People with negative Rh blood factor make up 15% of the total population of planet Earth. Why are there so few of them? What makes them special? Many scientists are trying to answer these questions. Many theories have been put forward about the origin of this rhesus, but none have a solid scientific basis.
Scientists pay special attention to the personal characteristics or unique capabilities of such people. Some theologians generally believe that such rhesus appeared on Earth due to the connection of mere mortals with the gods. Whether to believe in such theories or not is everyone’s business, but what is the secret of these people?
Minus or plus?
Tell me, how common are people with a negative Rh factor and what does this mean?
Valentin, Podolsk
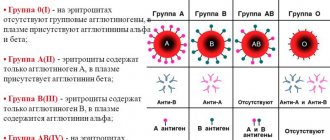
– The Rh factor is a special type of protein that is found on the surface of red blood cells (erythrocytes). 80% of the planet's inhabitants have this protein. Such people are called Rh positive. If there is no protein on the membrane of red blood cells, they are Rh negative. These are respectively 20%.
At the same time, the presence of “negative” blood does not cause any particular inconvenience to its owner. This is not a disease or pathology, but just one of the options for genetic inheritance.
Double risk
A year ago I had an abortion; then I couldn’t afford to have a child. Now the situation has changed, and I dream of a baby. But I have a negative Rh factor. Tell me, can that abortion affect pregnancy?
Olga, Mozhaisk
- Unfortunately yes. During the abortion process, fetal blood may enter the mother's bloodstream. Antibodies produced in response to this during subsequent pregnancy are able to penetrate the placental barrier into the bloodstream of the unborn child, destroying his red blood cells, threatening his life. Particularly dangerous in this regard is the termination of the first pregnancy, which can lead to infertility.
Recently, to prevent Rh conflict, women are given anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin after childbirth or abortion. If you have not received such prophylaxis, this drug should be administered immediately after the onset of pregnancy following an abortion. And regularly throughout pregnancy you need to take a blood test for the presence of anti-Rhesus antibodies.
Methods for diagnosing problems with negative Rh factor during pregnancy
The presence of antibodies in a young mother is determined at the very beginning of pregnancy. Many women know about their Rh factor long before conception and the onset of an “interesting situation.” The obstetrician-gynecologist puts such a mother on special registration. Having identified a negative antibody test result, the doctor prescribes a monthly venous blood donation for the expectant mother to monitor the rate of antibody formation. The closer the due date, the more often the young mother has to undergo tests to control the situation.
In addition to blood tests, the pregnant woman is prescribed routine ultrasound examinations, during which close attention is paid to the condition of the baby’s liver and spleen, as well as the condition of the placenta.
If any pathologies are detected, cardiotocography (CTG) and Doppler ultrasound are additionally performed. These studies make it possible to evaluate the functioning of the child’s cardiovascular system, as well as whether a sufficient amount of oxygen is supplied to him through the uteroplacental bloodstream.
If analysis for anti-Rhesus bodies shows their rapid growth, invasive diagnostic methods are used. This diagnostic method is dangerous due to leakage of water surrounding the fetus, the risk of infection, and the formation of a hematoma on the umbilical cord.
Analysis of amniotic fluid is the most reliable study, which indicates the exact amount of bilirubin produced by the baby, which allows us to assess the condition of the fetus. Taking material from the umbilical cord also provides reliable information about the composition of the fetal blood.
Problem filter
I heard that the problem of Rh sensitization can be solved with the help of plasmapheresis. But can pregnant women do this?
Margarita, Yaroslavl
– Not only is it possible, but it is also necessary! By removing antibodies that are harmful to the fetus from the bloodstream or reducing their concentration, plasmapheresis (blood purification method) is a very effective prevention of Rh conflict. True, if a woman has so-called complete antibodies in her blood, which are slowly synthesized and more difficult to pass the placental barrier. It is much more difficult to “pull out” a pregnancy with incomplete antibodies: they are synthesized in 10–14 hours, and it is impossible to “cleanse the blood” every day. Minimum – in 1–1.5 days. In order to maintain a normal antibody titer, some women have to undergo this procedure throughout their pregnancy.
Plasmapheresis has become a real lifesaver in the treatment of toxicosis in the first and second half of pregnancy, as well as in placental insufficiency, which is the main cause of intrauterine hypoxia (oxygen starvation) and fetal growth retardation.
How does it affect the course of pregnancy?
Rh incompatibility between mother and child does not guarantee the occurrence of an immune conflict. Normally, between the blood flow of the fetus and the pregnant woman there is a hematoplacental barrier, which prevents the mixing of the two types of blood and the development of an immune reaction.
A certain amount of the baby's red blood cells can enter the mother's body during the period of 8-12 weeks, because at the 8th week of pregnancy, the hematopoietic system begins to form in the fetus, and until the 12th week the forming element of the hematoplacental barrier (placenta) does not yet have a clear structure.
During the pregnancy of the first child, in the absence of risk factors, sensitization is rarely observed. This is due to the fact that upon contact before the formation of the placenta, short-lived antibodies M (Ig M) are formed, which are present in the blood in small concentrations, practically do not penetrate the hematoplacental barrier and do not pose a threat to the fetus.
For example, if a woman has group 2 negative, and the fetus has group 3 positive, then the likelihood of isoimmunization during the first pregnancy is low, but there is a risk of blood group incompatibility. If the second child has group 3 negative, which is possible due to the dominance of the positive Rh factor in the father, the immune reaction will not affect the second fetus.
Risk factors for Rh conflict are:
- history of Rh-positive blood transfusion;
- invasive studies of fetal health (chorionic villus tissue biopsy, collection of umbilical cord blood and fetal amniotic fluid);
- the occurrence of bleeding due to early placental abruption;
- development of pathologies affecting the integrity of chorionic villi (preeclampsia, diabetes mellitus, some viral infections, including influenza);
- intrauterine isoimmunization of a Rh-negative girl at birth from a Rh-positive mother;
- artificial termination of pregnancy for more than 8 weeks;
- spontaneous abortion (miscarriage);
- bleeding due to damage to the placenta during separation of the baby's place or during childbirth;
- entry of umbilical cord blood into the mother’s body during natural childbirth;
- C-section.
Important information: What is the most common (frequent) blood type in humans and what Rh factor is most common in the world
In the presence of additional risk factors or during repeated pregnancies, long-living antibodies (Ig G) are formed in the mother’s blood, which form permanent immunity. When antigen D enters the body again, Ig G, which is small in size, is actively released into the blood, penetrates the placental barrier and provokes the breakdown of foreign red blood cells of the unborn child (intravascular hemolysis).
A conflict in the antigenic set of red blood cells does not cause specific symptoms in a woman who is carrying an Rh-positive child. The only sign of conflict may be functional disorders resembling the course of late toxicosis. The diagnostic criterion is the presence of antibodies to the D-antigen in the blood of a pregnant Rh-negative woman.
If the immune reaction begins early, miscarriages and stillbirths may occur. Women with the first group are at risk of gestational complications: even in the absence of Rh conflict, they often experience group incompatibility with the fetus. In groups 2 and 3, the child’s probability of conflict in the group is 80%, in groups 4 - 100%.
The presence of a negative Rh factor during pregnancy affects the list of diagnostic tests and treatment procedures. Diagnosis of the conflict between maternal immunity and the child’s red blood cells includes the following measures:
- Analysis to determine the concentration (titer) and class of antibodies to antigen D. For the first pregnancy and there are no signs of isoimmunization, this study is carried out every 2 months. When carrying further children or if there are signs of sensitization up to 32 weeks, the test must be taken every month, at 32-35 weeks - every 2 weeks, at 35-40 weeks - every 7 days.
- Ultrasound of the fetus. Ultrasound diagnostics of the fetus if a Rhesus conflict is suspected is carried out 4 times during the period 20-36 weeks of gestation and again before birth. Ultrasound assesses the size of the placenta, internal organs, abdomen and body of the fetus, the volume of amniotic fluid, and the thickness of the umbilical veins.
- Study of fetal heart function (ECG, FCG, CTG). Carrying out phonocardiotocography, cardiotocography and electrocardiography allows us to determine polyhydramnios, cardiac dysfunction caused by pericardial edema, and the degree of hypoxia.
- Samples of amniotic fluid and umbilical cord blood. Amniocentesis and cordocentesis make it possible to study the titer of anti-Rhesus Ig G, the degree of maturity of the child’s internal organs, the concentration of bile pigment and hemoglobin, the gas composition of the blood, the level of albumin, hematocrit, the content of reticulocytes and dangerous antibodies in the umbilical cord blood.
To prevent and treat complications of the immune reaction, Rh-negative pregnant women are prescribed several courses of nonspecific therapy. It includes:
- vitamins;
- metabolism;
- mineral complexes with iron and calcium;
- antihistamines.
In parallel with drug treatment, oxygen therapy is carried out. The first maintenance course is prescribed at 10-12 weeks, the second at 22-24, and the third at 32-34. If the Rhesus conflict begins early or the condition of the fetus is severe, the pregnant woman is prescribed a procedure for purifying the blood of antibodies to the D-antigen (plasmapheresis).
Important information: Table of food products for women according to the 2nd (second) blood group positive (negative) and diet (menu) for weight loss for men
Pregnant women at risk of isoimmunization are administered RhoGAM immunoglobulin at week 28. If the woman has had bleeding or amniotic fluid and cord blood samples have been collected, a repeat injection may be required at 34 weeks.
Analyze it!
In what situations is it necessary to determine the Rh factor of blood? And in case of emergency, do you need to carry with you a reminder about what kind of blood you have?
Evgeniya, Voronezh region.
– Such an analysis must be done before planned surgery, blood transfusion and during pregnancy planning.
But it makes no sense to constantly carry with you a reminder about what kind of blood you have. According to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development, which is valid in all medical institutions in our country, before each blood transfusion, each person entering the hospital must have their blood type and Rh factor rechecked, since there is no guarantee that they were determined correctly.
Will there be no conflict?
I have negative Rh blood, and my husband has positive Rh. I recently found out that I am pregnant. They say that with such a combination big problems await me. This is true?
Ekaterina, Kaliningrad
– During the first pregnancy, special problems for Rh-negative women (even if she is expecting the birth of a Rh-positive child), as a rule, do not arise, since the mother’s immune system first encounters red blood cells that are foreign to her and, therefore, harmful to the fetus There are still few antibodies produced in her blood.
Everything is much more serious when such a woman becomes pregnant for the second time. After all, her blood now contains protective antibodies (“memory cells”) left over from her previous pregnancy. Therefore, the likelihood of Rh conflict (a kind of allergic reaction when the mother’s body begins to perceive the fetus as a foreign element) increases. Such a development of events is fraught with very serious consequences, including intrauterine fetal death.
Fortunately, modern medical technologies can solve this problem. It can be prevented by the introduction of a special vaccine - anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin, which suppresses the development and synthesis of anti-Rhesus antibodies and helps a woman endure pregnancy and give birth to a healthy baby.
Situations leading to the development of Rh conflict
Rh conflict is possible only if the Rhesus characteristics are different: negative in the mother and positive in the fetus, which leads to the production of certain antibodies.
The possibility of developing Rh conflict increases in the following situations:
- abortions, ectopic pregnancy in the past;
- threat of miscarriage in the 2nd trimester;
- instrumental examinations;
- history of difficult childbirth, ending with manual examination of the uterus;
- abdominal trauma with concomitant placental abruption;
- blood transfusion of the expectant mother, different in Rhesus status.
If this is your first pregnancy, the risk of developing Rh conflict is usually minimal. This is due to the lack of antibodies in the mother’s blood, the formation of which depends on the above negative factors. They usually remain in a woman's blood for the rest of her life.
Incredible? Obvious!
My child has negative Rh blood factor, while my husband and I have positive blood. My husband still teases me about this: they say, from whom did she cheat? I know that nothing happened. But the question haunts me: how could this happen? After all, a child will definitely inherit the blood of his parents. Is not it?
Olga, Kostroma
- No not like this. There is nothing supernatural in your situation. It is explained by the fact that a person with a positive Rh factor may be a carrier of a negative Rh gene, which is suppressed by a stronger positive gene.
But when this negative gene is present in the blood of both parents, then, doubling its strength, it can be passed on to the child and form a Rhesus with a minus sign. According to statistics, for Rh-positive parents this situation is possible in 25% of cases.
Characteristics
Despite the fact that specialists have long known what a negative Rh factor means, the origin of people whose blood does not have antigens remains a mystery. According to scientists, people with Rh (-) appeared about 35,000 years ago. Some researchers even believe that this feature arose due to alien intervention. This opinion is due to the fact that the absence of antigens in the blood is not found in monkeys, from which, according to Darwin’s theory, man descended.
According to statistics, people with a negative Rh factor most often belong to the following nationalities:
- Spanish Basques - 30%;
- Caucasians and Israeli Jews - 25%;
- Europeans - 15%;
- African Americans - 7%;
- Indians and Asians - 5%.
Czech scientists managed to find out how the Rh factor influences predisposition to certain diseases.
Don't need stock?
I will soon have major heart surgery. But I have Rh negative blood. They say that in such cases you need to go to a blood transfusion station and donate it “in reserve” - in case of bleeding. Is it worth doing?
Vsevolod, Moscow
Article on the topic
Where to donate blood faster and cheaper?
– Rh negative blood is always in short supply. But, if we are talking about a planned operation, like yours, the medical institution, as a rule, orders blood for it in advance. Especially if the risk of bleeding is expected.
A difficult situation with Rh-negative donor blood can arise in the event of an emergency operation, when a person is admitted to the hospital after a traffic accident or other accident. You can't think about it anymore. We need to act. How? Contact blood transfusion stations located in large (preferably federal) medical centers. Or look for the blood you need in the city’s medical network. If it was not possible to resolve this issue in this way, you need to call out friends and acquaintances or go to the nearest military or fire station and look for voluntary donors with the blood Rh blood you need.
By the way, when getting ready for surgery, remember if you have ever had a massive blood transfusion (blood transfusion). In this case, you need to select donor blood especially carefully. Otherwise, with your next blood transfusion, you may experience serious or even life-threatening problems, regardless of your Rh factor.