Scintigraphy is a type of medical examination that uses radioisotope substances. This method is safe and high-tech. It is used to study organ pathologies and the functionality of the thyroid gland. Another name for the study is radionuclide diagnostics of the organ.
The peculiarity of this type of medical research is the identification of pathologies at an early stage of their occurrence. The procedure is noted to be painless for the patient and side effects are rare. The use of scintigraphy does not disrupt the patient’s usual lifestyle and does not require complex and multi-stage preparation steps. This diagnostic is used to study the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular system, human skeletal system (skeleton), thyroid gland, and other organs and tissues of the body.
But the use of such a complex medical study is advisable after identifying pathology during early diagnosis, for example, by ultrasound. Scintigraphy is not prescribed as a primary study due to its high cost and complexity.
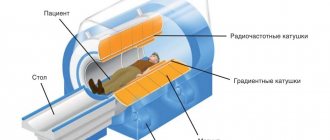
Few medical centers are able to purchase equipment and drugs for conducting nuclear medicine research. However, it is worth noting the safety of scintigraphy, the detail of the examination, and the accuracy of the results. The procedure takes place on a special device called a gamma scanner. The device includes the components necessary for diagnostics:
- gamma detector;
- transmitting device;
- lead limiters;
- image fixer.
Thyroid scintigraphy is a study of the main endocrine gland using a gamma scanner in order to identify pathological processes in the activity of the gland, as well as in the tissues and cells of the organ.
Papillary thyroid adenoma
Thyroid
The thyroid gland is one of the endocrine glands, located in the human body in the trachea area. The appearance is comparable to the wings of a butterfly, reminiscent of a kind of letter “H”.
The correct functionality of the gland ensures a stable course of metabolic processes in the human body due to the formation of two hormones:
- The hormone thyroxine is responsible for the functioning of the immune system, ensures thermoregulation of the body, and the correct growth and development of a biologically complex organism. In addition, it enhances oxidative processes in the brain and is responsible for heart rate.
- Triiodothyronine hormone - the main function is to control the course of basic life processes. An increase in the level of this hormone causes thyrotoxicosis. With thyrotoxicosis, the intensity of metabolic processes increases, diarrhea, weight loss, and dystrophy occur.
Disruption of the thyroid gland leads to the development of a large number of pathological processes in the human body. Impaired functionality leads to an incorrect ratio of hormonal components in the human body, which can externally manifest itself as dystrophy or obesity. The structural functioning of the body depends on the presence of a history of dystrophy or obesity. The gland is also responsible for the development of the bone structure of the body, skeletal development.
Taking into account possible diseases of the thyroid gland, timely medical examination of the functionality and the presence of pathological processes in the anatomical area of the organ will allow taking the necessary medical measures to preserve human health.
Selection of radiopharmaceutical
How many times can an ultrasound be done?
- The behavior of the drug in the human body should be identical to the behavior of natural organic substances.
- The drug must contain a radioactive nuclide or a radioactive label that allows its location to be determined using recording equipment.
- The radiation dose during diagnostics should be minimal.
An important aspect when choosing a radiopharmaceutical is the half-life, the duration of which should not exceed permissible radiation levels, but at the same time allows for the necessary diagnostic manipulations. The use of iodine isotopes (123Ι and 131Ι) in nuclear medicine can be considered a classic, since the first studies carried out with their help were described back in 1951.
Thanks to the ability of the thyroid gland to capture iodine, it became possible to record the rate of its accumulation and distribution in tissues. However, today, the use of 123Ι and 131Ι isotopes is limited by the need for a subsequent course of therapy for cancer or toxic thyroid adenoma.
Due to the fact that the half-life of the 123Ι isotope of iodine is 13 hours, and the 131Ι isotope is 8 days, the latter, as the most traumatic, is used to destroy malignant cells, and the use of the 123Ι isotope for diagnostic purposes allows us to estimate the rate of uptake of molecules and calculate optimal therapeutic dose.
Modern radiopharmaceuticals are isotopes that, as a result of decay lasting about 7 days, form a new unstable element called a radionuclide label. A feature of such a mark is the ability to create symbiosis with any chemical element involved in the metabolic processes of a particular organ. The most common drug in medical practice is technetium (99mTc).
The advantages of technetium can be considered an extremely short half-life (6 hours) and the absence of the need to introduce iodine into the body, which makes it possible to obtain a more “clean” picture from a diagnostic point of view. Another advantage of technetium, which allows minimizing the risks of the negative effects of radiation, is the ability to obtain it from the parent isotope stored in a container immediately before the diagnostic procedure, as well as the ability to adjust its optimal activity.
Container for storage and generation of technetium 99mТс
Advantages of scintigraphy when examining the thyroid gland
The use of modern research methods allows us to achieve significant results in diagnosing the disease. And the use of scintigraphy reveals a number of positive aspects:
- It allows, with minimal risk to the patient’s health, to perform an in-depth analysis of the activity and structure of the thyroid gland. In terms of detailed information content, the method is comparable to a diagnostic operation. But the non-invasiveness of the method makes it easier to tolerate the medical procedure.
- The degree of radioactivity of the drugs and the dosage are selected individually for the patient, so the procedure is less harmful than analogues.
- Scintigraphy involves simultaneous examination of the structure of the gland and the activity of the organ.
- In case of pathology, the focus and degree of damage from the pathology process are immediately recorded.
- During the diagnosis, the patient does not experience negative sensations, pain, or discomfort.
- Safety of research for children. But there is a risk of distortion of the final results due to the impossibility of making the child sit without moving during the procedure.
- If necessary, it remains possible to carry out repeated diagnostics.
Evaluation of the method
Thyroid scintigraphy of the thyroid gland is carried out taking into account the advantages and disadvantages of the procedure. Before performing radionuclide diagnostics, the doctor explains to the patient all the possible consequences, introduces the procedure, and how to behave after the study.
The advantages of the method include:
- non-invasiveness of the method and minimal harm of the procedure to the body of the person being studied. The amount of isotope used is selected to provide a clear picture of the problem area. The risk of negative effects on the body at such doses is extremely small;
- the possibility of a one-time examination of the specifics of the structure of the organ and its activities;
- recording the degree of damage;
- the ability to repeat the procedure several times for accurate diagnosis without harm to health;
- no discomfort or pain during the procedure;
- the ability to conduct radioisotope studies of the thyroid gland in patients of any age. However, when scanning children, it is necessary to take into account that they cannot remain motionless throughout the entire procedure, and even the slightest movement can cause a distortion of the actual picture of the disease and serve as the basis for an incorrect diagnosis.
The disadvantages of this method include:
- duration of the study. Sometimes it takes about 7 hours to get accurate information;
- clarity and contrast of the image. The image may be blurry;
- the possibility of carrying out diagnostics using this method only in specific clinics;
- preparatory measures, which include refusal to take certain medications and disinfectants.
Disadvantages of scintigraphy
Despite all the positive aspects, the use of scintigraphy contains a minimum set of significant disadvantages that also need to be taken into account:
- The procedure is not done everywhere. To pass, you will need to make an appointment at a specific medical center that has the appropriate equipment and medications at its disposal, for example, at the Endocrinological Research Center (ENDC).
- High duration of the procedure. Under appropriate circumstances, scintigraphy lasts up to seven hours.
- There is a possibility of loss of image contrast and image quality.
- During preparatory measures, it is necessary to abandon the use of drugs, the use of which is important for maintaining the optimal condition of the human body.
Scientific basis of scintigraphy
The study using scintigraphy is based on the ability of the thyroid gland to accumulate iodine-containing substances. In addition to accumulation, these substances are eliminated from the body due to the functions of the thyroid gland.
The procedure is carried out under the direction of an endocrinologist or oncologist.
To conduct the study, iodine-based radioisotopes are used, which allows the device - a gamma scanner - to analyze the entire functional potential of the thyroid gland and its structure.
The main iodine-based drugs administered to the patient before the procedure:
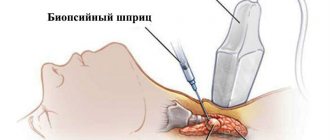
- Radioisotope iodine 123 - intravenous administration of the drug is used. It is more expensive than other drugs, which affects the rarity of its use in diagnosis.
- Radioisotope iodine 131 is given to the patient to take orally in the form of a solution or tablet. Scintigraphy is performed the next day (iodine uptake test).
- Technetium isotope 99 – intravenous administration of the drug. It is distinguished by the fastest speed of leaving the body. When diagnosing children, only the drug technetium can be used for the safety of the diagnostic procedure.
- Pertechnetate - the drug is administered intravenously and interacts with the tissues of the thyroid gland faster than the above analogues. The procedure with pertechnetate is considered the fastest, since scanning can begin within 20 minutes. after entering.
- Technetril 99 – scintigraphy with technetril is intended to identify malignant tumors in the thyroid gland.
It is possible to use other isotopes when performing diagnostics, but the selected group is most often used.
Preparation of the specimen for scintigraphy
Thyroid tissue exhibits a significantly higher intensity of iodine absorption than tissues of other organs. Scintigraphy with technetium 99 is also easily absorbed by thyroid tissue, as in studies with iodine. This isotope, unlike iodine, does not participate in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, and therefore leaves the body of the test subject without leaving any traces of its presence. It is characterized by minimal toxicity and a fast half-life. After the isotopes are absorbed by the thyroid gland, they are distributed throughout the tissues.
To accurately deliver the radioactive contrast agent into the organ being examined, the patient is given the appropriate set of medications.
Then the thyroid gland is scanned using a gamma scanner. Using special computer equipment, a three-dimensional image is recorded - a scintigram. Thanks to it, the location of the thyroid gland, its structure, and functionality are determined. Foci of pathological changes in the structure and activity are identified, the level of hormonal activity of each lobe of the thyroid gland is established.
Patient reviews about the procedure
Patient reviews of the procedure vary, but are generally positive. The study does not cause any discomfort. Most of the studied side effects did not occur.
Everything took a day. On the first day at the radiologist's office, they gave me a small capsule to drink, like a regular medicine. It contained a diagnostic microdose of I-131. The capsule is tasteless and odorless. I washed it down with water. And I was asked not to eat anything for three hours after that. I didn’t feel any sensations at all. A day later I came to the same clinic. I was placed on a couch under a device hanging above it, which did not emit any sound or light signals. And they asked not to move for several minutes, not to yawn, not to cough or to swallow saliva. In my case, I did not experience any discomfort, fear or unpleasant sensations during scintigraphy.
Tigrrra
https://irecommend.ru/content/svintsovye-pokryvala-rastvor-s-radiatsiei-v-venu-shokirovali-podobnye-otzyvy-moya-stsintogra
The procedure is long and tedious (it’s better to do it when you don’t have to go anywhere else). The procedure can aggravate your long-standing diseases (which you have long forgotten), consult your doctor in advance and be sure to ask what to do if something goes wrong after the procedure.
Mimishka88
https://irecommend.ru/content/otzyv-patsienta-0
I didn’t feel bad, I didn’t feel anything at all. Chronic diseases have not worsened. So, if you have been prescribed this procedure, do not be afraid, everything will go well.
Asikumata
https://irecommend.ru/content/stsintigrafiya-shchitovidnoi-zhelezy-sovsem-ne-strashno
This procedure made it clear what to do with the thyroid gland and the nodule. This procedure is not recommended, but prescribed by endocrinologists, it will help deal with the thyroid gland, and if the doctor told you it is necessary, then you need to do it and not read reviews (as it happened to me) of incompetent people who say that “it’s better to do without this procedures". Regarding the assessment: if we evaluate it as a procedure, it is not entirely safe, it is frightening, but if we evaluate the diagnostic aspect, then this procedure is the best for making a diagnosis, for making a decision on further treatment of the thyroid gland.
Zheshka
https://irecommend.ru/content/stsintigrafiya-shchitovidnoi-zhelezy-rezultat-sovet
Types of thyroid scintigraphy
To obtain the most detailed information about pathologies in the thyroid gland, one of 4 diagnostic options is used:
- Planar – two vertical images of the problem area are created.
- Dynamic method - used to determine how a radioisotope drug is absorbed by the thyroid gland. With this method, the time spent under the scanner is 3 hours.
- Static - the accumulation of the isotope in the thyroid gland is accompanied by a series of images recording the process.
- Tomographic – allows you to create a three-dimensional image of the examined area.
The essence of the method
Scintigraphy - nuclear medicine for the benefit of health
Fadeev V.V.: “Scintigraphy allows you to differentiate variants of thyrotoxicosis”
Scintigraphy has the following advantages:
- the method is almost completely harmless, because radiation in a limited dose does not affect the body, with the exception of isolated cases of allergy development;
- there is the possibility of carrying out this procedure monthly, which is important when monitoring the patient’s health status;
- the functionality of the thyroid gland can be assessed;
- can determine quantitative organ damage and calcium metabolism disorders;
- does not require special preparation of the patient, he only needs to limit the intake of medications containing iodine;
- no pain appears during diagnosis;
- there is no need to take other medications;
- no side effects observed.
Scintigraphy also has some disadvantages:
- produces less clear images than MRI or CT;
- the patient comes into contact with radioactive atoms;
- the relative high cost of the examination;
- inaccessibility.
Thyroid scintigraphy is a radionuclide method for assessing the functional activity of the thyroid lobes (TG), based on the properties of its tissues to absorb iodine and use it to produce hormones. The use of radiopharmaceuticals (RPs) in the diagnostic process - chemical compounds perceived by organ tissues as a necessary participant in metabolism and containing radioactive isotopes in their structure, makes it possible to record the intensity and uniformity of absorption, accumulation and distribution of the substance in the thyroid gland.
In the absence of alternative imaging modalities available to diagnostic medicine today, such as ultrasound, MRI or CT, scintigraphy was the only way to obtain an image of an internal organ. Today, using all of the above methods, it is possible to obtain maximum useful information about the shape, structure and location of the thyroid gland, however, none of them is able to assess its functional state.
The mechanism for obtaining information is the introduction into the body of a radiopharmaceutical (for example, radioactive iodine), which is actively absorbed or not absorbed by the endocrine organ. When subsequently recording the radiation intensity, it is possible to obtain a flat or three-dimensional image (in the case of using an emission computed tomograph), reflecting areas of normal, increased or decreased concentration of the radioactive substance.
Areas with increased radiation, highlighted in color or shading, indicate tissue hyperactivity, and areas with reduced or absent radiation indicate their partial or complete functional failure. The use of scintigraphy is advisable only for the purpose of determining the activity of hormone production of one of the parts of the thyroid gland (node or lobe), the pathological condition of which has already been identified using laboratory or instrumental research methods.
On color photographs, inactive thyroid tissues are depicted in blue, and active ones in red.
Important! Scintigraphy cannot be considered an independent research method, based on the results of which any diagnostic decision can be made. Its use is justified only if it is necessary to obtain additional information.
Indications for use
To prescribe any type of diagnosis, which is a type of nuclear medicine, a suspicion of the presence of a significant pathological process is required. Initial signs will be established during the initial examination, interviewing the patient and standard medical procedures, for example, ultrasound examination of tissues, magnetic resonance imaging.
The study is carried out when indicated:
- Abnormal location of the thyroid gland - positioned incorrectly relative to the norm.
- There is a pathological change that occurs as a result of erroneous development of the gland.
- The presence of neoplasms on the tissues of the gland is visible.
- With excessive production of thyroid hormones.
- The presence of obstructed blood flow around the gland, blood outflow.
- Examination of the thyroid gland bed after resection.
- Suspicion of cancer (highlighted by pertechnetate).
Is a re-examination necessary?
After making the initial diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a repeat scan after 2 months. This is necessary to clarify.
Which areas of the endocrine system organ began to work more actively after taking medications. This approach to treatment allows you to evaluate its effectiveness and make corrections if necessary.
When relapses and metastases occur in cancer, there is a need to conduct additional studies - a blood test for thyroglobulin in the serum.
If the level of this indicator increases, then the patient is necessarily sent for re-diagnosis.
Contraindications for
Medical statistics show that there are only two contraindications that prevent diagnostics using scintigraphy:
- Pregnancy at any stage until delivery.
- The patient is obese to a weight level above 150 kilograms.
In the first case, radioisotope diagnostics can be dangerous for the development of the child inside the womb. During lactation, it is necessary to provide a break; do not feed the baby with breast milk for 24 hours. During these days, the radioactive isotope will completely leave the mother’s body and the milk will become completely harmless to the baby.
In the second case, when the patient’s weight is 150 kilograms or more, the procedure is simply impossible due to the excess weight that the gamma scanner equipment can withstand.
The study should be carried out with caution in patients suffering from increased sensitivity to allergens, as minor side effects are possible.
Preparing for the study
Special preparation for thyroid examination does not imply changes in vital activity and does not make significant changes to the patient’s lifestyle. Compliance with the requirements established for the patient by the attending physician will allow achieving maximum clarity of the results of the procedure. Maximum information content of the analysis is achieved. To fully prepare for scintigraphy, you need to follow the recommendations:
- It is prohibited to conduct radiographic studies using a contrast agent in the period of 3 months before scintigraphy.
- It is prohibited to conduct magnetic resonance imaging studies in a tomograph for the same period of time.
- The same period of time should pass after the last procedure of angiography and urography (three months).
- A month before scintigraphy, you need to remove seafood from your diet that contains iodine and its components. A special diet may be prescribed.
- One month before the procedure, stop taking medications containing iodine (in consultation with your doctor).
- Stop taking medications containing thyroid hormones three weeks before the procedure.
- Do not apply iodine solution to the skin.
Before scintigraphy, you should remain hungry (at least 6 hours after your last meal). Before the procedure, you need to empty your bladder.
The specialist conducting the study instructs the patient and introduces the likely consequences of the procedure.
From the moment the diagnosis begins, the patient should not wear metal objects, body jewelry, or objects containing metals and metal compounds. The same rule applies to dentures. They will have to be removed during the procedure.
To speed up the process of removing radioactive substances from the body, it is recommended to actively drink warm drinking water in sufficient quantities. Radioactive elements will be excreted from the body in urine through the kidneys.
Hospitalization for scintigraphy is not applicable unless the patient has limited mobility or the patient has a serious health condition.
Side effects
Manipulation in terms of radiation is not hazardous to health. Side effects in most cases are recorded as a result of individual intolerance and increased sensitivity of the person being studied.
The patient may experience a temporary increase or decrease in blood pressure and a frequent urge to urinate. Uncommon, but there is a risk of fever, dizziness, redness, itching and weakness .
In case of increased sensitivity to iodine, scintigraphy of the thyroid gland is performed with technetium, which practically does not cause negative findings.
The likelihood of exposure of subjects in contact with the patient to radiation after the procedure is practically non-existent. To avoid re-entry of the radiation dose into the body, strict adherence to hygiene standards is required. You need to wash your hands often, take baths, showers, and often change your linen and bedding, and towels.
After completion of the radioactive manipulation, materials used must be left in the clinic, where they will be placed in specially designed containers for substances in contact with radiopharmaceuticals.
To prevent side effects and harmful effects on the body, the following precautions are required:
- Women (of reproductive age) should have a scan 12 days after their last menstrual period to avoid possible pregnancy;
- When scanning children, it is mandatory to adjust the dose of the radiopharmaceutical in accordance with the child’s weight;
- nursing mothers should stop breastfeeding;
- a person undergoing this examination must exclude contact with children, women expecting a baby, and nursing mothers for a specific period of time, the duration of which depends on the markers used.
Carrying out the scintigraphy procedure
Isotopes are introduced into the body of the patient on an empty stomach and given time to be absorbed into the patient’s blood and tissues. The absorption time of the drug depends on the method of administration and is determined by the doctor based on clinical information about the patient’s health and the performance of the drug.
If the isotope of iodine 131 is used, administered orally, the time to diagnosis will be up to 6 hours. With intravenous administration of the isotope, the waiting time is reduced to half an hour. The individuality of each organism is taken into account.
Diagnosis is carried out in a supine position. The patient's physical activity is excluded due to the risk of obtaining an incorrect diagnostic conclusion and the lack of quality of the images obtained. The subject maintains a natural and calm breathing rhythm. The operation of the gamma camera does not affect the patient’s sensations in any way and does not cause pain. The patient is placed on a special couch surface. The reading device is placed over the organ being examined, and the thyroid gland is scanned. Contrast images are necessary so that they can be correctly deciphered.
Decoding the research results
The results of scintigraphy are calculated from the scintigram. Correct interpretation depends on the quality of the images received.
Zones of increased and decreased activity are identified, which are called “hot” and “cold”. They are distinguished by color. The presence of such zones indicates the presence of thyroid pathology, because the norm is an even dark color of the gland on the scintigram. The color scheme is determined by a cumulative scale.
Thyroid scintigraphy picture
The presence of red and orange shades indicates the presence in the location of this color (hot zones - increased activity) of diseases such as toxic goiter, nodular thyroiditis.
Thyroiditis is a common pathology of the thyroid gland. Develops as a result of traumatic exposure, infections, radiation therapy, viruses. The thyroid gland enlarges due to a node at the edges of the organ. This node accumulates isotopes in the tissues, forming a hot zone.
Zones with a cool color from blue to purple (in these zones there is reduced activity) indicate the presence of:
- cyst;
- benign neoplasms;
- cancerous tumors (highlighted with technetril).
Cool colored areas may indicate cancer. In such a case, the examination is prescribed at the initiative of the oncologist. That is, there is functional degradation of the thyroid gland, which requires immediate participation in the process of diagnosis and treatment.
The positive side of using radioactive iodine is the effect of the radioactive isotope on tumors in cancer. In this case, radioactive components during their half-life irradiate cancer cells and stop reproduction. Scintigraphy is a safe assistant in radiation therapy used to treat cancer pathologies.
In what cases is scanning performed and when is it prohibited?
The procedure is prescribed to determine the nature of the nodal formations. Scintigraphy of the thyroid gland makes it possible to find out the reason for the decrease or increase in the activity of the organ. The method is also used to monitor the treatment course, to identify the dynamics of recovery and determine the further strategy of the therapeutic course.
Scintigraphy is also performed when:
- abnormal location of the lobes;
- the need for clear visualization and identification of auxiliary lobes;
- malfunction of the gland;
- differentiation of thyrotoxicosis;
- the need to calculate the dose for the correct organization of the procedure using iodine with increased radioactivity;
- increase in parathyroid hormone.
Scintigraphy of the thyroid gland is carried out by introducing a radiopharmaceutical, but a stenography of the picture is not performed.
There are certain contraindications for the procedure.
Scintigraphy is not allowed for pregnant women or during lactation. It is prohibited to perform radiodiagnostics if an X-ray or CT scan has already been performed on the day intended for scanning. A radioisotope study of the thyroid gland of this type is not carried out if the patient’s weight is 150 kg or more.