From this article you will learn:
- what is chronic apical periodontitis,
- differences between acute and chronic forms,
- Diagnosis based on symptoms and x-rays.
Apical periodontitis (according to Lukomsky’s classification) is usually divided into several forms. First of all, this is 1) acute periodontitis, 2) chronic periodontitis. The acute form of inflammation is characterized by severe pain and swelling, while the chronic form is characterized by sluggish symptoms or may be completely absent. In the latter case, patients sometimes turn too late for treatment of the inflammation at the apex of the tooth root, and often the treatment of such teeth can only be surgical.
In addition, there is such a form as exacerbation of chronic periodontitis. As a result of the influence of unfavorable factors, such as colds, immunity deteriorates, which most often leads to an exacerbation of chronic inflammation. The period of exacerbation is characterized by the same severe symptoms as in the acute form of the disease. Below we will talk about the symptoms and diagnosis of each form separately.
Clinic, ICD 10 code
To make a preliminary or main diagnosis, dentists use the following characteristics:
| Types of periodontitis | Clinical symptoms | Complaints |
| Serous form | The diseased tooth becomes mobile, soft tissues swell, lymph nodes enlarge, leukocytosis is observed, and ESR increases | Increased sensitivity and pain when biting, malaise, increase in body temperature up to 39°C |
| Chronic fibrotic | Change in tooth color, appearance of deep carious cavity, lack of response to cold and heat | Asymptomatic |
| Chronic granulomatous | Presence of carious cavity, bulging bone | Rare complaints of discomfort, minor pain |
| Exacerbated chronic | Swelling of the gums, enlarged lymph nodes, the presence of a deep carious cavity, tooth mobility, lack of response to cold and heat | Increasing pain when biting |
The disease goes through more than one stage of development, so specialists have developed several classifications of the disease for convenience. The officially recognized and used documentation remains ICD-10. Periodontitis corresponds to code K04 with the wording “Diseases of periapical tissues”.
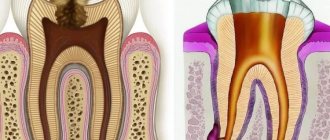
Photo 1. Schematic representation of a healthy tooth (left) and one with periodontitis (right).
Signs of chronic form
This disease can occur in acute or chronic form. The latter also has its own varieties, which will differ in certain clinical manifestations and symptoms.
Chronic fibrous form
This form of the disease can be diagnosed based on several signs. During its development, a person notices that the tooth has changed its usual color. Caries of varying depths may occur .
But in the presence of a chronic pathological process, the intact (healthy state) of the crown may remain.
With this disease, there is no reaction to cold or heat , and probing is not accompanied by pain. In rare cases, upon examination, necrotic pulp is detected, which has the smell of dead cells.
This type of periodontitis is difficult to determine by symptoms alone, since a sick person often does not have pronounced manifestations or any obvious complaints. To make a final diagnosis, a specialist needs to compare symptoms and x-ray results.
Chronic granulating form
Symptoms of this type of disease are:
- Unpleasant sensations in the gums, especially after eating . Sometimes there may even be a slight pain, but then it subsides.
- A person is constantly accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the gums or swelling . It feels like something is constantly getting in the way.
- fistulas can appear , causing pain to a person. In the area of the fistula, accumulated pus or granulation tissue is released.
- Experts identify this particular type of periodontitis by the presence of hyperemia on the gums . It is localized near the diseased tooth.
- Not only redness makes it clear to the doctor that this is chronic granulating periodontitis.
A sign is also characteristic “pushing” the area of hyperemia – when you press it, a depression appears that does not level out on the gum tissue for some time after the specialist stops the mechanical impact on the reddened area.In the event of such exposure, the patient notes the pain or discomfort that appears.
- This disease can also provoke an enlargement of nearby lymph nodes , as there is a deep inflammatory process with the formation of pus.
- A symptom that defines this particular form of the disease is also the presence of rarefaction of the jaw bone in the upper area of the tooth root in the picture .
These symptoms may appear simultaneously and intensely, or may not bother the person much, so additional diagnostics are carried out to make the correct diagnosis and determine adequate treatment.
Chronic granulomatous form
A person may not immediately realize that he has dental disease. This type of disease most often does not manifest itself clinically . There may be similar symptoms to the previous type, in particular, fistula, swelling and redness of the gums.
The main symptom based on which the diagnosis is made is a small area of rarefaction of the jaw bone in the image after the diagnosis . It can be round or oval in shape.
It is characteristic that the lesion has distinct edges, unlike the previous type, and its size is about 5 mm.
The doctor also pays attention to the patient’s complaints, indicating that sometimes there are exacerbations of inflammation . For this species, this symptom is a significant additional feature.
Pathogenesis
The development of periodontitis is most often characterized by the entry of microorganisms into the periodontal gap, which have a toxic effect . When immunological mechanisms are weakened, an acute diffuse inflammatory process develops, which leads to the appearance of abscesses with characteristic signs of general intoxication of the body.
Damage to periodontal connective tissue is observed. As a result, microcirculation is disrupted, all five signs of inflammation appear: pain, swelling, hyperemia, local increase in temperature, dysfunction.
If the process is observed in a diseased tooth, experts note chronic inflammation, often asymptomatic. With weakened immunity of the body, the chronic process worsens with the manifestation of all the characteristic signs of acute periodontitis.
Causes of inflammation
Experts urge you to visit the dental office every six months .
Such prevention is necessary for the timely detection of many diseases.
Damage to teeth, for example, chips and other damage to the enamel, creates conditions for the penetration and development of infection in periodontal tissues.
Reference. Periodontitis is a consequence of inflammation ( periodontal disease, gingivitis, pulpitis and others).
There are several reasons:
- Infectious: pathogens of inflammatory processes enter the gums through the bloodstream of internal organs during infectious diseases (ARVI, tonsillitis, sinusitis, influenza, measles).
- Contact: crowns destroyed by caries receive food particles and pathogens from saliva. “Thanks to” this symbiosis, decay products accumulate in the dental canals.
- Medication: often the cause of inflammation is an unqualified doctor who introduces an infection while performing dental procedures on the gums.
Various types and classification
Periodontitis is classified into two main areas.
According to the factor causing the disease
- Infectious . They can be divided according to the way the infection penetrates the tissue - extra- and intradental, that is, from the inside or outside.
- Traumatic . They can be acute and chronic, which are characterized by different symptoms and the nature of the injuries.
- Medication . They also consider diseases that arise as a result of allergic reactions to injected drugs.
By the nature of the discharge and its course
- Spicy . There are purulent and serous varieties.
- Chronic . Subtypes: granulomatous, granulating or chronic fibrous periodontitis.
- Separately, there is an exacerbation of the chronic form .
Visual diagnostics
Periodontitis is an insidious disease, divided into different types and forms.
Experts note common signs for all stages of the disease: putrid odor from the mouth, bleeding gums during hygiene procedures, pain of varying degrees, the feeling of an overgrown tooth.
It is difficult to identify periodontitis in the early stages of the disease, but it is possible thanks to careful visual diagnosis.
| View | Form | Often | Sometimes | Note |
| Chronic | Fibrous | Change in tooth color, presence of carious lesions | Necrotic pulp | X-ray examination required |
| Granulating | The appearance of fistulas with the release of pus, redness on the gums, pressing of the tooth into the gum after mechanical impact | Enlarged lymph nodes | Additional diagnostics required | |
| Granulomatous | Fistula, swelling, redness of the gums, weakening of the jawbone | Filling falling out | Diagnosed only by X-ray examination | |
| Spicy | Acute | Extensive inflammation, severe swelling, the tooth is pushed out of alignment, swelling of the cheek is observed | Discoloration of gum tissue, increased tooth mobility, enlarged lymph nodes, swelling of the face | Accompanied by an increase in body temperature |
| Purulent | Inability to close jaws due to pain, swollen lymph nodes | Increased body temperature, general lethargy | The pain decreases only after applying cold, x-ray diagnoses the disease 3-5 days after the onset | |
| Toxic | Edema, hyperemia | Burns and gum necrosis | Consequence of incorrect treatment | |
| Apical | Swelling of the lips, gums, face | General lethargy | Increase in body temperature up to 40°C | |
| Marginal | Asymmetrical swelling of the face (lip and cheek), swelling of the gums, enlarged and painful lymph nodes | Gum receding from tooth | Triggered by trauma, leads to abscesses | |
The main causes of the disease
This dental disease occurs due to several reasons. The most common ones are:
- pulpitis that is not treated in time, or its treatment is poor, in this case toxins and various bacteria can enter the periodontium;
- injuries or bruises;
- cracking a nut or bone with teeth;
- the habit of gnawing objects that are not related to food (pencil, biting thread, pen);
- a high filling can also lead to this disease;
- drug overdose, when some dental drugs linger in the canal longer than necessary.
Periodontitis comes in different types and forms. Depending on the type or form of the disease, a person may experience different symptoms.
A dentist will tell us briefly about this disease in the following video:
What does the disease look like on an X-ray?
Experts call X-ray examination one of the leading
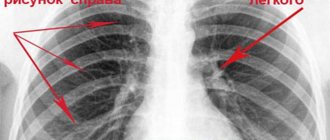
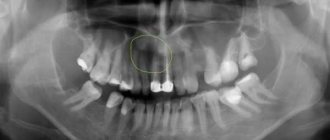
Photo 2. X-ray of a tooth with periodontitis. The area of inflammation is highlighted in red.
It is necessary to find out the condition of the jaw bone tissue, determine the presence of cysts or other formations and whether it is possible to save the tooth.
| Type of periodontitis | Signs |
| Granulomatous | Focal pathological formations (granulomas), partial bone loss, unclear contours, and shadows similar to flames are observed. |
| Chronic | Significant expansion of the periodontal fissure. |
| Fibrous | Scar tissue in the form of thickening, protrusions on the tooth root, darkening of the area in the upper part of the tooth root. |
| Marginal | Fractures, fragments of foreign objects, and cracks are clearly visible. |
Clinical picture of chronic periodontitis
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- soreness in the oral cavity (usually dull, aching pain),
- increased pain when biting on the affected tooth,
- yellowing and destruction of tooth enamel,
- inflammation, redness of the gums,
- development of a fistula in the affected area,
- enlargement of the jaw lymph nodes.
If the clinical picture described above develops, an x-ray examination is mandatory. If periodontitis is suspected, an x-ray will allow you to study in detail the features of the pathological process and determine treatment tactics.
- soreness in the oral cavity (usually dull, aching pain);
- increased pain when biting on the affected tooth;
- yellowing and destruction of tooth enamel;
- inflammation, redness of the gums;
- development of a fistula in the affected area;
- enlargement of the jaw lymph nodes.
Diagnostics
Periodontitis is a disease that has similar symptoms to other diseases. Its diagnosis is complicated by the fact that the appearance of the periodontal fissure practically does not change , and an x-ray may not show any signs of the disease. To correctly diagnose a disease, specialists must remember the main distinguishing characteristics of diseases with similar symptoms.
| Disease | Distinctive symptoms | Similar symptoms |
| Osteomyelitis | Pain in several teeth, intoxication of the body, fever, chills | Similar to the acute form of periodontitis |
| Periodontitis | Bleeding, abscesses appearing in different parts of the gums, large bone pockets | |
| Sinusitis | Darkening of the maxillary sinuses, nasal discharge | |
| Deep caries | Reaction to temperature stimuli is present | Similar to chronic periodontitis |
EDI during diagnosis
Electroodontometry , or EOD, helps identify dental pulp excitability. Normal values are 6-8 µA . The higher they are, the greater the likelihood of inflammation or even necrosis. The procedure is carried out using a special device.
Pathological indicators of EDI:
- For chronic periodontitis: 100-160 µA.
- For acute or aggravated: 180-200 µA.
Photo 3. Pathological anatomy or pathological anatomy of a tooth with chronic periodontitis. Dental tissues are shown under a microscope.
Dental periodontitis: what it is, how to treat it
| Treatment of periodontitis always begins with a doctor analyzing the patient’s complaints and studying the image. Only after this will it be possible to understand whether a tooth will need to be removed due to periodontitis, or whether it can be saved! |
Treatment of periodontitis: stages
- If the disease has reached an acute stage, then the doctor’s first priority is to create an opportunity for the pus to flow out, since otherwise it will not be possible to get rid of the acute pain.
- The crown (if any) is removed, the root canals are unfilled (this must be done on the patient’s first visit).
- If the gums are swollen, the abscess will need to be opened.
Open root canals will allow the pus to drain freely, which will significantly relieve the pain. In addition to this, the dentist will prescribe antibiotics and rinses. A repeat visit is scheduled no earlier than two to three days later. If the pus no longer drains by this point, an antiseptic drug is placed in the canals.
Further methods of treating periodontitis will largely be determined by the size of the inflammatory focus.
The danger of the disease for pregnant women
Periodontitis is almost always a complication of caries . The inflammatory process, moving through the tissues, destroys enamel, dentin and pulp. If treatment is not carried out, the disease enters a new stage - periodontitis. A focus of inflammation forms at the very top of the root. This disease is especially dangerous during pregnancy. The patient's general condition worsens, body temperature rises, and lymph nodes enlarge.
Attention! It is dangerous for pregnant women to self-medicate, as there is a risk of miscarriage.
When the pathology is complicated, pathogenic microorganisms spread throughout the body, penetrate the placental barrier, threatening the unborn child.
Treatment of expectant mothers is very limited , this applies not only to medications, but also to research methods. Therefore, you need to be prepared for complications, since it is not possible to carry out a full diagnosis in this situation.
Differences from pulpitis
Pulpitis should not be confused with the disease in question. They have significant differences in localization, despite often similar symptoms.
The fact is that pulpitis is also an inflammatory disease, but all processes occur exclusively in the pulp of the tooth. Pulp is the soft tissue that is located inside the teeth.
With any form of pulpitis, absolutely no changes are observed in the nearby tissues, and the tooth is firmly held in the gum. Periodontitis can occur as a complication of pulpitis , when the infection passes down to the apex of the root and comes out through the root canals.
Causes of exacerbation
experts identify two factors due to which the chronic disease takes an acute form
- The body's susceptibility to infections due to decreased immunity. ARVI, various viral infections, stress, weakness and general unstable condition reduce the body's resistance, which leads to the active proliferation of microorganisms and makes the patient even more vulnerable.
- The emergence of suitable conditions for the development of pathogenic bacteria . The cause is the accumulation of food debris, plaque inside an open dental tubule or under the soft gum tissue.
Complications of periodontitis
If periodontitis is not treated, there is a risk of serious complications.
Granuloma: what is it?
It resembles a small sac ( about 0.5 cm ) surrounded by granulation tissue, like a capsule. Inside there is inflammatory fluid . Location: apex of the tooth. This is the epicenter of the disease. The purpose of this complication is to destroy healthy tooth tissue. The inflammatory focus cannot be left without treatment , since further inaction will lead to disruption of many body systems.
Photo 4. Granuloma caused by periodontitis. It is a swelling on the gum.
Cyst
A benign inflammatory formation with very dense walls. It appears to protect the body from developing infection. Reaches up to 1 cm in size. The cyst can increase in size, destroying neighboring teeth. Rupture of the capsule walls in some cases can lead to infection of the patient’s blood.
Gangrenous form
An inflammatory process that is characterized by serious changes in the root part of the gums and periodontium.
How is the disease treated in the acute stage?
Treatment methods for the disease in the acute chronic stage include:
- Cleaning tooth canals using aseptic preparations.
- Antiseptic agents are placed into the resulting holes to eliminate the infection.
- Medicines are injected into the tooth cavity to accelerate tissue restoration.
- The tooth is filled with temporary material, and its condition is monitored for several months If positive dynamics are noted during the recovery process, the temporary material is changed to permanent. Medicinal mixtures are often used as temporary material.
- In the treatment of periodontitis, various physiotherapeutic methods are used: UHF therapy, electrophoresis, laser, microwave and magnetic therapy.
- Antibiotics are used in cases where surgical intervention is difficult or the disease is in an advanced state.
Possible consequences of treating pulpitis
No matter how well the therapy procedure is carried out, there is a chance of developing complications of pulpitis. After treatment, there is a risk of tooth fracture. To avoid this, the patient is given a crown, and if the tooth walls are adequately preserved, restoration is carried out with a photopolymer.
As a complication, in the absence of timely treatment, periodontitis may develop. The disease is accompanied by an acute inflammatory reaction in the tooth and adjacent tissues. The complication has several stages. In the first case, the inflammatory process can be stopped and the tooth can be saved; in the second case, it is removed.
Although x-rays are not able to unambiguously determine the presence of pulpitis, the study remains a key point in diagnosing the pathology. Thanks to an x-ray, the dentist identifies indirect signs of pathology, begins timely treatment and saves the tooth.
- We treated caries of the sixth tooth. The nerve in the tooth could not be saved. We performed root canal treatment with a microscope, as a result of which the pain in the teeth stopped. The treatment was performed by endodontist T.I. Matienko. The price of tooth canal treatment with a microscope is 20,000 rubles.
- Since a tooth without a nerve is more fragile, and its walls can break off under chewing load, a ceramic inlay was used for restoration. Dental technician Volk D.V., prosthetist Ivankov A.S. The cost of a ceramic inlay is 20,000 rubles.
- Treatment of caries of the seventh and eighth teeth was performed by dentist N.A. Kolesnikova. The teeth were restored with light fillings made of Estelite Sigma Quick material, the price is 4,500 rubles per filling.
The patient was once again explained the need to visit the dentist once every six months and selected products for oral hygiene.
See other examples of caries treatment at Family Dentistry here.
Compared to a dental cyst, pyogenic granuloma of the dental root is more successfully treated with conservative methods aimed at eliminating the affected lesion and preserving the crown. Therapeutic measures are effective in the early stages of the inflammatory process, until suppuration has developed, as opposed to a cyst.
Canals cannot be filled without x-rays. The first procedure is carried out before treatment and is considered diagnostic. The second photo is necessary for control. The doctor evaluates the correctness of the chosen treatment method. Pathological formation is eliminated using dental treatments. The therapeutic process is carried out in several stages:
- The previous filling is removed or the unfilled tooth is opened.
- The dental canal is cleaned mechanically, which makes it possible to better eliminate purulent fluid, and the affected tissue is excised.
- The canal is sterilized by washing with a disinfectant, ultrasound or laser.
- A medicine with calcium hydroxide is placed inside the canal, which inhibits the active spread of bacteria that provoke an increase in bone material behind the root. The situation is visible through radiovisiography 20 days after administration of the drug.
- A temporary filling is placed.
When the doctor notes on the x-ray the cessation of the inflammatory process and intensive healing of the wounds, the following measures are taken:
- The medicinal paste is removed and the dental canals are re-treated with disinfectants.
- The filling of teeth is completed. An effective option is to use modern vertical condensation methods. The method involves heating and compacting medical gutta-percha in the root canal, filling the lateral area and taking the form of branches.
What do the statistics say?
The statistics on the incidence of periodontitis is unfavorable: in children it is 20-30% , in adults it is 30-50% . Modern dentistry successfully treats this complex disease, but only if the patient follows all the specialist’s recommendations. Pain and fear when treating an illness are a thing of the past.
Modern techniques and medications help treat teeth completely painlessly . It is worth noting that unfounded fears aggravate the development of inflammation, in which periodontitis can result in a serious complication. Take care of your teeth and be healthy!