In modern medicine, computed tomography is actively used to diagnose various diseases. Using CT equipment, doctors can identify diseases such as:
- benign and malignant tumors;
- diseases of the heart and the entire cardiovascular system;
- thrombosis, hemorrhage;
- pneumonia, stomach ulcers, atherosclerosis and others.
Computed tomography provides an opportunity to see pathological changes in various systems of the human body and promptly select an effective treatment regimen. But the specifics of diagnostics do not allow it to be used for all patients. It should be taken into account that CT has contraindications for use in a number of cases, which limits the use of the tomograph for certain categories of patients. Before prescribing any examination, especially one involving x-ray radiation, the doctor should always examine the patient's medical history to identify contraindications.
What is computed tomography?
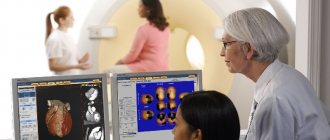
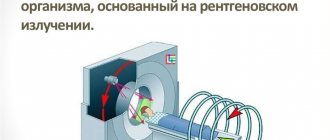
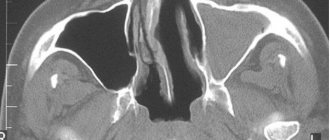
Computed tomography is a method of radiation diagnostics, the essence of which is layer-by-layer scanning of a certain area of the human body with a narrowed beam of X-rays. When radiation passes through biological tissue, it is attenuated according to their density and atomic composition. This is recorded by special sensors and converted into a digital signal.
As the study progresses, a series of images of organs or anatomical structures is taken, which is subject to computer processing for the purpose of image reconstruction . The latter have a three-dimensional structure and are highly informative.
Help The sensitivity of CT in relation to small differences is 10 or more times higher than that of conventional radiography.
What contrasts are used for CT
As a rule, various iodine-containing preparations are used to increase the contrast of the resulting image. All of them are divided into two groups - fat-soluble and water-soluble. Medicines of the first group are very viscous, so their use is limited. They are administered only locally, for example, into the peritoneal cavity to identify fistulas, etc. If we are talking about computed tomography with bolus contrast (the drug is administered into a vein with a special injector) or about the drug being administered orally, water-soluble contrast is used. The toxicity of such drugs is several times lower, and they also quickly enter the blood vessels.
#!KTseredina!#
Restrictions
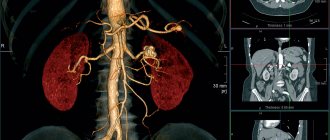
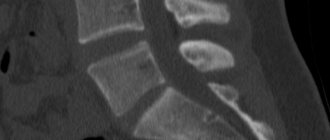
Computed tomography can be used to diagnose diseases of the abdominal organs - liver, spleen, pancreas, gall bladder, stomach and intestines, abdominal aorta.
Despite the fact that the method allows the doctor to obtain important information about the condition of the internal organs, the indications for its use are strictly limited.
- This is primarily due to the negative impact of ionizing radiation on the patient, which can accumulate in the body.
- In addition, to enhance image clarity, especially when examining vessels or suspected highly vascularized formations ( tumors ), a special enhanced CT technique has been developed. It is carried out after intravenous administration of a contrast agent to the patient, which is associated with additional risks. After all, contrast is an inert, but foreign substance, and the reaction to its introduction into the body can be different for each person. Some people do not experience any unpleasant sensations, while others experience severe reactions similar to allergies.
How does computed tomography work?
Indications for the study
The main indications for the study are:
- Head injuries;
- Brain pathologies;
- Spinal cord pathologies;
- Violation of the integrity of the spine;
- Diseases of the ENT organs;
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- Diseases of the reproductive system;
- Pathologies of the respiratory system;
- Musculoskeletal disorders;
- Pathologies of blood vessels and lymphatic system;
- Violation of the integrity of the bone structure and other diseases.
Despite the many positive aspects of the study, such as non-invasiveness, speed of execution, and good tolerance of the procedure, CT has contraindications, like any other instrumental examination:
- Pregnant women. Computed tomography is an absolute contraindication for examining pregnant women. If there is documentation that a woman will soon have a baby, the doctor tries to delay the examination and reschedule it. In emergency situations, the procedure should be replaced with a non-radiation diagnostic method. Such extreme caution is due to the fact that even small doses of X-ray radiation can have a detrimental effect on the condition of the baby’s growing body;
- Children. A relative contraindication for CT scanning is age under eighteen years. A child’s body is five times more susceptible to any type of radiation, and it is not always possible to reduce the dosage. Computed tomography is not prescribed due to the fact that the tissues of a growing body contain a lot of water (compared to adults), which makes it difficult to diagnose various pathologies. But if other diagnostic methods cannot provide sufficient information about the child’s disease, then the specialist may decide on the need for a computed tomography scan. Very often, radiologists in such situations resort to the help of anesthesiologists who intravenously inject the child with sedatives (sedatives) or even prescribe anesthesia;
- People with increased body weight. Sometimes performing a computed tomography scan can be difficult in patients with excess body weight. This is due to two factors
- The CT scanner is not designed to support a weight greater than 150 kg;
- Excess fat makes it difficult to visualize some organs and systems, for example, the pelvic and abdominal organs.
- Patients with increased body weight are recommended to go to clinics that have an open-type computed tomograph - such equipment has no weight restrictions;
- Plaster and metal objects. If the patient has plaster or metal inserts in the examination area, computed tomography is not performed, since glare or darkening may appear on the images, which will complicate the diagnostic examination of diseases;
- Inappropriate behavior and mental disorder. If the patient is in a violent state and cannot calm down, or has a history of mental illness, then scanning such a patient will be difficult - he will not be able to remain still during the entire study. Or the doctor can wait until the person calms down. In some cases, sleeping pills, sedatives, or even general anesthesia are used. This state should be maintained for twenty to thirty minutes until the study is completed.
At the Yusupov Hospital, computed tomography scans are performed daily for hundreds of people with various pathologies. The level of medical qualifications allows us to give a competent opinion even in the most difficult diagnostic situations. At the Yusupov Hospital, emergency examinations are carried out even at night; for this purpose there is a special team, which includes a radiologist.
Radiation dose
During the study, the person is exposed to radiation. The radiation exposure may vary. It is impossible to say exactly how much it will be for each patient, since it depends on many parameters. On average, the radiation dose ranges from 15-50 mGy. However, it differs in locality, because the beam of X-rays during CT passes through a narrow layer of tissue. As a result, organs that do not fall within the scanning area are practically not irradiated.
In medicine, there are several parameters to describe the radiation dose. Let's look at the most important of them.
Table 1. Dosimetric parameters for CT.
| Term | How is it designated? | What does it mean | What role does it play? | In what units is it measured? |
| Local dose | CTDI | Average radiation dose within the scanned volume | Determined by the technical capabilities of the device and the scanning protocol. In modern tomographs, such information is displayed on the screen. This allows you to compare and adjust the dose at different scan parameter settings. | mGy |
| Total scanning dose | DLP | Product of local dose and length | The indicator takes into account not only the average dose inside the object, but also the length of the scanned area. It makes it possible to calculate in advance what radiation exposure the patient will receive when examining a particular organ. | mGrhsm |
| Effective dose | E | Radiation risk | With the help of special computer programs, through mathematical modeling, it is possible to calculate the risk of exposure to ionizing radiation for a patient (standard man or woman), and also compare it with other x-ray studies. | mSv |
It seems, why does an ordinary person need these indicators? Of course, their knowledge and understanding is more necessary for specialists. But, if a potential patient is interested in what dose of radiation he can receive during the procedure, he should still familiarize himself with them. Below we present a table with average radiation doses during the study of various organs and anatomical areas. The main differences will be indicated taking into account the main parameters of the radiation dose.
Table 2. Average exposure dose in surveys from different countries compared to European Union guidelines. EU – European norms, G – German review (Glansky, 2001), A – Austrian review (Novotny, 2002).
| Organ | CTDI, mGy | DLP, mGrxsm | E, mSv | |||||
| G | A | EU | G | A | EU | G | A | |
| Neck | 38 | 33 | – | 603 | 638 | – | 2,4 | 2,4 |
| Thoracic cavity | 18 | 15 | 30 | 415 | 326 | 590 | 6,4 | 4,7 |
| Abdomen | 21 | 15 | 45 | 748 | 469 | 780 | 12,9 | 8,6 |
| Liver | 21 | 16 | – | 327 | 321 | – | 5,9 | 5,9 |
| Kidneys | 21 | 17 | – | 327 | 383 | – | 5,9 | 6,2 |
The absolute values of the radiation dose during CT directly depend on several factors:
- scanning parameters (image quality, slice thickness, number of slices, size of the study area);
- time (the longer the scan takes place, the higher the dose);
- characteristics of the tomograph (each device indicates the local radiation dose, but the more modern the tomograph, the lower it is);
- sensitivity of organs and tissues to the effects of ionizing radiation.
They can be from 5 to 100 times higher than with radiography of the same anatomical area. This highlights the importance of customizing scanning parameters. In each specific case , by selecting the optimal scanning protocol, the specialist reduces the radiation dose to the patient.
Please note: In obese people, with an increase in the diameter of soft tissues for every 4-8 cm, the dose is doubled. While for thin patients it, on the contrary, can be reduced.
How to remove radiation after a CT scan
The radiation dose after diagnosis may vary depending on the organ being examined and the type of computed tomography.
Harmful effects are rarely observed, but if the patient has an irresistible desire to get rid of the radiation received, this can be done by following a diet. List of products that will help remove radiation faster:
- Lentils;
- Almond;
- Sea kale;
- Apples;
- Pumpkin;
- Beans;
- Walnuts;
- Oats.
Careful attention to radiation diagnostics allows you to get maximum results with minimal harm!
Consequences
All negative consequences of CT are associated with radiation and the body’s reaction to contrast.
For the average person, the radiation exposure received from a CT scan is not dangerous. Although it is much greater than with radiography, it is not capable of reaching those values beyond which radiation sickness occurs (3 Sv or more).
Of course, ionizing radiation can accumulate in the body and increase the likelihood of developing cancerous tumors, but that is why it is used in medicine only according to strict indications and in cases where the benefits of it outweigh all possible risks .
A special category of patients are pregnant women and children under 14 years of age. The first study is strictly contraindicated. Research is carried out for children, but if it really cannot be done . special pediatric regimes are used with a reduction in all study parameters to a level at which the radiation dose corresponds to the size of the child’s body. You can read more about CT scans for children here.
As a rule, contrast agents used for enhanced CT are well tolerated by patients. But some patients experience an individual reaction in the form of side effects in response to their administration. Consequences may appear 20-60 minutes after administration of the drug . These include:
- nausea, vomiting;
- bronchospasm (spastic cough, suffocation)
- swelling of the larynx;
- urticaria (an itchy, urticarial rash on the body);
- diffuse erythema (redness of the skin);
- drop in blood pressure;
- feeling of heat;
- anaphylactic shock.
Less commonly, subjects develop late side effects (after several hours or even days):
- skin reactions (rash, itching, swelling);
- cardiac arrhythmia;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- influenza-like syndromes (fever, chills);
- hand pain.
These consequences are based on anaphylactoid reactions (reminiscent of an allergy, but are not caused by the interaction of an antigen with an antibody, but with other substances that activate the release of biologically active substances) or direct irritation of the wall of the vessel into which the contrast is injected. Their frequency depends:
- on the type of contrast;
- its concentration;
- volume and rate of administration;
- individual characteristics of the body (allergies, previous reactions to contrast, bronchial asthma, kidney and liver diseases).
In patients with any kidney pathology, CT scanning with contrast increases the risk of developing nephropathy.
In most cases, mild and short-term side effects are observed. They resolve quickly without medical intervention or with supportive care.
Important: Severe reactions are extremely rare, but we should not forget about them. After all, they pose a threat to life and require immediate assistance.
Therefore, after the end of the study, even if a person feels well, it is advisable that he be under the supervision of medical personnel or relatives for several hours. He is advised not to travel, especially while driving a vehicle.
Contraindications to contrast
- CT with contrast should not be performed in patients with obvious renal impairment. If serum creatinine is, for example, 200 µmol/liter or more, administration of contrast may lead to worsening renal failure. Contrast is possible after normalization of creatinine and urea levels.
- Contrast should not be administered to patients with a history of allergic reactions, even after a negative skin test. Otherwise, you can get swelling of the walls of the respiratory tract, pulmonary failure, and shock.
- Another contraindication is chronic inflammatory lesions of the veins at the site of catheter insertion.
More rare CT contraindications to contrast injection:
- bronchial asthma;
- severe cardiovascular failure;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- planned scintigraphy of the thyroid gland;
- treatment with radioactive iodine.
Caution: contrast is contraindicated before thyroid scintigraphy and may delay radioiodine treatment. Warn your doctor about this.
Effect on the body
Long-term CT rarely used in clinical practice . It is carried out using special methods. Its goal is to clarify and localize pathological changes identified during a standard study. The question of the appropriateness of such a procedure is decided by the radiologist based on the tasks set for him by the attending physician. This study is associated with an increase in radiation exposure and is used according to strict indications.
Important Even with long-term computed tomography, radiation doses
do not cause pronounced changes in organs and tissues , as they are strictly controlled by a specialist.
CT and MRI: which is more harmful?
Both research methods can lead to complications. MRI uses contrast, but in lower doses and of a different type than CT scans.
MRI contrast agent can also cause allergies. The drug is administered by hand, therefore the risk of vein damage, phlebitis and extravasation is much lower.
The risks of magnetic resonance imaging are related to the magnetic field, not the x-rays. Any magnetic object in the field tries to move, heats up, and affects neighboring tissues. Surgical vascular clips based on steel alloys, once in the tomograph field, can disrupt the integrity of the vessel.
To the question about which method is more harmful - CT. When planning a procedure, you need to take into account indications and contraindications and weigh the risks.
There are alternative research methods, for example, ultrasound diagnostics. Their presence must be taken into account and replaced with tomographic procedures when required.
Main purpose of CT
Computed tomography is prescribed in the process of diagnosing various diseases of the urinary and digestive systems, as well as the pelvic area and retroperitoneal lymph nodes.
They resort to this research method in the process of determining pathologies of organs that are located in the retroperitoneal region or in the pelvis.
Other organs that may change shape under the influence of a number of developing formations are also examined.
A modern diagnostic procedure, with proper preparation for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity with or without contrast, allows for the most accurate diagnosis to identify diseases and health problems such as:
- Various inflammatory pathologies;
- Congenital anomalies;
- Cysts and abscesses;
- Malignant and benign formations;
- Damage to abdominal vessels in accidents and injuries;
- Vascular damage due to tumors, liver cirrhosis, and also with a high probability of blood clots.
Modern tomographs make it possible to conduct a virtual examination of the large intestine without causing discomfort to the patient.
The study can be carried out either with or without a contrast agent. This issue is resolved strictly on an individual basis.
It all depends on the patient’s condition or diseases that need to be clarified and investigated.
Before the procedure, it is imperative to prepare for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity without contrast or with the introduction of a substance, which consists of eating before the event.
Because this is a gastrointestinal examination, much of the preparation process is to maximize overall abdominal imaging. If gases form in the intestines, this will seriously interfere with examinations such as an abdominal CT scan with contrast.
It is for this reason that you need to prepare as properly as possible before performing a CT scan. In about three days you will have to adhere to a certain diet, which will reduce the amount of feces and reduce the amount of gas. Preparing for the procedure requires eliminating foods such as:
- Gas-increasing foods - beans, sauerkraut;
- Fruits and berries;
- Nuts and prunes;
- Flour products made from flour of the first raw material;
- Rice and semolina porridge;
- Alcohol;
- Excessively strong tea or coffee;
- It is worth excluding dairy products if lactose intolerance is present.
Thanks to the high quality of CT images, doctors can determine the presence of pathology with 100% accuracy.
During preparation, a special diet is needed before an abdominal CT scan. The diet should include foods such as lean meats, fish, meatballs and soufflé. Boiled vegetable soups, low-fat cottage cheese, as well as crackers.
You need to prepare for a tomographic examination not only by consuming special foods. It is also worth making sure that the following rules are followed. Any form of computer research is carried out strictly on an empty stomach.
After eating, especially if it was the wrong food, many organs greatly change their shape. All this leads to the fact that the survey results in a highly distorted picture.
To prevent the picture from being greatly distorted, the last meal should be taken approximately 7-8 hours before the examination.
To obtain a more accurate result, the doctor may prescribe special medications that will improve the condition of the intestinal tract and allow you to obtain the most accurate results. These may be medications such as:
- Activated carbon, Lactofiltrum or Smecta, which are carried out to reduce gas formation;
- Preparation includes the use of laxatives, which will help to effectively empty the intestines, which will automatically improve the visual inspection of the gastrointestinal tract;
- If the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract is increased, before the procedure it is worth taking antispasmodics, for example, No-shpa.
These medications should not be taken on your own, but only as prescribed by the doctor who performs the CT scan.
If an X-ray examination was performed before the CT scan, at least 5 days should pass between these procedures.
The reason is that the remains of special radiopaque substances may affect the overall results of the tomography, and the abdominal image may be incorrect. Visualization of blood vessels and organs is greatly distorted.
CT is considered an absolutely safe research method.
Before the procedure itself, the patient must remove all metal objects, such as jewelry, glasses, watches and piercings. Also, avoid wearing underwear, such as bras, that have metal underwires. The patient's hearing aids and cell phones are also prohibited.
The procedure of computed tomography with the introduction of contrast is performed if it is necessary to study hollow organs. An iodine solution or medications containing barium can be used as a contrast. Almost immediately after administration, they paint the abdominal organs a different color from other organs.
This is what makes it possible to clearly visually examine certain formations, as well as features of structural changes. These substances are completely harmless to the body and can be used to identify areas with increased blood supply.
Before performing a CT scan, you should definitely consult with a specialist. This could be a radiologist. The reason is that the generally accepted scheme for administering contrast is slightly modified in direct dependence on the goal and the nuances of the study.
Written consent from the patient for the administration of a special radiocontrast agent is also required.
The doctor will need to find out whether or not the patient is allergic to drugs that contain iodine or to various seafood that contain significant amounts of iodine.
If a contrast agent is administered orally, the patient must first prepare, and the drug itself must be prepared, that is, diluted in full accordance with the instructions.
Administration can also be done rectally. Then the day before an enema is done and laxatives are taken.
Modern computed tomography is a relatively safe examination for the patient. The radiation dose level for the longest procedure does not exceed the normal X-ray rate. Despite this, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the main contraindications to this procedure. Among these factors are:
- Excess weight – more than 120 kg;
- Pregnancy;
- Patient anxiety;
- Age up to 14 years;
- Inflammatory kidney diseases;
- Lactation period;
- Severe diabetes mellitus;
- Allergy to contrast agents;
- Severe diseases of the liver, heart and blood vessels;
- Blood diseases.
Also, CT is not performed if the patient has undergone gastrointestinal tract examination using contrast in less than a week. In some cases, other preliminary examinations may be required. This could be an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, FGS of the stomach, colonoscopy, regular x-ray or examination by an oncologist.
Important Tips
Preparation for the procedure involves fulfilling certain conditions. In almost all cases, an enema is performed. To cleanse the intestines very thoroughly, the procedure can be performed twice.
In most cases, this event is combined with preliminary use of laxatives.
This procedure must be carried out strictly on an empty stomach, that is, the last meal is taken strictly 8 hours before the medical event.
If you plan to conduct a kidney examination, no special preparation is required. If this part of the body requires the administration of a contrast agent, you do not need to eat for 4 hours first.
When examining the bladder, you will need to drink a contrast mixture approximately 5 hours before.
Just before the start of the study, urine is removed through a special catheter and air is introduced into the bladder through it, which will significantly improve visualization and contrast, and accordingly, higher-quality images will be obtained.
In some cases, diabetes mellitus may be a contraindication.
During a female examination, when it is necessary to diagnose the appendages and uterus, contrast may not be used. The doctor makes the exact decision. If the decision was made to introduce contrast, the woman will need to prepare approximately 5 hours in advance.
The X-ray substance is taken orally. Before the procedure itself, another type of contrast agent is injected into the bladder cavity, and a gauze swab is injected into the vagina.
When studying a man's reproductive system, he will need to take a contrast agent approximately 5 hours before the procedure.
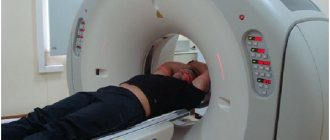
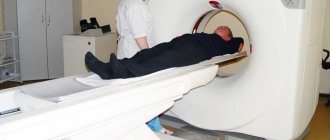
A modern computed tomograph is a device that consists of a movable table and a fairly large cube. There is a tunnel in its central part.
During the examination, the patient is placed on his back and remains completely motionless throughout the entire procedure. During the operation of the tomograph, the scanner, which is located inside the device, rotates around the person in a special way. In this case, no discomfort is felt, there is no pain.
You must have a referral from your doctor and the results of other diagnostic tests with you.
During the operation of the tomograph, a person hears the faint noise of a normal operating computer device, and also follows the doctor’s instructions regarding the characteristics of the respiratory process.
X-ray radiation, which is used for tomography, is emitted in very small doses.
As for time, this procedure takes an hour on average, then a certain amount of time will be required to process the data.
Conclusion
PET CT with contrast agent
Separate mention should be made of positron emission tomography, which is one of the newest modern CT techniques and allows the most accurate examination of human organs, helping to detect cancer in the early stages or during its development. That is why PET CT with contrast is most often prescribed to patients preparing to treat tumors of the lungs, head, larynx, tongue, intestines, liver, mammary glands and kidneys, as well as to treat melanoma and lymphoma. Indeed, with the help of such computed tomography, doctors are able to detect about 65% of cancer tumors.
In addition, this type of study is prescribed for problems with memory or the nervous system, to identify foci of epilepsy, to clarify the degree of development of Alzheimer's disease, to identify the presence of consequences of a heart attack, for coronary heart disease and to study cerebral circulation. In all these cases, tomography will help determine the treatment method and find out how effective it is.
This study is carried out in almost the same way as a regular computed tomography. True, here a contrast agent for CT scanning of the abdominal cavity or retroperitoneal space is injected into a vein 45 minutes before the start of the study, and all this time the patient must remain silent and not move. Then the patient is placed on a moving couch and sent to the scanner, the sensors of which begin to pick up signals that will be transmitted by the tomograph to the computer screen in the form of an image of the organ, on which the diseased areas will be highlighted in color.
Risk assessment of X-ray examination
It is worth saying a few words about the dosage of radiation exposure. It is important to note here that the degree of impact is determined taking into account the following bodies:
- absorbed dose is the energy that affects a unit of patient’s body weight;
- equivalent dose - an indicator multiplied by the absorbed dose coefficient, characterizing the varying degrees of damaging ability of ionizing effects.
To get a complete picture of this issue, a special plate is used, which indicates the indicators for each type of survey. Based on the indicators in this table, the total dose of exposure to the patient’s body is calculated and compared with the minimum that can provoke the appearance of oncology. For an ordinary person, this figure is 50 microroentgens per year. With conventional examination methods, it is almost impossible to obtain such a dose. The risk group includes specialists who work in this field.
Preparing for a CT scan with contrast agent
In order for the study to give the correct results and be as safe as possible, you need to prepare for it. Two days before it, you will need to start following a diet, giving up foods such as alcoholic drinks, fruit juices, carbonated drinks, fermented milk products and products prepared with yeast. And at the time of the examination, you need to try to empty your stomach of food as much as possible, so if the CT scan is scheduled for the morning, then you need to do the examination on an empty stomach, and the night before you should limit yourself to a light dinner. If the CT scan is scheduled for lunch, then 5 hours before the procedure you can have a light breakfast, and if the tomography is scheduled for dinner, then you can have a hearty breakfast, but under no circumstances have lunch. And just a few hours before the tomography, you will need to give yourself a cleansing enema or take a mild laxative to empty your intestines.
And after the examination, in order to get rid of the received dose of radiation, it is recommended to eat more apples, seaweed, almonds, lentils, pumpkin, oats, walnuts and beans.