List of indications for MRI examination
A cardiologist recommends MRI diagnostics of the heart if there are dysfunctions of the system and the patient complains of pain in the local area.
Indications for the procedure:
- congenital heart defects (divergence of the great arteries, septal defects, etc.);
- dysfunction of the cardiovascular system (examination with contrast is indicated);
- suspicion of thrombosis, neoplasms on the heart and nearby tissues;
- pericardial cysts;
- progression of exudative pericardium;
- checking the contractility of the heart in the period after myocardial infarction;
- preparatory stage before surgical intervention in the local area;
- postoperative control;
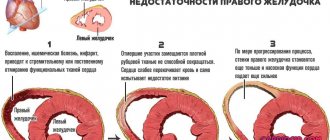
- suspicion of cardiomyopathy, determination of the degree of development of the disease;
- diseases of the main vascular network: aortitis, atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels, etc.;
- monitoring the condition of the pulmonary vessels.
Basic methods of vascular examination
At the moment, modern medicine has a significant list of various laboratory techniques that allow for effective examination. This can be general or highly specialized research.
In each specific case, a certain type of diagnosis will be required. The main methods are presented in the table with the exception of ultrasound diagnostics and magnetic resonance therapy, which are described in more detail below and in the video in this article.
Table. The main instrumental methods for examining blood vessels (without ultrasound and MRI):
| Method | Short description | Important points |
Antiography | This is a contrast X-ray examination of blood vessels, which allows you to study the speed of blood flow, identify blood clots and narrowed areas due to cholesterol deposition, aneurysm, as well as anatomical or morphological anomalies. | The method is quite traumatic and has a wide range of contraindications, for example, thrombophlebitis, heart failure and others. The study requires local anesthesia and tranquilizers. |
Spiral computed tomography | A highly accurate diagnostic method that can only compete with MRI. SCT allows you to examine even the coronary vessels, which cannot be done with conventional CT. The essence is the constant spiral rotation of the table and the radiating tube. The result is three-dimensional images. Contrast can be used. | SCT is not traumatic than the above method, but the person receives a larger dose of ionizing radiation. |
Rheography | In this case, by passing an electrical impulse through the veins and arteries, a graph is displayed on the monitor, which is subject to subsequent decoding. In this way, blood circulation in large vessels is studied. | The method is not dangerous |
Thermography | This study allows you to measure temperature based on natural infrared radiation. Any differences from normal values indicate a pathological process. | The method is not dangerous, however, it is not accurate. Often used as an extra. Helps to identify the initial stages of varicose veins of the legs, when venography is not used due to trauma. |
Phlebography | Contrast x-ray examination of blood vessels, which is indicated for varicose veins, thrombophlebitis and for monitoring after sclerotherapy. | The patient is exposed to ionizing radiation. |
MRI
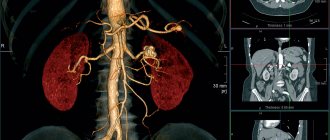
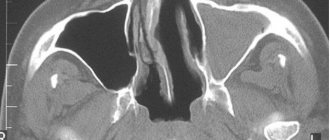
MRI of cerebral vessels
Magnetic resonance imaging, along with CT, is one of the modern and ultra-precise diagnostic methods for studying organs of the human body. It differs from the latter in that the patient is not exposed to ionizing radiation, because the method is based on the analysis of the vibrations of hydrogen atoms in the liquid media of the body under a magnetic field of a certain voltage. The only drawback of this method is its high cost, but the price justifies the accurate diagnosis, which is established after an MRI.
The technique does not require any preliminary preparation and can be carried out at any time. There are quite a few contraindications. People with metal implants and pregnant women should not undergo the study.
People suffering from claustrophobia, as well as children, may experience certain difficulties. In this case, you can find clinics with an open tomograph, which eliminates the factor of fear of closed spaces.
The study lasts approximately 30-45 minutes. The procedure is absolutely painless and does not require the use of analgesics. Instructions on how to behave while in the tomograph will be given by the nurse.
The main condition is that the patient must remain motionless during diagnosis. When using diagnostics with contrast, the substance is first administered by injection or orally.
Note. Sometimes, during MRI, a slight increase in temperature in the organs being examined is possible.
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to see:
- anatomical or morphological pathologies of blood vessels;
- places of their narrowing or expansion;
- the presence of even very small plaques and blood clots;
- identify aneurysms, neoplasms, wall fusions and other anomalies;
- study various features of blood and lymph circulation.
Indications for vascular MRI:
- brain diseases;
- headaches of unknown etiology;
- oncological diseases;
- atherosclerosis;
- stroke or microstroke;
- dissection of large arteries and other pathological conditions.
Ultrasound
Color duplex ultrasound scanning of blood vessels
Ultrasound diagnostics in the general sense is a simple, accessible and fast diagnostic method. All types of ultrasound are non-invasive, do not require special training, and have virtually no contraindications.
During the analysis, the patient can move, usually without any discomfort. The operating principle of the analyzer is determined by the ability of ultrasonic waves to be reflected or absorbed by tissues depending on their density.
When studying blood vessels, more advanced techniques are used, which have their own specifics:
- Doppler ultrasound (USDG). This method reveals vascular tone, structural transformations and pathologies associated with impaired blood flow (ultrasound is reflected from red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets). In some cases, there are some peculiarities, for example, when examining the head, it takes about half an hour, but the contour of the vessels itself is not determined, and the results obtained are deciphered based on secondary signs.
- Color duplex scanning of blood vessels is one of the subtypes of Doppler analysis, showing the dynamics of blood flow. Most often used to diagnose veins and arteries of the head, neck, and legs. The essence of the method is a combination of the properties of ultrasound and the Doppler effect. This determines the presence of blood clots and plaques, stenosis and other abnormal phenomena. As a result, the doctor sees the arteries in red and the veins in blue on the computer, as shown in the photo below.
- Intravascular ultrasound examination. This diagnostic method is often in demand in cardiology. It is especially important when performing operations on the heart or large arteries, because the method provides a more accurate representation of the pathological condition than with angiography and has a smaller list of contraindications. The technique is carried out in the same way as with other endoscopic techniques: a catheter with a microscopic ultrasound analyzer is delivered into the blood vessel, which, moving along the channel, transmits an image to the monitor. Thus, this type of diagnosis is slightly invasive. Its main purpose is to control the therapy performed to remove atherosclerotic pathologies and treat coronary heart disease.
Contraindications for MRI diagnostics of the heart
The examination is usually well tolerated by patients and does not cause adverse reactions. However, there are a number of factors that can reduce the quality of the diagnostic result and can harm the patient.
The first group of contraindications includes absolute restrictions on the procedure:
- claustrophobia;
- neurological disorders;
- the patient’s serious condition as a result of the course of the disease;
- heart failure;
- the presence on the patient’s body of tattoos containing “metallic” dye.
- pregnancy (1st trimester)
The second group of contraindications includes conditional restrictions. This means that if you follow medical recommendations, diagnosis when they are detected is quite possible. In this list:
- the presence in the patient’s body of metal elements (staples, implants, pins, clips, fragments, bullets, etc.) and electronic medical devices (pacemaker, etc.);
- allergic reaction to a contrast agent (during a detailed MRI examination).
Excess weight of the patient (more than 120 kg) can also limit MRI diagnostics. In such a case, they resort to the use of specialized equipment.
The possibility of performing an MRI after bypass surgery is permitted after 1.5 months, otherwise it is contraindicated.
Preparing for an MRI
MRI of the heart and blood vessels does not require special preparatory measures. Women of childbearing age should be sure that they are not pregnant. People suffering from kidney and liver diseases are required to undergo preliminary tests.
Immediately before the MRI scan, you need to get rid of metal objects (jewelry, glasses, watches, etc.).
If a contrast study is planned, the patient should refrain from eating and drinking 6-8 hours before the procedure. In some cases, before the tomography, the specialist prescribes sedatives to the patient.
Progress of the examination
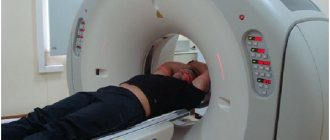
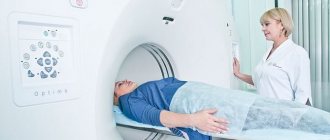
MRI is performed according to the following plan:
- Before entering the diagnostic room, the patient is convinced that there are no metal elements on the body.
- The patient changes into disposable clothing and lies on the tomograph table.
- In order to ensure the immobility of the subject, his head and limbs are secured with special belts.
- The movable table, together with the patient, moves inside the equipment - a magnetic cylinder.
- The tomograph ring begins to move, the device makes noise (if necessary, the patient is given headphones or earplugs).
- The examination time is 30-60 minutes (depending on the type of scan).
- At the end of the MRI diagnostics, the table is pulled out, the patient is released from the straps - he changes clothes and leaves the office.
During the examination, the patient does not experience discomfort and remains completely motionless. If health deteriorates inside the tomograph, the patient can contact a specialist using a microphone equipped inside the tomograph.
When is contrast needed for MRI?
When diagnosing arteries and other vessels, it is impossible to obtain reliable results using traditional MRI.
To study diseases of this type, it is necessary to use a contrast agent. The substance stains blood vessels and demonstrates a clear clinical picture.
This measure is resorted to when it is necessary to timely identify the risk of myocarditis, heart attack and assess the post-infarction state. Contrast is administered intravenously before placing the patient in the tomograph.
Differences between ultrasound and MRI
- They use different physical phenomena: ultrasound and magnetic field, respectively.
- MRI requires expensive and large equipment; ultrasound can be easily done at the patient's bedside.
- Ultrasound does not see organs behind the bones; with MRI, you can get a projection of the organ in any given plane.
- MRI is a longer procedure; during it ( 30-60 minutes ) you must lie still.
- A specialist is needed to interpret ultrasound results; with MRI, image processing is performed by a computer, and the human factor is reduced to a minimum.
- Images obtained with MRI are usually of better quality , all structures can be studied in more detail, changes in tissues are noticeable earlier than with ultrasound. This makes it possible to identify the disease at an early stage, which improves the prognosis and facilitates treatment.
- Ultrasound can be performed while performing physical activity (stress test, when a person pedals a bicycle ergometer or walks on a treadmill), MRI - only at rest.
What are the advantages of MRI diagnostics of the heart?
MRI is an expensive method that justifies itself due to its level of safety and information content. Advantages of magnetic resonance imaging:
- helps to diagnose the smallest pathological processes at the initial stage of their development;
- eliminates radiation exposure to the patient’s body;
- the contrast component used in MRI rarely causes an allergic reaction (unlike iodine-containing drugs);
- no pain.
Alternative diagnostic techniques
MRI is far from the only method for diagnosing cardiac pathologies. If there are contraindications to tomography, the specialist’s responsibilities include finding an alternative way to examine the patient.
For example, in case of suspected development of a malignant neoplasm, magnetic resonance imaging is required, however, if scanning is not possible, CT is preferred.
MSCT is suitable if specialists do not need to make a differentiated diagnosis, but only confirm it based on other symptoms.
When there is a need to establish the fact of the development of a cancerous tumor, preference should be given to PET-CT. In some cases, coronary angiography is advisable.
CT is the most harmful method
Another alternative diagnostic method is ultrasound. For example, ultrasound during pregnancy in the 1st trimester is the best option if surgical examination is necessary.
However, you will have to count on receiving general information about the state of the organ (not including data on the ventricles and atria, septa and other structural elements).
It’s impossible to say for sure which is better. The choice of technique depends on the indications, features of the clinical picture, the patient’s condition and the results of previous examinations.
How often can I do it?
When there are no contraindications to the study, doctors can prescribe, depending on the pathology and the characteristics of its course, scanning as often as required by the treatment regimen: to obtain the optimal course of treatment and its adjustment.
The safety of the procedure has been proven; it is allowed to be carried out at minimal intervals. The frequency of scanning is determined by the attending physicians. However, if there is an urgent need or according to the treatment plan, MRI examinations can be performed several times during the day.
Cost of MRI examination
The price of the procedure starts from 6,000 rubles. The cost is determined by taking into account the level of equipment used, the qualifications of medical personnel, the examination area and the type of diagnosis. The use of contrast is added to the price tag separately.
Due to the safety and painlessness of the cardiac MRI procedure, it can be performed on both children and adults.
The level of information content of magnetic resonance diagnostics turns out to be an order of magnitude higher than in the case of alternative techniques.
Coronary angiography
The procedure helps to diagnose pathologies of the heart and nearby tissues, assess the condition of the structural elements of the organ, and the level of functionality of the system. The list of contraindications is standard. There are no preparatory activities on the eve of the study.
Diagnostics takes from 30 to 60 minutes. If it is necessary to assess the condition of the vascular network, a contrast component is used.
The result is given to the patient and transferred to the attending physician for diagnosis and planning of a therapeutic course. Alternative methods can be offered: ultrasound, MSCT, coronary angiography, PET-CT.
How does the procedure work?
After completing the preparatory stage, the nurse guides the patient to the equipment.
During the procedure, you need to know its features:
- The person being examined is placed on the table.
- The nurse secures the patient with belts, fixes him to prevent any movements, since even the most minimal movements can blur the image, and the procedure will need to be repeated.
- If necessary, the area to be examined is secured using a special coil.
- During operation of the equipment, a specific noise is produced by the tomograph. In some diagnostic centers, to prevent patients from reacting to sound, they are given headphones with music playing, which also serve to convey instructions to the doctor conducting the scan.
MRI of the heart shows the structure and function of the organ. The examination results are processed immediately after the procedure. The patient receives a photograph captured on film or disk.
The examination conclusion is issued by a radiologist. Sometimes processing a document can take half an hour. Some diagnostic centers practice issuing a conclusion the next day; it is possible (if desired) to send it by email.
After the procedure is completed, the person being examined can ask the doctor any questions they may have. The approximate time for conducting a study in a closed-type tomograph with a high level of magnetic field voltage (1.5 Tesla) is 15-20 minutes.
A similar study, but on an open-type apparatus, takes up to 40 minutes. Diagnostics on lower power devices can take up to 60 minutes.