Ultrasound examination is popular due to its informativeness, reliability of results and painlessness.
When choosing between other non-invasive procedures, ultrasound wins due to its minimal health risks. To date, any immediate and long-term consequences are unknown to medical science. This is a very important point when conducting research on a woman’s reproductive organs. Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages has virtually no contraindications and can be performed at any period of a woman’s life, including during pregnancy. The procedure requires little preparation.
Types of research
Currently, there are several ways to visualize a woman's genital organs using ultrasound.
The most popular among them are:
- Transabdominal. In the first case, the study is carried out by scanning organs through the anterior abdominal wall using a convex sensor.
- Transvaginal. Transvaginal examination allows you to visualize the organ through the introduction of a special small sensor into the vaginal cavity. This is how no additional tissue obstacles are created.
Transrectal examination is performed quite rarely in gynecological practice. To perform it, you need to insert a sensor into the rectal area.
Examination technique
During the session, the patient is asked to expose the abdominal area if it is a transabdominal ultrasound. If the procedure is performed using a transvaginal probe, you must be naked from the waist up. After this, the woman lies down on the couch. The legs should be spread to provide the doctor with access to the genitals.
During a transabdominal examination, the doctor lubricates the girl’s stomach with a special gel and begins to move a sensor over it. In some places it may slightly adhere the sensor to the skin. If the technique is performed using a vaginal sensor, then it is inserted directly into the vaginal area. The session does not provide any physical discomfort or pain. The only thing the patient can feel is some psychological discomfort and embarrassment.
Expert opinion
Ksenia Dunaeva
User experience expert and comment moderator. Higher medical education and more than 5 years of actual practice.
Ask Ksenia
Reviews from specialists indicate that gynecological ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic technique. It is considered completely safe and is carried out without damaging the skin. After the ultrasound examination there are no side effects or complications. If necessary, you can do the procedure several times without harm to health.
When should diagnosis be carried out?
When is it better to perform an ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages:
- First of all, you will be interested in suspicion of any pathology, which the specialist wants to confirm.
- The age of the woman and the nature of her menstrual function. During menopause, as well as before the onset of menstrual function, ultrasound examination is carried out on any day, since the nature of organs and tissues does not change under the influence of hormones.
- In women with preserved menstrual function with acute pain or a condition that may be life-threatening (for example, ovarian apoplexy or ectopic pregnancy), the study should be carried out urgently, without any preparation, as well as with any available sensor.
- In most cases, an ultrasound examination is performed 5-7 days after the start of menstruation.
- If the endometrioid nature of the pathology is suspected, it should be carried out on days 7-10 of the menstrual cycle.
- In case of pregnancy, to determine the size of the uterus and the location of the fetal egg, an ultrasound is performed on any day, but subsequently screening dates are set.
Preparing the patient for the procedure
The genitals are close to the intestines, and flatulence may impair visualization. To eliminate it, drink carminatives and follow a diet for a couple of days before diagnosis. All types of food that contribute to gas formation are removed from the diet.
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the uterus and/or appendages:
| Access method | |||
| Transabdominal | Transvaginal | Transrectal | Combined |
| They go to the ultrasound with a full bladder. An hour before the procedure, drink about a liter of water or take a diuretic tablet 15 minutes before the diagnosis. | They go to TVUS with an empty bladder. | The evening before TRUS, they take a laxative or in the morning they do a microenema “Proctum” or another remedy. The procedure begins after defecation and washing. | They are prepared for both transrectal and abdominal ultrasound. |
| Before the diagnosis, you are allowed to eat lightly. It is advisable to dress in clothes that are comfortable for the procedure (you will need to expose your stomach or take off your underwear). | |||
Important! Before a laparoscopic ultrasound, a pregnancy test is performed, blood, urine and smear tests are done.
Indications for ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages
Conducting an ultrasound examination is a fairly common practice among obstetricians and gynecologists.
In what cases is it necessary:
- An examination of the uterus and appendages may be necessary for the purpose of preventive examination of organs, especially if the patient has not been seen by a doctor for a long time or examination of her genital organs is currently difficult due to the presence of painful formations, a large amount of subcutaneous fat, etc. d.
- An ultrasound examination is one of the main ones if an examination of a girl’s genital organs is required.
- During pregnancy, an ultrasound examination of the uterus is mandatory and has several purposes. First of all, this may be confirmation of the fact of pregnancy, as well as clarification of the location of the fetal egg, examination of the attachment of the membranes.
- At later stages, this is the diagnosis of developmental defects , as well as the state of uteroplacental blood flow, etc.
- Diagnosis of infertility , with clarification of the possible cause, monitoring the condition of the ovaries in preparation for assisted reproductive technologies. Much attention is paid to the condition of the follicular apparatus, as well as the presence of a dominant follicle. In some cases, it is under the control of ultrasound of the uterus and appendages that a puncture is performed to collect the egg.
- Identification of pathology, if a woman has complaints and discovers assumptions from a doctor. In some cases, it is necessary to monitor the ultrasound of the uterus and appendages during the treatment of the identified pathology.
- Diagnosis and exclusion of possible malignant neoplasms.
Who needs an ultrasound of the female internal genital organs?
Ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus can help make a diagnosis, assess the reserves of the reproductive system and the effectiveness of the treatment. In what cases an ultrasound examination is necessary, only a doctor can answer you. An approximate list of problems for which it is indicated:
- heavy and/or prolonged menstruation;
- intermenstrual discharge;
- assumption of the presence of a formation in the pelvis;
- uterine fibroids;
- ovarian cysts/tumors;
- genital endometriosis;
- doubt about the location of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity;
- screening examinations at different stages of pregnancy;
- spotting/pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy;
- lower abdominal pain;
- menstrual irregularities;
- pregnancy planning;
- infertility.
Preparation for the procedure
Transabdominal examination
Stages of preparation for transabdominal examination:
- Preparation for transabdominal ultrasound examination of the uterus and adnexa requires filling the bladder. To do this, the woman is advised not to urinate for at least 4-5 hours. If this turns out to be impossible, then it is suggested to drink a volume of liquid corresponding to 1 liter. You should drink clean boiled water at room temperature; do not drink carbonated drinks, alcohol, or thick fruit or vegetable juices. They can not only change the pattern and echogenicity of the contents of the bladder, but also increase the time it takes for fluid to pass through the urinary system.
- Before conducting the study, you need to follow a diet like this for 1-2 days , depending on the nature of the intestines. It includes the consumption of foods that do not lead to gas formation and a decrease in peristaltic movements. These are baked goods, sweets, and excess protein, which can cause fermentation.
- If there are problems with bowel movements, then on the eve of the study a light cleansing enema is performed. The use of medications and any special means is not required.
Transvaginal examination
The transvaginal method of ultrasound diagnosis of the pelvic organs, in particular the uterus and appendages, is the most convenient.
This is due to the fact that no special advance preparation is required.
It is advisable to empty your bladder before the test.
Women suffering from constipation can undergo a cleansing enema or simply follow a diet for two days.
This is due to the fact that clogged intestinal loops can shield the appendages and their visualization will be difficult.
Transrectal ultrasound examination
This method may only require emptying the rectal cavity so that there are no obstacles to the movement of the sensor.
In some cases, inflammation of the hemorrhoidal veins or their severe enlargement may complicate the procedure, which will cause discomfort during insertion of the sensor. This method is used quite rarely.
Intrauterine diagnostics
This is a less common way to detect pathology of the uterus and appendages; to detect them, it is enough just to agree with the doctor, depending on the type of pathology of the menstrual cycle on a certain day.
Also a prerequisite is the absence of inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity and vagina, as this can lead to generalization of the process.
Types of gynecological ultrasound
Ultrasound of the appendages and uterus varies in type and mode of examination. Depending on the indications, a woman is prescribed one of the types of ultrasound in gynecology:
- Transvaginal. The examination of the female genital organs is carried out using a special sophisticated sensor, which is inserted into the vagina. The instrument is first lubricated with gel. Transvaginal ultrasound diagnostics is often used in obstetrics to determine pregnancy in the early stages.
- Transrectal. An ultrasound probe passes through the rectum. The research method is used mainly among virgins.
- Transabdominal. Another procedure is called ultrasound through the abdominal cavity. The gel is squeezed onto the lower abdomen, after which the sensor is passed. The study allows you to thoroughly examine the uterus and appendages. The examination method is used in case of suspicion of the development of tumors, monitoring pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimester.
Sometimes, to identify the cause of infertility, a woman is referred to ultrasound hysterosalpingography. A special feature of this ultrasound is the intrauterine injection of a contrast agent to examine the fallopian tubes.
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages is carried out in different modes, each of which has its own special capabilities for research:
- Two-dimensional ultrasound diagnostics. The internal organs of the pelvis are visualized in one plane. Using this mode, the shape and size of the uterus, the location of the cervical canal, and the condition of the ovaries and their appendages are determined.
- 3D static mode. The method combines a three-dimensional image in two or more planes at once. Internal organs are examined in layers at different depths up to 1 millimeter. Ultrasound of the uterus in 3D mode during pregnancy in the second trimester determines the sex of the child, reveals the presence of neoplasms and their nature.
- 4D graphics in ultrasound. When examining the uterus and appendages, the image is broadcast in real time. So, during pregnancy, a woman can see the intrauterine movements of the child. 4D mode shows the direction of blood flow and its condition.
Ultrasound devices with 3D and 4D modes are often combined with CID diagnostics and color Doppler mapping (CDC). Sometimes several modes and types of ultrasound of the uterus and appendages are combined simultaneously. This technique is mainly used when examining pregnant women.
Additionally, see a specialist’s review of the technical capabilities of ultrasound:
How is the research conducted?
Methods for performing ultrasound:
- Ultrasonography of the uterus and appendages is performed in a lying position. To do this, you should sit on the couch;
- During transabdominal ultrasound, it is enough to lie with your legs closed.
- When performing a transvaginal ultrasound, you must be in a position lying on your back with your legs slightly apart and your knees bent.
- With transrectal access, the same position is maintained as with transvaginal access. The duration of the procedure is on average no more than 30 minutes.
- For pregnant women, ultrasound is also performed in the supine position , with the woman’s well-being of particular importance due to possible compression of the inferior vena cava and the development of collapse. And since the Doppler study is carried out for quite a long time, sometimes lasting more than 30 minutes, the woman is recommended to take a position with the left side elevated. This way, the inferior crawling vein will not be compressed and there will be no threat of worsening the condition.
Norms and decoding
During the diagnosis, the specialist immediately announces the results of the examination. Normally, a woman should monitor the following parameters:
- No neoplasms, fistulas, cysts or free fluid are found in the area of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- In patients of childbearing age, follicular cysts may be observed in the ovaries. This is not considered a pathology.
- If the examination is carried out to assess the location of the intrauterine device, the device must be in place.
- The bladder and its shape are not changed and correspond to normal parameters.
- There are no neoplasms, polyps, or stones in the bladder.
- After going to the toilet, the bladder is completely emptied.
A woman should be attentive to her health.
For the purpose of prevention, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs should be performed every year. If any disorders or diseases are identified, such services can be carried out much more often.
Procedure errors
You should know that ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages is not 100% confirmation of the diagnosis. This is a rather subjective method that only allows you to suspect a process.
It is necessary to take into account several factors that may affect the assessment:
- Of these, there are such as the level of equipment and the degree of specialist training, as well as the level of readiness of the specialist, the day of the menstrual cycle, etc.
- In some cases, if the assessment is not complete enough, a repeat examination may be necessary , especially if serious pathological changes are detected.
- If there is an assumption of a possible fetal malformation, an expert-level ultrasound examination is required with the participation of several specialists and additional laboratory tests.
- If an oncological process is detected or suspected, additional assessment of the lesions with the participation of an oncologist is required. This is due to extensive experience in diagnosing these pathological changes.
The value of the method in gynecology
An ultrasound scanner is a multifunctional tool. Reveals pathologies, clarifies diseases, and helps monitor the effectiveness of therapy. And all this is absolutely harmless and can be repeated an unlimited number of times.
The procedure is an integral part of medical support during pregnancy and gives an idea of the intrauterine development of the fetus, without the risk of harming it.
If a pathology is suspected, the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound of the endometrium or pelvic organs, examine the peritoneum and the peritoneal space. The method detects urolithiasis and cholelithiasis, changes in the kidneys and bladder, the presence of blood clots, abscesses, tumor formations and cysts.
Decoding the results
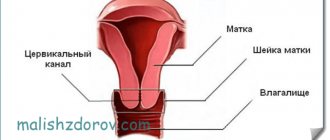
Uterus
Standards:
- Normally, the uterus should be in a position along the midline , a deviation of 20 to 30 degrees relative to the axis is allowed, as well as an anterior tilt.
- Sometimes the uterus may be positioned straight or deviated posteriorly . The presence of adhesions can deviate the uterus to the left and right.
- The normal shape of the uterus should be pear-shaped or round.
- The size of the uterus in women who are in the reproductive period and have not had pregnancies should not be more than 45-34-46 mm, and if a woman has already had a pregnancy, but without the process of childbirth and gestation, they can reach 51-37 -50 mm, if a woman carried a child and gave birth, regardless of the method of delivery, the dimensions will reach values of 58-40-54 mm. If the number of pregnancies is more than 3, then the size may increase slightly, provided that there are no complaints or other pathological changes.
A reduction in size should also not be considered a variant of the norm, since this can be a manifestation of genital infantilism.
There are three main stages:
- In the first degree they are 48-30 mm;
- At the second 42-26;
- With the third, these values are in the range of 30-21 mm.
As a variant of the norm, a decrease in size after menopause can be considered, so already 30 years after the cessation of menstruation they are 25-15-20 mm.
Cervix
The cervix is also a rather subjective value.
The dimensions may also depend on many factors, including the birth of a child through the natural birth canal or through a cesarean section, the presence of surgical interventions, previous inflammatory processes, etc.
Normally, the cervix should have a uniform and homogeneous structure; in some cases, Nabothian cysts are located in it, which are a consequence of blockage of the ducts of the glands that produce mucus.
Its dimensions average 25-45 mm in length and not exceeding 30 mm in thickness. An exception is the physiological condition in which the uterus is deviated posteriorly or is in a state of natural bending, and the thickness can reach 45 mm.
An increase, the appearance of uneven echogenicity, as well as the acquisition of a barrel-shaped or irregular shape is a pathological criterion and requires additional diagnostics.
Appendages
Normally, appendages are formations located on the sides of the uterus or in the area of the ribs of the uterus.
By structure, these are echo-positive inclusions, which contain in their structure the presence of a varying number of echo-negative elements, predominantly oval or round in shape.
The size of the ovaries is also a strictly individual value; it primarily depends on the woman’s age and the state of her reproductive function, as well as the duration and day of the menstrual cycle.
When examining and subsequently assessing the size of the ovaries, the use of various medications is also taken into account.
Dimensions:
- So, in normal condition, their dimensions can be 25-40 mm in length, in thickness they can be from 10 to 20 mm, while the width should be no more than 15-30 mm. In diagnosing the size of the ovaries, their volume also plays a great role.
- The dimensions of the follicular apparatus should not be large and on average no more than 10 mm . Moreover, among the entire follicular apparatus in the normal reproductive cycle, one follicle can be found, which measures up to 25 or 30 mm. Exceeding this value is defined as an ovarian cyst.
- Taking into account age and functional characteristics, it should also be noted that after the onset of menopause, the size of this organ begins to gradually decrease , this is due to the fact that the follicular apparatus is not defined, and its reserves are exhausted. After 10 years of menopause, their volume should not be more than 1, 5 cu. cm.
- The volume of the right and left ovaries should be approximately the same, the maximum difference should be no more than 1.5 cm cubed. In this case, sizes larger than the prescribed values should alert the doctor and think about possible additional diagnostics.
The fallopian tubes
In normal condition, a woman’s fallopian tubes are invisible to the ultrasound machine.
In some cases, they are visualized in the form of thin strands with small sizes and a uniform structure; their shape is also the same throughout their entire length.
If formations appear, as well as unevenness in their volume, additional diagnostics should be carried out to identify inflammatory reactions or ectopic pregnancy.
In case of a mass formation in the area of the fallopian tube, surgical intervention is required, since inaction can lead to death or life-threatening conditions.
Free liquid
The presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity is a pathological sign, with the exception of the presence or just past ovulation. So at this time it is allowed to appear in the posterior fornix, where it drains a small volume of liquid contents.
An increase in volume may indicate the presence of pathological conditions such as the presence of inflammatory processes accompanied by the formation of an infiltrate or effusion, the presence of an ectopic pregnancy that led to bleeding into the abdominal cavity, etc.
Sometimes the presence of fluid in the posterior fornix or other parts of the abdominal cavity may indicate the presence of ascitic fluid, which requires excluding an oncological process, portal hypertension and liver disease.
With a bicornuate uterus, there are no specific standards; in this case, the ratio and type of enlargement will play a big role. Dynamic assessment of the organ plays a fundamental role.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries
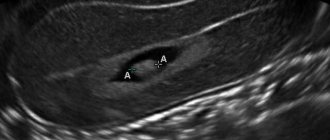
The ultrasound protocol is deciphered by a gynecologist. Normally, the uterine tissue in the photo is painted a uniform gray color, the corpus luteum and the uterine cavity are marked with a black background with smooth borders, the ovary is fine-grained, and the dominant follicle is visible. There are no deviations from the norm in the structure and age-related sizes of organs.
In pathologies, the foci of changes are heterogeneous in echogenicity and are visible in the photo as a lightened or darkened gray color.
The ultrasound image shows:
- cyst - a black cavity with gray even borders;
- inflammation of the uterus - the walls of the organ are thickened and colored a heterogeneous gray color;
- fibroids - a dark gray compaction inside the uterine wall with smooth borders;
- polyp - a gray protruding process from the uterus or cervical canal;
- cancerous tumors - hyperechoic (gray to white) spots with uneven borders;
- ectopic pregnancy - a light gray lesion inside the oviduct;
- bicornuate uterus - the fundus is divided into 2 hollow protrusions;
- salpingoophoritis - an increase in the size of the ovary, oviduct and their heterogeneous color, there is fluid behind the uterine body;
- polycystic – in the places of the follicles black cavities measuring 25 mm or more are visible;
- endometriosis is a thickened mucous layer with a low degree of echogenicity.
You can see the bending and displacement of the reproductive organs. If the ultrasound report states, for example, “the ovary is located behind the uterus,” this means that there is adhesions, ligament deformation, or a congenital structural anomaly. Ultrasound examination cannot determine the malignancy of neoplasms and their clear boundaries. For this purpose, ultrasound with elastography is used.
Pathologies that can be detected by ultrasound
Physiological processes
The ultrasound method is widely used for frequent examination of a woman and monitoring the condition of her genital organs from a physiological point of view:
- This is, first of all, a regular examination to confirm the absence of diseases in this area , especially in cases where a vaginal examination is difficult. This applies, for example, to girls whose examination is impossible due to the presence of a hymen.
- Monitoring the ovulatory function of women who cannot become pregnant and this method can accurately mark the onset of ovulation and the process of maturation of the dominant follicle.
- Well, the most important physiological state is pregnancy. Ultrasound examinations are now often carried out during the period of gestation. This is primarily due to the fact that for many it is indicated specifically to confirm the presence of intrauterine pregnancy. In case there is a threat of development of ectopic attachment of the ovum, aggravated obstetric and gynecological history, which may require early therapy aimed at maintaining pregnancy. Ultrasound examinations are also carried out in the future; it is mandatory to conduct ultrasounds three times during pregnancy, these are the so-called screenings, which are regulated by the state.
Abnormalities of the uterus
This is perhaps one of the safest and non-invasive methods, which allows you to obtain an accurate image of an organ in the presence of defects in its development and structure.
An ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages is performed at any age, but most often at the onset of puberty.
Since it is at this time that pathologies of organ development are most often detected.
In some cases, this may be an incidental finding in early childhood or adulthood, to determine possible causes of infertility.
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages helps:
- First of all, visualize all parts of the reproductive system, in which their functioning is assessed. The connection between the cervix and the vagina is checked, as agenesis or underdevelopment of the latter may develop.
- The size of the uterus, its structure, location and degree of functioning are assessed. Very often, an accidental finding during ultrasound reveals a change in the size of an organ, which does not lead to dysfunction as a whole. This may be a manifestation of a saddle-shaped uterus, a horseshoe-shaped one, and also, in some cases, a bicornuate one. Ultrasound examination also allows one to suspect structural anomalies, such as intrauterine septums, which cannot be detected during a routine examination.
- Developmental defects are also identified in which a pathological clinic can be detected in the form of pain in the lower abdomen, intoxication, etc. At the same time, it is possible to detect such anomalies as atresia of the duct of the double uterus, incomplete duplication, etc. even in adolescence.
Diseases
Uterine fibroids
Ultrasound examination is the main non-invasive method, after digital examination, if uterine fibroids are diagnosed.
It is performed on women of any age if there is a suspicion of fibroids or an increase in the size of the organ.
No special preparation is required for better visualization of the node.
It can be performed on any day of the cycle in women during the reproductive period, and during menopause on any day.
Scanning allows you to:
- Assess the size of the organ , as well as the location of the identified myomatous node.
- Of great importance is the identification of a submucosal node , or a pedunculated node, which can lead to the development of an acute abdomen later.
- An experienced specialist helps to identify the approximate composition of the node based on an ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages. This is of great importance in determining the further course of the disease, as well as the degree of risk of malignancy and possible disintegration of the lesion.
- Sometimes it is important to assess the degree of blood flow in the area of the fibroid, since this may not only be a risk of transition to a malignant process, but also further growth of the lesion and possible necrosis due to poor circulation.
Determination of uterine fibroids is necessary if a woman is planning a pregnancy or has been diagnosed with infertility, the cause of which is a node located in the cavity that can deform it or disrupt the implantation of the fertilized egg.
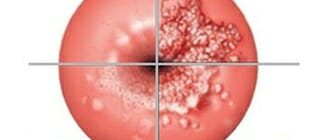
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a pathology that leads to a large number of pathological symptoms:
Endometrioid lesions can be located in the ovaries , uterine body, and other parts.
- In the body of the uterus with internal endometriosis, one can see uneven structure, the appearance of foci with reduced echogenicity, and an increase in the size of the organ.
- With endometriosis of the cervix, the size of the organ increases, looseness of the structure appears , as well as the discovery of other shadows.
- In the ovarian area, endometriotic lesions most often appear, representing cystic changes. Dynamic assessment is of great importance in confirming the diagnosis.
- At the same time, at different periods of the menstrual cycle, unequal sizes of lesions are detected ; they can increase before the onset of menstruation. As a rule, they do not have vascularization. When detected, severe endometriosis is determined.
Cystic changes in the ovaries
This is a pathology that is detected in most cases only after an ultrasound examination.
The size of the ovaries is determined, as well as the number of follicles and their size are determined.
It is the size of the follicles that can determine the state of the reproductive system.
In the presence of cysts, i.e. formations larger than 2 cm in diameter, the location, structure, their contours, as well as the presence of inclusions inside the cyst are assessed.
When performing an ultrasound of the appendages, the doctor assesses the degree of vascularization, as well as the blood flow and the presence of partitions, determines the diagnosis and further tactics with possible vascularization.
Tumors
Diagnosis of tumor processes of various nature is an important point in the use of ultrasound.
It is this that can alert a specialist to the possible cause of changes in an organ, determine its structure, and also note the condition in relation to surrounding organs and tissues.
Ultrasound and uterine fibroids
Ultrasound of uterine fibroids is a study of choice for making a diagnosis, assessing the dynamics of node growth and the effectiveness of therapy. Uterine fibroids are clearly visualized on ultrasound and represent a formation with clear contours, which can have a submucosal, intramural and/or subserous arrangement of nodes. For a comparative assessment of the dynamics of node growth, it is necessary to conduct research immediately after menstruation, since under the influence of progesterone, the size of nodes can change during the cycle.
(Be the first to rate this article!)
Where to get tested?
Thanks to the wide availability of ultrasound machines, examinations can be carried out in almost every medical institution.
In this case, preference is given to large medical centers that are equipped with devices of modern generations or those of an expert level.
In addition, almost all private medical institutions are equipped with this equipment.
In this case, great importance will be given to the qualifications of the specialist, as well as the level of equipment.
Methodology
Now you need to understand how a gynecological ultrasound is performed. As detailed above, this examination can be carried out in three ways: transabdominal, transvaginal and transrectal. Of all the above methods, transvaginal examination raises the most questions.
How is an ultrasound performed? To carry out the procedure, a special sensor is used, which is inserted into the vagina. It looks like an elongated cylinder. Before starting the test, a condom is put on. When performing the examination, the woman lies on her back, with her legs bent at the knees. A gel is applied to the sensor, ensuring painless penetration into the muscle organ.
As a rule, during the examination the woman does not feel pain. Although with severe inflammation in the lower abdomen, cutting pain may prevail during the study. You should tell your doctor if you experience any discomfort.
The advantage is that between the sensor and the examined organs there is only the thinnest vaginal wall. In this regard, various “interferences” in the form of nearby organs or the fat layer of the abdominal wall are excluded.
After the study is completed, the gynecologist gives the patient a conclusion. Thanks to modern equipment, you can take photographs and transfer them later to any digital media. In the future, another specialist may need them to familiarize themselves with the patient’s medical history.
Ultrasound examination has become widespread in various fields of medicine due to its minimal impact on the patient’s body, high information content and relative low cost of manipulation.
Gynecology has not remained aloof in the application of this diagnostic technique. In this area of medicine, various methods of ultrasound are widely used, which make it possible to diagnose and promptly treat various pathologies of the female reproductive system.
What does the study show? How should you prepare for manipulation? On what day of the cycle will a pelvic ultrasound be the most informative?
What does the diagnosis show?
Using transvaginal and abdominal echography, the doctor gets an idea of the structure of female internal organs, determines the shape and size of the uterus, the condition of the endometrium and its correspondence to the menstrual cycle. The size of the follicles is examined and the location of the ovaries relative to the uterus and fallopian tubes is determined. Based on the diagnostic results, a pelvic ultrasound protocol is drawn up.
If the patient requires a more thorough diagnosis, folliculometry and echohysterosalpingography techniques based on ultrasound technology are used in medicine.
Folliculometry is a method for monitoring folliculogenesis. In the first phase of the cycle, the doctor monitors the maturation of the follicle and changes in the endometrium. In the second phase of the cycle, the process of ovulation is studied using ultrasound, its timing and signs are determined.
Echohysterosalpingography is prescribed if it is necessary to exclude the presence of intrauterine pathologies and examine the patency of the fallopian tubes. A sterile liquid is injected into the uterine cavity to improve visualization of the tubes, and then the condition of the organs is assessed using ultrasound.
Conducting research
If a woman undergoes such an examination for the first time, then she is interested in how an ultrasound scan of the uterus is done. There is nothing complicated in this procedure; it is painless and does not cause any discomfort to the patient.
With the transabdominal ultrasound method, the doctor lubricates the patient’s abdomen with gel and moves the sensor over the surface of the body. At this time, an image of the genital organs is projected onto the monitor; you can see their size, structure and condition.
If the examination is done transvaginally, the doctor inserts a probe with a sensor into the patient’s vagina and monitors the condition of her organs through a monitor. Transrectal ultrasound is performed in a similar way, only the probe is inserted into the rectum and a thin sensor is used.
Cost of examination
Diagnostics are carried out free of charge in local clinics. Costs at private centers vary depending on the scope of the study.
| City | Price, rubles |
| Moscow | 250-700 |
| Saint Petersburg | 300-700 |
| Ekaterinburg | 250-600 |
| Novosibirsk | 250-700 |
| average cost | 262-675 |
Transabdominal pelvic examination is used in the diagnosis of pregnancy and various diseases. The procedure is available in any medical institution at a low cost.
Leave comments on the information you read. Share the article with your friends on social networks.
Preventive research
Today, ultrasound diagnostics is one of the most accessible and safe methods for preventing infertility, cancer in the early stages, as well as identifying other pathologies that threaten women’s health.
Ultrasound examination has become extremely popular in gynecology in recent years, as it allows you to accurately, quickly, painlessly and without negative consequences examine the structure and condition of the pelvic organs.
This ultrasound can be used by women of any age and any condition, children, teenage girls, those who are sexually active or not, to monitor fetal development.
But in order to get the most accurate and objective picture in each of these cases, one of three types of gynecological ultrasound is used:
- transvaginal,
- transabdominal and
- transrectal.
Transrectal ultrasound
In rare cases, if neither transvaginal nor transabdominal ultrasound is possible, a transrectal examination may be prescribed. In this case, the probe, which is usually used for transvaginal examination, is inserted into the rectum. It is used quite rarely, but it also allows you to get a fairly accurate and objective picture.
To prepare, you need to remove food from your diet a few days before the test that can cause bloating and gas, and do a cleansing enema in the morning.
The choice of a specific type should be made only by the attending physician.
He will subsequently decipher the result and give recommendations on additional types of examination or treatment. Articles
Ultrasound of the female genital organs, or gynecological ultrasound, allows you to assess the condition of a woman’s reproductive organs. Gynecological ultrasound can visualize the periuterine space, ligaments supporting the uterus and many other structures of the reproductive system.
Ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology is performed using three different methods. All of them have minor differences in the mechanism of operation, but each of the methods is specific and tailored to specific situations.
In this article we will talk about what methods are used to perform a gynecological ultrasound, how to prepare for a gynecological ultrasound and how much it costs to do such a procedure. We will also talk about what can be detected on such an ultrasound.
1.1 Reasons for diagnostics
A gynecological examination of the internal organs of the pelvis (including the vagina) is carried out for various indications. The most notable and important of them are the following:
- when it is necessary to detect pathologies of the pelvic organs at any stage of their development and on any day of the cycle;
- when you need to evaluate the anatomical features of the formation of the uterus, fallopian tubes, its cervix and ligamentous system;
- when it is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy for pathologies of the pelvic organs;
- when it is necessary to make not an empirical, but an accurate diagnosis of pathologies of the reproductive system with scant symptoms.
In this case, it is best to supplement any ultrasound examination with Doppler measurements. You can perform examinations for the indications listed above on any day of the cycle. But it is better to discuss the timing of the procedure with your doctor during your consultation.
How is a transabdominal examination performed?
The procedure is absolutely painless, but if you are sensitive, it may cause slight discomfort. In the specialist’s office, the patient undresses from the waist down, exposes her stomach and lies on her back.
During external ultrasound, the skin in the pelvic area is lubricated with a special gel, which ensures contact of the sensor with the body. With light pressure, the device moves over the skin. Using sensors, a dynamic, accurate image of the tissues and structure of the organs being examined is obtained. The picture can be enlarged many times.
results
The visualized structures are assessed directly during the manipulation. The doctor looks at the monitor screen, simultaneously determines the size of the structures being examined, and the nurse keeps a protocol.
Based on the diagnostic results, the patient can receive a photograph of the detected formations with a decoding and dimensions of certain structures. This is necessary for consultation with other specialists.
Ultrasound is the leader of modern non-invasive diagnostics. The ultrasound imaging method is based on echolocation technology.
The ultrasound wave is reflected from the organ and captured by the sensor, after which a detailed image is transmitted to the screen of the ultrasound machine.
Imaging allows the doctor to assess the patient’s health status in a short time and confirm or exclude the presence of neoplasms and pathological processes.
Video
The video will tell you in detail about the types of ultrasound of the pelvic organs and preparation for the examination. Published by Andrey Klokov.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the HROMOSOMA website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author
Discuss the article:
Pelvic ultrasound when planning pregnancy: is it necessary for everyone?
What organs are located in the pelvis and why is it so important to examine them? The reproductive organs (uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes), bladder and rectum are located there. Due to the fact that these structures are located in a relatively small volume, pathological changes in one organ can affect the function of neighboring ones.
Do you need to prepare for an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs?
A pelvic ultrasound can be performed in two ways: through the surface of the abdomen (abdominal) and intravaginal (transvaginal).
- To perform an ultrasound of the uterus and appendages (ovaries and fallopian tubes) through the abdominal wall (abdominal), preparation is required: a full bladder is required, for which it is recommended to drink at least 0.5 liters of non-carbonated liquid 1–2 hours before the procedure. A full bladder pushes aside the intestines (which are filled with air), allowing a clearer view of the pelvic organs. If this is not done, the research will be uninformative. If you periodically suffer from stool problems and bloating, then for 2 days before the test you must adhere to a diet that normalizes stool and does not contain gas-forming products. If necessary, consult your doctor about whether you need to take any medications to improve your stool before the test.
- For a more detailed examination of the ovaries and uterus, an intravaginal method , in which a special sensor is inserted into the woman’s vagina. With this option, on the contrary, it is necessary to empty the bladder before the study, otherwise it will “cover” the image of the internal genital organs. Before inserting the sensor, a sound-conducting gel is applied to its scanning surface and a special disposable latex nozzle or condom is put on. If you are allergic to latex, be sure to tell your doctor!
At the end of the study, the area of the rectum and bladder is visually examined. If any abnormality of these organs is suspected, the woman is referred for additional examination.
When is it better to perform an ultrasound of the uterus and appendages?
Despite the fact that ultrasound of the uterus and appendages can be performed on any day of the menstrual cycle, when searching for various pathologies, the phase of the menstrual cycle is important for the correct interpretation of the results. So, for a preventive examination, as well as to identify focal formations (fibroids, cysts) in the uterus and ovaries, it is better to do an ultrasound of the uterus and appendages immediately after menstruation. To detect abnormalities in the development of the uterus (bicornuate uterus, duplication, presence of septa in the uterus) and check the condition of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium), it is better to perform a study before menstruation. Sometimes it may be necessary to repeat an ultrasound of the uterus and appendages after a few days, for example, with endometriosis and to determine ovulation.
What will an ultrasound of the uterus and appendages show?
During an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, the doctor examines the internal structure of the body of the uterus, its cervix, ovaries and surrounding organs (fallopian tubes, if changed (normally they are not visible during the study), bladder, adjacent intestinal loops), the size and shape of these organs are determined , the presence of tumor formations and cysts, the thickness of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) is necessarily measured, and other possible changes are determined that can lead to problems in preparation for conception or cause complications during pregnancy.
How and why to do an ultrasound of the uterus
The dimensions of the uterus vary depending on the constitution of the woman and her age; normally they are: length 4.5-6.7 cm, thickness - 3-4 cm, width - 5-6.4 cm. If the size of this organ is smaller, they say about the infantile (underdeveloped, childish) uterus. Large sizes occur in pathological formations, inflammatory diseases, pregnancy or in women who have given birth many times. The ultrasound picture can clearly distinguish two of the three layers of the uterus - the inner (endometrium) and the middle (myometrium).
Particular attention is paid to the endometrium - the inner layer of the uterus, which is renewed every month with the onset of menstruation and which becomes the “home” for the fertilized egg when pregnancy occurs. Disturbances in the structure of the endometrium cannot be determined either during a gynecological examination or with the help of tests, but only with the help of ultrasound. And the vast majority of problems with pregnancy are associated with disorders of this particular layer of the uterus. Normally, on an ultrasound of the uterus, the thickness of the endometrium depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle: normally on days 5-7 this figure is 4-6 mm, on days 15-28 – 7-14 mm. Throughout the menstrual cycle, the endometrium should be homogeneous.
The myometrium (muscle tissue) of the body and cervix provides the necessary contractions of the uterus. For example, thanks to this layer, menstruation occurs and the process of childbirth takes place. A homogeneous state of the myometrium without any formations is considered normal.
An ultrasound scan of the uterine scar after a cesarean section is mandatory if a woman plans to become a mother again. This is necessary in order to check the condition of the scar and predict the risk of uterine rupture along it during subsequent pregnancy and childbirth.
Ultrasound of the ovaries
Ultrasound of the ovaries shows the shape, size, location and structure of this paired organ.
Normally, in the first days of the menstrual cycle, several follicles with a diameter of 4-6 mm are detected in the ovary. In the middle of the cycle, a dominant follicle should be visible (an egg ready for fertilization will come out of it), measuring 10–24 mm. As the dominant follicle grows, the other follicles become smaller. After ovulation (the release of an egg), the dominant follicle “disappears” or significantly decreases in size. Then, in the same place, from the 12th to 14th day of the cycle, the corpus luteum is detected, producing the hormone progesterone. If fertilization and implantation occurs (attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus), the corpus luteum remains and can be detected until the 14th week of pregnancy. The doctor will see all this during an ultrasound examination.
Ultrasound of the ovaries, performed several times during one menstrual cycle, allows us to judge the reproductive function of a woman: whether eggs are formed in her body, whether ovulation occurs, whether the fertilized egg can attach to the inner lining of the uterus. A single study may not be enough if ovulation, for example, occurs too early or at the end of the cycle.
Ultrasound of the fallopian tubes
Ultrasound of the patency of the fallopian tubes is a separate type of examination, which can only be performed when the uterus and tubes are filled with a special contrast agent. With a regular ultrasound, it is impossible to see the full picture of the condition of the pipes, since their lumen will not be visible. Therefore, doctors resort to a special technique that allows them to clearly determine the patency of the fallopian tubes. Such a study is performed only if there are indications for it, for example, to determine the cause of infertility. It is not performed on all women planning a pregnancy, as it is not as harmless as a regular ultrasound.
Optimal time. It is best to perform this procedure from the 5th to the 11th day of the menstrual cycle (on the eve of ovulation). It is at this time that the cervix is most dilated, and the endometrium is thin, which provides the best research result.
Preparation. Since during the examination a contrast agent is injected into the uterus, before carrying out the examination it is necessary to ensure that there is no risk of infectious complications. To do this, the day before, a woman is recommended to undergo general blood and urine tests, a gynecological smear for flora and an analysis for sexually transmitted infections (mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis). Immediately before the procedure, the patient must have her genitals treated with an antiseptic. Unlike a regular ultrasound, the examination can be painful, so antispasmodics and painkillers are prescribed half an hour before it.
How is the research conducted? To carry out the procedure, the patient lies down on a gynecological chair, speculum is installed in the vagina, and a thin plastic catheter is inserted through the cervical canal. Using a vaginal probe, an ultrasound of the fallopian tubes is performed to ensure that the catheter is in the correct position, after which a sterile solution is injected through it, which, moving along the fallopian tubes, allows you to see their internal structure and the presence of adhesions in them. Normally, at the end of the study, all the fluid exits into the abdominal cavity and accumulates behind the uterus. If it fills the uterus and fallopian tubes without entering the abdominal cavity, then this indicates obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
What diseases can be identified?
Using ultrasound of the pelvic organs, it is possible to identify various pathological processes of the reproductive system in women:
- Congenital anomalies of the uterus and vagina are detected in 3% of women of reproductive age with various gynecological pathologies. These include underdevelopment of the uterus when it is small (child-sized). Such a uterus is called infantile. In addition, there is a saddle-shaped, two-horned or one-horned uterus, a uterus with a complete or incomplete septum inside, complete or partial duplication of the genital organs, etc.
- Uterine fibroids are a benign tumor formed from the muscle tissue of the uterus. An ultrasound examination can determine the size of the nodes and their location. Thus, the node can be located in the thickness of one of the walls of the uterus, protrude on its outer surface, or protrude into the uterine cavity, deforming it. Particularly dangerous are nodes that deform the uterine cavity. They can cause infertility and miscarriage. During repeated examinations, the size of the nodes is always determined: this makes it possible to identify growing formations and prescribe treatment in a timely manner.
- Endometriosis is the spread of the endometrium (the inner layer of the uterus) beyond its limits to the peritoneum, fallopian tubes, etc. To diagnose some forms of endometriosis, such as ovarian endometrioid neoplasms, it is difficult to do without ultrasound. Endometriosis often causes blockage of the fallopian tubes, which leads to infertility.
- Cysts and tumors of the ovaries. Upon examination, a rounded formation is detected in the ovary, the contours of which are clearly visible. In addition to cancer risks, ovarian cysts can disrupt the hormonal balance in a woman’s body, leading to menstrual irregularities, infertility and miscarriages. May cause infertility and miscarriage.
- Endometrial polyps and hyperplasia are pathological growths of the inner layer of the uterus.
- The inflammatory process and its consequences. Chronic inflammation may be accompanied by the appearance of fluid in the fallopian tube (hydrosalpinx), which is clearly visible on ultrasound. Also on ultrasound you can see signs of chronic endometritis (inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus). With hydrosalpinx, the patency of the fallopian tube is disrupted, which leads to infertility and increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy. Also, prolonged inflammation can lead to fusion of tissues of the ovary, peritoneum, intestines and fallopian tubes. In such cases, full functioning of the ovary and fallopian tube is impossible, which, of course, cannot but affect the possibility of conceiving and bearing a child. Endometritis can complicate pregnancy or lead to complications. This pathology causes irregularities in the menstrual cycle; cycles occur without ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary), which, in turn, leads to infertility, since in the absence of ovulation the egg is not released.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) . This is a condition in which the ovary produces many follicles that do not reach normal maturity. To be sure of making this diagnosis, in addition to U3I, the doctor will prescribe additional tests and examinations.
Of course, ultrasound is a valuable diagnostic method that allows you to make the correct diagnosis of diseases of the internal genital organs. Safe and accessible research makes it possible to identify many reasons that interfere with conception.