Hello, dear readers! In order to increase the chances of bearing healthy offspring, it is better to prepare for pregnancy in advance, this means that it is better to undergo an examination before conception. But, if pregnancy has taken place, this does not eliminate the need for examination.
Today we will talk about one of the mandatory examination points - various blood tests, including the presence of antibodies. Why take a blood test for antibodies during pregnancy, how to take them correctly: on an empty stomach or not, is any other preparation needed for this?
Antibodies are specific proteins produced by the human body to protect itself from agents that the body considers foreign. Otherwise, antibodies are called immunoglobulins. During pregnancy check:
- antibodies to TORCH infections;
- to some sexually transmitted infectious agents (mycoplasma, gonorrhea);
- antiphospholipid antibodies;
- group and alloimmune (if rhesus incompatibility or group conflicts are suspected), women with negative rhesus must undergo this test.
This analysis identifies two groups of immunoglobulins IgM and IgG. The situation is dangerous for the fetus when both globulins are detected or when IgG is not detected, but IgM is detected. This means that the infection (if determined by immunoglobulins to infectious agents) occurred recently (during pregnancy). This can be dangerous for the fetus by disrupting development and its complete cessation.
Antiphospholipid antibodies increase due to the development of autoimmune processes. For the mother, this is fraught with the development of thrombosis, which increases the risk of developing ischemia of the heart and brain. Thromboembolism of cerebral vessels, pulmonary artery, as well as vessels of the brain and liver can cause death of the mother and fetus. Thrombosis of the placenta is one of the causes of impaired fetal development and death.
The presence of group and alloimmune antibodies indicates a Rhesus or group (blood type) conflict between mother and fetus. This condition threatens babies with the development of hemolytic disease during the newborn period, which can cause:
- death of a child within a few days after birth;
- and even stillbirths;
- developmental delays;
- liver failure;
- encephalopathy and other disorders.
These proteins begin to be produced literally a week after conception. They are controlled by:
- 8-30 weeks once a month;
- from before delivery - once every 14 days.
As a result of the study, the antibody titer is obtained (for example, 1:4, 1:8, 1:16, 1:32, 1:64). These values may persist throughout gestation or may persist:
- increase gradually;
- decrease gradually;
- change abruptly.
Just keep in mind that the antibody titer is not a clear criterion for a complicated pregnancy. Healthy children were born at high titers and the fetus died at low titers. But high numbers are still considered riskier. The conflict can be avoided by introducing a special globulin that inhibits the production of immunoglobulins.
Group AB0 conflict rarely causes complications; it usually goes unnoticed. If antibodies indicating group conflict are detected, titers should be checked regularly so that specialists have time to intervene if necessary.
More often it leads to pregnancy pathology and the birth of a baby with hemolytic jaundice. The threat increases with each subsequent pregnancy. Therefore, special prevention is recommended for such women.
How are indicators for rhesus conflict assessed?
Normally, there are no specific globulins. Decryption is required when these proteins are detected:
- a ratio of 1 to 2 is considered not dangerous to the fetus;
- with a ratio of 1 to 4, they already speak of a developing conflict;
- a ratio of 1 to 16 is considered dangerous and the woman may be offered amniocentesis.
With the above ratios, natural childbirth is possible. With indicators from 1 to 32, a woman is indicated for operative and early delivery.
How are antibodies tested?
The material is taken from a vein. Is it possible to eat before such an analysis, you ask? After all, it is much more difficult for a pregnant woman to fast than outside of gestation, and you can even lose consciousness. You cannot eat; blood must be donated on an empty stomach.
In answer to your question about how to take such tests, it should be noted that you should not do:
- They do not take tests for immunoglobulins at high temperatures or in case of any illness of the mother (infection with respiratory infections or exacerbation of chronic diseases).
- You should not donate blood after physiotherapeutic procedures.
- It is advisable to refrain from taking any medications at the time of blood collection. If medication cannot be stopped, the doctor should know what medications the woman is taking.
Preparation for the procedure
Before you donate blood, you need a little preparation. It concerns diet. 3-4 days before donating blood, it is better to refuse:
- from ;
- drinks containing gas;
- fatty and spicy foods;
- meat products.
It is better for a woman during the gestational period not to consume most of these products at all. And preparing for antibody tests is a great way to bring your diet to a healthy one if the expectant mother has not already taken care of this.
This concludes our review. Before we leave, we want to answer one more question: what is the antibody test called? There is no special term for these studies. The name will depend on the type of globulins being determined and the laboratory.
For example, for infections, the name of the pathogen is usually indicated; when determining immunoglobulins for Rh factors, the analysis may be called “alloimmune antibodies,” including the determination of the Rh antigen.
Share our information with your friends via social networks and be healthy.
During pregnancy, the expectant mother is faced with the need to periodically undergo tests and examinations. At what time and what tests should I take? Obstetrician-gynecologist Galina Klimenko introduces the examination plan for the trimesters of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, a woman undergoes a lot of examinations. Why is this necessary, how to take tests correctly and learn to read their results? The survey plan will be approximately the same. If there are any complications, the list of tests may increase.
Examination plan for pregnant women by trimester HERE:
Important information about antibody titers during pregnancy
Pregnancy is one of the most exciting and joyful periods for a woman. At this time, it is important to be under the supervision of doctors and attend routine examinations in order to reduce the risk of problems with the child’s health.
Tests for blood type and Rh factor (Rh) are common basic diagnostics that are prescribed to both partners.
Important information about Rhesus conflict
Why is it carried out?
Blood type and Rh factor are genetic, individual, innate characteristics, such as eye, hair or skin color. They cannot indicate any health problems and do not affect the quality of life.
Moreover, they are very important during pregnancy if the spouses have a different Rh or blood type.
A Rh-positive (Rh+) father and a Rh-negative (Rh-) mother may have a baby with (Rh+) inherited from the man. In this case, the mother's Rh turns out to be incompatible with the child's Rh, and a conflict arises.
The mother's body identifies the fetus as foreign and begins to produce antibodies that pose a serious danger to the health and life of the child.
Blood type incompatibility (AB0 system) is also dangerous, but is less common than the situation with Rh. To prevent problems with the development of pregnancy, a specialist prescribes a woman an analysis to determine the amount of antibodies to fetal antigens.
Additional useful information on this topic
Blood analysis
Antibodies begin to be produced approximately on the seventh day from conception. They are specific serum proteins in the blood, the action of which is aimed at destroying the fetus. To prevent spontaneous miscarriage, a woman will have to undergo routine blood tests throughout her pregnancy:
- From 8 to 30 weeks it is prescribed monthly.
- From 30 weeks until the onset of labor once every two weeks.
Regular examination is important for the health of the fetus. During pregnancy, the permeability of the vascular wall increases, which leads to greater penetration of fetal antigens into the mother's body and active production of antigens.
Doctors consider the first pregnancy to be the most favorable in this regard. If there is a Rh conflict, the risk of developing antibodies is much less than in subsequent conceptions. Maternal IgM antibodies are so small that they cannot penetrate the placental barrier; conflict with the Rh+ fetus does not develop.
The danger of antibodies
Blood conflict poses a danger not only to the life of the child when he is in the womb, but also after his birth. The mother's antibodies continue to destroy the baby's red blood cells for some time. This process is manifested by hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) with the following symptoms:
Note! Blood incompatibility does not affect the mother's health in any way. It only poses a danger to the child.
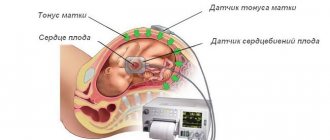
Signs of tension-type headache according to ultrasound:
- Swelling of the soft tissues of the fetal head.
- The fruit is in the Buddha pose.
- Enlargement of the abdomen, spleen, heart, liver.
- Increase in the diameter of the umbilical vein.
- Swelling of the placenta and its thickening.
What is noteworthy is that Rh incompatibility leads to the most severe consequences. A blood group (AB0) conflict occurs less frequently if the woman has group 0(I) and the fetus has A(II), less often if there is incompatibility in groups III and IV. It manifests itself in a milder form of HDN. Most often, babies are born healthy or require minimal postpartum care.
Analysis technology
The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. The patient is allowed to drink only plain boiled water. The last meal should be 8-12 hours before blood sampling.
- The specialist collects venous blood, places it in a test tube and sends it to the laboratory.
- Serum is extracted from the blood and titrated so that the next dilution differs from the previous one by 2 times. Red blood cells are added to each diluted sample.
- They look at the reaction. The reacted cells are treated with a special reagent.
- If antibodies are detected in the material being studied, a reaction occurs, accompanied by the precipitation of red blood cells.
- On this basis, the number of antibodies is calculated.
Results, values
Normally, antibodies should be absent. If they are detected, the indicator may vary (1:4, 1:8, 1:16, etc.). The obtained values can remain unchanged throughout the entire pregnancy (which is most favorable). The number of antigens may also decrease, increase, or experience sudden changes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tRhA_5chf3Q
It is important to know that the number of antibody titers will not always indicate the acquisition of HDN and its severity. There were cases when, with a high titer (1:16, 1:32), healthy children were born, and with a low titer, fetal death occurred. But high rates are always critical and pose the greatest danger to the child.
If the first analysis does not show the presence of antibodies, but there is a danger of conflict, Rh sensitization can be avoided by administering immunoglobulin . It stops the production of antibodies in the mother's body and brings them closer to normal. A specialist may prescribe the introduction of a special vaccine at 28 weeks to protect the body as the titer increases (1:8, 1:16, 1:32).
Examples of indicators
The risk level of HDN depends on the following indicators:
- Titer 1:2 is a low indicator that does not pose a threat to the life of the fetus. If it is detected at the very beginning of pregnancy, a re-diagnosis will need to be done 7-10 days later.
- The indicator 1:4 indicates the beginning of the development of an immunological reaction. A similar ratio can often be observed during the first pregnancy. It can remain unchanged until the birth of the child and does not pose a threat to the life of the fetus, although it requires constant medical monitoring.
- Title 1:16 is the most dangerous. Level 1:16 may be an indication for amniocentesis, during which a specialist punctures the amniotic fluid with subsequent study and identification of possible pathology. At titers of 1:16, the risk of intrauterine fetal death increases by 10%.
- Titles 1:32, 1:64 may be an indication for early delivery in the third trimester of pregnancy.
The IgG titer together with medical history data allows 60-70% to predict the development of tension-type headache, and ultrasound and amniocentesis increase the diagnostic accuracy to 90-95%.
Rh factor analysis
If it is discovered that a woman has a negative Rh factor and a man has a positive Rh factor, then she will need to have a blood test for antibodies every month. The presence of an antibody titer indicates an Rh conflict between the body of the mother and the fetus, when the mother’s immune system perceives the Rh-positive fetus as a foreign agent and begins to defend itself against it. As a result, the child suffers in utero. Rh-conflict pregnancy requires observation of the expectant mother in a hospital setting.
How to submit?
Why do antibodies appear in the mother's body?
An immunological conflict (the mother's body produces antibodies that attack the fetus) can arise due to incompatibility in both blood group and Rh.
Blood group incompatibility (so-called ABO), causes:
- 1 group women, 4 group men (100% incompatibility),
- Group 2 women, group 4 men (66% probability),
- Group 3 women, group 4 men (also 66%),
- Group 1 women, group 2 or 3 men (50% chance of incompatibility),
- Group 2 women, group 3 men (50%),
- Group 3 women, group 2 men (25%).
The isohemagglutinins “living” in the blood of the expectant mother stand in opposition to the antigens in the blood of her partner - this is called incompatibility.
By the way, the body of some women takes up arms against foreign blood long before conception. The reason for this may be incorrect blood or serum transfusion (without taking into account group compatibility, that is, ABO), or vaccination.
In addition, women with:
- frequent miscarriages,
- abortion on the big line,
- premature pregnancies,
- death of the fetus
- births with cesarean section,
- births with complications (such as premature abruption or manual separation of the placenta).
Blood chemistry
Allows the doctor to evaluate the functioning of many internal organs - kidneys, liver, pancreas; shows which microelements are missing in a woman’s body. Blood biochemistry may indicate disturbances in the functioning of internal organs when there are no external symptoms of the disease.
How to submit?
On an empty stomach. Blood is taken from a vein. It is better to have dinner early the day before, so that at least 12 hours pass after eating. Eliminate fatty foods from your diet the day before the expected test.
What danger lies in incompatibility?
There are no external factors of incompatibility between the fetus and mother. The woman still goes to work, sleeps peacefully at night, makes her favorite sandwiches - and at this time her immune system is trying to destroy the fetus's red blood cells.
A woman’s body does not sound the alarm with pain or ailments - of course, incompatibility does not pose a danger to it. The same cannot be said about the fetal body!
Red blood cells have a very important function - they carry oxygen throughout the body. If they are destroyed, a large amount of fluid will accumulate in all tissues of the fetal body.
Moreover, the process of action of the woman’s antibodies will continue even after the birth of the child. This is precisely the cause of HDN (hemolytic disease).
This disease of newborns occurs:
- Anemic.
- Jaundiced (as the above-mentioned bilirubin accumulates in the skin, its color becomes yellowish).
- Edematous (the most dangerous form, in which unresolved fluid accumulates in the baby’s body).
The likelihood of the appearance and development of this disease can be seen by an ophthalmologist. He will be alarmed:
- the so-called “Buddha pose” of the fetus,
- swelling visible on the arms, legs and head,
- enlarged heart
- fluid in the chest and/or abdominal cavity,
- little fetal movement
- high echogenicity of the intestine,
- placental hyperplasia.
Worth remembering! Blood type incompatibility does not affect the little one’s body too much, so long-term treatment in this case is not necessary. Rhesus incompatibility is another matter. It can lead to pathology of the fetus and even kill it.
Blood test for hepatitis viruses, HIV, syphilis (RW)
Why is this test taken three times during pregnancy? The fact is that viral infections have a certain period from the time the pathogens enter the body until the production of antibodies begins. When a woman is tested for viral diseases early in pregnancy, they may give negative results. And after 6 months, tests may show that she is infected. If the expectant mother is not tested for viral diseases in the last trimester, in the maternity hospital she will be placed in the observation ward (where untested patients or those with infectious diseases are kept).
How to submit?
No preparation required. Blood is taken from a vein.
What is dangerous about deviation from the norm - possible consequences for the fetus
In case of Rh conflict, the baby is at risk of impaired blood metabolism and lack of oxygen, which often leads to the following diseases:
- hepatitis;
- anemia;
- impaired development of the brain and cardiovascular system;
- enlarged liver, spleen.
If there are signs of hemolytic disease in a child, an immediate blood transfusion is given to the mother. However, it is worth noting that it can only be detected in the early stages by taking an antibody test. The disease cannot be detected by external signs, and ultrasound examination shows only a progressive, advanced stage.
If immunoglobulins to certain infections are detected, this can cause serious consequences:
- The appearance of antibodies to toxoplasmosis at the beginning of the gestation period after conception threatens to infect the fetus with this disease, which will lead to disruption of the development of the liver, spleen and central nervous system. To avoid undesirable consequences, pregnancy is terminated. In the 3rd trimester, the risk of infection of the baby decreases to 70%.
- If antibodies to rubella are detected in the early stages, it is suggested to have an abortion, since there is a danger of damage to the heart, eye and nerve tissues. At a later date, no dangerous consequences were found, but a delay in the baby’s development was noticed.
- Cytomegalovirus infection leads to fetal death or congenital diseases of the brain and internal organs.
- Elevated TPO levels may signal the development of hyperthyroidism or lead to postpartum thyroiditis.
- An increase in the level of antiphospholipid antibodies indicates the likelihood of developing immune aggression. Antiphospholipid syndrome leads to spontaneous miscarriage or intrauterine pathologies due to impaired blood metabolism in the placenta.
Doctor's comment on the topic of AT analysis: