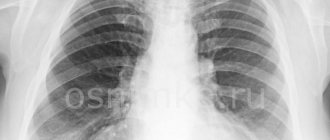
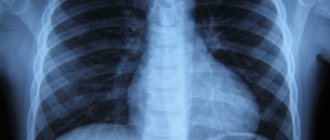
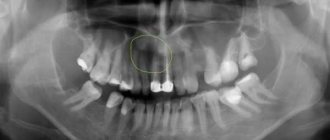
Modern diagnostics for adenoids includes many different types of examinations. One of them is radiography, which helps the doctor determine the size of the pathological growth in the nasopharynx, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment in a timely manner.
Adenoids cause a lot of trouble mainly for children. Growths in the pharyngeal tonsil block the nasal passages, complicate breathing and provoke inflammatory processes. To clarify the degree of growth, a specialist often prescribes an x-ray procedure of the adenoids for children.
Causes
Pathological vegetation of lymphoid tissue in children occurs for the following reasons:
- chronic tonsillitis;
- childhood infections (whooping cough, diphtheria, scarlet fever);
- frequent viral diseases (flu, ARVI);
- allergic mood of the body (the baby has a reaction to foods with chemicals and excessive consumption of sweets);
- immune failure (weakness of defenses);
- artificial feeding (with breast milk the baby receives the mother’s immune cells);
- vaccinations (inadequate reaction to vaccination often provokes adenoids in the nose);
- hereditary predisposition (abnormal functioning of the lymphatic system, usually combined with endocrine pathology);
- external environment (dust, polluted air, plastic releasing toxins, household chemicals);
- pathological pregnancy/birth (viral infection of the pregnant woman in the 1st trimester, fetal hypoxia, birth asphyxia).
Depending on the size of the growth, it is customary to distinguish three degrees of adenoids in children. This division is very appropriate and important in terms of patient management tactics. In particular, large growths require the most active intervention, because they significantly worsen the quality of life and can quite soon provoke complications.
Visual cues
Much depends on the stage of development of the process in a person. Where to look for adenoids, in the throat or nose and is it possible to find them yourself?
It is impossible to detect the growth of the pharyngeal tonsil in the early stages. This can only be done by a doctor using a special device (mirror laryngoscope).
The pharyngeal tonsil in its normal state appears as a comb-like structure covered with small hairy papillae.
Some definitions
The vomer is a bony structure that is part of the nasal septum.
Choanae are small openings through which the nasal cavity communicates with the pharynx.
Photo: Vomer and choanae
Diagram: What adenoids of different degrees look like
What adenoids of different degrees look like in the photo (can be enlarged)
What do grade 1 adenoids look like?
Photo: Stage 1 adenoids through an endoscope Enlarged adenoids at the first stage do not grow to such a significant size that they can be seen with the naked eye.
When conducting an examination using mirrors, a hyperemic area of lymphoid tissue measuring 0.5-2 cm is determined. It grows unevenly.
We can talk about the first degree of adenoids when no more than a third of the vomer and choanae are closed.
Inflamed adenoids of the first degree cause almost no discomfort to the patient, which is why the diagnosis is rarely made at such an early stage.
Symptoms
Problems with inflammation of the adenoids should be suspected if a child has the following symptoms:
- often has a slightly open mouth;
- breathes through the mouth instead of the nose;
- signs of adenoid in children often suffers from ear and upper airway infections;
- sleepy, lethargic and whiny (this is due to hypoxia);
- difficult to concentrate;
- complains of headaches;
- speaks vaguely;
- hears worse.
All signs of adenoiditis that occur with inflammation depend on what causes their inflammation, but include:
- pain in the larynx;
- difficulty breathing due to nasal congestion;
- swollen lymph nodes in the neck;
- middle ear pain and other hearing problems.
When the nose is blocked, breathing through it becomes a problem. Other symptoms of adenoid inflammation associated with nasal problems include breathing through the mouth, difficulty sleeping, and developing a resonating effect when speaking.
How to recognize?
How to determine adenoids in a child at home? Compare his condition with the symptoms described above. If they coincide, there is a reason to urgently make an appointment with an ENT specialist. Only a doctor can absolutely accurately determine whether such a pathology is observed.
How to recognize adenoids in a child? A special examination is required. As part of this, the pharynx is examined in mirrors. A special device with a small round mirror (no more than 10 mm) in diameter is used. With its help, the tonsil area starting behind the soft palate is examined.
How to recognize adenoids in a 3-year-old child? With the help of this mirror device, which helps to examine the pharynx where it cannot be seen with the naked eye. Next, the doctor determines the stage of progression of the pathology. Based on observations, he can identify the cause of the disease.
In addition, the mirror device helps to discern the condition of the enlarged tonsil itself. It may be inflamed, covered in mucus, pus, or swollen due to an allergic reaction.
Adenoids 1st degree
First-degree adenoids cover only a third of the lumen of the nasopharynx and do not cause serious complications, which allows the child to lead an active lifestyle and breathe calmly during the day. Difficulties in the process of nasal breathing most often appear during sleep in a horizontal position, as this changes the location of the adenoids. They begin to close most of the lumen of the nasopharynx, forcing the child to breathe through the mouth.
An important sign for parents that signals the beginning of the growth of adenoids can be poor sleep in the child and frequent nightmares due to lack of oxygen. Against this background, chronic daytime sleepiness and fatigue develop. The child may also experience nasal congestion and serous discharge.
Tips for parents
If you have removed grade 3 adenoids from a child, you need to focus all your efforts on strengthening the immune system and eliminating the risks of relapse of the disease. So what to do:
- Every year, relax by the sea for at least 2 weeks.
- Take regular walks in the fresh air and visit the pool.
- Maintain nasal hygiene and regularly rinse the nasopharynx.
- Provide proper nutrition. After treatment of adenoids, the diet should be free of spicy and fried foods. Food should not be too cold or too hot.
- To strengthen the immune system, take vitamin complexes and immunostimulating drugs.
- Provide cool, moist indoor air. Regularly ventilate the child’s bedroom and carry out daily wet cleaning. Get rid of things that accumulate dust: carpets, soft toys.
Where to go? ENT clinics in Moscow:
ENT Clinic No. 1 on Garibaldi Moscow, st. Garibaldi, 3 Children's clinic Fantasy on Garibaldi Moscow, st. Garibaldi, 36 Family Doctor Clinic on Baumanskaya Moscow, st. Baumanskaya, 58/25, bldg. 12, p.2 SM-Doctor on the street. Kosmonavta Volkova Moscow, Kosmonavta Volkova, 9/2 Center for Motherhood, Natural Development and Child Health Moscow, st. Gasheka, 9 (entrance from the yard) Medical center Family clinic on Izmailovskaya Moscow, st. Pervomaiskaya, 42 All ENT clinics in Moscow on the map
Adenoids grade 2
Adenoids not only grow, but from time to time they can also become inflamed. In this case, an acute disease called adenoiditis occurs. Its signs:
- the thermometer confidently surpasses 38 degrees;
- the appearance of liquid, possibly mixed with blood, discharge that turns into mucopurulent;
- It is difficult for the baby to fall asleep, he snores at night, and short-term pauses in breathing occur - apnea.
The doctor prescribes treatment to which the disease responds, but with repeated exacerbations of the disease, the adenoids have to be removed.
Adenoids of the second degree are manifested by significant difficulty breathing, which increases at night. The constant lack of oxygen explains the baby's weakness and lethargy, drowsiness, developmental delays, weakness and headache. Bronchial asthma, bedwetting, and hearing and speech impairment may occur.
Why are adenoids dangerous?
Due to constant breathing through the mouth, the child’s body does not receive enough oxygen. It is necessary to treat adenoids in the nose in a timely manner, otherwise complications cannot be avoided. The danger is not the proliferation of lymphoid tissue itself, but the diseases associated with it. Among the complications:
- chronic otitis;
- chronic sinusitis (sinusitis);
- hearing impairment;
- the appearance of speech defects;
- hypoxia;
- stopping breathing during sleep.
Chronic otitis is a sluggish inflammatory process in the middle ear. It is dangerous due to perforation of the eardrum and hearing loss. Otitis media does not lead to deafness, but a person with a chronic form hears about 20% worse than healthy people.
Chronic sinusitis, in particular sinusitis, is another common complication of adenoids. The disease manifests itself as inflammation of the nasal sinuses and requires complex treatment.
Note! Quite often, otitis media and sinusitis “go hand in hand” with grade 2 and 3 adenoids.
Another common complication is the appearance of speech defects. Since the child cannot breathe through his nose, he does not pronounce some sounds. Also, if nasal breathing is impaired, a noticeable nasal voice is observed.
Hypoxia, or oxygen starvation of tissues, is a complication of grade 3 adenoids. This is due to the fact that when breathing through the mouth, the body lacks oxygen. As a result, metabolic processes deteriorate, sleep quality decreases, and cognitive functions suffer. This is especially noticeable in children of primary school age who have problems concentrating in class due to the fact that the brain does not have enough oxygen.
The most dangerous complication is sleep apnea. This disorder manifests itself as a short-term cessation of breathing during sleep. In severe cases, there is a risk of complete respiratory arrest.
Adenoids grade 3
With a significant increase in adenoids, their effect on the child’s body becomes more and more destructive. Constant inflammation contributes to the uninterrupted production of mucus and pus, which easily enter the respiratory system. Laryngitis, pharyngitis, tracheitis and bronchitis become frequent guests, and purulent otitises also join them.
The process of normal development of the bones of the facial skeleton is disrupted, and this affects the development of the baby’s speech in the most unfavorable way. Inattentive parents do not always notice the nasal sound that appears, and the inability to pronounce many letters is attributed to other reasons.
A constantly open mouth changes the appearance of a hitherto attractive child, and he begins to have psychological problems due to the ridicule of his peers. There is no need to hope that the child will outgrow it; at this stage, visiting a doctor becomes a necessity. [adsen]
How to prepare your child for x-rays
After an initial examination by an otolaryngologist, the child’s parent is given a referral for examination, which includes a mandatory x-ray. You should not ignore, delay, or delay completing this technique. You should arrive a little earlier before your scheduled appointment, give your child the opportunity to get used to the unusual hospital environment.
The day before, give your baby a haircut, bathe him, and prepare him mentally. Speak in a calm, friendly tone and try to explain in a language accessible to him the essence of the upcoming “event.” Never show your excitement or anxiety; children are very sensitive and will immediately feel the insincerity in your words. For him, the main thing is how you lead. How confident are adults in the correctness and necessity of X-ray examinations and trust in doctors? This confidence and calm will be passed on to the child. The radiographic result will make a significant contribution to the plan for curing a nasopharyngeal disease in a child. It will help establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the selection of the correct and targeted medications. Prescribe those types of physiotherapeutic procedures that are individually suitable for each child. They will facilitate the work of surgeons in radical therapeutic interventions (minimally invasive or surgical). This method (X-ray forms) is used in many countries. Despite the fact that, as already mentioned, its radiation is harmful. So far, the comprehensive research technology program has not excluded this “outdated” option for X-ray exposure from its list. Parents are wary of it, having heard a lot about how harmful it is. They try, believing that they are doing something better for their child, to avoid X-rays.
Related articles Diagnosis of adenoids: endoscopy - an innovative method
In vain! If a pediatric ENT specialist considers it necessary to include it in the examination scheme, it means that he has quite good reasons for making such a decision. Doctors expect mutual understanding, restraint, a friendly attitude, and respect for their work from adults and relatives of the child. Through joint and united efforts directed in a single direction, the effect of successful treatment of adenoid infection will come much faster than in cases of mutual misunderstanding.
Diagnostics
Comprehensive diagnostics consists of conducting a full examination, consisting of several stages:
- Determination of complaints and medical history.
- Digital examination of the nasopharynx.
- Rhinoscopy (anterior and posterior) – examination of the upper parts of the nasopharynx using a mirror.
- X-ray of the nasopharynx (currently used extremely rarely).
- Endoscopy (examination using a probe with a camera).
- CT.
Endoscopic examination and computed tomography are considered the most informative diagnostic techniques, which make it possible to accurately determine the degree of growth of adenoid vegetations, the reasons for their increase, the structure of the tissue, and the presence of edema. And also find out the condition of neighboring organs, determine the possibilities of conservative methods of therapy (local treatment, laser therapy, therapy with folk remedies and homeopathy, physiotherapy) or the need for surgery and the adenotomy technique. [adsen1]
What is the procedure
An X-ray of the nasopharynx if adenoids are suspected is a non-invasive procedure that allows you to obtain an image of this organ using X-ray radiation on a special film or paper. X-rays pass through the human body, “transparenting” it. As a result, the specialist receives a black and white image of the nasopharyngeal tonsils on X-ray film or other photosensitive material.
Radiography has established itself as a fast, accessible method widely used in the diagnosis of ENT diseases. An undoubted advantage of radiography is that there is no need for special preparation of the patient for this study.
How to treat adenoids in children?
Doctors know several ways to treat adenoids - without surgery and with the help of surgical placement. But recently, the newest method of getting rid of the disease has come to the fore - laser.
General treatment regimens are based on the following:
- Laser therapy - today this method is considered very effective, and most doctors consider it safe, although no one knows the long-term consequences of laser exposure, and no long-term studies have been carried out in the field of its use. Laser therapy reduces swelling of lymphoid tissue, increases local immunity, and reduces the inflammatory process in adenoid tissue.
- Drug therapy for adenoids consists primarily of thoroughly removing mucus, discharge from the nose and nasopharynx. Only after cleansing can local medications be used, since the abundance of mucus significantly reduces the effectiveness of therapy.
- Physiotherapy is ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, UHF - procedures that are prescribed by a doctor endonasally, usually 10 procedures each.
- Climatotherapy - treatment in sanatoriums of the Crimea, Stavropol Territory, Sochi has a positive effect on the entire body, improves immunity and helps reduce the proliferation of adenoids.
- Massage of the collar area, face, breathing exercises are part of the complex treatment of adenoids in children.
- Homeopathic remedies are the safest method of treatment, the effectiveness of which is very individual; homeopathy helps some children very well, while for others it is poorly effective. In any case, it should be used, since it is safe and can be combined with traditional treatment. It is especially recommended to take Lymphomyosot, a complex homeopathic medicine produced by the well-known German company Heel, and thuja oil for adenoids is considered a very effective remedy.
The child's diet should be rich in vitamins. Eating low-allergic fruits and vegetables and lactic acid products is necessary.
When else is an X-ray of the nasopharynx prescribed?
As mentioned earlier, adenoids are one of the most common reasons for X-ray diagnostics aimed at the nasopharynx. But one should not assume that this is the only reason for such research. The problem may also be the need to identify the consequences of mechanical damage to the bones of the nose, a deviated nasal septum, or congenital anomalies related to the sinuses. Diagnosis can also be carried out if there is a suspicion of sinusitis or any other disease in this area.
Note! Unfortunately, it is not always possible to see a sufficient amount of information on an ordinary x-ray. In such cases, adults are usually prescribed the same research method, but with the use of a contrast agent. As you might guess, this option is not recommended for pediatric diagnostics, so preference is often given to magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
X-rays are good because they can be used to inexpensively and accurately determine the problem, and all this will be accompanied by minimal radiation to the body. The procedure can show not only the appearance of any inflammatory processes, but also the formation of various changes associated with the paranasal sinuses. Note that this kind of problem is diagnosed using radiography in almost all cases.
Important! According to the Ministry of Health, it is strictly prohibited to carry out this procedure without special reasons. The fact is that the method is still based on ionizing radiation, which poses a danger to humans due to radiation exposure, albeit a relatively small one. This is especially important when it comes to children, since their bodies are not yet strong enough. Despite this, if we are talking about a serious threat to health or even life, canceling the procedure is still not recommended.
Adenoid Removal Options
Removal of adenoids in children can be performed in a classic way - with an adenotomy, using a laser knife, and endoscopically using a microdebrider shaver.
Laser removal is becoming more popular. This method is considered the least traumatic, allows you to remove adenoids in children without anesthesia and causes the least number of complications. The rehabilitation period after such an operation takes no more than 10-14 days.
Contraindications to adenoid removal:
- congenital anomalies of the hard and soft palate;
- diseases that are accompanied by an increased tendency to bleed;
- blood diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- severe cardiovascular diseases;
- skin diseases;
- bronchial asthma;
- inflammation of the adenoids – adenoiditis;
- severe allergies;
- age up to 3 years (only for strict indications).
Indications for adenotomy:
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment;
- frequent relapses (up to 4 times a year);
- development of complications - arthritis, glomerulonephritis, vasculitis or rheumatism;
- difficulty in nasal breathing, which constantly leads to the development of sinusitis, sinusitis and otitis, while conservative treatment did not produce the desired results;
- sleep disorders;
- respiratory arrest at night;
- persistent otitis media and severe hearing impairment;
- deformation of the maxillofacial skeleton (“adenoid face”) and chest.
Beloved doctor Komarovsky, answering questions from concerned mothers, explained that the reason for removing adenoids is not the fact of their presence, but specific indications for surgical intervention. Getting rid of enlarged adenoids at the age of three or four years is fraught with their reappearance. However, if hearing problems arise, there is no positive dynamics with conservative treatment and the child constantly breathes through the mouth, there are undoubtedly indications for surgery, and the child’s age is not an obstacle to its implementation.
Indications for the procedure
Indications for X-rays of the adenoids may include signs indicating the presence of adenoiditis. These include:
- The presence of mucous or mucopurulent discharge from the nose.
- Difficulty in nasal breathing, resulting in the patient having to breathe through the nose.
- Nocturnal snoring that does not depend on body position. Snoring usually becomes less intense if a person sleeps on their side. But in the case of adenoids, its intensity does not decrease.
- Swelling and tenderness of the cervical lymph nodes.
- A feeling that mucus is flowing down the back wall of the nasopharynx.
- Cough that gets worse at night.
A doctor can prescribe an x-ray only after a preliminary examination of the patient. He examines the throat, nose, ears, collects anamnesis and asks about symptoms. If adenoiditis is suspected, a specialist may prescribe an x-ray.
Indications for inflamed adenoids
Adenoids are easily treated if you consult a specialist in time. It is worth considering the indications for inflamed adenoids. The presence of the following factors indicates that the adenoids are growing and the help of a specialist is needed:
- breathing occurs through the oral cavity;
- severe snoring occurs;
- decreased hearing, ear problems, otitis media;
- headache;
- nasality appears;
- the breathing cycle is disrupted;
- there is purulent discharge;
- weakness occurs.
All this points to a diagnosis of adenoids, and urgent intervention is required. There is no need to delay, because the child’s health is at stake.
At what age can the disease be treated?
Many parents are interested in at what age can adenoids be removed. The peculiarity of the structure of the immune organ is that the amygdala actively grows up to 6 years of age. If this problem occurs at a very early age (1-3 years), the likelihood of relapse is very high.
Therefore, in case of inflammation of the adenoids, the optimal period for surgical intervention is 3-4 years. You shouldn’t delay it, as bad breathing affects your well-being and development. If the functions of enlarged adenoids are normal and do not harm the child’s health, then you can wait a little with the operation. However, your doctor will give you precise recommendations.
The operation will take place without problems or complications. Now you know at what age adenoids are removed. All that remains is to turn to specialists for help. Call us and find out the cost of effective treatment and all its details.