The paranasal sinuses (sinuses) are depressions in the bones of the skull. The mucous membranes of cavities are sensitive to the effects of bacteria and viruses and often become inflamed due to colds, flu, chronic diseases, and infections in the mouth. CT scan of the nose is one of the most accurate methods for diagnosing pathologies at any stage of development.
Sinuses are relatively small structures, and to study them requires a diagnostic device with high resolution. This condition is met by MSCT - modern multislice tomographs. The devices are equipped with a large number of X-ray wave emitters and detectors. During one rotation of the scanning system, several sections are recorded at once, which ensures maximum accuracy of information and reduces procedure time.
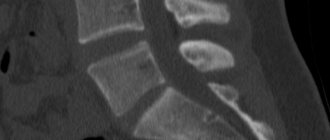
Total filling of the left maxillary sinus with fluid (blood?), damage to the nasal septum on a computed tomogram
What does a CT scan of the sinuses show?
The CT scan of the nose and paranasal sinuses makes it possible to study the structure of anatomical structures and identify the features of the pathological process. Examination of the area in question on a computed tomograph shows:
- congenital anomalies;
- destructive changes and traumatic injuries of facial bones;
- thickening of the mucous membrane of the nose and sinuses;
- deviated nasal septum;
- inflammation inside the sinuses (CT will show sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis, sphenoiditis);
- abscesses of the nasal septum;
- polyps, granulomas, cysts of the mucous membrane of the air cavities of the facial skull;
- tumors in the paranasal sinuses;
- accumulation of blood, exudate, pus in the sinuses;
- additional voids (ostia);
- foreign bodies in the nasal passages and bone cavities;
- hemorrhages in the sinuses and soft tissues;
- dental pathologies (root ingrowth or tooth displacement into the maxillary sinus);
- inflammation in the throat and nasopharynx;
- osteomyelitis of the facial bones;
- pathological communication of the sinus with the oral cavity in the form of an oroantral fistula.
Cyst in the sinus
Questions for the doctor
CT or MRI of the sinuses: which is better?
MRI is not advisable to study the features of the sinuses, since many solid structures are concentrated here. Computed tomography is better suited to visualize them.
Are CT scans of the nasopharynx and sinuses the same thing?
During the examination of the sinuses, the anatomical structures of the nasopharynx also come into view, therefore, if it is necessary to assess the condition of the adenoids, this procedure is also prescribed.
X-ray of the sinuses or CT: which is better?
Both methods are based on X-rays, but computed tomography allows you to study the structure and structure of tissues layer by layer, which provides much more information than with a standard X-ray examination.
Therefore, when choosing it, there is no need to perform additional invasive and risky procedures.
CT scan of the sinuses
How to do a CT scan of the sinuses
Not all patients know what a CT scan of the sinuses is, how the procedure is done, and how harmless it is. Like any x-ray examination, computed tomography gives a person a certain dose of radiation. But if you take precautions, there is no need to fear deterioration in your health.
The examination will not cause harm if the patient follows the following principles:
- undergo a CT scan as directed by a doctor if other diagnostic methods are insufficiently informative;
- take into account existing contraindications;
- take into account the total radiation dose during various studies throughout the year;
- if it is necessary to do a repeat analysis, consider not computer diagnostics, but MRI (it is considered safe even for small children).
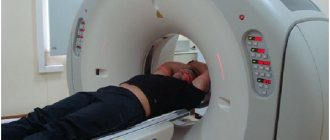
The tomograph, which performs CT scans of the nose and paranasal sinuses, includes a mobile couch and an X-ray unit. The device scans the nasal sinuses, the images are sent to a computer monitor, a specialist analyzes them and prepares a description.
Before the procedure, the patient is asked to remove anything that contains metal: glasses, dentures, hairpins, earrings, hearing aids, etc., to avoid distortion of the images. The doctor briefly talks about CT scanning of the sinuses - what it is, how long the session lasts, how to behave and what to do if discomfort occurs. The patient is positioned on a couch, which is placed in the tomograph ring. The scan takes about 10 minutes: you must lie still the entire time.
If contrast is required, the procedure consists of two parts. First, regular photographs are taken, then the examination is stopped, the necessary drug is administered and the diagnosis continues.
A CT scan of the sinuses is absolutely painless. The only irritating factor is the characteristic clicks of the device, but this problem is easily solved with the help of anti-noise earbuds or headphones.
Photo: Computed tomography procedure of the paranasal sinuses
Advantages of the method
Computed tomography of the sinuses is perhaps the most accurate and error-free method for diagnosing various pathologies.
The data obtained through such a study on the condition of the sinuses is quite detailed, as a result of which a specialist can clearly diagnose a particular ailment, and then prescribe the only correct treatment.
Main advantages of CT:
- Obtaining high-quality images of the nasal sinuses.
- Reduced radiation dose compared to conventional x-rays.
- Speed of research.
- The ability to conduct prompt diagnosis and promptly begin treatment of pathology.
- Absence of any negative impact of the tomograph on the patient’s body.
- The research method is completely painless.
In addition to all of the above, computed tomography helps determine not only the condition of the soft tissues of the paranasal area, but also the facial bones, blood vessels and tear ducts in the area being examined. In general, CT scan of the sinuses is one of the best methods for studying pathologies in this area of the skull. The procedure combines high efficiency and safety.
Computed tomography helps to timely identify serious illnesses and prescribe the necessary treatment measures to the patient. The promptness of diagnosis reduces to zero the risks of serious development of diseases and the appearance of subsequent complications, as a result of which ignoring CT is dangerous for one’s health.
Paranasal sinuses are pneumatized: norm and pathology
Preparation for examination of the paranasal sinuses
If you do not plan to use contrast, a CT scan of the nose does not require any preparation. You will not need to follow a diet or change your usual lifestyle.
Diagnosis with contrast is preceded by determining the level of creatinine in the blood. An increase in indicators indicates problems with the kidneys, for which the procedure is contraindicated.
CT scan with contrast: the process of intravenous injection of an amplifier - photo
Additional preparation is recommended for women during lactation. After the examination with contrast, you will have to give up two feedings in a row (the milk is expressed and poured out). It is better to take care of food supplies for the baby in advance.
Contraindications for CT
CT scanning has a number of contraindications. However, each case is considered strictly individually. A CT scan may be performed if the threat to health or life outweighs the possible harm caused by the scan. CT scanning is contraindicated in:
- diabetes type 1 and 2;
- allergies to contrast;
- liver cirrhosis;
- myeloma;
- liver and kidney failure;
- endocrine pathologies;
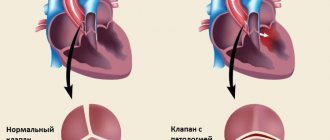
- cardiac disorders.
Also, CT is not advisable for pregnant women or during lactation. It is done with caution in children (only for serious indications). A CT scan of the nasal sinuses is not performed on people who cannot remain motionless for some time (with mental disorders, Parkinson's pathology, etc.).
Which is better - MRI or CT scan of the sinuses?
Many patients are interested in the question of which is better – CT or MRI of the paranasal sinuses. These diagnostic methods solve different problems, so the choice of examination method depends on the specific case.
MRI is based on the effect of radiofrequency pulses on an object placed in a high-intensity magnetic field. This technology is best used to study solid soft tissues. CT uses X-rays that most clearly visualize bones and hollow organs. The latter include the nasal sinuses.
Magnetic tomography is done:
- to confirm/exclude perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus as a result of trauma or dental diseases;
- if you suspect a tumor, polyps, cysts;
- to assess the condition of the mucous membranes of the sinuses;
- for headaches of unknown origin.
MRI also shows inflammation and hemorrhages in the paranasal cavities.
Magnetic tomography of the paranasal sinuses: left-sided sphenoiditis
CT diagnostics of the paranasal sinuses is done for acute inflammation and recurrent sinusitis. A computed tomography scan will show cracks and fractures of the facial bones, osteomyelitis complicating an injury or dental disease, metastases that have spread from neighboring anatomical areas.
Computed tomography scan of the nasal sinuses: right-sided sinusitis
When giving preference to a magnetic resonance examination or CT scan of the nose, the doctor takes into account the limitations. MRI is not performed if there are metal elements on (in) the body. The processes occurring in the tomograph can cause damage to these structures and the device itself. A CT scan of the sinuses is not a magnet, but an x-ray. Metal objects do not interfere with the operation of the device, but may appear in the photo and cause errors in the description.
Due to radiation, pregnant women are not allowed to undergo CT examinations of the maxillary sinuses (any dose of radiation is harmful to the fetus). In such a situation, the best option is MRI; diagnostics are carried out strictly according to indications.
What is a CT scan of the paranasal sinuses?
CT is a special examination method that allows you to determine the presence of nasal pathologies. During a CT scan, a special device is used to irradiate the nose with X-rays - this allows you to obtain a series of detailed images of the paranasal sinuses. The images have a high degree of clarity, so they can be used to determine the presence of even the smallest inflammation, fracture and tumor.
Unfortunately, CT scanners are large and expensive devices, so CT examinations are usually performed in large city clinics. Before tomography, a special contrast agent is injected into the person’s blood, which increases the accuracy of diagnosis . During computed tomography, the body is exposed to radiation, so CT can be performed no more than once every 6 months (however, in the presence of severe pathologies, CT can be performed more often, when tomography will cause more benefit than harm).
This material will tell you why ear congestion occurs with sinusitis.
CT scan of the nose with contrast
Multispiral devices are able to provide enough information about bone structures and the presence of fluid in the sinuses, so CT analysis of the nose and paranasal sinuses is often done without contrast. If a tumor is suspected, more detailed images are needed. To improve the quality of the image, a contrast agent is used.
A special preparation containing iodine is injected into a vein. The substance quickly spreads throughout the tissues of the body and stains the smallest vessels, including those that feed the tumor. After a new series of CT images of the nasal cavity, the doctor receives reliable information about the location and size of the tumor, which has its own vascular network. By identifying areas of additional blood supply, spiral tomography (MSCT) helps detect tumors in the initial stages.
Squamous cell carcinoma on CT scan of the nasal sinuses with contrast. The tumor tissue is marked with a long arrow, destructive changes in the bone of the left maxillary sinus are marked with a short arrow.
Carrying out a computed tomography scan - what the procedure shows
Before prescribing a computed tomography scan, the doctor must familiarize himself with the results of a blood test for sinusitis. A CT scan is performed only as prescribed by a doctor if there is reasonable suspicion of moderate or severe pathologies of the nasal sinuses. The tomograph is usually installed in a separate office, which is divided into two small rooms - in one room there is a machine for creating a series of images, and in the second room there is a computer control panel.
All information about the types of unilateral sinusitis is presented here.
Contrast agent
At the request of the doctor, before a CT scan, a special contrast agent is injected into the human body to improve the quality of the images. The contrast is usually an iodine-based compound , and this compound is injected into the body intravenously 10-20 minutes before the procedure.
The contrast is a safe substance, and within 12-24 hours it is completely eliminated from the body.
Some people are allergic to certain components of the contrast agent, so a test injection of contrast is recommended before a CT scan.
What catarrhal sinusitis is is described in this article.
Preparation
It is necessary to prepare in advance for a CT scan:
- It is recommended to carry out the examination in the morning on an empty stomach.
- The last meal should take place 5 hours before the procedure.
- It is recommended to donate blood for a creatinine level test 1-2 hours in advance (the test is carried out in the hospital itself).
- Immediately before the examination, you need to remove all metal objects (jewelry, piercings, etc.).
Performance
Computed tomography is done as follows:
- The patient removes metal objects and puts on a special robe.
- The doctor injects contrast into the body intravenously (if necessary).
- The patient lies down on the couch. The doctor fixes the patient's arms and head.
- The doctor leaves the room with the CT scanner and starts the CT scan using a control panel from the next room.
- After the doctor's warning, the couch and the tomograph ring begin to move. During the examination, the person is prohibited from moving (the quality of the images will deteriorate).
- During movement, the human body is irradiated with invisible radiation.
- The duration of a CT scan is either 5-10 minutes (without contrast) or 15-20 minutes (with contrast agent).
- After the examination, the person can go about his usual activities (work, household chores).
- Typically, tomography is well tolerated by the body.
We also recommend that you study the material about viral sinusitis at this link.
Decoding the result
After a CT scan, the doctor must process the information received using special programs. On average, decoding the results takes no more than 2 days . This diagnosis will help to immediately identify and take measures to combat parietal sinusitis. If necessary, after a CT scan, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations to clarify the details. However, such examinations must not use radiation exposure, since frequent radiography causes radiation poisoning of the body.
Indications and contraindications for tomography
First of all, computed tomography of the sinuses is done to diagnose inflammation of the mucous membranes, especially with the formation of pus or recurrent sinusitis.
Other indications for the procedure:
- craniofacial injuries;
- frequent headaches, facial pain, toothaches due to nasal congestion and heavy discharge;
- chronic colds with regular exacerbations;
- repeated nosebleeds not associated with increased blood pressure;
- pain, feeling of fullness in the sinuses;
- chronic rhinitis;
- difficulty in nasal breathing;
- inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct;
- suspicion of a cyst, polyp, abscess, tumor;
- orbital and intracranial complications of infectious diseases of the ENT organs;
- entry of a foreign object into the air cavity;
- suspicion of hemorrhage in the sinuses;
- swelling, pain in the nasal area;
- granulomas, cysts near the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw.
CT scanning of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses is an important measure in planning operations and monitoring dynamics after surgery. Examinations are carried out when treatment for sinusitis is ineffective in order to correct treatment tactics.
Contraindications to computed tomography:
- pregnancy;
- early age (due to the harm of radiation, CT scans are not recommended for children under 5 years of age);
- The patient's weight is more than 150 kg and chest (abdomen) girth is more than 150 cm.
Examination with contrast is not performed if:
- allergies, iodine intolerance;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- severe liver or kidney failure;
- taking metformin in patients with diabetes.
CT scan of the nasal sinuses (frontal section). Arrows indicate thickening of the mucous membranes
Comparison of CT with other diagnostic methods
There are many ways to diagnose organ pathologies: X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, MSCT. Which of these methods can provide more accurate information?
Radiography is currently used as a primary diagnostic method. On an x-ray of the sinuses, purulent accumulations can be clearly seen, but it is not always possible to detect neoplasms, especially small ones. Ultrasound examination is also quite effective in studying soft tissues, but it is almost impossible to determine deformations of the skeletal system in this way.
The most effective diagnostic methods today are CT (MSCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The difference between these diagnostic procedures is in the method of exposure. CT or MSCT of the paranasal sinuses uses X-rays, which are retained in the tissues of the organ with different densities. After this, the resulting difference is detected by detectors and a contrast image is formed. MRI uses electromagnetic radiation. The method for obtaining images is not based on different densities of tissues, but on the difference in hydrogen contained in tissues. It is worth noting that the radiation produced by a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is harmless. However, such a procedure is impossible if there are metal objects in the patient’s body.
Photo tomography of the sinuses
MSCT images show the contours, structure, and density of all parts of the sinuses. Based on the photo, the doctor can assess:
- sinus conditions;
- location of the nasal septum;
- sinus drainage pathways;
- symmetry of the sides of the nose and sinuses;
- degree of pneumatization of the accessory cavities;
- condition of the tear ducts.
CT provides images in a transverse (axial) projection. In a special program, you can enlarge the photo and see the smallest details. Using reformatting, the radiologist reconstructs the image in the desired anatomical plane. Most often, these are two additional projections - coronal (frontal) and sagittal (divides the object into left and right parts). It is also possible to create a three-dimensional model and cut off “extra” fragments, which simplifies the study of the area of interest and facilitates the interpretation of data.
Physician evaluation process of CT scan
CT scan of the nasopharynx for a child
CT scan of the paranasal sinuses of a child with a congenital isolated cleft palate in frontal and axial projections - photo
X-ray examinations in childhood are performed exclusively for health reasons, if the results of other diagnostic methods (endoscopy, MRI) require clarification. The decision is made collectively by doctors of several specialties. CT scans of the nasopharynx for children under 12 years of age are often performed in radiology departments at pediatric clinics. You should not refuse diagnosis because of false health concerns. In some situations (trauma, suspected tumor), the consequences of inaction are worse than a CT scan.
How is the CT procedure performed?
For the session, it is recommended to take with you loose clothing without metal objects that absorb X-rays, distorting the image. Tomography of the paranasal sinuses in the usual mode does not require preparation. If a contrast agent is used, the patient informs the doctor about allergic reactions to iodine preparations and seafood. Preparation for a contrast session includes an 8-hour fasting period.
Computer tomograph
How to do the procedure so that the pictures turn out clear:
- the patient removes hairpins, chains, and glasses from his head and leaves them in the reception room locker;
- if necessary, changes into clothes without metal rivets, zippers and buttons;
- in the X-ray room, the staff helps the patient assume a supine position;
- to obtain accurate images, the human body is fixed with special soft belts;
- the patient's head is placed strictly straight;
- the table with the patient slides under the dome of the device;
- After the scan, the tomograph turns off and the patient goes to another room where he changes clothes.
The procedure takes no more than 20 minutes, after which the patient waits another half hour for the conclusion. The operator uses a computer to transfer information to flash drives. The patient is given x-rays and a CD.
Features of the structure of the maxillary sinus on CT
The shape of the maxillary sinuses resembles a truncated tetrahedral pyramid. On average, the volume of each cavity is 10-13 cm³. The dimensions are not constant and change with the development of the facial skeleton. In a healthy person, the thickness of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses is approximately 1.0–1.5 mm. During inflammatory processes, allergies, and colds, tissues swell and hypertrophy, which contributes to thickening of the walls and a decrease in the volume of cavities. The pathology is clearly visible on CT images of the upper jaw and maxillary sinuses.
The left and right bone cavities are usually symmetrical. But in some patients, examination reveals anomalies, such as the division of the cavity by partitions into several chambers. This structure of the sinus creates certain difficulties in the treatment of sinusitis.
In the CT photo you can see that the maxillary sinuses communicate with the nasal cavity. Mucus is constantly discharged through these anastomosis. In infectious diseases, polyps, tumors and some congenital abnormalities, narrowing of the passages is observed. As a result, the passage of secretion is hampered, and it begins to accumulate in the sinuses, which leads to increased proliferation of microbes and the development of sinusitis.
CT scanning of the upper jaw is valuable not only for studying the structure of the maxillary sinuses. Diagnostics using a computed tomograph makes it possible to study in detail the structure of the alveolar process (the area of the maxillary bone where the teeth are located) and the anatomical and topographic relationship of the roots of the teeth with the bottom of the sinus cavities.
Decoding the results
Experts decipher the results immediately after the end of the session. Clear images allow the specialist to clearly see all the features and changes in the sinuses.
With sinusitis, there is fluid in the sinus lumens, and thickening of the soft tissue of the nose is clearly visible.
If the polyp is single, then the image will show a distinct growth on a small stalk. The formation is localized in the membrane of the axillary walls. With multiple growths, the structure and size of the mucous membrane will be greatly changed.
When a tumor occurs, the bone and cartilage tissue of the nose is destroyed. The sinus will have a heterogeneous destroyed structure during a malignant process. On CT scan, the neoplasm is clearly visualized in the soft tissue.
With odontogenic cysts, a strong darkened spot in the organic structures is observed in the image. Its contours have boundaries. The mucous membrane around the cyst is noticeably thickened. The development of the disease is also indicated by other characteristic signs that the doctor can easily visualize.
A rhinogenic cyst of the maxillary sinus is also characterized by a clear darkening in the tissues adjacent to the sinus wall. Education is homogeneous. Its contours are very clear, but no thickening of the mucosa is observed.
All pathologies are usually well visualized using CT. With tomography, the shadow of the bones is eliminated by the device itself. Therefore, cysts and tumors are clearly visible in the resulting image. To find out the exact boundaries of the formation, you can perform an MRI of the sinuses.