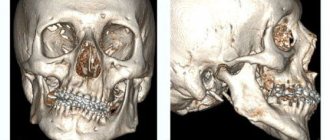
Before the introduction of 3D CT of teeth in St. Petersburg, orthopantomography was the leading method for studying teeth, jaw, and oral cavity. The advantages of CT are three-dimensional modeling of the area under study, which allows every millimeter of tissue to be examined with maximum accuracy in a spatial image. Maxillofacial surgeons and dentists use a 3D model to evaluate the nature of the pathology and choose treatment tactics.
Cone-beam tomographs are considered the gold standard for dental diagnostics. The equipment allows for detailed examination of the oral cavity, but does not indicate fine details when compared with a CT scan of the head.
Digital X-ray is a planar image. A three-dimensional computed tomogram is a model of the dental system that helps predict the progress of implantation, prosthetics, and correctly remove damaged teeth. Low radiation allows scanning to be used in children and adolescents to detect unerupted rudiments and identify anomalies.
Operating principle
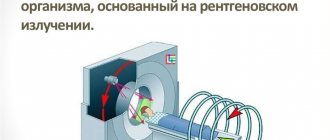
All tomographs for CT diagnostics of dental units are based on the measurement and software processing of the difference in the transmission of an X-ray beam through tissues of unequal density. Currently, dental computed tomography of teeth is the leading method of dental research using x-rays.
A dental CT scan is much more informative than a classic x-ray of the dental system. With its help, you can get a targeted image of a bone segment and an orthopantomogram - an image of all the teeth in the oral cavity at once. A very convenient diagnostic method when “global” restoration is required.
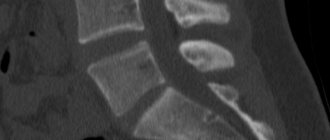
What does a dental CT scan look like? The picture is a three-dimensional model that helps to visualize bone tissue, roots and canals of teeth, bundles of nerve fibers, and the maxillary sinus. In other words, a photograph allows you to see what is hidden from view. In this case, the teeth, as a denser component, will be white, and the soft tissues, depending on the density, are determined by different shades of gray and black.
Oncological center in Moscow
Oncological Center in Moscow ¦ Oral Cancer
Despite its rarity (the disease accounts for approximately 3% of the total number of cancer patients), oral cancer poses a serious danger. The disease is diagnosed both in smokers and in people who never use tobacco products, but still the main risk group consists of the first category. The main cause of oral cancer is smoking of any type of tobacco products, the use of chewing and pipe tobacco.
It is worth noting that in the Russian Federation alone, up to 30 thousand cases of oral cancer are registered every year. As for the countries of Southeast Asia, in addition to regular smoking, chewing regular tobacco and drinking betel nut are widely practiced, so the number of patients exceeds 50,000. Alcohol abuse appears to be an aggravating factor.
Like most malignant neoplasms, oral tumors are not a death sentence for the patient. But in order to get rid of the disease you need to be conscious and vigilant. The key to successful treatment, as in any other case, is early diagnosis and treatment. The oncology center in Moscow provides effective treatment for this disease. Survival rates with early diagnosis approach 100%. Neoplasms of the oral cavity are very diverse, but their additional threat is associated with localization. The proximity of the upper respiratory tract, the brain, as well as the intense blood supply pose a considerable danger.
Tumors of the oral cavity, like other neoplasms, can be benign or malignant. They develop from various tissues of the dental system: muscles, epithelium, blood vessels, nerves and bones. Sometimes oral tumors are metastases of other tumors located more distantly (for example, the prostate or lungs).
Forms of the disease
Visually, oral cancer can take different forms. Modern medicine divides all types of disease into three groups based on appearance:
- knotty;
- ulcerative;
- papillary.
Half of all oral cancer cases are diagnosed as non-healing ulcers on the oral mucosa. The ulcer quickly increases in size.
With the nodular form of cancer, a compaction forms in one of the areas. If we talk about the mucous membrane located above it, then it either does not change or becomes covered with whitish spots. These seals are nodules with a very clear shape. They are characterized by rapid growth.
The neoplasm in the papillary form looks like a dense growth that hangs into the oral cavity. Its surface is usually covered with unchanged mucous membrane. This type of tumor is most treatable due to the fact that the disease does not spread to nearby tissues.
Types of oral cancer:
- tongue cancer;
- cancer of the floor of the mouth;
- cancer of the buccal mucosa;
- cancer of the palate.
Most often, tongue cancer occurs on the lateral surface of the tongue, less often on the lower surface, back and tip. As for the root of this organ, the disease affects it in approximately 40% of cases. Squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue arises from the minor salivary glands.
Patients usually discover this type of cancer on their own, with the only exception being neoplasms of the distal parts. This is facilitated by early-onset disturbances in swallowing, speech, and chewing, and pain increases over time.
If we talk about cancer of the distal parts, it manifests itself as breathing problems due to blockage of the oropharynx. The lymphatic network in this area is very well developed, so the disease very quickly metastasizes to regional lymph nodes. In some cases, they are detected even earlier than the tumor focus.
With oncology of the floor of the mouth, rapid tumor growth is observed, spreading into the lower surface of the tongue, into the salivary glands, and into the muscles of the oral cavity. In addition, the disease spreads throughout the artery system of the tongue. Patients may detect a node with a tumor as a foreign growth; over time, pain, increased salivation, metastases and bleeding appear.
Oncological diseases of the buccal mucosa are characterized by the formation of a tumor at the level of the line of mouth closure, the corner of the mouth, as well as in the retromolar region. Cancer quite often masquerades as an unremarkable ulcer. In the later stages, pain occurs when swallowing, talking, chewing; if the tumor grows into the internal pterygoid or masticatory muscle, then the patient’s mouth opening is limited.
Symptoms
The appearance of a pathological focus in most cases is called the first symptom of the disease. Most often, such manifestations are not accompanied by pain. The tumor can be located on the inner surface of the cheeks, tongue, and also in the salivary glands. At the early stage of tumor formation, the patient may experience mild pain in the area of the affected area. The pain may intensify as the tumor grows, radiate to the ear or temple, and over time becomes painful for the patient. In addition, the disease may be accompanied by difficulty swallowing and chewing food, and increased salivation. In the later stages, a sign of oral cancer may be bad breath (indicative of infection and tumor disintegration).
Stages of the disease
There are four stages of oral cancer. The difference between the stages lies in the size of the tumor, as well as the presence of metastases.
Diagnostics at the oncology center in Moscow
Experts recommend in any case to conduct a self-examination of the oral cavity in order to promptly identify any deviations from the norm. Due to the fact that there are areas that are very difficult to examine, you should visit the dentist every six months for a thorough examination. If alarming symptoms are detected, it is imperative to conduct an unscheduled examination of the oral cavity. If suspicious factors are detected at the oncology center in Moscow, doctors perform a biopsy. In this case, no special surgical intervention is required; tissue samples for research are collected in an office setting. The presence of metastases in the cervical lymph nodes is determined by palpation and confirmed by biopsy.
When examined by a maxillofacial surgeon, the following procedures may be prescribed:
- pharyngoscopy;
- nasopharyngoscopy;
- X-ray of the chest, skull bones;
- PAT;
- blood biochemistry;
- laryngoscopy;
- biopsy with cytological and histological examination;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- scintigraphy;
- CT;
- MRI.
Treatment of oral cancer at an oncology center in Moscow
When treating tumors of the oral cavity (cancer of the tongue, oropharynx, nasopharynx, etc.), various treatment methods are used. These include surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Doctors at the oncology center in Moscow choose the ideal treatment method/methods depending on the type of tumor and stage of the disease.
Radiation therapy
Malignant neoplasms of the oral cavity respond well to radiation therapy. In some cases (for example, small tumors of the oropharynx and oral cavity), this technique works as the main one during treatment. Often, radiation therapy complements surgical treatment, its goal is to eliminate swallowing difficulties, relieve pain, stop bleeding, or destroy remaining infected cells.
Separately, it should be noted that neoplasms of the oral cavity are often treated with internal radiation (brachytherapy). The essence of this technique is that rods with radioactive material are injected directly into the tumor or into neighboring tissues for some time.
Chemotherapy
This method is used to reduce the size of the tumor. Specialists at the oncology center in Moscow prescribe drugs to patients that have a detrimental effect on tumor cells. Chemotherapy is used in combination with surgery or radiation. The choice of drugs to treat the disease is determined by various factors: the stage of the tumor, age, the body’s response to such treatment, etc.
Surgical intervention for oral tumors
The type of surgical intervention to remove a tumor is determined taking into account the type of tumor, its location and stage of the disease. In addition, doctors at the oncology center in Moscow take into account the need to perform restorative (reconstructive) interventions after removal of the tumor. The purpose of such manipulations is to restore the aesthetic effect and lost functions.
Risk factors
It should be noted that oral tumors are six times more common in people who regularly drink alcohol. As is known, oral cancer is a disease that occurs mainly due to external factors. Therefore, it is important to know the reasons for their development. Today, modern medicine knows for sure about the causes that can provoke this disease:
- drinking alcohol (the risk is six times higher than the risk of cancer in people who lead a healthy lifestyle);
- chewing tobacco, smoking (the vast majority of patients with oral tumors are smokers; chewing tobacco provokes cheek cancer, smoking a pipe causes lip cancer; oral tumors are often found in passive smokers);
- a diet low in vegetables and fruits (increases the possibility of tumor formation);
- constant exposure to ultraviolet radiation (for example, prolonged exposure to sunlight) increases the likelihood of developing lip cancer by 35%;
- chronic damage to the mucous membrane (use of low-quality dentures or tube mouthpiece).
Most often, cancers of the oral cavity have a squamous cell structure, much less often - adenocarcinomas. Approximately 95% of all oral cancers are squamous cell carcinoma.
Quite often, various precancerous processes develop in the oral cavity, which over time degenerate into malignant forms. These conditions include Bowen's disease, which is characterized by the appearance of yellowish-brown plaques with an uneven surface. In such plaques, histological examination often reveals atypical cells. Therefore, doctors at the oncology center in Moscow consider Bowen's disease as a precancerous condition.
Cancer of the oral mucosa is considered one of the most difficult types of cancer. It spreads at a rapid pace, destroying surrounding tissues and changing the anatomical structure. During the course of the disease, ulcers form, often taking the form of deep fissures. This form of cancer is extremely aggressive. At the same time, cancer of the mucous membrane of the anterior half of the oral cavity is not as intense as that of the anterior half. It should also be noted that it is much more difficult to treat cancer in the back of the mouth than in the front.
Like other diseases, oral cancer is easier to treat when it is diagnosed in the early stages. Large lesions are treated with radiation or surgery. A combined approach to treatment is used at the PET CT center in Moscow when large areas of lesion are detected. The ideal method of preventing oral cancer is undoubtedly the avoidance of risk factors (alcohol and tobacco) and timely prevention.
Forecast
Doctors say that the prognosis always depends on the form of cancer: the ulcerative form of the disease is the most unfavorable and difficult to treat. The highest rate of complete cure is given by the papillary form, and cancer of the posterior parts of the oral cavity is more malignant than cancer of the anterior parts and oncology of the lip.
For lip cancer, the five-year survival rate is 90%, for oral cancer - approximately 65%, which is a fairly high figure.
(495) 506-61-01 — urgent organization of treatment in the clinic
REQUEST TO THE CLINIC
Indications and contraindications
A description of computed tomography of teeth today is required by dentists of various specializations before implantation, for the prevention and treatment of dental diseases or to identify the causes of pain of unknown etiology.
Dental tomography may be prescribed in the following cases:
- jaw injuries,
- congenital structural defects,
- incorrect bite, more about bite→
- presence of unerupted teeth,
- inflammation of the temporomandibular joint,
- detection of cracks and other damage to the tooth root,
- tumor neoplasms in bone and soft tissues.
One of the important indications for a CT scan is the removal of a wisdom tooth. A tomogram makes it possible to assess the condition of the root, see the interweaving of nerve fibers, and, in the case of a tooth lying under the gum, determine which side is best for removal.
Advantages and disadvantages
CT diagnostics of teeth is by far the best study that helps detect many periodontal diseases. Instead of taking x-rays several times, the patient can get a complete picture of the condition of the teeth in one office visit with a tomograph.
Other advantages of dental tomography:
- takes minimal time,
- allows you to see a layer-by-layer section of the jaw in a three-dimensional image with visualization of the smallest details,
- makes it possible to take accurate measurements and select the implant of the required size,
- facilitates positioning during transplantation,
- CT scan results can be saved on digital media,
- eliminates the need for repeated research.
In addition, a CT scan of the teeth allows you to accurately determine the source of pain, even if it is unclear and occurs from time to time.
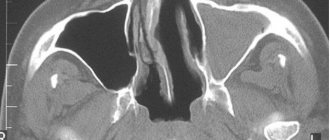
Another advantage of CT diagnostics is the ability to obtain a panoramic image of the jaw. This image simultaneously covers the lower and upper jaws with the temporomandibular joints, sinuses and nasal bones.
The only disadvantage of dental tomography of teeth is the high cost of the procedure.
What does a CT scan show?
A visit to an orthodontist, implantologist, maxillofacial or plastic surgeon most often ends with a referral for a tomography. A 3D dental image gives a complete picture of the condition of the patient’s jaw, because the doctor gets the opportunity to examine the object in three dimensions, rather than in a flat image. The difference from an orthopantomogram is precisely this: the doctor sees a three-dimensional image, without any distortion.
The picture shows a kind of virtual layer-by-layer slice, available for inspection in any projection. You can examine soft and bone tissue layer by layer without performing traumatic additional procedures. The picture is complete enough to accurately assess the condition of the jaw and teeth and establish a diagnosis for the patient.
How harmful is a dental CT scan?
Any radiation is harmful to the body. Dental CT is no exception. True, the radiation dose during this type of examination is minimal.
X-ray radiation standards are regulated by SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03, which states that during 1 CT session the patient receives only 40–50 μSv. And this is with a permissible dose of 3500 microsieverts per year. Even a panoramic CT image of teeth produces 10 times less radiation than standard radiography. With such a radiation exposure, almost 100 tomographies can be performed per year without harm to health.
Therefore, when a doctor prescribes a dental CT scan before implantation, there is no need to refuse. The radiation received during the examination is minimal, but the harm from neglecting the procedure can be unexpectedly great.
Carrying out the procedure
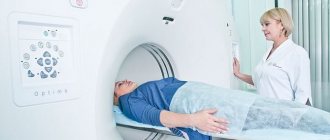
Tomography of the dental jaw does not cause problems for patients. CT scans are most often performed in a standing or sitting position. In this case, the chin is placed on a special support-fixator, the head is fixed in a stationary position. A protective apron is placed on the patient's chest.
During CT diagnostics, the radiation source and detector rotate in unison around the head of the subject. A panoramic image takes 20–40 seconds, a CT scan of a dental segment is performed even faster – in 7–10 seconds. All this time you cannot move or swallow saliva.
In one revolution around the patient’s head, the device manages to take more than 200 high-resolution three-dimensional images. Then the CT image of the upper and lower teeth is processed by a computer and displayed on the screen as a clear image.
Indications for CT scanning of the jaw
- carrying out differential diagnosis of complications of dental caries;
- obtaining additional information to choose the optimal treatment method;
- prediction and assessment of long-term results of implantation in patients;
- assessment of orthopedic treatment;
- obtaining cephalometric data for planning orthodontic treatment in children;
- planning of surgical interventions in maxillofacial surgery, dental surgery, otorhinolaryngology;
- monitoring the condition of tissues in the postoperative period.
Decoding the results
Photo from the site stoma9.ru
A dental CT scan is interpreted by a radiology specialist. Processing the images takes 15–20 minutes, then the images, along with digital media and a written report, are handed over to the patient.
The description of a dental CT scan contains a lot of useful information for the dentist. A tomograph helps to identify the following changes:
- Hidden pathologies. Detection of disease processes is possible in the early stages, when symptoms have not yet appeared. The image clearly shows tumors, cysts, abscesses and other formations.
- Anomalies in the structure of bone tissue (congenital or acquired). The information is of great value when preparing for dental implantation.
- Localization and size of inflammation. The 3D picture clearly shows the lesion with clear boundaries. The nature of the inflammation is also visible.
It is necessary to take into account that the information content of deciphering different localizations of dental CT scans is very different. An example can be seen in the table.
| CT segment of teeth | CT scan of one jaw | CT scan of two jaws |
| Information content is low. CT scan shows the condition of a small area of the jaw, usually 3–5 teeth | The information content is high. The CT image shows only the teeth of the lower or upper jaw | The information content is high. CT visualizes the condition of the entire dental system, including the chin and sinuses |
The table shows that the most informative is a CT scan of two jaws at once. Thanks to the resulting transcript, it is possible to perform prosthetics or implantation of several teeth at once, as well as carry out orthodontic measures and eliminate adentia.
What X-ray equipment is needed for 3D images?
X-ray diagnostics, which make it possible to obtain 3D photographs of teeth, are carried out using modern digital devices with minimal radiation. The procedure takes place using a computed tomograph using ultra-sensitive detectors. This helps to obtain accurate results and study the oral cavity in detail.
Digital X-ray diagnostics, in addition to detailed visualization of the jaw, provides information about the following anatomical structures:
- paranasal sinuses;
- three walls of the nasal cavity;
- nasal septum.
The structures can be seen in 5x5 cm or 8x5 photographs. In the absence of such images, it will not be possible to carry out high-quality dental implantation.
In addition to the device, specialized software is needed to obtain results. The task is to show the condition of the dentition, to identify hidden pathologies and diseases in the initial stage of development. If necessary, a computer installation performs a multilayer study and presents the dentition in ten projections.
How often can a dental CT scan be done?
The frequency of dental computed tomography of teeth is also regulated by SanPiN (2.6.1.1192-03). The document states that the procedure can be performed 2 times a year, and the interval between scheduled CT examinations of the teeth should be 12 months. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the type of tomograph, the individual characteristics of the body and accompanying circumstances.
Digital diagnostics is considered the safest type of dental tomography for dental implantation. The procedure using a film machine is more harmful, so it is recommended to do it as rarely as possible.
Some patients are interested in the validity period of a dental CT scan. There is no such concept in dentistry. The doctor can prescribe a diagnosis at any time if there is evidence for it.
Price
The cost of a dental CT scan depends on many factors. This includes the number of teeth being examined, the type of apparatus, and the need to transfer a digital image to film or recording on a medium.
The average prices for cone beam tomography of teeth are as follows:
- CT scan of a segment of 3 teeth - 1500 rubles,
- CT scan of the jaw on one side - RUB 2,700,
- CT scan of the upper and lower jaw on one side - RUB 3,700,
- CT panoramic — 4500 rub.
A complete tomogram of the teeth of both jaws and sinuses ranges from 5,000 to 5,500 rubles. If a dental CT image is performed on a simpler device, the cost of all services will be 1000–1100 rubles lower. Additional recording of results on flash media is estimated at 100 rubles.
It is obvious that CT dental diagnostics is a simple but effective procedure. The quality of the research largely depends on the completeness and accuracy of the transcription. Without dental tomography, it is very easy to make a mistake, which will then have to be difficult and time-consuming to correct. That is why CT examination should not be neglected. Otherwise, all material costs for treatment may be in vain.
Author: Elena Medvedeva, doctor, especially for Karies.pro
How to prepare for a CT scan
If you are about to undergo a CT scan of the jaw, no special preparation is required. There is no need to limit yourself in food or drink. Be prepared to stand or sit still for some time. Directly at the appointment, you will be asked to remove all metal jewelry - this is necessary so that the metal does not interfere with the operation of the device and does not distort the diagnostic results.
“I remember when I underwent a CT scan, they immediately asked me to remove all metal jewelry. It was necessary to stand still; in my opinion, it was impossible to even swallow saliva. But it’s only half a minute, so it’s tolerable. I didn’t see anything wrong with the procedure itself. Yes, the device made a buzzing noise, but it didn’t scare me. Personally, I took a picture before implantation, but I did not go to the clinic, but to the diagnostic center...”
Marina_74, Samara, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru.
By the way, you cannot undergo such an examination with metal braces in your mouth - the picture will turn out to be of poor quality, and the fastenings of the braces may become loose. In this case, it is better to choose an alternative diagnostic technique.