Kinds
Among all types of headaches, migraine and standard tension were the most common. Both types can be accompanied by mild stiffness, or maybe serious and severe pain.
The pain is felt in the temple area or radiates to the eyes, to the back of the head, or to the area of the cranial vault.
Quite often, with various pains in the head, there may be a vegetative disorder, that is, problems during the respiratory process, rapid fatigue, and so on.
Migraine has a paroxysmal form, which is also accompanied by severe pain in the head. The pain comes through pulsation. Such attacks can be caused by bright light or other types of irritants, as well as constant fatigue. As a rule, such headaches last up to several hours; at best, they end in half an hour.
Experts also identify a third common type of headache, which is called cluster pain or, in other words, beam pain . The main distinguishing feature of such pain is its immediate appearance. In addition, a person feels a cluster headache exclusively on one side of the head. These types of attacks can be repeated over several months, or can end in a week.
Headaches after MRI: what to do?
Today, MRI is considered one of the safest diagnostic techniques, but in some cases patients complain of severe pain in the back of the head or the top of the head. Sometimes a person feels nauseous and dizzy.
This symptomatology occurs due to the individual characteristics of the body and increased sensitivity to influences of this kind. Usually the symptoms are temporary and disappear within 24 hours. If necessary, the doctor can give recommendations to relieve symptoms.
#!MRTVRA4!#
Migraine: MRI or CT?
Often, painful sensations in the head indicate migraine, which is a neurological disease, the main symptom of which is attacks of pain on one side of the head, with regular or episodic frequency. Diagnosis of the disease is made using MRI or CT, computed tomography. Despite some similarities, the presented diagnostic techniques allow us to consider different changes:
- MRI. Detects migraine by the presence of multiple ischemic foci. As the pain subsides, a change in blood flow becomes noticeable. Before the onset of an attack, the blood vessels in the head first dilate, and then they sharply narrow.
- CT. Allows you to identify the presence of tumor and cystic neoplasms, which cause the creation of high intracranial pressure, which provokes severe pain.
The presented instrumental methods for diagnosing headaches make it possible to exclude oncology and the development of other dangerous complications in a timely manner.
One hundred and one reasons why your head hurts
A general classification that would structure the causes of headaches has not yet been invented in the modern world. Medicine distinguishes 4 types of their nature:
- organic: this type includes diseases that affect the brain, spinal column, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, intestines and excretory system;
- psychogenic: the cause is overload of the nervous system. A painful symptom appears as a result of prolonged and intense tension. This may be nervous or mental fatigue, short-term or long-term stress, a state of fatigue in which a person is constantly, emotional distress and overstrain, problems in life;
- intoxication: as a consequence of an ongoing or previous viral or bacterial disease that affects the nervous system, poisoning (both food and chemical), smoking, frequent and large doses of alcoholic beverages, work in hazardous production conditions, as a side effect of use of medications;
- hormonal: occurs due to disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland, changes in hormonal levels, which lead to minor pathologies in the blood supply to the brain or cardiovascular system. With this type, painful sensations appear in the temples and in some parts of the head.
Causes
Pain in the head can have a completely different onset, from banal fatigue to infection with some kind of infection. But, despite the initial cause, the mechanism for creating pain is the same. Let's look at it in more detail.
First, the inflammatory process begins, which affects areas of the human central nervous system. Next, irritation of the membranes of the brain occurs.
This happens for two reasons, first of all, there is an increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure , and the second reason is poisoning of the body . At the end of the process, a spasm occurs and the blood vessels dilate.
Some experts highlight a theory about the mental source of headaches. At first glance, the cause of this type of pain is obvious. But in fact there can be a very large number of reasons. Let's look at the most common of them :
- diseases that were caused by infection;
- various tumors in the head area;
- increased blood pressure;
- diseases in the sinus area;
- disruption of hormones;
- human sensitivity to weather conditions.
Rules for preparation and safety precautions for MRI
No special preparation is required for MRI of the brain, either in conventional or vascular mode. But there are some recommendations that it is advisable to take into account:
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages at least 2-3 days before the procedure. Alcohol affects the condition of the blood vessels in the brain, and this can affect the results of magnetic resonance imaging.
- To avoid changing into a hospital gown or shirt, come to the diagnosis in loose clothing without metal fittings. Women should not wear underwear with metal inserts (we are talking about bras).
- If you are worried, take a sedative beforehand. Ask your doctor which drug is suitable for this. You should not choose it yourself, since the side effects of some medications can affect MRI results, especially when examining cerebral vessels.
- If you are undergoing drug therapy, ask your doctor if you can take the prescribed medications before the tomography. You may have to interrupt the treatment course for 1–2 days.
If you have metal implants, dental crowns or braces, find out what they are made of. If they contain steel, you must inform your doctor about this. You may have to abandon MRI of the head, since ferromagnets can reduce the information content of the study to zero.
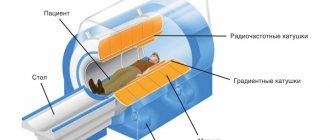
Comprehensive MRI of the brain - what does it show?
The technique includes the study of all structures: the ventricular system, the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum, the brainstem, and the pituitary gland. For headaches, a comprehensive MRI is performed in three projections, with a slice thickness of no more than 5 mm. During a native examination, brain structures are displayed in sagittal, axial and transverse projections.
The pituitary gland, temporal lobes and other small structures require targeted study, using coronal planes with a slice size not exceeding 3 mm. If necessary, magnetic resonance imaging with a contrast agent is performed. The technique makes it possible to visualize with high accuracy the locations and boundaries of the pathological focus and assess the extent of the process. Indications for the diagnostic procedure are suspicions of the following diseases:
- anatomical abnormalities of the brain structure;
- Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases;
- multiple sclerosis;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke;
- tumors and cysts;
- intracranial hypertension.
The images clearly visualize areas of ischemia, deformation of the pituitary gland, violations of the boundaries of white and gray matter, small focal hemorrhages, and hyperplastic nerve endings.
If you do an MRI when you don't have a headache
Multiple ischemic foci in vascular dementia on MRI: lack of memory for recent events and inappropriate behavior are not signs of old age; timely diagnosis of dementia and pathogenetic therapy will help slow down the progression of the disease
MRI is an examination that is performed not only for headaches. Magnetic resonance imaging will help determine the causes of the following complaints:
- short-term loss of consciousness unexplained by primary diagnosis;
- flickering of spots before the eyes, progressive deterioration of vision (as part of a comprehensive ophthalmological diagnosis);
- increased blood pressure, resistance to taking antihypertensive drugs;
- periodic nausea, vomiting when changes in the fundus are detected (signs of increased intracranial pressure);
- epileptic seizures;
- memory impairment, dementia (dementia);
- constant ringing in the ears;
- lack of coordination of movements (shaky gait, dragging of the lower extremities, etc.);
- dizziness.
The doctor determines not only the type of examination, but also its scope. Sometimes it is necessary to evaluate not only the structures of the brain, but also the collar area: the head may feel dizzy and hurt due to cervical osteochondrosis, hernia, nerve inflammation, etc.
MRI of the brain is necessary for some endocrinological pathologies, since hormonal disorders can be caused by tumor compression of important structures responsible for the activity of the glands. Tomograms show changes in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. MRI for headaches and dizziness, if you suspect a tumor or vascular pathology, can be done at the Northern Capital Medicine diagnostic center.
Surveys
The primary doctor to contact is a neurologist . What examinations do patients undergo if they have a headache? Only a doctor can give a list of directions. First of all, the patient is interviewed, the doctor is interested in the duration of the pain, its nature, and so on.
Help: In order for the primary diagnosis of the disease to be completed, you need to be examined by several doctors, such as a neurologist, dentist, ophthalmologist, and undergo tests . But, as a rule, it is necessary to undergo examinations using the latest medical procedures.
Benefits of the procedure
Obviously, to the question: “What tests should you undergo if you have a headache?” The doctor’s response will be to prescribe a comprehensive diagnosis, where magnetic resonance imaging rightfully takes the leading role. Unlike CT and radiography, the technique allows you to obtain high-quality images, eliminates radiation exposure and is irreplaceable today.
If you don’t know where to conduct head examinations for headaches, then we invite you to the MDC Medical Center. There is no need to waste precious time—we employ the best specialists and have expert-class equipment installed! The cost of the procedure is affordable, which is made possible thanks to a flexible pricing policy and an individual approach to each patient.
Differential diagnosis
Due to the fact that headache can have a large number of symptoms, it is imperative to carry out a differential diagnosis. For each doctor, the main task is to determine the connection between a specific headache and a specific disease. You need to understand that there will be no benefit in treating an exceptional symptom.
We present to you the sequence of all necessary examinations:
- The first step is to interview the patient. It is important for the doctor to find out the duration of pain, their sequence, nature and location of pain. It is also important to find out the patient’s body’s reaction to taking analgesics. Often, most people cannot describe such pain when they first see a doctor with such a problem;
- After the general survey has been completed, doctors prescribe certain tests that need to be completed in the near future. But it is important to choose the right diagnostic measures so that the patient receives his course of treatment faster.
MRI of the cervical spine for headaches
MRI of the cervical spine will identify or exclude the following pathologies:
- Osteochondrosis
- Spondylosis
These diseases can create pain in the neck and back of the head that radiates to the head.
At the MART clinic on Vasilyevsky Island
- Experienced doctors (including those practicing in the USA and Europe)
- Prices affordable for everyone
- Expert level diagnostics (MRI, ultrasound, tests)
- Daily 8:00 — 22:00
Make an appointment
Defined types of headaches
Headaches come in different forms and occur under different circumstances, and are also characterized by different symptoms.
Sinus pain
This type of pain appears due to inflammation in the nasal sinuses, which is characterized by a runny nose, nasal congestion, and swelling of the mucous membrane. At the same time, the forehead and the entire area around the nose begin to hurt. Sinus pain disappears when the cause of its occurrence—inflammation—subsides.
In case of circulatory problems in the brain
Cerebral circulation disorders can be acute or chronic and be accompanied by headaches. With a different clinical picture, it can be acute pain in the head and eyeballs or pain along with dizziness, nausea, poor sleep, etc.
After damage to brain tissue
This type of headache occurs after injuries (injuries to superficial tissues), oxygen deprivation of tissues, accumulation of fluid in tissues, etc. The soft tissues of the brain have a large number of nerve endings. Soreness often occurs on the surface of the head and may be neurological in nature.
For osteochondrosis of the neck
With osteochondrosis, headache appears in the neck and back of the head, and then moves to one of the halves of the head. The pain may vary in intensity and nature, and may be accompanied by dizziness and nausea.
Which MRI should I do?
If the pain in the head is incredibly severe and lasts for quite a long period, and also has many symptoms that are associated with irritation, poor sleep, upset stomach, vomiting and nausea, then this indicates some serious diseases in the brain area. If an MRI of the brain is prescribed during diagnosis, this should be done to check for vascular pathologies.
Migraine occurs due to the fact that the blood vessels in the human brain contract at a certain moment.
Due to this, a spasm occurs in the brain. A tomograph of this type allows you to learn about blood flow disorders, as well as reflections of various ischemic types.
Some patients encounter a problem after an MRI - their headaches begin to hurt more severely. The nature of this phenomenon has not yet been revealed - the construction of the image is carried out due to electromagnetic influence, and it is harmless to the body.
In any case, the various examinations must be complete. This will allow the doctor to see the whole picture of the disease and prescribe the most accurate treatment. Through a complete diagnosis, you will be able to find out the cause of the pain in your head. As a rule, specialists first do an MRI of the brain.
Important! If even after such a procedure the cause of the pain in the head does not become clear, then additional diagnostics will be required in the form of an MRI, but of the spine of the human body, namely its cervical region.
Such procedures are carried out regardless of whether there are headaches at the moment. A complete medical history will provide complete information for the doctor.
We invite you to watch an interesting video on the topic:
Diagnosis of migraine using MRI
Migraine is a neurological disease, the characteristic symptom of which is a severe headache. MRI for migraines must be done to exclude serious organic brain lesions that have symptoms similar to migraines.
The pain associated with migraine is not relieved by conventional analgesics. Most often, during an attack, the patient begins to uncontrollably drink pills, which do not alleviate his condition in any way; his head hurts, in some cases to the point of vomiting.
When diagnosing migraine, magnetic resonance imaging is performed in all cases to identify factors that provoke pain, as well as to select adequate drug therapy. Often MRI in this case turns out to be uninformative, so it is more advisable to do MR angiography to assess blood flow in the cerebral arteries.
On MRI, migraine can manifest itself in the form of multiple foci of ischemic origin, and if it was possible to conduct an examination during an attack, then a disturbance in blood flow is noted. Immediately before a migraine attack, the blood vessels of the brain dilate, and then a sharp spasm occurs.
Why do an MRI for headaches?
There are other diagnostic methods: laboratory tests, ultrasound... Why do an MRI? The answer is simple: MRI allows you to visualize brain tissue that is inaccessible to other studies, while MRI is absolutely harmless (unlike CT).
Therefore - do not tolerate pain! Make an appointment at the MART Clinic and find out the cause of your discomfort! Experienced doctors, an expert-class open tomograph and affordable prices are at your service!
Sign up at the MART medical center in St. Petersburg (see map) by calling 8 or leave a request on the website.
What tomography will show - a complete list of possible pathologies
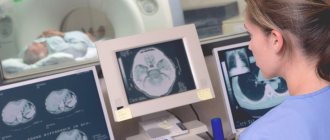
A radiologist interprets the MRI results of the brain. He prepares a report, which he sends to the attending physician. The patient, if desired, can pick up the study protocol and transcript on paper or electronic media (disk, flash drive). Typically, the waiting period for results ranges from two to three hours to several days, but in emergency cases they are prepared within an hour.
The deciphered results of MRI of the brain allow us to determine the following diseases and deviations from the norm:
- Inflammatory processes inside the brain (arachnoiditis, encephalitis, myelitis);
- Blood vessel pathologies (atherosclerosis, malformation, vasculitis, aneurysms);
- The presence of blood clots, pathologically narrowed or dilated vessels, impaired patency of arteries and veins;
- Heart attacks and strokes in the acute and acute periods;
- Blood flow disturbances as a result of ischemia and thrombosis;
- Foci of dementia, degeneration and dystrophy;
- Changes in tissue structure in the presence of neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature.
- Location of the tumor, its size, metastases.
Deciphering an MRI of the brain can show even those diseases that are at an early stage of development and do not yet have clinical symptoms.
X-ray
Using an x-ray, you can determine whether there is hydrocephalus, as well as any other injuries. This simple process is carried out due to the fact that so-called X-rays pass through the human body and all its tissues.
You need to understand that not all tissues can receive such rays, since they are different in density. A similar feature can be recorded on a certain film in the form of a less bright color.
As for soft tissues, they appear as a darker color.
Due to such features, the doctor can identify damaged tissue, find out the cause of this damage and prescribe direct treatment. This examination method is simple and does not require the use of serious equipment. In addition, it has a much lower price compared to the previous ones. It is for this reason that it is used as one of the first in all types of diagnostics. But it is worth knowing that x-rays in the head area are carried out to determine the integrity of the human brain bones.
Main types of headaches
Neurologists determine the types of cranialgia by clinical symptoms:
- The most common type is tension pain. Characterized by a feeling of circular soreness along the skull, inside the eye sockets;
- Cluster pain syndrome is accompanied by pulsation of a separate area of the head;
- Tumor pain occurs in the morning, is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, and can gradually progress;
- Intracranial hemorrhage leads to pain in a certain part of the skull, characterized by secondary symptoms (vision loss, unsteadiness of gait, hearing loss, hallucinations);
- Migraine is long-term pain on one side, intensifying against the background of photophobia and loud noises. Often before an attack there are precursors - visual photophobia (rings), auditory hallucinations;
- Temporal arteritis - characterized by local pain in the area of the temporal bone (lateral parts of the skull).
Treatment depends on the type of disease. The combination of several forms at the same time complicates therapeutic tactics. Magnetic resonance scanning makes it possible to study the morphology of the cerebral parenchyma and verify changes in the arteries.
MRI of the brain with and without contrast - what is the difference
Contrast is often used to visualize brain structures more clearly. Let's find out what it is and what the difference is between conventional MRI and contrast-enhanced MRI.
The main purpose of MRI with contrast is to identify tumors and determine their type (benign or malignant tumor). They stand out clearly against the general background of brain images due to the accumulation of contrast material in them. Using tomographs that support ultra-high-field mode, it is possible to diagnose the presence of tumors from 1 mm in diameter.
What drugs are used and how they are administered
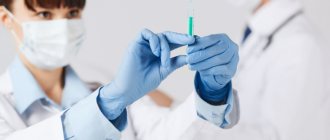
To perform MRI with contrast, drugs based on gadolinium are used, a chemical element from the group of metals that belongs to the paramagnetic group. It actively responds to the influence of a magnetic field, and therefore allows you to take clear pictures of the structure of the brain.
The patient is prescribed one of the following contrast agents:
- Dotarem;
- Gadovist;
- Omniscan;
- Magnevist.
The dye is injected into a vein. The radiologist, depending on the indications for the study, chooses one of two possible methods of its administration:
- In the first case, the drug is administered using a syringe once immediately before the procedure.
- In the second case, the patient is given an injector, which automatically calculates the dosage and rate of delivery of the substance into the vein. In this case, scanning is performed simultaneously with the introduction of contrast.
No special preparation is required. The recommendations are standard. However, it is best not to eat anything before using a contrast agent. The fact is that in isolated cases, after an MRI with the use of contrast, the patient develops nausea and vomiting. But if you tolerate all medications well, this recommendation can be ignored.
An MRI with contrast is performed in the same way as an MRI of the brain without the use of contrast. The only difference is that the patient is additionally injected with a dye before the procedure.
Is contrasting harmful to health?
Typically, patients feel equally well after an MRI of the brain without the use of contrast, as well as with its use. But 1 person out of 1 thousand still experiences side effects. They are associated with the characteristics of the patient’s body: individual intolerance to a contrast agent is a rare case.
Possible consequences of the administration of a contrast agent include headache, pain and dizziness, and skin rash. Sometimes a metallic taste in the mouth, nausea and vomiting are possible. Side effects quickly stop, as the drug is eliminated from the body within a few hours.
MRI of the brain with contrast is so accurate that it shows various pathologies, even when conventional tomography of brain tissue produces results within the normal range. Therefore, this diagnostic method detects tumors at an early stage of development. It also makes it possible to assess with great accuracy the nature of brain damage and the severity of identified diseases. This completely justifies the high cost of the procedure.