / M.: Medicine, 2000.