An ovarian cyst is a benign formation that is often found in women of any age. Modern research methods - ultrasound, MRI, CT of the pelvic organs make it possible to diagnose this pathology in the early stages and carry out conservative or surgical treatment.
Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is an important decision, since there is a possibility of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one.
This gentle, minimally invasive method allows you to effectively perform surgery, speed up the postoperative period and the length of hospitalization of the patient.
Definition and general characteristics of the operation
Ovarian laparoscopy is a surgical intervention in the abdominal cavity using a laparoscope equipped with a video system. A practically safe operation, laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is performed under general anesthesia.
Three or four small incisions are made on the woman's abdomen, through which surgical instruments and a miniature video camera are inserted.
Some women receive a positive side effect after surgery - they manage to lose weight after ovarian laparoscopy by following the regimen and diet.
How is the operation performed?
In order to answer the question about the duration of the intervention, it is necessary to take into account many nuances - the size of the cyst, the type of neoplasm, the qualifications of the surgeon, the age of the patient, the presence of underlying ailments and other individual characteristics.
Three incisions are made in the abdominal cavity and gas is pumped into it. It is necessary in order to lift the peritoneal wall, push apart the abdominal organs and thereby provide free access to the intervention site. Then all the necessary instruments and a small backlit camera are inserted into the incisions, which will display the image on the screen. A drainage tube is installed.
The doctor removes the tumor without affecting healthy tissue, removes it through the incision, removes the instruments and camera, pumps out the gas, stitches up the puncture sites and applies a bandage. If necessary, the drainage tube can be left in place for another day.
Important! The patient should know that if complications are detected during the operation, the doctor will be forced to proceed to laparotomy.
Anesthesia
After all the preparatory procedures are completed, the patient is taken to a special ward, placed on the operating table and given anesthesia. They do either local anesthesia with the woman completely switched off, or local or regional epidural anesthesia. Then the doctor installs a urine bag and treats the lower abdomen with a disinfectant.
How long does it last?
The operation itself can last on average from 20 minutes to an hour, but if you take into account the preparatory stages, then in this case you should expect 2.5-3 hours.
Reference! Standard removal of a moderate cyst takes about 40 minutes.
General indications and contraindications
Ovarian laparoscopy, like any other surgical operation, has both indications and contraindications. Indications: removal of cysts, making incisions on the ovaries, rupture of a cyst or torsion of a pedicle. Incisions on the ovaries during laparoscopy are carried out in order to destroy the follicle membrane, which makes it difficult for the egg to be released and pregnancy to occur.
Laparoscopy cannot be performed in the following cases:
- in the presence of malignant neoplasms;
- severe pathologies of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- hypertension, blood diseases;
- the presence of adhesions in the pelvic cavity;
- obesity or vice versa, exhaustion.
Before preparing for laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, the patient must be cured of infectious or inflammatory diseases.
The essence of the method and indications
Ovarian cyst is a common gynecological disease. The neoplasm appears mainly in nulliparous young women. Causes unpleasant symptoms (pain, menstrual irregularities). May provoke hemorrhages, abscess, infertility or cancer.
It is rarely possible to cure a cyst using conservative methods. Usually drug therapy does not bring results. When a tumor appears, removal of the ovarian cyst is required. If there is a suspicion of tumor rupture or torsion of its stalk, urgent surgical intervention is necessary.
During ovarian laparoscopy, the surgeon uses a gentle method to access the diseased organ. Three miniature incisions are made in the anterior abdominal wall, through which the doctor inserts instruments and performs the necessary manipulations. At the same time, a special video camera (laparoscope) is used, allowing the surgeon to achieve maximum precision when removing the tumor.
Advantages of laparoscopy over laparotomy
The main differences between laparoscopy and laparotomy:
| Laparoscopy | Laparotomy | |
| Peculiarities | Surgery using endoscopic instruments and video camera | Abdominal surgery, with an incision in the abdominal cavity |
| Aesthetics | Small holes after punctures are almost invisible | Large seams remain |
| Diagnostics | Makes it possible to establish the correct diagnosis | Impossible, the operation is performed only for therapeutic purposes |
| Duration of hospitalization | Up to seven days | Up to 11 days. Recovery is slow |
| Terms of rehabilitation | One, two weeks | Rehabilitation is long, at least a month |
| Injuries | Thanks to the video camera, injury is virtually eliminated | Possible damage to internal organs |
| Organ safety | Thanks to micro-operations, the integrity of the organ is preserved | Organ damage may occur |
| Bleeding | Virtually excluded | May lead to organ loss |
| Consequences | Complications are rare | There may be damage to internal organs, the formation of adhesions |
As can be seen from the table, laparoscopy has more advantages and is used more often.
Types of laparoscopy
There are several techniques for removing pathologies. They are determined by the type of formation, the presence of a malignant process and damage to neighboring organs. Surgical techniques of laparoscopy:
- Ovarian cystectomy. Enucleation, i.e. enucleation of an ovarian cyst while fully maintaining the integrity of the latter. Prescribed for small formations that do not damage the epididymal capsule.
- Laparoscopic resection of ovarian cyst. Necessary when a formation grows into an organ cavity, characterized by partial removal of the appendage.
- Ovariectomy. Complete removal of pathology and the affected organ. It is used for suppuration, ruptures, and malignant processes.
In all of these cases, the woman’s reproductive ability is preserved, because Conception is possible even with only one appendage.
With a full abdominal operation of another type, it is possible to perform a hysterectomy - the complete removal of the woman’s genital organs. This is required if there is an oncological process or if there is a high risk of its occurrence.
Kinds
Cysts that occur in women can be divided into two main groups - functional ones, which can be treated with medication, and those that can only be removed surgically (paraovarian, endometrioid, dermoid). To remove tumors of the second type, laparoscopy of the ovaries or the cyst itself is recommended.
The paraovarian cyst grows slowly and is located near the appendages. Having reached a size of up to 20 cm, it compresses nearby organs.
Other types of cyst removal surgeries
Surgical treatment of pathology is also possible during other types of operations. The type of intervention depends on the characteristics of the disease:
- Laparotomy. Making one large incision in the abdominal wall. This type of operation is used for large formations, the need to remove the appendage itself and/or the uterus. Laparotomy of an ovarian cyst can be used when it is impossible to fully assess the condition of the organs with a laparoscope or in emergency cases.
- Laser. Minimally invasive surgery. It consists of using a laser for surgical treatment, removing the ovarian cyst and cauterizing the tissue, eliminating bleeding. Suitable for small types of formations, not used in the presence of malignant cells. Does not require making incisions on the ovaries.
Most often, laparotomy or laparoscopy is used to eliminate pathology. Laser surgery is highly effective, but is only suitable for certain types of formations.
Preparing for surgery
Preparation for surgery to remove an ovarian cyst is not particularly different from the preoperative period for other diseases and includes several stages:
- Collection of mandatory tests before surgery to remove a cyst: general examination of urine and blood, vaginal smear for microflora.
- Biochemical blood tests (determination of glucose levels, blood clotting).
- Blood test for RW (Wassermann reaction to syphilis), HIV, hepatitis.
- Carrying out ECG, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, fluorography.
- Selecting a day for surgery, excluding the menstrual cycle.
- Direct preparation for laparoscopy of a cyst in a hospital.
On the eve of the operation, light meals are allowed no later than 18.00. Until 22.000 you can drink liquid. In the evening, the genitals are thoroughly processed and the hairs are shaved off. Before going to bed and in the morning, a cleansing enema is performed.
Attention: Drinking water or any other liquid on the day of surgery is strictly prohibited.
Features of preparation
Preparation for surgery includes a number of standard tests. Their number and types are prescribed depending on the general condition of the woman’s body and her age.
Preparation before surgery
| Taking tests | Kinds |
| Urine | General analysis. |
| Vaginal smear | For microflora. |
| Blood | General and on: · coagulability; · HIV AIDS; · hepatitis; · amount of glucose; · presence of infections. |
Fluorography, electrocardiogram, and pelvic ultrasound are performed. A few days before the procedure, the woman must go on a special diet. The diet excludes the consumption of foods that can cause increased gas formation:
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- fat;
- sweet;
- butter;
- coffee;
- milk;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- Rye bread.
The diet should include porridge, lean meat or fish, and mashed potatoes. The last late dinner before the day of surgery is at 6 pm, drinking fluids is at 10 pm. In the morning (immediately before surgery) you should not eat or drink.
The final preparations are shaving the pubic hair and a cleansing enema. If all medical recommendations are followed, a woman can be sure that the operation will be easy.
First day
On the first day after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, the patient is under constant supervision of medical personnel. This is due to not missing possible complications and starting the necessary treatment on time. For severe pain, analgesics are prescribed.
In the afternoon, the first treatment of postoperative wounds is carried out. If necessary, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent inflammation.
After 7-8 hours, you are allowed to carefully get out of bed, drink clean, still water, juices or compotes that do not cause bloating.
Attention: On the first day, sudden, active movements are prohibited. Movements should be slow to avoid dizziness and loss of consciousness.
Limitations after laparoscopic ovarian surgery
A woman’s lifestyle changes after surgery. Certain restrictions are imposed to protect against excessive loads. Following the doctor’s recommendations makes the recovery period easier and allows you to quickly return to your normal lifestyle.
Important aspects:
- It is not recommended to have sexual activity until the bleeding stops. Sex is prohibited for at least 2 weeks (according to some recommendations - up to a month);
- You should not overexert yourself, engage in heavy physical work or lift weights exceeding 3 kg;
- You cannot play sports until your body is completely restored. In the first days after surgery, only therapeutic exercises are allowed. Loads should increase gradually;
- You should not take a bath until the stitches have healed. You need to wash in the shower.
Until the wounds heal, a woman should wash only under running water.
- You cannot sunbathe on the beach or in the solarium, or visit the bathhouse or sauna for a month after the operation;
- It is recommended to wear the brace for 1-2 weeks after surgery. The bandage protects the seams from negative effects and strengthens the muscles of the abdominal wall;
- You should not drink alcohol or smoke until your body is completely restored.
Physical activity after cyst removal deserves special attention. If the postoperative period is successful, exercises from the complex of therapeutic gymnastics are recommended. You can exercise on the second day after surgery, but only with the agreement of your doctor.
Training scheme:
- Starting position: on your back, legs straight, arms extended along the body. Raise your hands on the count of one or two, lower them on three or four. Do 4-6 approaches;
- Starting position: on your back, legs straight, arms bent at the elbows. On the count of one, bend your legs at the knee joints and pull your toes towards you, on the count of two, return to the starting position;
- Starting position: on your back, legs and arms straight. On a count of one or two, smoothly bend your knees and slide your heels along the surface. On the count of three or four, straighten your legs;
- Starting position: on your back, lower back pressed to the floor, legs bent at the knees. Raise your back, go into a half-bridge and return to the starting position.
Therapeutic exercises will help a woman recover faster after laparoscopic surgery to remove an ovarian cyst.
Such gymnastics reduces the risk of developing adhesions and helps preserve a woman’s reproductive health.
Postoperative period
The duration of the postoperative period after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst within the hospital walls ranges from 3 to 7 days. The length of hospital stay depends on the woman’s general well-being, the speed of healing of the sutures, the formation of scars, the absence or development of complications.
Behavior rules
On the second day after surgery, the patient is advised to move more. This is necessary to ensure that there is no stagnation in the pelvic organs and that the intestines work effectively.
Every day, the patient's sutures are treated with antiseptic materials and the bandages are renewed. Usually on the seventh day, the sutures are removed and the patient is prepared for discharge.
Is it possible to play sports?
After being discharged from the hospital home, you should forget about sports for at least 2 months. Heavy exercise will not be possible for 4 months. Only the attending physician can say for sure when you can start training, since it depends on many individual characteristics of the woman.
Expert opinion
Olga Matveeva
Gynecologist-obstetrician Experience 6 years
However, moderate physical activity is allowed a couple of weeks after the intervention, but the emphasis should be on static load. Breathing exercises and a set of physical therapy exercises are very useful.
Recovery
But the recovery period of the body after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst and discharge from the hospital does not end. Over the course of three to four weeks, the processes of normalization of the vital functions of the female body continue.
After laparoscopy, a woman needs to abstain from sexual activity for at least two weeks. It is also worth postponing active sports and visiting the pool for a while.
After ovarian laparoscopy, during the rehabilitation period, it is not recommended to take a hot bath, carry heavy bags, move furniture, or lift a stroller or child. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the recovery period after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst passes quickly.
If the patient had to undergo a laparotomy (resection of the abdominal cavity to remove a cyst), the end of the recovery period is lengthened.
What it is?
Scheme
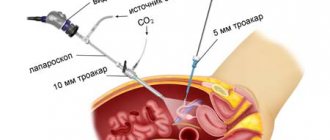
Laparoscopy is an surgical intervention during which the surgeon makes only three incisions in the wall of the anterior peritoneum, 1.5 cm in size, and all the instruments necessary for the operation and a backlit camera are inserted there.
The surgeon watches the progress of the operation on the screen.
Advantages of the method
This intervention is considered minimally invasive and has the following advantages over the classical type of operation - laparotomy:
- The risk of developing adhesive disease is significantly reduced.
- Since there is no dissection of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, the likelihood of developing a postoperative hernia is reduced.
- Small wounds after intervention, thanks to which they heal faster.
- The operation does not affect neighboring organs, which reduces the likelihood of intestinal hypotension in the postoperative period.
- The patient is discharged from the hospital faster, and restrictions in the postoperative period are minimal.
- After the operation, there are no large scars left that deform the skin.
Expert opinion
Anna Alekseenko
Obstetrician-gynecologist Experience 5 years
Thus, laparoscopic intervention allows a woman to get rid of an ovarian cyst, and at the same time return to normal life as quickly as possible, without fear of deformation of the skin in the future and without worrying about long-term postoperative complications.
What can you eat after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst?
Nutrition after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is aimed at improving intestinal function, reducing increased gas formation, and preventing constipation.
On the first day after surgery, no food is provided. You can only drink clean, still water. On the second day, pureed soups, light broths, and occasional porridges are allowed. Later, you can add lactic acid products, non-acidic fruits, boiled or stewed vegetables to your diet.
During the recovery period, dishes with fatty, spicy, fried foods are not allowed. Portions should be small. Food can be taken frequently, at least 5 or 6 times a day.
Mechanism
Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is done under general anesthesia. Once anesthesia is administered, a catheter is inserted to drain urine. Next, the skin in the area of the operation is disinfected with an anesthetic.
The surgeon makes three small incisions. Through them, the laparoscope and instruments are lowered into the peritoneum. Then the peritoneum is filled with air, which allows you to better see the tumor.
The operation involves suctioning fluid from the cyst or cutting it off along with the ovary. If there is excess epithelium, it must be removed, otherwise adhesions may form after laparoscopy. At the end of the manipulations, gas is released from the abdominal cavity.
Sutures are placed on two incisions. A drainage is inserted into the third. It remains for some period after laparoscopy. The entire procedure takes from 20 to 60 minutes.
Possible complications
The probability of complications after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is no more than 2%.
It can be:
- Discomfort from the digestive system (nausea, vomiting);
- hyperemia, inflammation, suppuration of sutures;
- increased temperature, increasing weakness, feverish state;
- bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- symptoms of thrombophlebitis.
Symptoms of complications requiring immediate medical attention after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst:
- heat;
- heavy bleeding;
- bloating, constipation;
- pain syndrome.
All these unpleasant consequences of laparoscopy require identification of the causes of complications and mandatory medical care.
Types of procedure
Laparoscopy of the ovary is diagnostic and therapeutic. The first is carried out to obtain information about the condition of the organ if other methods have not produced results. Having identified a tumor during diagnosis, the doctor decides to remove the tumor. The procedure changes from diagnostic to therapeutic status.
During surgery, only the cyst can be removed or the affected ovary can be additionally cut off. Based on the type of tumor, laparoscopy is classified according to the removal of:
- endometrioid cyst formed by endometrial tissue;
- paraovarian tumor formed from appendages;
- dermoid cyst formed by various types of tissue (fat, bone, etc.).
Surgical interventions of different types are performed using uniform techniques. Some differences are in the medications prescribed, the duration of the procedure, and the features of rehabilitation after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst.
Reviews
Marina
“I recently had to have surgery for a cyst. The cyst, as my gynecologist said, was functional. But the treatment did not produce results, so I decided to have surgery. The operation was performed in our regional hospital. Everything went well. The stitches healed completely on the 7th day. My husband and I are planning to have a child. But the doctor recommends abstaining from pregnancy for another couple of months.”
Svetlana
“In a week I will have an ovarian laparoscopy. I don’t have a cyst, but the doctors said that with this procedure it is possible to destroy the follicle membrane and I will be able to get pregnant. I hope that everything will be successful, because my husband and I have been waiting for a child for 5 years.”
Karina
“I have health problems; my right ovary was removed. But a month ago, a cyst was removed on the left ovary. The operation was performed in our capital, in a private clinic. Although the procedure is not cheap, I decided to do it in order to maintain the hope of becoming a mother.”
Pregnancy after removal
The period of time after which you can become pregnant directly depends on the underlying disease on the basis of which the operation was performed. If a woman has undergone enucleation, removal of adhesions, then pregnancy is allowed after removal of the ovarian cyst within 1–6 months.
If there has been surgery for a complicated cystoma, endometriosis, or extensive adhesions, it is advisable for the couple to refrain from conceiving for 5–6 months. The female body needs to fully recover with the help of hormonal medications.
Enucleation of ovarian cysts is well tolerated by patients and has a number of features and advantages. After a minimally invasive intervention, women of fertile age have a chance to get pregnant and bear a healthy baby.
During pregnancy
A diagnosed cyst during pregnancy is not an emergency indication for surgery. Removal of the formation is indicated only if there are symptoms of capsule rupture, pedicle torsion, intra-abdominal bleeding, or the threat of peritonitis.
What discharge is considered normal?
After surgery on the ovary, a woman experiences mild bleeding. After two or three days they become yellowish, slimy, without an unpleasant odor. The discharge can be long-lasting (up to three weeks), but a woman should not worry - this is a natural process.
If the discharge after ovarian laparoscopy turns green or brown, there is an unpleasant odor, or abdominal pain, you should immediately consult a doctor. These symptoms may be caused by inflammation or an infectious process in the body.
Advantages of laparoscopic surgery
Unlike classical laparotomy, endoscopic intervention has a number of advantages:
- Minimal damage to soft tissues and pelvic organs;
- Minor trauma to the ovary and preservation of the ovarian reserve;
- Minimal risk of developing adhesions;
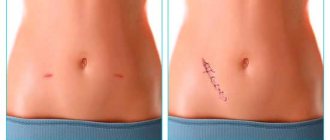
- Good cosmetic effect. After removal of an ovarian cyst using laparoscopic access, subtle scars remain on the skin of the abdomen.
And the most important advantage is the relatively short recovery period. A few hours after the operation, a woman can get up in the ward and take care of herself, after 3 days she can be discharged from the hospital, after 10 days she can return to work, after 3-4 weeks she can get rid of all restrictions and lead a normal life. For this reason, doctors give priority to endoscopic interventions and always, if technically possible, perform minimally invasive surgery.
On a note
There are contraindications to laparoscopy, including obesity of III-IV degree and severe adhesions. Large cysts and malignant tumors can also be removed during abdominal surgery.
In case of pathological completeness, removal of an ovarian cyst by laparoscopic method is contraindicated.
On what day are stitches removed?
Sutures after ovarian laparoscopy are removed after 7 or 9 days. Almost invisible scars remain at the site of the sutures. To make punctures heal faster, they are treated with a scar resorption agent - Contractubex.
Attention: Contractubex is a gel based on onion extract, heparin and allantoin. Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to these components.
When using the drug, you should avoid exposure to cold and ultraviolet irradiation on areas of fresh postoperative scars.
Regime and diet
What can you eat after laparoscopy? After such a minimally invasive intervention, you can drink still water at room temperature almost immediately, but in small quantities and in small sips. But it’s better to eat only the next day - start with a small amount of boiled vegetables, slimy soup or steamed chicken cutlets. If you suffer from heartburn, do not “eat” it with oatmeal or crackers, but take omeprazole.
Many doctors claim that there is no specific diet after surgery. You just need to give up alcoholic drinks and eat light foods in small portions, without washing them down with water. This is not entirely true. According to their requirements for postoperative nutrition, the diet after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is similar to the diet prescribed by nutritionists for a tendency to flatulence and constipation.
| Recommended | Forbidden |
|
|
The diet for those prone to flatulence includes 1 fasting day every 7-10 days. During a fasting day from food, you can drink alkaline mineral water without carbon or herbal tea. In order to get rid of gas, you should heat water such as Borjomi, Essentuki-4 or Luzhanskaya to 42 degrees. To prepare herbal infusions, it is better to take dill seed, chamomile, cinnamon, cardamom and ginger.
Dill seeds have a carminative effect
Another recommendation from nutritionists is to separate the consumption of drinks and solid food. You should drink liquids at least 30 minutes, but it is better 1 hour before meals, and 1-1.5 hours after. It would be useful to remind you that the amount of free liquid consumed should be between one and two liters per day. Drinking before bed and at night is not recommended.
You can return to your usual diet 30 days after laparoscopic surgery. Nevertheless, it is better to adhere to two nutritional rules - eat small meals in small portions, consume protein and carbohydrate-containing foods separately - in the future.
On a note. Many people do not know that increased gas formation is caused by eating cold foods and drinks. Therefore, for the diet to be effective, eat your meals warm and drink your drinks at room temperature.
Questions
Do I need to use antibiotics after laparoscopy?
It all depends on the reason for which the laparoscopy was performed. If it was performed due to inflammatory changes in the genitals or abdominal cavity, then antibacterial therapy may be prescribed in the postoperative period. The drugs are administered either through a catheter left in the abdominal cavity after laparoscopy, or through the mouth in the form of tablets. Antibiotics are sometimes prescribed prophylactically when there is an increased risk of postoperative complications.
Find out more on this topic:
- Suprax and Suprax Solutab - instructions for use (suspension, tablets, capsules 400 mg). Analogs, reviews about the drug, price
- Benzylpenicillin - drugs (sodium salt, potassium salt, novocaine salt, benzathine benzylpenicillin, etc.), action, instructions for use (how to dilute, dosage, methods of administration), analogues, reviews, price
- Normix (Alpha Normix) – instructions for use (tablets, granules), analogues, reviews from doctors and patients, price of the drug
- Klacid (125, 250, 500 mg) and Klacid SR - instructions for use (suspension, tablets, solution), features of use in children, analogues, reviews and price of the drug
- What antibiotic is best to take for a sore throat? Rules for the treatment of sore throat with antibiotics in children and adults
- Augmentin tablets, solution, suspension (125, 200, 400) for children and adults – instructions for use and dosage, analogues, reviews, price
- Laparoscopy of the ovaries (removal of a cyst, fallopian tube or the entire ovary, etc.) - advantages, description of types of laparoscopy, indications and contraindications, preparation and progress of the operation, recovery and diet, reviews, price of the procedure
- Laparoscopy of the gallbladder (removal of stones or the entire organ by laparoscopic surgery) - advantages, indications and contraindications, preparation and progress of the operation, recovery and diet
Similar questions New question
Search questions and answers
Find the answer using the key words of the question. Our service operates during the daytime, during business hours. But our capabilities allow us to efficiently process only a limited number of your applications. Please use the search for answers (The database contains more than 60,000 answers). Many questions are already answered.
Antibiotics
Laparoscopy
www.tiensmed.ru
Contraindications
Laparoscopy is not performed if the patient has the following diseases and conditions:
- exacerbation of cardiac pathology and bronchial asthma;
- ARVI or influenza that occurred less than a month ago;
- severe obesity (3-4 degrees);
- blood clotting disorder;
- any abdominal surgery performed less than six months ago;
- malignant neoplasm of the ovary;
- presence of blood in the abdominal cavity;
- bleeding;
- a large number of adhesions;
- pustular rashes on the skin of the abdomen.
In some cases, surgery may be performed after recovery. In other situations, laparoscopy is completely contraindicated, and abdominal surgery cannot be avoided.
How long to stay in the hospital
The duration of sick leave after laparoscopic surgery depends on many factors, the main ones being:
- General health of the patient;
- The need for a rehabilitation period, even taking into account the good condition of the patient;
- Possibility of undesirable consequences;
- The complexity of the operation.
In approximately 80-85% of patients, after laparoscopy they begin work a day later. This is due to the minimized invasiveness of the procedure and the rapid (compared to other operations) recovery period.
Active movements are highly recommended by doctors after laparoscopy, which promotes accelerated wound healing and prevents negative consequences in the form of postoperative abdominal adhesions.
Features of laparoscopy
It is important for many girls and women to know on what day of the cycle a laparoscopy is performed, how it goes, how long the operation to remove an ovarian cyst lasts, and whether anesthesia is used during it.
Doctors believe that the most optimal time for performing laparoscopy surgery for an ovarian cyst is the first phase of the menstrual cycle, preferably 6–7 days after the end of bleeding.
If the surgeon does not encounter complications or oncology, then the average duration of surgery is from 40 to 90 minutes. The duration is related to the size of the cyst to be removed, the volume of ovarian tissue excised, and existing diseases.
Laparoscopy of ovarian cysts is performed using 2 micro-incisions made to insert very small medical instruments into them. The third incision is for a laparoscope equipped with a tiny camera and LED. At the initial stage of surgery, a small volume of carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity to lift the peritoneal wall above the internal organs in the pelvis. In an enlarged operating space, it is easier for the doctor to monitor the removal process and easier to manipulate the instruments.
The volume of excised tissue depends on the degree of development of the cyst, its germination into the ovarian capsule, the number of endometrioid foci, detected oncology and other features.
During diagnostic laparoscopy, a specialist will examine the internal organs. If nodular structures are detected, the doctor will be able to remove them immediately. After the excision procedure, the surgeon will stop the bleeding, remove inserted instruments and carbon dioxide, and apply stitches and dressings.
In young patients, if no cancerous changes are detected in the cells, they try to affect the gonads to a minimal extent, preserving their functions for further pregnancy. For women over 47 - 50 years old, it is often recommended to remove the ovary with excision of the cyst in order to maximally protect the patient from malignancy (cancerous transformation of cells) of the gonad, the risk of which increases during this period. This also helps prevent the recurrence of new cystic structures and tumors from developing.
The scope of surgical intervention is often determined by the doctor at the time of the procedure:
- Cystectomy (husking out the cystic lump). This operation is performed in the absence of signs of cancerous cell degeneration and with intact ovarian tissue. Doctors recommend cystectomy for women of reproductive age and teenage girls.
- Partial resection of the ovary (removal of part of the organ along with neoplasm). Wedge resection is performed when the ovary partially preserves its functions. Such an operation in Moscow costs from 18 to 25 thousand rubles.
- Ovariectomy (removal of the ovary along with the cyst). This procedure is indicated for necrosis and replacement of healthy organ structures with connective tissue. Ovariectomy is often performed during menopause. The cost varies from 15 to 20 thousand rubles.
- Adnexectomy (removal of the cystic capsule, ovary, fallopian tube). Such removal is carried out when cancer is detected, the pathology is complicated, or it has spread to nearby organs.
Removing one of the ovaries does not interfere with conception, since the second one remains. Thanks to this, a woman gets the opportunity to maintain reproductive health and bear a healthy baby.
Laparoscopy of a cyst of the left and right ovary is carried out according to the same scheme.
The following complications may occur after laparoscopy:
- heavy bleeding;
- infectious lesion and further inflammation, suppuration;
- seam divergence;
- injury to the pelvic organs.
When does a cyst require surgery?
Whatever the diagnosis of ovarian cyst, its treatment cannot be delayed, since complications such as suppuration, hemorrhage, “torsion” of the pedicle, rupture of the cyst with the release of its contents into the abdominal cavity may occur.
All these complications can lead to peritonitis, then a low-traumatic laparoscopic operation will no longer be enough - a serious surgical intervention (laparotomy) will be required.
One of the hidden threats of a cyst is its danger of developing from a benign to a malignant cancerous tumor (malignancy).
Treatment methods for cysts are divided into conservative and surgical, but conservative ones are not often used, because they are ineffective.
The choice of treatment method largely depends on the type of cyst, its neglect, the age of the patient, and also on whether the woman plans to have children in the future.
Conservative treatment methods are used if the disease is asymptomatic, the cyst is small in size, if the woman is pre- or postmenopausal and does not plan to have more children. If there is pain, the cyst is large or tends to grow, surgery is required.
The operation is not performed if the patient has cancer of the reproductive system, advanced obesity, diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, or postoperative adhesions.
Video: “What are the types of ovarian cysts? How is laparoscopy performed?
Recovery after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst: treatment and consequences
An ovarian cyst is a dangerous disease for a woman’s body and reproductive function. If the cyst reaches a large size and there is a risk of rupture, it is surgically removed. Proper recovery after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is very important, since after any surgical intervention there is a risk of complications.
Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst in the postoperative period is an important topic that we will discuss in this article. Let's consider possible complications and what measures need to be taken in their case.
Is laparoscopy dangerous?
Click to enlarge
Laparoscopic surgery is performed using an endoscope equipped with an optical system. Among the advantages of this method are a low degree of trauma (small punctures are made), usually a quick recovery of the patient after surgery, a short stay in the hospital, and little blood loss.
The scars become almost invisible and usually disappear within a couple of months. Abdominal surgery to remove an ovarian cyst is a much less gentle way to remove a cyst; recovery from it will take longer, but among the advantages it can be noted that with such an operation the doctor can better examine the diseased organ.
Postoperative period
After surgery to remove an ovarian cyst, the body needs recovery. The postoperative period is considered to be the period after completion of the operation until the patient is discharged from sick leave. Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia and after its effect wears off, the woman usually experiences pain.
Pain after removal of an ovarian cyst is neutralized with analgesics. But if, after some time, sharp or cutting pain occurs in the lower abdomen, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this may be a sign of the development of an inflammatory process and complications.
The laparoscopic method of cyst removal is characterized by minor intervention in the body, so the patient remains active, she can get up to go to the toilet on her own, 8 hours after the operation. In the first 5 hours, you are allowed to drink still water, and if you have an appetite, broth is acceptable.
Weakness, slight fever and pain in the area of the stitches should disappear after 4-5 days. The postoperative period during laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst for 2-3 days is accompanied by aching in the neck, collar area, and legs, due to the fact that the operation is performed using a gaseous substance. To remove residual substances from the abdominal cavity, there are a number of exercises that are performed while lying in bed (the nurse helps to carry them out).
Discharge after laparoscopy (bloody and mucous) appears in a small volume immediately after surgery and can last up to 3-4 weeks. There is no need to worry about them. But if the discharge becomes brown or greenish in color and has an unpleasant odor, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this is a sign of infection and inflammatory process. The doctor will take a smear for analysis and further treatment. The temperature after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst can rise to 37-37.5 degrees. This is considered acceptable, since aseptic inflammation develops at the surgical site. If the patient’s temperature lasts for more than 2-3 days, an infectious complication may begin in the body.
Menstruation after laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
According to medical practice, the onset of menstruation occurs in most patients on time and menstrual irregularities are usually not observed. Sometimes after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, patients experience menstrual irregularities, which may begin with a delay or, conversely, ahead of schedule.
Such violations are associated with many factors, such as the qualifications of the doctor who performed the operation, the characteristics of the woman’s body, age, weakened immunity, stress suffered during the operation, etc. In this case, it is very important to pay attention to the processes occurring in the body, the symptoms and nature of the discharge and seek advice from a doctor. In such cases, the attending physician prescribes medications and vitamins that strengthen the immune system.
To treat patients who have not had menstruation for six months or more, hormones are prescribed. After laparoscopy, ovulation reappears and pregnancy is possible, usually after six months or a year. If ovulation does not return after several cycles, consult your doctor; you will most likely need to resort to medication.
Treatment after laparoscopy
Treatment after removal of an ovarian cyst is aimed at neutralizing the risk of developing an inflammatory process and therefore antibiotics are required. Despite minor tissue damage after laparoscopy, the likelihood of infection still exists. It is also mandatory to take fortified medications, hormonal medications according to individual indications, as well as physical therapy.
After laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, the patient must remain in a supine position at rest for a certain time. In this regard, thrombosis can sometimes be provoked. To eliminate it, chemicals and medications are prescribed that inhibit the activity of the blood coagulation system and prevent the formation of blood clots. Compression stockings, which are required before surgery and worn during the postoperative period, also help.
What can you eat during the recovery period?
After laparoscopy, due to a sedentary regime and as a result of taking medications, intestinal discomfort, digestive problems and constipation are possible. Therefore, with proper nutrition, rehabilitation will go faster. On the first day, if your condition allows you to have an appetite, then you need to consume weak broth. An increase in the amount of food consumed is necessary with the introduction of boiled, lean dishes into the diet, which are recommended to be steamed.
In the first week after laparoscopy, you can eat cereals, soups, beef, and low-fat steamed chicken cutlets. In the first month you need to eat vegetables (baked and stewed), fish, and lean meat. Food in the postoperative periods should be correct and consumed in small portions, then digestive problems can be avoided and the body’s performance can be restored. For approximately 3 months, you need to completely eliminate alcohol, sweets, fried and fatty foods, chocolate, coffee and strong tea.
Consequences after surgery for ovarian cysts
When laparoscopy is performed by a qualified specialist, the development of complications is negligible. But the possibility cannot be ruled out 100%. Possible problems include: bleeding after laparoscopy, vascular damage, thrombophlebitis, damage to nearby organs, infectious disease of the abdominal cavity, infertility, cyst recurrence.
It should also be noted that complications after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts are individual and depend on certain factors, such as pregnancy, abortion, hormonal imbalance, excess weight, chronic diseases, alcohol or drug abuse, smoking, hypothermia, and non-compliance with medical recommendations. The reappearance of an ovarian cyst is a postoperative complication and occurs quite often.
The cyst may reoccur after laparoscopy due to hormonal imbalances and the risk factors described above. After laparoscopy, the doctor may prescribe the necessary course of drugs that stimulate the production of male hormones (very often such treatment methods are used after removal of an endometrioid cyst). To prevent the recurrence of a cyst, be sure to follow your doctor’s recommendations, do not neglect the prescribed treatment, be sure to periodically visit your gynecologist, eat right and avoid stress.
Ovarian adhesions - a possible risk of infertility
In terms of postoperative complications, it is very important to prevent so-called adhesions. Adhesions are a pathology due to prolonged inflammatory processes, operations, endometriosis, which is an fusion of tissue in places of inflammation. If the onset of postoperative inflammation in a woman is not treated on time, it develops into chronic inflammation, resulting in an adhesive process of tissue fusion in the female genital organs. Women often suffer from constant pain in the lower abdomen, which cannot be treated with painkillers, as it is caused by anatomical disorders. Among the consequences of the disease are kinks in the fallopian tube, difficulty in fertilization, ectopic pregnancies, and infertility.
Postoperative period at home
Most of the time after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, the woman is at home, and therefore, for successful recovery, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Protect yourself from injury and overload during the healing period of the sutures.
- It is worth excluding physical activity and sports, heavy lifting, and sudden movements.
- Do not wear clothes that squeeze the seams with elastic bands while walking and not only.
- Sexual activity should be limited to 1 month.
- Postpone treatment with folk remedies and absorbable ointments for postoperative scars.
- Do not scratch the seams.
- Saunas, steam baths, tanning on the beach and in the solarium, and the like should be excluded.
- A shower is recommended for quality water treatments.
- Follow your diet.
Symptoms of complications requiring immediate medical attention
Recovery after removal of an ovarian cyst lasts on average one month. The recovery period is much better compared to open abdominal surgery. Throughout the entire postoperative rehabilitation period, carefully monitor your body. Among the symptoms that require emergency medical care, we highlight the following:
- severe pain after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, which does not disappear a week after the operation.
- pronounced redness of the skin around the stitches;
- uterine bleeding;
- dark colored discharge with an unpleasant odor,
- increased body temperature up to 38–38.5 C;
- increasing weakness;
- stomach discomfort: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
The occurrence of at least one or more of the listed symptoms may indicate serious post-operative complications in the body, so consult a doctor immediately.
A new way to cleanse the body of parasites for 1 ruble! A federal program for the treatment and prevention of parasites has been launched! It’s hard to believe, but an effective drug for deworming the body is financed by the budget and special funds. The cruel truth is that more than 10 million people die every year as victims of parasites living in fish, vegetables and fruits! And to protect yourself and your loved ones you need to take a cheap remedy...
kistaplus.ru
How is laparoscopy performed?
Laparoscopy for removal of an ovarian cyst is performed under general anesthesia (anesthesia). On the day of the operation, the woman is consulted by a resuscitator to identify possible contraindications and make a final decision on the type of anesthesia. Most often, tracheal intubation is used, which allows you to control breathing and maintain the required depth of immersion in anesthesia. Before this, premedication is carried out, when a sedative with a hypnotic effect is administered intravenously; tranquilizers are usually used for this. Instead of such an injection, you can use mask anesthesia.
The operating table is tilted with the head end down by 30º so that the intestine moves towards the diaphragm and opens access to the ovaries. After processing the surgical field, a puncture is made in the navel, through which the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide. This allows you to increase the distance between organs and creates space for the necessary manipulations. A laparoscope, a special instrument with a camera and a light source, is inserted into the same hole. It is advanced to the pelvis, where the ovaries are located. Under the control of a video camera, 2 more punctures are made in the lateral sections of the abdomen, closer to the groin, which are necessary for introducing manipulators with instruments.
After a thorough examination of the ovaries and cysts, a decision is made to continue laparoscopy or whether wide access to the abdominal cavity is necessary (which is quite rare). In the latter case, all instruments are removed and the classic operation begins.
During laparoscopy, the doctor can perform enucleation of the cyst, wedge-shaped resection (excision) of a fragment of the ovary with a cyst, or removal of the entire ovary. The extent of surgical intervention is determined by the type of cyst and the condition of the tissues surrounding it. At the end of the operation, a check is made for the absence of bleeding, the instruments are removed, and carbon dioxide is sucked out. External sutures and sterile dressings are applied to the puncture sites.
After removing the endotracheal tube, the anesthesiologist checks the patient’s breathing and her condition, and gives permission to transfer to the ward. In most cases, the patient does not need to be admitted to the intensive care unit, since vital organs are not disrupted and massive blood loss does not occur.
Temperature after laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure that is a good alternative to open surgery. Thanks to this method, using special instruments, it is possible to carry out diagnostic and therapeutic manipulations in the abdominal or pelvic cavity without making large incisions on the anterior abdominal wall.
Laparoscopic surgical techniques are most widespread in gynecology, urology, endocrinology, and abdominal surgery.
How to explain the increase in body temperature after the intervention?
Temperature after laparoscopy may increase for various reasons.
Physiology of the wound process
An operation is also a kind of wound, which is stressful for the body and forces it to work at its maximum capabilities. The only difference between such wounds is that they are inflicted under aseptic conditions and their purpose is to diagnose or perform any therapeutic procedures.
The wound process has a typical course. In the first phase, which lasts about a week, catabolic processes predominate, the patient may even lose a little weight. At this time, there is an increase in body temperature, and this is a normal reaction. Subsequently, recovery processes are activated, and the level of anabolic hormones (insulin, growth hormone, etc.) in the blood increases. At this stage, electrolyte balance is restored, all types of metabolism in the body are restored, and body temperature usually returns to normal. Then the patient regains the lost weight, the body recovers completely.
Thus, usually the body temperature should return to normal within a week after the operation.
The temperature after operations performed using laparoscopy is usually lower than during open operations and rarely rises above 38°C. The temperature after laparoscopy (of an ovarian cyst or, for example, after an appendectomy, removal of the gallbladder) can be up to 37-37.5 ° C in the evening, which directly depends on the scale and severity of the intervention and is explained by the course of the wound process.
Can it be longer than this time and how long? Yes, it can, if, for example, the patient has a drainage installed after surgery and the resulting elevated body temperature is a reaction of the immune system to it. After the drainage is removed, everything will return to normal.
Despite the fact that the morbidity of laparoscopic operations is much lower than open ones, they were and remain significant stress for the body. And sometimes they end up with some complications, despite all the doctors’ attempts to prevent them.
When should you be wary?
Complications can occur with any type of surgery. This may result from infection entering the body, damage to internal organs, blood vessels, nerves, etc.
You should be concerned if:
- Elevated body temperature does not decrease for more than a week without apparent reason.
- The temperature remains high (above 38°C).
- Surgical wounds do not heal, their edges are dense, red, and pus may ooze out.
- Symptoms of infection appear (for example, pneumonia: cough, wheezing in the lungs).
- Intense pain persists in the area of the surgical wound.
What other warning signs might there be? First of all, this:
- Dry tongue, rapid heartbeat - may be signs of intoxication.
- Sweating, chills.
- Symptoms of peritonitis.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Doctor's observation
The recovery period after laparoscopy should be under the supervision of a doctor.
The entire postoperative period should be under the supervision of a doctor. He monitors the recovery process, does the necessary research and makes adjustments to the treatment.
In addition, the doctor decides on the advisability of prescribing analgesics and antipyretics in each specific case.
Typically, Nimesulide, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen and other drugs are used as antipyretic therapy. Rarely, if the body temperature rises to high values, a lytic mixture is used.
If there is any suspicion of impaired recovery after surgery, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible to determine the possible cause and combat it.
Prevention
Most complications are easier to prevent than to treat, and this can be achieved by following certain principles:
- Prevention of nosocomial infections, control over the processing of instruments, surgeons’ hands, etc.
- Reducing the time a patient spends in the hospital, both before and after surgery, usually reduces the incidence of complications.
- Identification of foci of chronic infection in the patient and their early elimination (carious teeth, chronic infectious process in the tonsils).
- Prophylactic use of antibiotics before, during and for some time after surgery.
Antibiotics are used to prevent bacterial complications
- Use of high-quality suture material.
- Timely correction of postoperative disorders (for example, elimination of intestinal paresis).
- The most complete examination and early diagnosis of disturbances in the course of the postoperative period.
- Early activation of patients after surgery, involvement of a physical therapy doctor.
Thus, elevated body temperature can be both a sign of the normal course of the postoperative period and a manifestation of the disease. Any surgical intervention and recovery after it should take place under the supervision of medical personnel; then, most likely, many possible complications will be identified and corrected in a timely manner.
diagnostinfo.ru
Indications for laparoscopy
The decision to operate is made:
- if conservative treatment has shown unsatisfactory results;
- when the leg of the formation is torsed;
- with a large cyst size - from 6 cm in diameter;
- with the rapid growth of education;
- with endometrioid, mucinous, dermoid ovarian cysts;
- at risk of cyst degeneration into cancer.
Indications for abdominal surgery: cyst rupture, suspected malignancy.