Laparoscopy of uterine fibroids is a modern minimally invasive method that allows you to remove this tumor painlessly and without trauma to the abdominal cavity. The entire procedure is carried out under anesthesia using a special device - a laparoscope, with the help of which all tumors are removed. Carrying out this operation does not deprive a woman of the ability to become a mother, while improving her general condition by eliminating the symptoms of the disease. Another advantage of laparoscopic removal of fibroids is the absence of traces on the body after all manipulations.
Causes and symptoms of fibroids
The main reasons that cause the formation and further formation of fibroids in the female body are as follows:
- hormonal disorders that have occurred in the body, and not only in the state of sex hormones;
- heredity;
- absence of full-term pregnancies;
- defective sexual relations with lack of orgasm, interrupted sexual intercourse;
- injury to the uterine mucosa during diagnostic procedures and artificial termination of pregnancy;
- excessive physical activity with heavy lifting;
- overweight with excess adipose tissue.
Of course, the presence of any of these factors is not a direct cause that can provoke the formation of fibroids, but if several of them are present at once, the likelihood of developing fibroids increases.
A characteristic feature of this pathological condition are insufficiently expressed manifestations, so often fibroids cannot be detected at the beginning of their formation. But if a woman takes care of her health and regularly visits a gynecologist, then advanced forms of the tumor do not threaten her.
However, you should not lose sight of even minor symptoms, such as:
- emerging acyclic bleeding with heavy blood loss;
- pain of a pulling nature in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back, to the sacrum or rectum;
- the appearance of attacks of pain in the form of contractions during menstruation;
- inability to conceive when trying without using contraception;
- difficulty in defecation with frequent urge to urinate.
Most often, such symptoms accompany large fibroid nodes, and can also occur when the tumor is localized in certain places on the surface of the uterus, when it begins to interfere with the functioning of nearby organs. Based on these symptoms, diagnostic tests are prescribed, one of which is ultrasound, which can confirm the diagnosis or ensure the absence of myomatous nodes.
Symptoms of pathology:
- menorrhagia - heavy menstruation, often occurring in the form of bleeding, leading to a decrease in hemoglobin;
- pain in the lower abdomen of varying severity - from minor to extremely intense (with necrosis of the node and the development of peritonitis);
- reproductive dysfunction (infertility or miscarriage);
- constipation – when the rectum is compressed by a fibroid node;
- urinary disorders in the form of frequent urge or acute urinary retention;
- an increase in the size of the abdomen - in the presence of large nodes of uterine fibroids.
Depending on their location, myomatous nodes are divided into:
Subserous (subperitoneal) - located mainly on the outer surface of the uterus, on a thin stalk or wide base through which feeding vessels approach. Therefore, when the subperitoneal nodes are large, the blood flow is insufficient and ischemia or tumor necrosis and peritonitis occur. Since subserous fibroids are located predominantly in the abdominal cavity, compression of neighboring organs (bladder, ureters or rectum) may occur and, as a result, disruption of their function.
Submucosal (submucosal) - located mainly in the uterine cavity, prevent normal contraction of the uterus and emptying of the uterus during menstruation and lead to an increase in its duration, profuseness, and the occurrence of pain. In addition, submucosal nodes can prevent implantation of the fertilized egg and the development of pregnancy.
In rare cases, submucosal nodes may be “born,” which is accompanied by severe pain and bleeding.
Interstitial (intramural, intermuscular) - nodes are located in the myometrium and often tend to be subperitoneal (centrifugal growth) or deform the uterine cavity (centripetal growth). When small in size, it is often asymptomatic.
Uterine fibroids with an atypical location of nodes – interligamentous, cervical, “parasitic”, etc. – manifests itself, as a rule, with symptoms of compression of neighboring organs or pain.
Some women do not even realize that they have a problem, since the neoplasm may not manifest itself for a long period of time. Often a tumor is detected during a routine examination.
Even in the absence of symptoms, the disease requires observation at least once every 6 months. When the uterus enlarges due to neoplasms up to 8-9 weeks of pregnancy or one of the nodes is more than 2-3 cm, most often symptoms appear that require treatment. It should be noted that submucosal uterine fibroids of any size can be accompanied by pronounced clinical manifestations in the form of heavy menstruation and uterine bleeding.
What is laparoscopy
The laparoscopic method involves surgical penetration into the abdominal cavity without making an incision. The method consists of using several small punctures in the peritoneum, allowing the removal of nodes on the uterus under the control of a video camera. Due to the small traumatized surface, small scars remain almost invisible, and the possibility of developing an infection from the penetration of pathogenic microflora is significantly reduced.
Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia, since the procedure requires complete relaxation of the muscles in the abdomen and diaphragm. The patient undergoes punctures used to access the operation site, and the surgeon has the opportunity to observe the further progress of the operation on the monitor screen.
How the operation is performed
Removal of uterine fibroids using the laparoscopic method is always carried out in a gynecological clinic or hospital in a sterile operating room.
Elective surgery is usually performed in the morning or early afternoon and lasts from 30 minutes to two hours, depending on the extent of the operation and the size of the tumor.
Any day of the cycle is suitable for laparoscopic manipulation, except for the period of menstruation. During menstruation, increased bleeding is observed, so the risk of bleeding during surgical procedures increases.
Anesthesia - endotracheal with the use of mechanical ventilation. The patient sleeps, hears nothing, sees nothing and does not experience pain.
Before the operation begins, combined anesthesia is used - endotracheal anesthesia, which helps to endure the entire surgical process without pain and stress.
Before the operation, the woman signs an informed consent, thereby confirming that the doctor explained to her how the fibroids will be removed and the possible change in the scope of the operation if complications arise. In the event of an unforeseen development of events, surgery may result in the removal of the uterus, which the doctor also warns about before the operation.
What happens in the operating room
- The patient is placed on the operating table. After treating the abdominal skin, the surgical field is covered with sterile sheets;
- After the anesthesia has taken effect, punctures are made at the navel and on the sides of the abdomen in the iliac regions, through which endoscopic instruments are inserted;
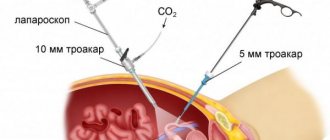
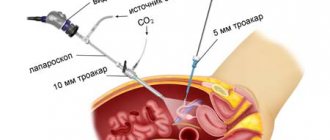
- For a better view of the uterus, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity, which is completely harmless to the body. The intestinal loops move from the pelvis to the upper abdomen and do not create an obstacle to the operation;
- The surgeon examines the uterus, appendages, and fibroid nodes. An image of what is happening in the patient’s abdominal cavity is transmitted to the monitor screen. During the operation, the doctor does not touch the pelvic organs with his hands.
Operation stages
- Cutting off a fibroid node (if it has a stalk) or enucleating a tumor located in the muscular wall of the uterus. To do this, an incision is made on the surface of the capsule, the knot is fixed with two clamps and removed by successive pulling. Myomatous nodes are characterized by the presence of a clearly defined capsule, due to which they are easily removed without additional trauma to the uterine wall. The tumor bed (the place where it was located) is washed with saline, and then the bleeding areas are carefully coagulated;
The process of myomectomy begins with cutting off or enucleating the tumor.
- Suturing a defect in the muscular wall of the uterus. The myometrial defect formed after tumor removal must be sutured. The surgeon also performs this manipulation without touching the organ with his hands, but only by looking at the screen and using instruments inserted into the woman’s abdominal cavity. Applying an endoscopic suture is the most time-consuming and labor-intensive stage of the operation. The suture must be reliable so that there is no threat of uterine rupture in this place in subsequent births. This requires some experience on the part of the surgeon;
- Removal of fibroids from the abdominal cavity. Small myomatous nodes can be easily removed through existing incisions in the abdominal wall. To extract large nodes, you will need to use a special tool - an electric morcellator, which, using a system of rotating knives, first crushes and then “sucks” parts of the tumor into itself, like a vacuum cleaner. In this way, large fibroid nodes are removed;
- Inspection and sanitation of the abdominal cavity is the final stage. At the end of the operation, the surgeon once again examines the abdominal cavity, removes accumulated blood clots, checks the integrity of the sutures on the uterus, performs hemostasis of small bleeding vessels and removes instruments. The total volume of blood loss during surgery is no more than 50 ml;
- To prevent the formation of adhesions, a special anti-adhesion mesh is used, which dissolves after 14 days and does not allow the intestines or omentum to be soldered to the postoperative scar;
- Intradermal cosmetic sutures are applied to the puncture site, which dissolve on their own within 2-3 months and subsequently become pale and invisible;
After laparoscopy, the punctures are sutured subcutaneously, and cosmetic stitches are applied to the skin.
The progress of the laparoscopic operation is recorded on video, and each patient has a video protocol.
It is also useful to read: Use of the Almag-01 device for uterine fibroids
Indications
To carry out an operation to remove fibroids, good reasons are needed; often the tumor does not show activity and it can be left, observing the nature of changes in its condition.
Only those myomatous neoplasms that become a threat to the patient’s health are removed. So, there are specific indications for laparoscopy, primarily:
- rapid increase in tumor size;
- deformation of the uterine body as a result of pressure exerted by growing fibroid nodes;
- nodes that have a complex structure and special structure;
- myomatous nodes that interfere with pregnancy;
- myomatous subserous nodes;
- bleeding with heavy blood loss, which causes anemia;
- compression of organs located near the uterus, interfering with their full functioning.
The method is used for small nodes from 4 to 6 centimeters formed on the surface of the uterus. Nodes that are too large and those that form in places inaccessible to the use of an endoscope are removed by other surgical methods, otherwise, the inability to control the progress of the operation can cause internal bleeding.
Laparoscopic surgery: advantages and disadvantages
The main, obvious advantage of laparoscopic removal of uterine fibroids is that it is a minimally invasive operation. It is performed without incisions, through several punctures in the abdominal wall. At the same time, tissue is less injured, bleeding is minimized, and the recovery period is shortened. The woman can be discharged from the hospital earlier and return to her normal life.
When using laparoscopy, compared to open interventions, in the postoperative period there is less pain, and body temperature increases less frequently and less strongly. Lower risk of adhesions forming.
The disadvantage of laparoscopic interventions for the removal of uterine fibroids is that the possibilities of their use are limited. This operation cannot be performed on all women. Using laparoscopy, it is possible to remove only nodes that are subserosal (protrude externally above the surface of the organ) or intramural (in the thickness of the wall), are relatively small in size (up to 8–10 cm), and if there are no more than four of them.
The problem with any myomectomy is the relatively high risk of recurrence. Studies show that in 14% of women operated on, the nodes return within a year. Thus, after 4–5 years, approximately half of the patients are diagnosed with uterine fibroids again. After UAE, the risk of relapse is very low.
The advantage of a myomectomy over a hysterectomy is that the woman's uterus is preserved and she can become pregnant in the future. In addition, the uterus plays an important role in the body. posthysterectomy syndrome may develop , which manifests itself in the form of metabolic, neurovegetative disorders, and reduces the quality of life.
Features of the operation
Laparoscopy is a surgical treatment method aimed at removing myomatous nodes using equipment designed for this purpose. It is known that any type of operation involving excision of a myomatous tumor causes significant damage to the tissues of the abdominal cavity, which does not always heal quickly and without complications. Laparoscopic removal is performed without incisions and does not damage the peritoneum to the same extent as abdominal surgery, using only small punctures, which allows us to consider this operation low-traumatic and gentle on the patient.
Indications and contraindications for surgical intervention
In what cases is surgical removal of such tumors performed:
- Ineffectiveness of conservative therapy.
- The presence of subserous uterine fibroids, which grows towards the abdominal cavity and can interfere with the functioning of nearby organs.
- Large knots.
- Pronounced tumor growth.
- Moderate or severe anemia caused by regular blood loss.
- Multiple myomatous nodes that change the shape of the organ.
- Presence of neoplasms during pregnancy planning.
Surgical intervention is prohibited in the following cases:
- Hernia of the anterior abdominal wall.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- The presence of severe pathology of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
- Pronounced adhesive process.
- Exacerbation of infectious diseases.
- Too much or too little weight.
Contraindications to laparoscopy
Despite the huge number of available advantages, there are some conditions of the body when this method is contraindicated. They must be taken into account when deciding on the advisability of removing fibroids and determining the possibilities of using one or another method.
Laparoscopy is not performed in the following cases:
- the presence of pathological disorders in the condition of the lungs, heart or vascular changes;
- suffered a heart attack or stroke;
- blood clotting disorders;
- in the presence of a hernia;
- deviations in the patient’s weight in one direction or another;
- myomatous nodes are too large;
- pathologies in the condition of the kidneys or liver;
- oncological processes developing in one of the pelvic organs.
In this case, you have to use other surgical methods, which may be more traumatic, but nevertheless quite effective. Which one is preferred is determined by the doctor based on the examination and existing indications.
Contraindications
Due to possible complications, the laparoscopy method for removing a benign uterine tumor is not recommended for use in:
- assumption of a malignant nature of the neoplasm;
- the presence of cancer tumors of other organs of the reproductive system;
- the size of neoplasms exceeding 60 mm;
- acute infectious diseases (surgical intervention is impossible until complete recovery);
- pathologies of the kidneys and liver;
- weight discrepancy with standard indicators (obesity or underweight);
- heart disease;
- disorders of the respiratory system.
Preparation
During the period of preparation for the upcoming operation, the patient must undergo tests and receive their results, as well as listen to the necessary recommendations from the doctor and be sure to follow them, namely:
- do not allow intimate relationships without the use of contraceptives;
- stop eating and drinking at least 12 hours before surgery;
- 3 days before surgery, do not eat foods that promote flatulence in the intestines;
- Before the procedure, it is important to cleanse the intestines with an enema.
There are other requirements that apply individually to each patient, depending on the condition of her body. Any questions that arise should be addressed with your doctor.
Recovery period
Rehabilitation after laparoscopic myomectomy usually takes 1–3 days, in the elderly – 4–5 days. You are allowed to get out of bed on the second day. Pain in the area of postoperative wounds is moderate or minimal.
On day 1, symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and weakness are possible. All of them are related to the consequences of anesthesia. Nutrition is restored on the second day. It is recommended to consume fermented milk drinks (low-percentage kefir, fermented baked milk), mashed potatoes with water, and broth from low-fat poultry varieties. The diet is followed for 2-3 days, after which they return to their usual diet.
The sutures are removed on the 10th day, however, the need for hospital stay is limited to 2–4 days. The woman’s performance returns as quickly as possible.
For a month, it is advisable to avoid heavy physical activity, sports, active sex life, thermal procedures, namely visits to the sauna, bathhouse, solarium.
Operation stages
Myomectomy begins with anesthesia, and this can be done in two ways: general anesthesia and epidural. After this, punctures are made in a certain place of the peritoneum, and the necessary instruments are inserted through them. To create space between the organs, the walls of the peritoneum are lifted by introducing carbon dioxide. This allows free access to the operated organ without the risk of damage to nearby internal organs. The injected gas does not have a harmful effect on the body and is removed after manipulation.
The next stage is to use a laparoscope, with the help of which visual control of the operation is carried out, and the exact location for additional punctures is determined. The further action is to cut off the node or remove the entire organ, depending on the purpose of the surgical intervention.
Thanks to this method, the entire procedure is quick and painless. After recovering from anesthesia, patients usually feel well and begin to move independently the very next day, which prevents the formation of painful adhesions.
Anesthesia during laparoscopy
Therapeutic laparoscopy of uterine fibroids in women is always performed under general anesthesia. This is due to the fact that the manipulations can be so painful that even strong local anesthetics will not ease them. In addition, the procedure takes quite a long time, and by the end of it, local anesthesia may weaken.
Immediately before the laparoscopy procedure, the anesthesiologist injects anesthesia into the venous bloodstream, after which a tube is inserted into the patient’s airway. It will supply anesthesia and oxygen during the operation. This scheme allows you to monitor pulmonary activity and, if necessary, increase or decrease the dose of anesthetic.
Advantages of laparoscopy for fibroids
The use of the laparoscopic method is used not only to remove fibroids, but also during many surgical interventions, as it has a number of advantages:
- Minimal risk of injury and guarantee in the absence of severe complications, which often arise when using other methods.
- Low degree of painful manifestations after the end of the operation, rapid completion of the postoperative rehabilitation period.
- Rapid restoration of reproductive organs with minimal risk of adhesions and postoperative bleeding.
- The operation is organ-saving, which is especially important for young women.
- The ability to live independently after surgery is quickly restored; on the fourth day the patient can leave the medical facility.
- Minimal risk of relapse with the formation of new myomatous nodes.
An equally important advantage of laparoscopy for most women is the absence of scars on the body, which always remain after operations using traditional surgery.
The main methods for diagnosing uterine fibroids include:
- gynecological examination, which makes it possible to detect an increase in the size of the uterus, a change in its shape and the presence of subperitoneal nodes.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs - allows not only to accurately establish the diagnosis of fibroids, carry out differential diagnosis with other gynecological diseases, but also to monitor the growth of nodes. If there are uterine fibroids, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs should be performed at least once every 6 months.
- MRI of the pelvic organs with intravenous contrast - allows you to clarify the location of the nodes, as well as identify possible compression of neighboring organs.
- computed tomography of the pelvic organs with intravenous contrast makes it possible to assess the condition of the pelvic vessels, including in preparation for embolization of the uterine arteries, as well as to identify compression of the ureters and changes in their location.
- hysteroscopy examination of the uterine cavity with an optical system connected to a video camera, which is inserted through the cervix and is often accompanied by separate therapeutic and diagnostic curettage to remove intrauterine pathology. During this intervention, the location of the submucosal nodes and their type, and the possibility of removal by hysteroresectoscopy, are clarified.
Possibility of complications
Despite all the advantages of the method and the minimal risk of complications, some of them still occur. Most often this manifests itself in injury to internal organs or the vessels feeding them during use and during penetration of instruments.
There are also other possible disturbances in the normal state that occur during laparoscopy:
- disturbances in breathing processes;
- formation of hematomas on the surface of the uterine body;
- penetration of pathogens of infectious diseases with further development of infections;
- improper stitching.
Occasionally, complications of a specific form may occur in the form of uterine bleeding or the formation of a peritoneal hernia. Symptoms of discomfort may return in the form of mild nagging pain, which disappears after surgery, but can reappear throughout the recovery period. When removing fibroid nodes formed in the lower part of the uterus, the bladder with ureters and some parts of the intestine may be affected.
Possible complications
Complications after laparoscopy are quite rare. But, as with any other surgical operation, they are possible. These may include:
- Unsuccessful introduction of gas into the abdominal cavity, which causes subcutaneous emphysema (on palpation, a characteristic crunch is detected in the subcutaneous fat layer);
- Puncture of the intestine with a needle while filling the abdominal cavity with gas. To avoid this, it is very important to have a good bowel movement before surgery;
- Injury to organs (ureter, bladder) and large vessels;
- Bleeding from the bed of myomatous nodes;
- Formation of hematomas in the wall of the uterus;
- Infectious complications in the early postoperative period.
Postoperative period
The period after surgery also requires special attention to yourself and your feelings. First of all, it is necessary to ensure proper functioning of the intestines, preventing constipation and the absence of irritation. To do this, it is important to follow a diet and eat small portions.
It is important to include more foods with a high fiber content in the menu, avoid spicy, fatty foods and alcohol.
It is important to remember that the restoration of physiological functions during the rehabilitation period occurs differently for everyone, so you should not panic if for some it happens more slowly than for others.
During the recovery period, it is necessary to avoid physical activity, during which the abdominal and pelvic muscles may be involved. Swimming, long walking and therapeutic exercises will be possible after the body has fully recovered.
In some cases, wearing a bandage may be recommended for one to two months after removal, but it is better to check with your doctor whether this is necessary in a particular case.
Rehabilitation period
After laparoscopy of uterine fibroids, the woman recovers very quickly and returns to her normal lifestyle. If the course of the postoperative period is favorable, the woman is discharged from the hospital home on the 2-3rd day after surgery. In case of complications, which are rare, there is a need for a hospital stay of up to 7 days.
Sick leave is usually issued for 7-14 days. If a woman’s work does not involve heavy physical labor, she can begin her duties, if desired, on the 4th day after the operation. The temporary disability certificate can be extended if necessary (for example, if complications arise or if general health is unsatisfactory).
Full restoration of working capacity occurs in 15-30 days.
Menstruation after surgery usually begins within 28-30 days, but their delay is not a reason to panic. This may be due to previous surgery. Surgery is stressful for the body and can cause menstrual dysfunction. Intermenstrual discharge is also acceptable.
After surgery, possible intermenstrual bleeding is considered normal.
Physiotherapy during the rehabilitation period is not a mandatory procedure and is prescribed at the discretion of the doctor to prevent adhesions or inflammation.
For six months after the operation, the woman is under dynamic observation by a gynecologist. She should return for examination and ultrasound 1, 3 and 6 months after fibroid laparoscopy.
Until the scars on the uterus completely heal (and this will take 3-6 months), hormonal contraception is prescribed. The choice of the appropriate drug is made by the doctor depending on the condition of the woman’s reproductive system.
6 months after the follow-up examination and ultrasound, when the doctor is confident that the uterine scar is intact, the patient is allowed to plan a pregnancy.
It is important to know
After laparoscopic myomectomy, delivery is possible either through the birth canal or by cesarean section. The method of delivery is determined by the doctor based on obstetric indications.
During the rehabilitation period for 1 month it is recommended:
- Wear a bandage to reduce the load on the anterior abdominal wall;
- Limit heavy lifting and physical activity;
- Abstain from sexual intercourse;
- Follow a diet and organize proper nutrition - exclude from the diet fatty foods, foods that cause bloating and increased gas formation (legumes, fresh vegetables and fruits), as they can cause abdominal pain and cause diarrhea;
- Postpone sports activities for up to 4-6 months to ensure complete healing of the uterine scar.
To reduce the load on the abdominal wall during the rehabilitation period, it is advisable to wear a postoperative bandage.
Reviews
My story, like the stories of millions of women, is too banal. At the age of 31, I was diagnosed with uterine fibroids up to 18 weeks of pregnancy (ultrasound showed the presence of six fibroids of varying sizes). Moreover, the fibroid put pressure on the bladder, and my back hurt.
I’ll say right away that I decided to fight for my uterus to the end. Although I already had a 10-year-old son, I really wanted to have another one. Moreover, there was no desire to be “stuck” in hospitals for a long time and writhe in pain in the postoperative period.
They operated on me at the endoscopy medical center. The team is wonderful! Everything went like clockwork. Before the operation, I read many sources from the Internet. So, in my case, everything was as described: early activation, no antibiotics and a minimum of painkillers (painkillers were given once at night). It even seemed to me that my throat was more sore and sore from the anesthesia tube than from my uterus.
4 hours after the operation, he was allowed to eat liquid food. I took with me plain yogurt, baby fruit puree and oatmeal in bags.
On the 2nd day, in the evening, my husband and son took me home. And after 5 days I already went to work. I felt great.
Six months have passed. There was no trace left of the huge fibroid on the ultrasound. My doctor gave me permission to plan my pregnancy.
Veronica, 32 years old, Moscow
Today, laparoscopic intervention is the most modern operation. And perhaps it will help you get rid of uterine fibroids without ugly scars and scars, without pain and large blood loss, and then safely carry and give birth to a baby.
Useful video about laparoscopic surgery to remove uterine fibroids with comments and explanations from a specialist
Bleeding and discharge after laparoscopy
For some time after the operation (usually within 3-4 weeks), vaginal discharge of a different nature may occur. As a rule, they are sparse, transparent, with small streaks of blood. This condition is considered normal and should not be a concern, since in this way the body is freed from blood particles and other substances obtained during the operation.
At this time, it becomes especially important to comply with all hygiene requirements, and this must be done especially carefully. In order to avoid the spread of infections, you need to abstain from sexual relations, any kind, for this period.
Only the appearance of more intense bloody discharge containing blood clots should be alarming, as this is a sure sign of internal bleeding. This condition is dangerous and requires immediate attention to a gynecologist. In some cases, when the intensity of bleeding does not decrease and is accompanied by painful contractions, it is better to call an ambulance.
An unpleasant smell of discharge and a change in its color to a brown, yellow-green hue most often indicate the development of a bacterial infection. Since during the period after surgery a woman has to take certain medications that disrupt her own microflora, this significantly weakens the immune system and increases the activity of pathogenic bacteria. In no case should you ignore this, hoping that everything will go away on its own; you must urgently contact a specialist for the necessary treatment. Otherwise, the pathological process will begin to develop and spread to the internal organs located near the uterus, which can result in serious consequences, often threatening not only the health, but also the life of the patient.
Preparing for surgery
Laparoscopic myomectomy is performed routinely. The woman is first consulted by a doctor, and an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs is performed to assess the size, location, and number of myomatous nodes. The surgeon sets a date for hospitalization and surgery in advance and gives a list of tests that the woman needs to undergo. Typically, preoperative examination includes:
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- General urine analysis.
- Tests for infections.
- Determination of hormone levels in the blood.
- Blood clotting study.
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor.
- Smears from the cervix for cytology and flora.
- Electrocardiography.
- Ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities.
- Chest X-ray.
- According to indications - colposcopy, hysteroscopy, biopsy and other diagnostic methods.
During the consultation, the woman should tell the surgeon about what chronic diseases she suffers from, what medications and dietary supplements she takes, and whether she is allergic to medications. This information is needed in order to correctly assess the risks associated with surgery and anesthesia and take the necessary measures.
You should not eat anything 8 hours before surgery. On the day of surgery you should not drink. Before a woman is taken to the operating room, she is examined by an anesthesiologist and given premedication - drugs are administered that help her relax and calm down.
Treatment after removal of uterine fibroids
No special therapy will be required after a radical measure, since the organ with the pathology has already been removed. It is important that women take a vitamin complex, at least during the first period of rehabilitation. Also, special emphasis is placed on proper nutrition and quality products.
In some cases, hormonal drugs are prescribed, because due to an imbalance in the balance there is a risk of developing dangerous ailments. Women with early menopause may suffer from the development of cancer, problems with the cardiac system, atherosclerosis, and tumors in the mammary gland.
Sometimes taking certain medications is delayed for several years, this will guarantee the patient’s normal well-being.
Monopreparations containing estrogens:
- Klimara. The medicine in the form of a patch is applied to the skin once a week. At the same time, a different location is chosen for the new application. Due to this drug, the blood is saturated with estrogen through the skin.
- Gynodian Depot . Prescribed immediately after surgery. The action of the active substance lasts for one and a half months, after which a new administration is required.
- Divigel . Once a day, about a gram of ointment is rubbed onto clean skin, selecting an area on the stomach or buttock. The place where the gel was applied must be washed very thoroughly every day. By the way, the area for rubbing needs to be selected differently so that an allergic reaction does not occur. The cover with the gel form must not be wetted for the next hour and a half.
Divigel
Gynodian Depot
Klimara
Pros and cons of laparoscopy
Among the advantages of this type of surgical intervention are:
How long after laparoscopy can you get pregnant?
- Low traumatic. During the operation, the surgeon makes several small incisions, which are subsequently closed with a minimum number of stitches.
- High aesthetic effect. The scars from these wounds are almost invisible.
- Minimal blood loss. The chance that a blood transfusion will be needed during surgery is quite small.
- Reducing the risk of developing adhesive disease.
- The ability to identify and eliminate other pathologies of the genitourinary system, for example, an ovarian cyst.
- Easy postoperative period. After surgery, the patient quickly begins to move independently. She also does not need potent analgesics, since the pain is characterized as “quite tolerable.”
The disadvantages of laparoscopic removal of tumors are much smaller, but they do exist. Firstly, there is the possibility of bleeding. In this case, the operating doctor will have significantly less space for active actions than with a more invasive laparotomy (larger incision in the anterior abdominal wall). Secondly, the inability to conceive a child earlier than after 12 months.
Surgical methods
This practice is required if the patient does not have positive dynamics after conservative treatment.
It is worth understanding that any intervention may lead to complications, recurrence of pathology and other reactions. Various techniques are used to remove myomatous formation; their more detailed description is given below.
Laparoscopy
Among modern surgical techniques, laparoscopic methods are most often used by specialists. To carry it out, you will need minimal punctures in the peritoneum, after which there are no traces, and they are highly healing. After only 7 days of sick leave after laparoscopy, the patient can recover and return to work.
When is laparoscopy required:
- nodal elements have not reached a volume of more than a centimeter;
- the body of the uterus does not exceed 15 weeks;
- the main goal of surgery is to eliminate several nodules, with a total volume of up to one and a half centimeters;
- if the patient is diagnosed with interstitial or subserous formations, then their diameter should not be more than 5 cm.
Due to the fact that a laparoscope is used during the operation, tissues and neighboring organs are not injured. In the future, there are no adhesions or inflammation in the pelvis.
Hysteroscopy
If the patient has a single node, which is localized on the back or front wall of the organ, then the hysteroscopic method is used to remove it. The surgeon immerses it into the uterine cavity using the intravaginal method.
To perform hysteroscopy, you do not need to be in a clinic or hospital. It is best to schedule manipulation during the first week of the monthly cycle.
Also, the technique allows you to preserve reproductive function, does not injure the cervix or ovaries, does not need to give up intimate life for a long time and allows a woman to become pregnant in the future.
Hysterectomy
During this operation, the entire uterus must be removed; due to the complexity of its implementation, patients are prescribed a hysterectomy as a last resort. Only when other therapy does not bring the desired result.
Indications for hysterectomy:
- pronounced progress in the course of concomitant endometriosis;
- myomatous nodes are multiple in nature and may differ in type and structure;
- gigantic size of the tumor process;
- degeneration of the node into a malignant state.
Almost all patients in menopause undergo this therapy to remove fibroids. Also, if there is a high risk that malignancy will occur in the future, the surgeon eliminates the problem immediately.
Laparotomy
A medium-sized incision is made on the abdominal wall, through which the nodular tumors will be removed. Doctors rarely resort to laparotomy, because there is the option of more gentle operations.
Most often, the surgeon prefers this manipulation if the patient’s nodes have reached large sizes. In this case, there may be germination into the abdominal cavity with compression of neighboring organs. The active progress of the disease often provokes deformation of the uterine body.
The patient should remain in bed for the next week after laparotomy. The wound healing process can bring discomfort and pain. Complete rehabilitation can take about a month.
Abdominal surgery
The radical measure is necessary, since doctors always reserve such operations as a last resort.
Regardless of the chosen method for extirpation, there is a high risk of side effects and serious pathologies.
Women are very worried about this, since sometimes emergency abdominal surgery is required and there is no time to think about complications.
Of course, there is no need to be afraid of death, since the abdominal method has been performed for a long time and surgeons have accumulated enormous experience in this operation.
In most cases, death can occur due to problems with anesthesia, allergies to drugs, or due to the inexperience of the anesthesiologist.
In some cases, injury to blood vessels, nerve endings and neighboring organs is noted. Of course, everything depends on the professionalism and skill of the surgeon, although sometimes even the most competent doctor can make some mistake.
It is dangerous to perform a hysterectomy laparoscopically, since significant blood losses are observed when the organ is removed. It is impossible to ligate the vessels when they are cut and stop the problem using an endoscope.
Extirpation is one of the most complex surgical interventions, during which blood can accumulate in the uterine cavity. Also, there is no complete certainty that talc will not get into the wound, which provokes the formation of adhesions and intestinal problems. Errors can be corrected only after a repeat operation.
So, what may occur in a patient who has undergone abdominal surgery to remove the uterus and fibroids:
- Abscess,
- Inflammatory processes in the peritoneum,
- Peritonitis.
All this can manifest itself due to poor quality work of the surgeon or as a result of poor sanitary treatment of the operated area.
Rehabilitation after surgery
The duration of the recovery phase directly depends on the type of treatment performed. The more complex the manipulation, the more restrictions the doctor imposes. Provided that a radical measure is chosen, the rehabilitation stage may be delayed. For a certain period of time, the patient undertakes to change the schedule and diet of her diet, and abandon the established rhythm of life.
If the patient is disciplined, she will experience a minimum of complications after surgery. After about 4 months, the obedient patient will be able to return to her usual work and life.
To speed up the recovery process, doctors recommend a number of measures:
- Kegel exercises. Due to the fact that the uterus is removed from the pelvis, the position of the remaining organs may change. The intestines and bladder will begin to function much worse. In an advanced form, the patient may experience urinary incontinence and bowel dysfunction. There are frequent cases of vaginal prolapse due to weakening of the muscular frame. It is this set of exercises that helps eliminate this unpleasant problem.
- Hormone replacement therapy. A woman should take medications that contain large amounts of estrogen. Thanks to capsules or ointments, the onset of menopause will be delayed.
- Proper nutrition. Hormonal imbalance provokes excess weight gain, which means that there is a need to review the diet. Doctors advise not to eat harmful products and to look at foods that have minimal fat and salt content.
As a result of the extirpation, the onset of menopause is incredibly close. Due to the applied hormonal therapy, there is a chance to delay this moment and smooth out the specifics of the unpleasant symptoms that have arisen. In addition, doctors advise not to forget about sexual relations; refusal from them leads to the manifestation of serious pathologies.
In the absence of pathological processes, you can be sexually active within a month after the operation. Doctors advise not to isolate yourself, but to spend more time with loved ones.
Removal of an important female organ is not a death sentence, as many women mistakenly think. If medical advice is followed, the patient’s quality of life will not suffer at all. In the preoperative period, improvement of the psychological and emotional state is required. This will allow you to quickly return to your usual way of life.
Where to have the operation?
It is best to perform surgery for uterine fibroids in a specialized clinic where there are leading specialists. Laparoscopy is performed in all major cities of the country. If you live where the hospital does not have the necessary equipment, then it is best to undergo surgery at one of the capital’s clinics, having first studied it and patient reviews. It can be done in both public and private institutions. Treatment in a private clinic will of course cost more. The main thing is the availability of appropriate equipment and specialist doctors in this field.
Dimensions of fibroids during surgery
Any myomatous neoplasms, which can reach not just large, but also gigantic sizes, are suitable for the operation. Simply put, if a patient is diagnosed with fibroids at 12 weeks or higher, then it must be eliminated surgically.
In a number of situations, the help of a surgeon is required for smaller nodes, but there must be good reasons for this.
For example, necrotic changes in the tumor, problems with conception or pregnancy, individual reactions to the presence of fibroids. So, fibroids can be divided:
- small (nodule size does not exceed 2 cm, similar to pregnancy at 5 weeks);
- medium (tumor formation reaches a volume of up to 6 cm, the uterus expands up to 11 weeks);
- large (myoma neoplasm more than 60 mm);
- gigantic (the uterus becomes unusually expressed in volume, its size is compared with a pregnancy of more than 4 months).
Causes of fibroids
Overly aggressive treatment of uterine fibroids in the past was largely due to a lack of understanding of their nature. Open an old medical school gynecology textbook and you will read that fibroids are a benign tumor that occurs due to a hormone imbalance. The question immediately creeps in: what if this benign tumor turns into a malignant one? Isn't it better to remove it right away - along with the uterus, just to be sure?
To date, it has been proven that uterine fibroids are not related to cancer and do not increase the risk of cancer. This is a node that grew from an improperly developing muscle cell. It does not arise due to hormones, but grows under their influence.
Modern scientists do not know exactly why fibroids develop. Some believe that this is the result of a violation of intrauterine development. The muscle layer in the wall of the uterus in the fetus develops slowly and remains in an unstable state for a long time, so disturbances occur in it. According to another theory, the disease is caused by damaging factors that affect a woman throughout her life: abortion, curettage, multiple periods, infections and inflammatory processes.
Whatever the cause, fibroids are not life-threatening or cancerous, so aggressive treatment is often not necessary.
How is laparoscopy performed?
Laparoscopic surgery is performed under general anesthesia, which means the patient is sound asleep during the procedure. The duration of the operation is from forty minutes to three hours, it all depends on the case. When performing an operation, the day of the cycle does not matter, but the operation cannot be performed during menstruation, as this increases the percentage of blood loss.
To clearly see the operated area and surrounding pelvic organs, the doctor inserts a trocar and injects carbon dioxide into it. The abdominal wall rises, and the surgeon, having introduced another trocar, can freely examine the operation area through a microvideo camera. And determine where to start. Thus, the tumor, its diameter, location, shape of the reproductive organ and appendages are clearly visible. Are there any adhesions or other complications?
Typically, during laparoscopy, three to four punctures are made through which trocars are inserted to remove fibroids. The surgeon cuts through adhesions, if any, makes cuts in the tissue above the tumor, and pulls it out of the membrane. If necessary, coagulation of blood vessels is performed. It all depends on the specific case. Small and medium-sized fibroids are removed through the punctures that were made to insert the trocar. If the neoplasm is large or the uterus is removed, the doctor first excises the tissue using a morcelator. It is inserted into one of the punctures. The crushed pieces of tissue are removed through punctures, so no additional cuts are made. After the fibroids are removed and removed, the doctor will re-examine the operated area to make sure there is no internal bleeding. The instruments are then removed from the abdominal wall. Stitches are placed on the punctures.
Types of assistance for fibroid removal
Often the problem occurs in women who have not yet reached the age of 40 or have not given birth before. In such a situation, the priority is to take measures to preserve the reproductive organs and the ability to conceive and bear offspring.
Surgical assistance is required if there is a certain clinical picture. After all, a number of women suffer from concomitant pathological processes.
The patient’s well-being depends on the location of the tumor formation, its size and nature. Additional factors can be listed ad infinitum, since all patients' cases of the disease are considered unique.
Experts identify another type that contributes to the patient’s recovery and removal of her fibroids. It partially relates to surgical manipulations, since it affects the feeding artery nodules. Artificial blockage allows tissue to die and the tumor to die. The opinions of specialists and patients differ regarding this technique, since it has a high price and does not always have a positive result.
Other methods of fibroid removal
There is not always a need to use radical measures to remove the tumor process. There are indications for using more gentle techniques to eliminate the problem.
Laser
The risks when performing laser manipulation are minimal, safety is at a high level.
The effect of the laser is dosed and differs in directionality. During the operation, unhealthy tissue will be affected, but the layer without pathology will be intact.
After this procedure, no scars or scars were noted in the patients. There will be almost no bleeding, because there is no mechanical effect on the body.
Probably, when using this type of treatment, the rehabilitation period will last the shortest.
Doctors often suggest removing restrictions from the patient 3 days after surgery. Laser therapy is highly effective, which is why many women want to remove myomatous nodes using it.
Embolization
UAE is also very popular among patients, but is distinguished by its high cost.
If we compare a radical measure to remove fibroids, then when used, the disease can return in 40% of cases. The effectiveness of embolization is much higher, because doctors detect new lesions in only 2% of patients.
After local anesthesia, a catheter is inserted into the patient through the main artery of the thigh.
A special solution flows through it, allowing you to clog the vessels and stop the nutrition of the myomatous nodes. Subsequently, they shrink and die.
There is a certain unpleasant nuance: after a medical procedure has been performed, the patient may feel a painful sensation in the lower abdomen. The spasms can bother her for several hours and are not always relieved by medications.
If the doctor lacks professionalism, then purulent lesions or heart attacks may appear on the uterus. Such complications cannot be eliminated by anything; a radical measure will be required, in the form of removal of the uterus. It is noted that if the nodular formations are of the subserous type, then this type of treatment will not be suitable.
Unfortunately, there is little information about the manifestations of the consequences and effectiveness of this treatment. Since there have been no studies conducted in the field of studying reproductive function after UAE. But now we can say with confidence that 5% of women complain about the absence of menstruation. As a result of the manipulation, amenorrhea developed, which cannot be overcome.
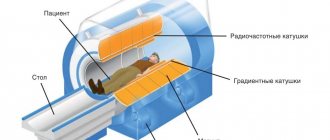
FUS ablation
A complex technique that is a conservative type of therapy against uterine fibroids.
When controlled by a magnetic resonance imaging scanner, the patient's formations are evaporated using ultrasound. In this case, the fabric and its layers will remain undisturbed.
By heating to 90 degrees, the liquid from the capsule is completely evaporated. Then the myomatous node itself disintegrates. In this case, the patient does not experience severe pain during the removal of the pathology
Unfortunately, no precise study of the technique has been carried out, so its use is rare. Moreover, there are limitations; the use of ultrasound therapy is indicated if the fibroid is localized on the uterine fundus or in the area of the anterior wall. Also, the tumor volume should not exceed 9 cm, otherwise there is a risk of complications.
Women who suffer from infertility or have not previously given birth to children will have to refuse treatment with this method. Also, subserous formations growing on a stalk cannot be removed with ultrasound.