Sometimes it happens that a seemingly healthy tooth suddenly begins to hurt, eating food brings some discomfort, and ulcers begin to appear on the gums. Pain medications and herbal decoctions for rinsing the mouth based on folk recipes are used. If the cause is a cyst on the root of the tooth, then you need to consult a doctor, otherwise the consequences will be extremely negative.
- 2 Reasons for education
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Course of the disease
- 5 Complications
- 6 Diagnostics
- 7 Treatment
7.1 Therapeutic treatment
- 7.2 Surgical treatment
Main points
- X-ray is the only reliable test for detecting a dental cyst.
- The method has virtually no contraindications.
- There are several types of the disease, and they differ in the photo.
- You cannot refuse diagnostics: the disease can lead to serious complications that can threaten the health or life of the patient.
- Based on the results of the study, the dentist prescribes appropriate treatment tactics.
In the image, the dentist can identify a cavity formation
Why is a dental cyst dangerous?
It is safe for the body only at the very beginning of its development. Subsequently, the tumor grows, causing a deterioration in health. Having reached large sizes, the tumor leads to complications:
• Osteomyelitis; • Abscess; • Sepsis; • Inflammation of the periosteum; • Pathological fractures of the jaw; • Tooth loss; • Benign tumor; • Phlegmon; • Cancer.
A dental cyst poses the greatest danger to pregnant women. At this time, its negative impact on the body increases, and treatment methods are sharply limited.
In addition, the cyst negatively affects the tooth root itself, undermining it.
That is why you should immediately seek help from specialists. Early treatment is more effective, less labor-intensive and costly.
What kind of disease is this?
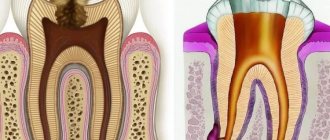
A dental cyst is understood as the formation of a formation with a cavity, inside of which there is exudative fluid. The disease affects people of any age category.
Typically the cyst develops without symptoms. However, over time, such a tumor can grow and threaten the patient’s health. A dental cyst is often detected in patients by chance when they undergo a survey radiography for the treatment of other teeth.
In most cases, the tumor occurs under the influence of pathogenic microflora. The body protects the inflammatory process so that it is not transmitted to healthy tissue. A dense capsule is formed, which isolates them from infection.
Types of pathology
What does the neoplasm look like?
Experts identify several types of the disease. They have their differences. To choose treatment tactics, the dentist must know them.
Depending on the location and nature of the cavity, several types are distinguished
Table: “Types of cysts.”
| Type of tumor | Characteristic |
| Keratocyst | Most often it forms on the lower jaw. The appearance is associated with improper dental development and growth. The epithelial layer of the capsule becomes keratinized and can recur and become malignant. As the tumor grows, it moves into the body, angle and ramus of the jaw. Such violations are dangerous because the bone is increasingly destroyed. |
| Residual | It is typically more developed on any jaw: lower or upper. This neoplasm appears above the tooth at the dental roots. It includes thin fibrous walls. They contain lymphoid cells inside. |
| Odontogenic radicular | More often than others, it occurs in patients. Formed due to the inflammatory process in the periapical tissue. Moreover, radicular cysts appear more often on the upper jaw than on the lower jaw. It usually affects people aged 20–50 years. During inflammation, the epithelial cells of the perihilar granuloma grow rapidly, forming cysts. Microcavities appear in the epithelial proliferation, which over time fill with exudative fluid. Merging, they turn into a cystic formation. |
| Follicular | It grows from the dental papilla. It is formed when, after a baby tooth, a permanent tooth does not erupt for certain reasons and grows into soft tissues. A follicular cyst appears on the lower jaw at the site of the projection of the molars. Less commonly, it develops in the canine area above. The formation quickly increases in size and can move to other teeth. This leads to their extensive damage. They bend and root resorption occurs. |
| Cyst after tooth extraction | This is a common and dangerous complication. It occurs after surgical treatment. The neoplasm has a capsule, and inside it there is exudative fluid. Most often, the contents of the cyst are purulent. The main reason for its appearance is the addition of an infection. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the wound. |
Reasons for appearance
The causes of a cyst can be very diverse, ranging from infection getting inside the canal to an unfortunate injury to a tooth or jaw.
Causes:
- tooth injury;
- due to infection entering the root canal as a result of poor quality treatment;
- as a result of unfair endodontic treatment;
- due to a previous disease in which pathogenic bacteria entered the gums along with the bloodstream;
- as a complication of chronic sinusitis;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory processes under the crown;
- as a result of the patient having chronic periodontitis;
- after difficult eruption of wisdom teeth.
However, despite the rather impressive list of reasons, in fact they all come down to two main ones - infection of the root canals and injury to the tooth or jaw. Therefore, situations where injury may occur should be avoided. For example, you should not crack nut shells, since frequent microtrauma can also trigger the formation of a cyst. Entrust the treatment of your teeth only to experienced professionals, so as not to become a victim of poor-quality treatment, as a result of which an infection has penetrated into the root canals, causing an inflammatory process, which over time can lead to disease.
Is it possible to detect a cystic formation without an x-ray?
In the early stages, the cavity does not make itself felt and occurs without symptoms. In most cases, it becomes an accidental finding of the dentist when performing a survey radiography.
Over time, the disease progresses. The patient may notice some changes.
Manifestations:
- Painful sensations when biting, which have a pulling and intensifying character. They do not go away even after taking medications.
- The appearance of gingival swelling in the pathological area.
The patient may see swelling and swelling on the gums
The patient can recognize the growth of a cyst by the following signs:
- Swelling on the jaw.
- Increase in body temperature to 40⁰ and development of fever.
- The pain intensifies when touching the gum or tooth where the cyst is located.
Consequences of the appearance
The consequences can be very diverse, ranging from destruction of tooth roots to the formation of cancerous tumors. Periodically, the gingival cyst becomes active, becomes inflamed, gumboil forms on the cheek, the patient’s general condition worsens sharply, and severe toothaches and headaches appear. Moreover, even banal hypothermia, a cold, or severe stress can become an impetus for exacerbation of the disease.
If the cyst is not detected in a timely manner and it has grown greatly, destroying the jaw, even a spontaneous fracture of the jaw may occur. Fortunately, this happens extremely rarely, and you can avoid such consequences by systematically visiting a dentist and checking the condition of your teeth.
If pyogenic bacteria penetrate into the cavity of the cyst, an acute inflammatory process may occur, which threatens the occurrence of osteomyelitis and forms a fistula on the gum or cheek, through which purulent exudate flows out.
Patients are also interested in whether a malignant dental cyst can occur. In fact, it is a benign formation and in itself does not pose a direct threat to the patient’s life. But over time, if left untreated, it can cause cancer. Therefore, the formation of a granuloma or cyst should not be taken lightly.
How is a photo taken?
The dentist performs two types of radiography: panoramic and intraoral. In the first case, the doctor receives a complete image of all the teeth in the cavity. The doctor can make a conclusion about the integrity of the dental structure, bone tissue, and whether the patient has anatomical features.
Education in panoramic photo
The dentist takes a targeted photograph: on it he examines the changes in only one tooth. The doctor determines the size and shape of the cystic tumor and selects a treatment regimen based on the results.
Neoplasm on sighting image
Contraindications for the study
Since the diagnostic method involves radiation exposure, it may be prohibited for some people. Contraindications include:
- bearing a child and childhood. If there is a threat to health or life, an examination is performed;
- lactation period. After x-rays, it is not advisable to feed your baby milk for three hours. The woman must express it.
The dentist records radiation exposure in the outpatient chart. This way he makes sure that the patient is not exposed to excessive radiation.
What does the tumor look like in the picture?
Radiography is the “gold standard” in detecting the disease. In a photo of a dental cyst, the dentist discovers a uniform darkened area that has a round or oblong shape. They have clearly defined contours and are localized in the bone structure.
Small tumors are located on only one dental root, while large ones are located on two or more. If the doctor does not receive clear information about the cyst, he should take a repeat X-ray, but from a different angle.
The tumor can affect the upper or lower jaw. Depending on its type, certain changes appear on the x-ray.
Keratocyst: The doctor identifies sparse bone tissue with a clear contour. Additionally, its uneven resorption is revealed, which creates the appearance of multi-chamber. The periodontal gaps of the dental roots projecting onto the cystic area are determined.
Residual: the formation appears as radiolucency of varying sizes in the area of the previous tooth extraction.
Residual form in the photograph
Follicular: in the description of the image, the doctor notes the resorption of bone tissue of a round or oval shape. It is associated with a lack of tooth eruption. A molar tooth germ is identified in the cystic cavity.
What does the follicular form look like when x-rayed?
Radicular: in the photograph, the cyst is represented by a small oval or spherical shadow with clear outlines. The darkening is located on the apical part of the root closer to its side. Significant bone destruction is detected in the affected area.
Radicular formation in the picture
Cyst after dental extraction: damage to bone tissue, while the rounded cavity formed afterwards has smooth contours.
Cavity neoplasm at the site of the figure eight
Treatment
To eliminate the disease, the doctor uses various methods. He must take into account symptoms, indications and contraindications. This allows you to choose the appropriate treatment.
In any case, the dentist should sanitize the dental canals where the cyst is located. He opens the pulp chamber, drills, and then cleans them. Then the doctor washes them with antiseptics so that the inflammation subsides.
In the following video you will find out which treatment method is better:
Therapeutic
Sometimes the patient is treated without surgery. However, for this method there must be certain indications:
- The canals in the affected area were poorly sealed. The doctor discovers voids. Sometimes a specialist starts a conservative method at his own risk. However, in most cases, the cystic tumor is removed by surgery.
- The size of the neoplasm does not exceed 10 mm and provokes swelling of the gums and their pain.
- Dental canals do not contain filling material. There is free access to the cyst shell.
To treat the patient, the dentist prescribes the following medications:
- Antibiotics – Fluoroquinolones, synthetic Penicillins, Cephalosporins. They are effective in combating bacterial microflora.
- NSAIDs. Reduces temperature and eliminates pain.
In what cases is conservative treatment contraindicated:
- cyst size over 10 mm;
- filling dental canals for caries or pulpitis.
Surgical
This method is preferred to be used in the following cases:
- there is no effect from conservative therapy;
- pin in the root canal;
- artificial crown;
- the cyst exceeds 10 mm;
- the canals were previously sealed;
- The patient complains of constant pain and swelling of the gums in the affected area.
Typically surgery is performed under local anesthesia. In rare cases, anesthesia is given.
Types of surgical treatment:
- Cystectomy. The doctor cuts the anterior gingival wall and cystic membrane. The doctor cleans the affected area, removing the capsule and pus. He then sutures the wound.
- Cystotomy. The dental surgeon cuts the anterior gingival wall and the tumor membrane. Then he removes its surface so that the pus flows freely into the mouth. When the inflammation subsides, the doctor will stitch the wound.
- Hemisection. This operation is suitable for patients when the dental root is destroyed. The tip, body of the tumor, and sometimes part of the crown are removed. The remaining cavity is filled with composite materials.
Surgeon performing hemisection
In what cases is surgery contraindicated:
- The bone tissue has decreased in volume.
- The patient suffers from severe chronic illnesses.
- Dental canals are impassable.
- The root of the tooth is adjacent to the maxillary sinus.
In the video, the patient left a review about the surgical treatment of cystic formation:
Laser removal
This is the most progressive method. It allows you to save the tooth. Prevents infection of the patient, since it is performed without contact with the wound.
During treatment, the patient does not feel any discomfort. The recovery period occurs quickly. With other methods it sometimes takes longer.
Laser removal does not provoke the development of complications. However, many clinics do not have equipment.
Indications for laser:
- tumor is less than 10 mm;
- crown preservation exceeds 50%;
- dental roots are preserved and do not grow into the cystic membrane;
- the channels are passable.
The method is prohibited in the following conditions:
- the dental crown has collapsed by more than half;
- the neoplasm cavity exceeds 10 mm;
- the infection has entered the periodontal canal;
- the cyst affected the “eights” (wisdom teeth);
- the channels are curved or too narrow;
- the patient suffers from severe chronic pathologies;
- the patient contracted an acute viral infection.
How is laser treatment performed:
- The dentist must unfill the tooth. He should open and expand the channels.
- The specialist inserts a laser there.
- The device disinfects the pathological area and destroys the cyst.
Treatment with folk remedies
Using alternative medicine recipes, the patient can alleviate the manifestations of the tumor. An important advantage is that it is prepared at home and does not contain “chemicals” like tablets.
However, they should not be used as monotherapy. Would you like to undergo treatment using traditional recipes? Then be sure to consult your doctor.
- Herbal decoction.
Take 1 teaspoon of a plant (sage, chamomile or calendula). Let the drink brew for as long as possible until it cools down. Then strain the broth and rinse your mouth. Use the medicine up to four times a day.
- Clove oil.
Take a cotton swab. Dip it in oil and apply it to the affected area for half an hour. The product has antiseptic properties.
- Rinse with soda-saline solution.
Take table sodium chloride and baking soda one teaspoon at a time. Pour into 200 ml warm water. Rinse your mouth every 5 hours. The product has antimicrobial properties.
Tooth cyst, what is it?
- A cyst in a tooth is a pathology characterized by the formation of a round tumor-like cavity with walls covered with fibrous tissue and inside filled with yellowish pus. Dentists distinguish between a single cyst and multiple dental cysts. A cyst under a tooth is formed due to the penetration of bacteria into the root canals. Bacteria, penetrating into the jaw bone through the root canal, cause a protective reaction in the body. During inflammation, infected cells die, forming a cavity. A hard shell appears, serving as a barrier between uninfected and diseased cells.
Survey history
Inga: the doctor accidentally discovered a tumor (September 2018)
In the summer I went to the dentist. He discovered a hilar cyst and advised a surgeon to remove it.
Of course, I didn’t want to lose a tooth. Unfortunately, my fears came true. The doctor said that it needs to be removed.
In some cases, due to illness, it is necessary to remove a tooth
To prevent further cyst formation, I asked the doctor to recommend preventive measures. The doctor said to follow simple rules for oral care.
What do we have to do:
- Carry out regular examinations with a dentist (2 times a year) and do not refuse X-ray examinations.
- Perform hygiene procedures twice a day: brush your teeth, use rinses.
- Promptly treat dental diseases, including caries, pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Monitor the condition of treated teeth and inserted implants.
- Avoid jaw injuries.
Elena: cavity removed with laser (January 208)
Laser removal of tumors
During treatment, the dentist discovered a cyst in me. He explained that it was not cancer or any other tumor. However, he advised not to delay and remove the tumor.
The cyst was only 8 mm in size. I learned that the laser method is the most progressive method of eliminating it.
I started looking for information on the forums. Having become interested, I contacted one of the private clinics in my city.
What a surprise I was when I found out that the institution could not conduct it. The reason is the lack of necessary equipment.
I started calling other dental clinics. However, I heard only one answer: “We do not provide laser treatment for dental cysts.”
Then she called the medical center of a neighboring city. Here I was told that they provide this service.
A few weeks later, treatment was carried out. The doctor unsealed the tooth and inserted the device there.
Of course, the price is steep. But the removal of the cyst was quick and painless!
The recovery period also did not require much time. In general, I'm satisfied.
Complications
A cyst that is not detected in a timely manner grows over time, destroying bone tissue and replacing it with formations of connective tissue. In this case, complications can lead to its loss. Most often, dentists record the following complications:
- melting of the jaw bone;
- purulent inflammation of the cyst;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- chronic sinusitis;
- osteomyelitis or periostitis;
- formation of an abscess on the gum or cheek;
- spontaneous fracture of the jaw as a result of severe growth of the cyst and thinning of the bone;
- phlegmon of the neck;
- sepsis.
As we can see, some complications directly threaten the patient’s life. Therefore, if you have a tooth cyst that hurts, you should immediately contact your dentist - you may have a purulent inflammation.
If a patient is diagnosed with a dental cyst and complains of the smell of pus in the nose, this may be a sign of both the onset of a purulent inflammatory process and the fact that the disease has grown into the maxillary sinuses. In any case, you should consult a doctor immediately.