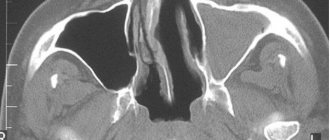
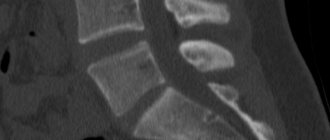
What is the method
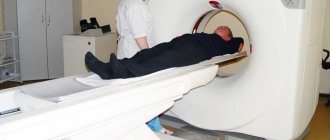
MSCT is an examination that is performed to diagnose diseases of internal organs, soft tissues and osteoarticular apparatus.
When scanning, the doctor receives from 4 to 64 sections, with a time interval of up to 0.5 seconds. The cut thickness is 0.5 mm.
The total number of images of the studied area reaches two thousand. A complete diagnosis of the whole body requires 10-15 seconds.
As a result, the resulting images of the sections are reconstructed and folded into a three-dimensional three-dimensional image of the organ.
Operating principle of the tomograph
The method is based on a combination of spiral CT (SCT) and a multi-row system of receiving sensors. MSCT devices are equipped with one or two X-ray tubes, signal receiving devices, and a mobile couch.
When scanning is started by the patient, the table begins to continuously move inside the gantry at a specified speed.
The X-ray tube rotates 360 degrees around the object being examined and emits rays that pass through the patient's body to sensors located on the opposite side.
X-rays are absorbed by tissues to varying degrees. Sensors record the weakening of the signal, then transmit information to the processing and analysis station.
MSCT
The radiologist looks at the received images, deciphers the data and draws up a description protocol with a conclusion.
Distinctive features of MSCT from CT
MSCT compared with classical computed tomography:
- examines the anatomical formations of the entire body in one inhalation phase;
- has a high diagnostic speed (up to 15 seconds);
- exposure to harmful ionizing radiation is reduced by increasing scanning speed;
- improved contrast, temporal and spatial resolution;
- the ability to build 3D models.
Conclusion: the difference between MSCT and CT lies in the number of detectors and the continuous translational movement of the table with the patient, that is, with CT the table moves step by step and this is an outdated version of equipment of 1-2 generations, SCT is 3 generations, and MSCT is 4 generations.
Differences between MSCT and MRI
MSCT and MRI techniques use different physical phenomena to visualize the internal structures of the human body.
MSCT uses ionizing radiation, MRI is based on the phenomenon of magnetic resonance. The examination speed with MSCT is 10-15 seconds, with MRI scanning lasts 15-60 minutes.
Application area:
- MSCT is preferable for visualizing bone structures, parenchymal organs, and the cardiovascular system;
- MRI clearly shows soft tissue, cartilage, brain and spinal cord.
What can be seen with MSCT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space
MSCT examination of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space allows us to detect:
- abscesses;
- tumors;
- consequences of injuries;
- the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites).
The examination reveals even the smallest changes in organs.
MSCT allows you to simultaneously examine both hollow and parenchymal (without internal cavities) organs and identify formations of varying densities (both solid and liquid).
When is an examination ordered?
Multislice computed tomography is indicated for identifying pathological changes of an inflammatory, neoplastic, degenerative-dystrophic nature.
To verify the nature of the formations, under the control of MSCT, biological material is collected using a puncture biopsy.
MSCT detects the following diseases:
- acute cerebrovascular accident of hemorrhagic, ischemic type;
- hemorrhages, hematomas between the membranes of the brain;
- consequences of traumatic brain injury: damage to the brain substance, fracture of the skull bones;
- foci of accumulation of pus in the medulla;
- disorders of the vascular architecture of the brain;
- thrombosis of the vessels of the venous sinus;
- developmental anomalies;
- neoplastic processes, metastatic damage to organs and lymph nodes;
- lymphoproliferative diseases;
- inflammatory diseases of the paranasal sinuses, middle ear;
- focal, purulent-destructive, infiltrative changes in the lung tissue;
- pulmonary embolism, thrombosis of the heart cavities;
- pathology of the aorta and peripheral vessels: lumen expansion, wall dissection, stenosis, occlusion;
- acute pathology of the abdominal organs: pancreatitis, perforation of hollow organs, bleeding, intestinal obstruction;
- inflammatory bowel diseases: granulomatous enteritis, ulcerative colitis;
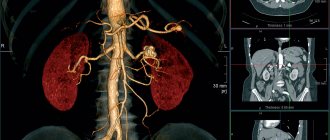
- kidney pathology of an inflammatory, tumor nature, obstruction of the urinary tract;
- purulent-necrotic process in bone tissue;
- focal bone necrosis;
- fractures of bones, spine;
- intervertebral disc herniation, protrusion;
- vertebrogenic radiculoneuropathy.
Extensive intracerebral hematoma in the region of the basal ganglia on the left
Peripheral cancer of the left lung with decay
Chronic cholecystitis
Metastatic lesions of L3, L4. Common osteochondrosis, spondylosis.
MSCT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum: area of study
The area of MSCT examination of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is a part of the human body, anatomically limited above by the dome of the diaphragm, and below by the beginning of the pelvic bones. The organs located in this area are covered with peritoneum - a thin translucent serous membrane. Some organs are covered by peritoneum on only one side, so their location is called the retroperitoneal space.
Subject to research:
- gastrointestinal tract (stomach, small and large intestines);
- liver, gallbladder, bile ducts;
- spleen;
- pancreas;
- kidneys, adrenal glands; urinary tract;
- The lymph nodes;
- abdominal aorta and other vessels related to this area;
- tissue of the abdominal walls, fiber of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
In what cases is MSCT not performed?
Contraindications to diagnosis are due to the negative effects of X-rays and the likelihood of an allergic reaction to the contrast.
MSCT is performed when the benefits of the information obtained outweigh the potential risks in the case of low information content, unavailability of additional diagnostic methods, or the presence of life-threatening conditions.
Limitations for the survey:
- pregnancy at any stage;
- children and adolescents;
- excess body weight more than 150 kg;
- intolerance to iodine contrast;
- history of severe allergic reactions;
- chronic renal failure in the stage of decompensation;
- alcohol or drug intoxication;
- mental disorders during exacerbation;
- hyperthyroidism;
- tachycardia in patients with heart pathology;
- state of agony.
Absolute contraindications to CT
Contraindications to computed tomography are associated with radiation exposure to the body. They are usually divided into absolute and relative.
- The main and absolute contraindication to CT is pregnancy due to the negative effects of X-rays on the fetus.
- Children under 14 years of age are not recommended to have a CT scan without a referral from a treating specialist due to the risk of developing cancer from radiation.
Frequent X-ray examinations may be a limitation for computed tomography. The recommended radiation dose for medical purposes per year is 25 mSv. Exceeding this radiation exposure is dangerous for the patient's health.
How patients are prepared for diagnosis
Before coming for an examination, the patient takes a referral from the doctor, pictures and data from previous diagnostic methods for diagnosing the area of interest.
Preparation for MSCT is carried out independently at home or in a hospital under the guidance of staff.
To scan the abdominal cavity, 2-3 days before the tomography, the patient is prescribed a light diet with the exclusion from the diet of foods that enhance intestinal motility and fermentation processes.
To reduce the amount of gases in the intestinal tube, carminatives are indicated. When using oral contrast agents, the drug is diluted in 600 ml of boiled water and taken orally 30-45 minutes before the procedure. To clearly visualize the internal organs, tomography is performed on an empty stomach.
The pelvic organs are scanned after the bladder is filled. To do this, an hour before the tomography, the patient must drink 500-1000 ml of liquid, and refrain from urinating 1.5 hours before the tomography.
When diagnosing with contrast agents, creatinine levels in the blood are additionally examined to exclude functional disorders of the kidneys.
3 hours before the administration of iodine-containing contrast, the consumption of food and liquids is prohibited. One day before and after MSCT with contrast, drugs from the group of biguanides, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory substances, and diuretics are discontinued.
Cardiac patients referred for coronary angiography with a heart rate of more than 65 beats/min are prescribed drug therapy to reduce the pulse rate.
Patients with severe allergies receive premedication with glucocorticosteroids 12 and 2 hours before contrast enhancement.
Contrast enhancement
The use of contrast agents in multislice CT improves the differentiation of organs and tissues, which increases the diagnostic value of the method.
More than 30-50% of all MSCTs are performed with iodine contrast agents. The drugs are administered into the vascular bed or taken orally in the form of solutions diluted with water.
The contrast is excreted from the body unchanged with urine, bile, tear fluid, and sweat.
For bolus administration of water-soluble iodine contrast, a catheter and an automatic injector with one or two flasks are installed in the elbow vein.
The injector automatically pushes the contrast into the vessels with an isotonic solution. The volume of the drug, speed and duration of administration are selected individually based on the patient’s body weight.
Preparation
Before diagnosis, special preparation is recommended, which will help increase the information content of the study. Therefore, during a planned study, a special diet is pre-prescribed, which helps reduce intestinal gas formation. It is also advised to refrain from eating for 6-8 hours before MSCT .
Before the study, an assessment of kidney function is also carried out ( blood test for creatinine ), and, if necessary, an assessment of the hormonal status of the thyroid gland .
Important If MSCT with contrast is urgently required, then most of the preparation principles can be neglected (except for a blood test for creatinine).
Positive and negative aspects of the method
When choosing MSCT as a research method, pay attention to the following indicators:
| pros | Minuses |
| high reliability | harmful effects of x-rays |
| detection of pathology at the preclinical stage | high price |
| ultra-fast diagnostics | |
| no artifacts during breathing and minor movements | |
| equipment availability | |
| high throughput | |
| standardization |
Decoding the results
Research results are provided in several formats. The paper reflects a description of the main organs, vascular elements and neoplasms, if any. If the description is qualitative, then the topography, or the relative position of the organs relative to each other, will be reflected.
In addition, the entire shooting is recorded on digital media in Dicom format. It is impossible for a person without a medical education to independently understand these graphic images, sometimes animations or video files. Therefore, you need to rely on the conclusion given by the doctor who interpreted the MSCT results.
First of all, you should pay attention to the size of the organ. The identified dimensions and normal indicators are described.
When the liver becomes enlarged, one should think about steatohepatosis (fatty degeneration), and when its size decreases, on the contrary, about cirrhosis. If the spleen is enlarged, blood diseases should first be excluded, and then infectious diseases. In the second case, the liver enlarges in parallel.
Normal bile should be visible in the gallbladder. Its walls are not thickened. Otherwise, we are talking about a diagnosis such as cholesterosis or biliary dyskinesia. If a stone is described in the lumen of the gallbladder, then this is a manifestation of cholelithiasis.
Neoplasms in any organ can be of any shape and size. Only an oncologist can determine their nature. They are differentiated from cysts, malignant and benign tumors, metastatic, purulent (abscesses) foci. It is impossible to identify them independently.
An ordinary cyst looks like a round formation with clear contours. Within one cystic cavity there may be several daughter ones. Cysts of parasitic origin pose a danger.
Blood flow in cystic cavities is not pronounced. Malignant tumors have a clearly defined intensive blood supply. They are characterized by uneven contours and heterogeneous contents. Purulent foci (abscesses) also look like rounded formations with a horizontal level of liquid.
MSCT of the abdominal cavity with contrast immediately after injection and after 10 minutes
Adenomas are considered benign neoplasms. They are also visible on MSCT. They often develop in the liver. When contrasted, an adenoma looks clearer because its tissues capture the contrast compound better and retain it longer. A fibrous field is visualized around it, the contours of which usually follow the contours of the tumor.
MSCT of the abdominal cavity with contrast allows you to determine the presence of hepatocellular cancer. The sizes can be absolutely any. At the same time, the structure of the intrahepatic formation is extremely heterogeneous; multiple collaterals and vascular shunts are visible. In pancreatic cancer, on the contrary, the vessels feeding the tumor are very rarely visible.
Cost of diagnostic session
The price of MSCT is determined by the scope of the examination, which is planned in advance by the attending physician together with the radiologist.
Depending on the area of scanning and the number of anatomical structures covered, the patient pays an average of 3-6 thousand rubles for tomography.
If bolus contrast enhancement is required, an additional iodine-containing drug is paid in the amount of 4-5 thousand rubles.
At the request of the patient, clinics provide the service of constructing a 3D reconstruction of the obtained images on an image or disk for 1-4 thousand rubles.
Photo and video recording of the scanning progress with recording on electronic media will cost 500-1000 rubles, printing an additional image will cost 1000 rubles.