How to increase hemoglobin in the body
You can completely restore normal hemoglobin levels both with food and by taking multivitamins. And sometimes complex therapy is necessary, and if this is not enough, then a repeat course. It will be easier to replenish hemoglobin levels if you know some of the features of its absorption:
- The body requires the divalent form of iron; the trivalent form is difficult to absorb and often causes heaviness in the stomach and difficulty with bowel movements.
- With reduced acidity, iron is absorbed worse, since it has long been established that iron is absorbed better in an acidic environment. This is one of the reasons why pharmaceutical iron supplements contain vitamin C.
- A protein found in milk and dairy products, called casein, can interfere with the full absorption of iron. This protein sticks to iron molecules, preventing it from being absorbed, and is then excreted. Therefore, you need to know that daily consumption of dairy and fermented milk products is beneficial for humans, but moderation is needed in everything. And it would be better to take milk separately from foods rich in iron; the interval should be at least 5 hours.
Food is the main primary source of easily absorbed heme iron. The maximum amount of this microelement is found in animal products, such as meat, liver, fish, eggs, and caviar.
The classification into divalent and trivalent iron specifically applies to non-heme iron. Ferric iron can be reduced to its ferrous state using ascorbic acid. But, nevertheless, the absorption of ferrous iron from plant sources is significantly inferior by several times to the absorption of heme iron obtained by consuming animal products.
For people who follow a predominantly plant-based diet, it is advisable to double their daily iron intake. Plant foods that are rich in iron include: dried mushrooms, dried apples, prunes, legumes, beets, carrots, pumpkin seeds and many other crops.
Low hemoglobin is not a disease - it is a deviation from the norm, and if measures to restore it are not taken in time, it can provoke some kind of pathology. Everyone knows the truism that it is easier to prevent any illness than to cure it later. It is necessary to clearly understand that treatment will have to be done, but in an advanced form this process will cost more and take longer. It’s better not to complicate your life and maintain your health at the proper level.
Folk remedies in the fight against low hemoglobin
If low hemoglobin is detected, treatment with folk remedies is an effective practice in combating this dangerous condition.
- A decoction of rose hips and strawberry leaves strengthens the body as a whole and enriches it with vitamins. You can drink it instead of your usual tea during the day.
- Fresh red beet juice, which you drink one glass a day, has a good effect. The peculiarity of beet juice is that it cannot be drunk immediately after squeezing; as soon as the juice is squeezed out of fresh beets, it should be put in the refrigerator for 3-4 hours so that toxic compounds evaporate, only after which the juice can be drunk.
- Currant berry infusion is rich in vitamin C and is good for anemia.
All the described medicinal compositions must be drunk for at least a month - only in this case are they effective. In general, all red fruits and berries, as well as green vegetables, are shown. After the course of treatment, clinical tests are taken again to determine the effectiveness of therapy.
Author:
Sabuk Tatyana Leonidovna hygienist, epidemiologist
Symptoms of low hemoglobin
Oxygen is a participant in redox reactions within our body, through which we obtain energy. Therefore, low hemoglobin immediately has a negative impact on almost all of our metabolic processes, which is immediately manifested in numerous external signs.
With a lack of hemoglobin in the blood, our tissues and organs experience serious oxygen starvation, which negatively affects our well-being and health.
In simple terms, the body begins to receive less energy and this is immediately reflected in very characteristic symptoms. Symptoms of low hemoglobin levels can be divided into several groups, the first of which is associated with a general depressed state of the body.
Here are the typical symptoms of low hemoglobin in our blood:
- general weakness and malaise;
- very rapid fatigue (especially during physical activity);
- shortness of breath (respiratory failure);
- tachycardia;
- decreased arterial blood pressure;
- drowsiness;
- dizziness and frequent headaches;
- in severe cases, fainting is possible;
- heartburn and vomiting;
- excessive sweating;
- sleep disturbance;
- feeling of coldness in the extremities;
- weakened immunity, which leads to frequent illnesses.
In our body, iron performs not only the function of transporting oxygen, and a low level of hemoglobin indicates a lack of this element in the body.
It is iron deficiency that causes the following symptoms:
- dry mucous membranes and skin (cracks in the corners of the mouth, they are very painful);
- nails begin to peel and break;
- lips become bluish and crack;
- hair loss and slower growth;
slight increase in body temperature (up to 37 degrees); bruises form on the body for no particular reason; the skin acquires a yellowish tint; the tongue becomes bright red; difficulty swallowing solid and dry foods; dysfunction of the sphincter muscles; there is a disruption in the functioning of the sensory organs.
The last sign of a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood is especially interesting. The patient has a strange craving for completely inedible products; he wants to try chalk, coal, clay, sand and other similar substances. A person wants to try raw foods: meat, minced meat, fish, pasta, cereals. Problems with the sense of smell begin: smells that previously caused disgust (gasoline, solvent, paint, exhaust fumes) now seem very attractive. All of these are typical signs of a decrease in hemoglobin concentration in the blood.
Another symptom of this disorder is frequent colds.
All of the above symptoms manifest themselves differently in people, it is not at all necessary to have the entire list of signs; in the initial stages of the disease, symptoms may be mild or not appear at all, but even if some of them are typical for you, you should immediately visit a doctor and take all the necessary tests.
During pregnancy
A reduced level of hemoglobin in the blood due to a lack of iron and folic acid is observed in 80% of pregnant women. The main symptoms of anemia in women during pregnancy include fatigue, pallor, shortness of breath from minor exertion, and dizziness.
Insufficient iron in pregnant women can be caused by physiological factors:
- repeated pregnancy in a short period of time or during lactation;
- heavy menstruation before pregnancy, if the loss of iron was not compensated by the intake of the microelement from food throughout the month;
- teenage pregnancy;
- severe toxicosis with frequent vomiting in the first trimester;
- excess amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios);
- multiple pregnancy;
- frequent colds in all trimesters;
- maintaining a vegetarian diet while pregnant.
Lack of oxygen in the body during pregnancy leads to negative consequences, such as placental abruption, fetal hypoxia, intrauterine growth retardation, bleeding, miscarriage, so treatment of anemia should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
During labor, especially after a cesarean section or the formation of a large number of ruptures, a woman can lose up to 300-400 mg of blood, which leads to a sharp onset of iron deficiency anemia.
2-3 months after birth, a gradual decrease in hemoglobin levels may be observed, also associated with the course of the previous pregnancy and subsequent changes in the female body:
- active consumption of hemoglobin in the last trimester for the formation of red blood cells and fetal organs;
- use of maternal iron reserves for further synthesis of hemoglobin in the child’s body;
- blood loss due to heavy bleeding after childbirth for 10-15 days or more;
- Hemoglobin levels may also decrease during breastfeeding, since iron is part of breast milk.
To increase hemoglobin after childbirth and during breastfeeding, you should use the indicated treatment methods, compensate for the lack of iron with the help of iron-containing drugs and adhere to diet rules.
How to identify low hemoglobin, what are its causes and consequences
Low hemoglobin, causes and consequences must be periodically checked and known to every person. Its indicator depends on the amount of iron received from food, the degree of absorption and assimilation of iron, as well as other vitamins and minerals in the stomach and small intestine, the presence of hidden and open bleeding, time spent in the fresh air, as well as blood donation, that is, donation.
Of course, in order to accurately diagnose low hemoglobin, you need to take a general blood test from a finger prick, as well as blood from a vein to determine the content of red blood cells in the blood serum. But for preliminary diagnosis, you can simply observe yourself. If you often feel tired, drowsy, headaches become more frequent, your pulse may increase, shortness of breath and tachycardia, or dizziness appear, then you need to sound the alarm, consult a doctor, and get blood tests. If tests show anemia, then possible causes should be determined and measures should be taken to restore it.
Causes causing anemia:
- nutrition unbalanced in vitamin and mineral composition, lack of iron in the food consumed, or poor absorption of microelements in the intestines and stomach;
- open bleeding, blood loss during surgery, injury or prolonged menstruation, hemorrhoids or bleeding gums;
- hidden bleeding, which occurs with peptic ulcers of the stomach and other digestive organs, gastritis, as well as in the presence of uterine fibroids or ovarian cysts;
- serious infectious diseases, tumors or other diseases, one of the symptoms of which is anemia;
— frequent blood donation (donation);
- blood diseases.
We looked at the concept of low hemoglobin, its causes and consequences may be as follows:
- decreased performance, weakness, drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue;
- tachycardia, rapid pulse;
- a slight increase in temperature of 37-37.5 degrees Celsius.
With prolonged anemia, if no measures are taken in time, brittle nails appear, hair falls out and grows poorly, in children there is a lag in psychomotor development, tearfulness, irritability, in schoolchildren it is also a poor concentration of attention, a lag in studies, since anemia affects nervous system. Negative consequences also include changes in the tissues of the mucous membrane, as well as internal organs. Due to lack of oxygen due to low hemoglobin, the workload on the heart increases, leading to heart disease.
Therefore, it is very important to recognize low hemoglobin in time, as well as its causes. The following doctors can help with this: gynecologist, nephrologist, infectious disease specialist, gastroenterologist, oncologist
Also, be sure to read the article low hemoglobin in newborns.
Symptoms and signs
When hemoglobin protein is low, symptoms of anemia can be noticed during an external examination of a woman:
- dry pale skin;
- brittle hair falling out;
- peeling nails;
- puffy face.
Depending on the cause that caused the decrease in Hb, the symptoms may be mild (acute heavy blood loss, characterized only by pallor) or the patient will develop a “classic” picture of chronic anemia.
In addition to external signs, in women, a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin causes the following symptoms:
- drowsiness;
- asthenic syndrome;
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- disturbance of the emotional background (nervous excitement or tendency to depression);
- hypotension;
- increased breathing;
- lack of coordination;
- muscle weakness;
- decreased sexual activity;
- menstrual irregularities.
Sometimes low hemoglobin provokes a change in taste preferences or a craving for unpleasant odors. A woman wants to eat soap or smell kerosene.
Despite the fact that the symptoms of anemia are similar to those of other diseases, you should not delay a visit to the clinic. To determine the level of hemoglobin, it is enough to take a blood test, but a thorough examination will help to determine why exactly Hb in the blood drops.
Interaction of iron with other microelements
When consuming iron in foods or as a separate supplement, you need to be aware of its ability to interact with other nutrients. Some vitamins and microelements interfere with the absorption of iron, while others, on the contrary, improve its intake into the body.
For reference. It is recommended to take iron supplements with ascorbic acid and vitamin A. Calcium, magnesium and zinc impair the absorption of iron. If you have low hemoglobin, it is recommended to limit the consumption of all cereals and dairy products.
Treatment
Foods that increase hemoglobin
If hemoglobin drops in a woman’s body, she should get rid of the underlying pathology as soon as possible and bring the level of the main element of red blood cells back to normal.
Both surgical and non-surgical tactics are used to treat the root cause, but the concentration of iron-containing protein can be normalized using conservative methods.
Patients are advised to take medications - the most effective drugs for increasing hemoglobin:
- "Hemobin";
- "Ferretab";
- "Maltofer";
- "Sorbifer Durules";
- "Totem";
- "Heferol";
- "Irovit";
- "Fefol";
- "Ferrogradumet";
- "Fenuls";
- "Actiferrin";
- "Tardiferon".
The daily dosage and duration of use are individual. To improve results, you need to take vitamin complexes.
Along with medications, nutrition plays a special role in treatment for low hemoglobin. It is recommended to enrich the diet with foods containing large amounts of iron. The basis of the menu should be:
- meat;
- fish;
- nuts;
- dried fruits;
- seafood;
- cheeses;
- whole wheat bread;
- cereals;
- legumes;
- citrus;
- cabbage;
- potato;
- pepper;
- tomatoes;
- beet;
- pumpkin;
- melon;
- watermelon;
- egg yolks;
- black chocolate;
- black currant;
- strawberry;
- any greens;
- pomegranate;
- weak green tea.
After the approval of the attending physician, you can use traditional medicine recipes that increase hemoglobin in the blood at home.
How to increase hemoglobin levels
Medication
Iron supplements are not all the same. In some, iron is in an accessible divalent form, in others - in a difficult-to-digest trivalent form. Absorption is promoted by ascorbic and succinic acid.
Popular medicines include maltofer, ferrum lek, hemofer prolongatum, tardiferon, actiferrin, venofer, ferkoven and others.
Some of them are intended for oral administration, some are administered intravenously or intramuscularly.
Courses of taking iron supplements are long, from several months to a year. The drug must be prescribed by a doctor.
Eating Right
It is not easy to cure serious anemia with the help of food, but changing your diet and focusing on healthy foods is necessary.
The menu must include:
- beef, chicken;
- offal;
- buckwheat, legumes;
- onions, tomatoes, potatoes, pumpkin;
- greenery;
- fruits - green apples, bananas, pomegranates, peaches, apricots, plums, quinces, persimmons;
- dried fruits;
- nuts;
- fruit and vegetable juices.
What to do if anemia cannot be treated? In severe cases of chronic anemia, doctors give blood transfusions.
Hemoglobin levels need to be monitored. If you feel symptoms of anemia, take a blood test to begin treatment for the disease in a timely manner.
(17 ratings, average 4.0 out of 5)
Low hemoglobin in pregnant women
The problem of low hemoglobin is especially relevant among children and expectant mothers. Hemoglobin levels decrease in pregnant women as a result of increased consumption of iron, which is required by both the expectant mother and her fetus. Therefore, this category of people is strongly recommended to regularly spend time in the fresh air (then the body will receive more oxygen).
Not all pregnant women understand why doctors are so concerned about this problem and pay so much attention to it. But the fact is that internal organs require oxygen in large quantities. As a result of lack of oxygen, aging and withering occur. Sometimes organs completely cease to fully perform their functions because they lack nutrition. The danger is that many organs do not have nerve endings, and therefore do not hurt. Signs begin to appear when the situation becomes quite acute.
When expectant mothers' hemoglobin levels drop sharply, negative consequences affect the development of the fetus
This problem is worth paying attention to, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy.
To do this, pregnant women must undergo regular blood tests. Otherwise, as a result of anemia, the fetus will not receive enough oxygen, which will significantly slow down its development or stop it altogether. Experts call this process fetal hypoxia, when the child receives little oxygen. This threatens atrophy of muscles, organs and nervous system disorders.
Among the consequences of low hemoglobin, urinary incontinence is also noted. This is due to the fact that the muscles become too relaxed. Such problems can not only worsen the patient’s condition and his life, but also cause quite serious consequences.
It is a mistaken belief that hemoglobin can be increased with food. Products containing iron cannot compensate for its deficiency. Hemoglobin can only be increased with the help of special medications. However, eating foods high in iron is beneficial and can improve the situation slightly. To maintain normal hemoglobin levels, you should consume iron-containing foods daily.
Diagnosis of anemia
All anemias are secondary conditions and, for the most part, act as a symptom of the underlying disease. Differential diagnosis of anemia is conventionally divided into 2 stages. In practice, two diagnostic stages are carried out simultaneously.
At the first stage, the pathogenetic variant of anemia is determined, namely the main mechanism causing the decrease in hemoglobin. In fact, this is a syndromic diagnosis, since all pathogenetic variants of hemoglobin deficiency represent only a separate syndrome. This stage is carried out in the laboratory. At this stage the following studies are carried out:
- Determination of hemogram using a hematology analyzer
- Examination of a blood smear with counting the number of reticulocytes and compiling a leukocyte formula
- Biochemical analysis of blood serum with determination of iron content, ferritin level and the total ability of serum to bind iron
- Microscopic analysis of bone marrow punctate
The second stage of the diagnostic search is entirely the prerogative of the attending physician. The doctor’s task is to diagnose the pathological process, which is the basis of the anemic syndrome in each individual. Simply put, the attending physician identifies the causes of anemia in the patient. As a rule, the doctor acts by the method of elimination. Initially, the most dangerous conditions are excluded:
- hidden bleeding (gastrointestinal tract, bleeding into the chest cavity, into the abdominal cavity, into the joint cavity, into the pericardial cavity)
- oncological pathology, for which the patient is prescribed additional studies (for example, MRI of the whole body to exclude oncology, fecal occult blood test to exclude bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, etc.)
- a thorough interview of the patient is carried out to clarify all the symptoms that alarm the person or have never appeared before
- it is necessary to clarify the nature of the diet, whether drug therapy was carried out, and with what drugs
Hemoglobin in women is normal
Until the age of twelve, the child’s gender does not affect the hemoglobin level. However, then there is a certain difference.
For women, the following norms for iron-containing protein are established:
With the onset of puberty, the upper limit of the norm decreases slightly. It remains unchanged for many years, and only after sixty it drops a little.
During reproductive age, hemoglobin levels are affected by the menstrual cycle. On critical days and immediately after their end, the content of complex protein objectively decreases. After all, during menstruation, a woman loses up to 35 milligrams of iron.
In professional athletes, hemoglobin can increase to 162 g/l. And among long-time smokers, the content of the substance approaches 150 g/l. Both of these situations are considered as variants of the norm.
Norm and permissible deviations
Hemoglobin standards are different for different age groups and depend on many characteristics of the human body, as well as gender. In women, in normal conditions, the norm is considered to be from 120 to 155 g/l, and during the period of gestation this figure decreases slightly and ranges from 105-110 to 120 g/l, since during this period the female body begins to use incoming iron much more actively .
If a woman is involved in any kind of sport professionally, her normal hemoglobin level can be up to 160 g/l, and this is not considered a serious deviation.
In women who smoke, this figure may also be overestimated and reach 150 g/l, which is also considered a kind of norm.
During pregnancy, this indicator is assessed on a completely different scale , and the gestation period is also taken into account. In particular, in the 1st and 3rd trimester, the hemoglobin level should not fall below 110 g/l, and in the 2nd trimester the lower limit is 105 g/l.
In this case, the maximum indicator throughout this critical period should not be higher than 120 g/l. More information about normal hemoglobin levels in pregnant women can be found here.
Deviations in indicators during pregnancy and in the normal state of women are explained by changes in physiological processes. When carrying a baby, the blood volume in the body naturally increases by almost 50%. For this reason, the bone marrow begins to fail to cope with the task and cannot supply the body with the required volume of hemoglobin, so its level decreases.
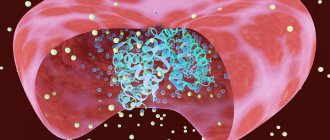
What is hemoglobin
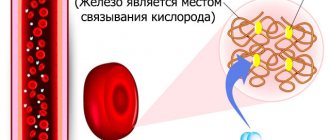
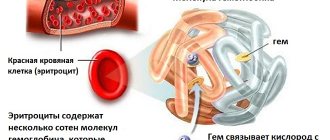
So, according to the definition, hemoglobin is a special protein that is found in human blood and is responsible for saturating all the cells and tissues of our body with oxygen.
Hemoglobin is actually the basis of red blood cells, because the red blood cell consists of 98% hemoglobin, and it is its content that gives our blood a specific red color
It is difficult to overestimate the importance and significance of hemoglobin for our body, because by transferring oxygen from the lungs to all cells and organs, and back - carbon dioxide, hemoglobin thereby provides those very redox reactions in our body, as a result of which the energy we need for normal full life activity
What is hemoglobin
From a school biology course we know that hemoglobin is a component of blood cells - red blood cells. Its function is the delivery of oxygen to the cells of organs and body systems.
Hemoglobin structure
A low protein level indicates the development of anemia and other conditions that pose a threat to human life. To understand at what hemoglobin level people die, it is necessary to study the characteristics of the male and female body at different periods of development.
Types of anemia
Anemia or low hemoglobin is a painful condition of the body associated with a significant decrease in the content of red cells in the blood - full-fledged red blood cells. Such a decrease can be caused by a number of reasons, due to which anemia is divided into: anemia associated with acute blood loss; anemia resulting from the destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic) and anemia resulting from a violation of the production of red blood cells. The latter type of anemia is divided into: aplastic, iron deficiency, megaloblastic, sideroblastic and anemia associated with chronic diseases.
According to the severity, iron deficiency anemia is divided into several degrees: mild, in which the hemoglobin content ranges from 110 g/l to 90 g/l; medium, ranging from 90 g/l to 70 g/l and, finally, heavy, in which its content is less than 70 g/l.
There is also hidden or latent anemia, in which the level of red blood cells is normal, but the level of serum iron is low. This form of anemia is often diagnosed in pregnant women. In this case, patients observe all the symptoms of anemia.
What are these symptoms?
Deviations from the norm in men
In representatives of the stronger sex, the critical hemoglobin in the blood begins at 70 g/l. To maintain health and well-being, a man needs to keep it at a level of 130 g/l. Deviation from the norm is possible in several situations:
- smoking;
- accommodation in mountainous areas;
- chronic diseases;
- oncology;
- hard physical labor;
- taking steroids while playing sports.
Violations of the indicator are sometimes diagnosed when working in polluted conditions or constant contact with chemicals or dyes. In men after 50 years of age, hemoglobin decreases due to decreased metabolism and decreased production of red blood cells due to the aging of the body.
Important! According to doctors' observations, some men over 30 years of age experience a sharp drop in hemoglobin during sleep. After waking up, it returns to normal within 1–2 hours, but this fact must be taken into account when taking tests.
Consequences
The consequences can be different, ranging from decreased immunity to enlarged liver. But more about this:
- anemia develops as a result of iron deficiency;
- immunity also decreases, which leads to the likelihood of the occurrence and development of infectious diseases;
- In children, as a result of a decrease in hemoglobin levels, growth and mental development are delayed. In addition, fatigue increases, the child begins to have problems with academic performance;
- adults feel constant fatigue;
- negative changes occur in tissues and organs;
- a decrease in hemoglobin increases the risk of developing cardiomyopathy. This happens because the body, trying to provide itself with a sufficient amount of oxygen, forces the heart to work with double load. This leads to heart failure. The amount of blood that passes through the heart increases;
- later the liver enlarges and swelling appears in the legs.
With low hemoglobin, epithelial tissues - the mucous membranes of the mouth, respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract - suffer quite severely. The skin also suffers from eczema and dermatitis. As a result of disruption of the gastric mucosa, the absorption of nutrients worsens. People with low hemoglobin suffer from intestinal infections and acute respiratory infections twice as often.
Students with this problem have trouble concentrating and get tired quickly. Their blood pressure often drops, they feel dizzy, and their heart beats faster
Insufficient hemoglobin levels in children under five years of age are considered to be below 110 g/l, in adults below 120.
In order to find out the level of hemoglobin in our body, each of us should regularly take a blood test. It will help to detect in time a low level of red blood cells and changes in their shape.
For prevention, it is recommended to eat foods that are rich in iron - kidneys, tongue, liver, beans, peas, chocolate and others. Iron elements are also found in beef, lamb, oatmeal, apples, nuts and spinach. Eat properly and nutritiously, then you won’t need to remember about iron supplements.
Bottom line
To summarize, we can say that hemoglobin is one of the most important elements in the life of the body from the very beginning of its development in the womb. Its slight decrease is easily restored with the help of beneficial vitamins and minerals in foods, but a critical shortage can lead to irreparable problems that entail not only pain, but also death.
On the website Vitaminstvo.ru you can find out not only what low hemoglobin means , but also the symptoms and causes of this disease. You can also read information about the best medications for low hemoglobin .
You can also find out detailed information - what hemoglobin is and how to increase it by watching the video “ Low hemoglobin ”:
In other articles of Vitaminstvo.ru you can learn more about low hemoglobin in children, low hemoglobin in women and men, and also find out what vitamins are necessary for the normal and full functioning of the whole body.
Why is a decrease in hemoglobin dangerous?
The health-hazardous consequences of a decrease in hemoglobin do not immediately begin to appear with obvious symptoms. A steady decrease in iron protein initially causes the following symptoms:
Drowsiness appears, the person gets tired faster. Shortness of breath occurs periodically, and tachycardia is observed. The skin becomes paler or jaundiced and becomes too dry. You can pay attention to the pallor of the ears and occasional blue discoloration of the lips. The condition of hair and nails is gradually changing, not for the better. The curls become dull, fall out more, the nails split and break when their length is insignificant. . The danger of low hemoglobin depends on the level of its reduction and on the duration of this condition in a person
The longer the effect of low hemoglobin on the body is observed, the more serious the consequences. Lack of oxygen leads to the development of a number of health problems:
The danger of low hemoglobin depends on the level of its reduction and on the duration of this condition in a person. The longer the effect of low hemoglobin on the body is observed, the more serious the consequences. Lack of oxygen leads to the development of a number of health problems:
- The functioning of the entire immune system is disrupted. And this, in turn, affects the frequent occurrence and severe course of infectious and colds.
- Heart failure develops. This may initially manifest itself as shortness of breath and tachycardia, then swelling of the legs occurs. Severe weakness is recorded, increasing with the slightest physical activity.
- The nervous system suffers, which affects the occurrence of paresthesia, irritability, and poor sleep.
- Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain is reflected in decreased concentration and memory suffers.
A decrease in hemoglobin also negatively affects the state of the muscular system. The muscles are almost always in a relaxed state, and this threatens adults with urinary incontinence. With low hemoglobin, all tissues, cells and organs do not receive the amount of oxygen they need and, as a result, the body ages much faster. That is, a person may suffer from diseases characteristic of older age, he gets tired faster, and there are fewer positive emotions.
With low hemoglobin, especially if it is not restored for a long time, a person’s appearance noticeably changes for the worse. Yellowness or pallor of the skin, decreased facial turgor, a large number of wrinkles, chapped lips, dull hair - all these manifestations are often signs of iron deficiency anemia.
Indicators of critical levels of hemoglobin in the blood, how dangerous is it and when to sound the alarm?
Everyone is familiar with the concept of hemoglobin. When taking blood tests, its indicator is always determined, the norms of which differ in men, women and children. A slight decrease can be successfully eliminated with nutritional correction and medications. But there is a threshold, the boundaries of which are mortally dangerous for human life.
Critical hemoglobin in the blood - what is it? Let's try to figure it out in the article at what hemoglobin level does a person die?
What is hemoglobin
From a school biology course we know that hemoglobin is a component of blood cells - red blood cells. Its function is the delivery of oxygen to the cells of organs and body systems.
Hemoglobin structure
A low protein level indicates the development of anemia and other conditions that pose a threat to human life. To understand at what hemoglobin level people die, it is necessary to study the characteristics of the male and female body at different periods of development.
Development of anemia in women
Normal hemoglobin levels in women are 120-160 g/l. The critical level of hemoglobin in the blood of women is an indicator that does not exceed the lower limit of normal.
A drop in hemoglobin below 50 g/l leads to death due to heart failure. Against the background of developing anemia, hypoxia of the body occurs with inhibition of functions.
The protein level changes throughout the month: during menstruation, a woman loses up to 30 mg of iron due to blood loss. Hemoglobin levels vary depending on age, the presence of chronic diseases, and living conditions. In old age, the body's need for iron decreases: the required minimum is 117-138 g/l.
Symptom complex for anemia in women
Is it dangerous to exceed the norm?
Excess hemoglobin is no less dangerous, as it increases the likelihood of capillary blockage. High levels of the substance thicken the blood, disrupting its movement through the vessels, promoting the formation of blood clots.
Common causes of the condition are congenital pathologies of the cardiovascular system, diabetes mellitus, intestinal obstruction, and pulmonary obstruction.
Normalization of protein levels occurs after eliminating the cause that caused the shift. Symptomatic therapy is aimed at alleviating the patient's condition. Symptoms to watch out for:
- general weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- mood swings;
- weight loss;
- cardiopalmus;
- low susceptibility to infections;
- headache.
Iron deficiency anemia during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a special condition during which the female body undergoes changes and does not always cope with the load. As the fetus develops and grows, the volume of circulating blood also increases. It naturally thins to normalize circulation, resulting in a decrease in hemoglobin levels.
There is a concept of anemia in pregnant women. To prevent pathology, iron levels are monitored throughout pregnancy. There are three degrees of severity of iron deficiency anemia:
- mild – hemoglobin level 90-110 g/l;
- average – 80-90 g/l;
- deadly - the indicator drops below 80 g/l.
Laboratory data are clinically confirmed by the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- digestive disorders;
- pronounced pallor.
Remember: low hemoglobin levels during pregnancy are especially dangerous!
What hemoglobin level is considered critical during pregnancy? Throughout the entire period, the child receives the necessary nutrients from the mother’s body. It must be taken into account that for full development it is necessary to consume an increased amount of vitamins and minerals, since deviations from the norm pose a danger to the development of the baby.
Another reason for the development of pathology is complications during childbirth, resulting in significant blood loss.
In severe cases, in order to increase the chance of the fetus to survive, critical hemoglobin is adjusted in all possible ways.
Elimination of pathology
To prevent anemia, it is necessary to eat well during pregnancy. Folic acid, B vitamins, copper, and zinc are of great importance. It is their deficiency that affects the absorption of iron by a woman’s body. Don't forget about an active and healthy lifestyle.
Deviations from the norm in men
In representatives of the stronger sex, the normal concentration of hemoglobin in the blood is 13.5-18 g/l. The critical level of hemoglobin in the blood of men is 70 g/l. Deviations are allowed depending on the constitution and state of health.
A man who systematically deals with excessive physical activity is at risk of serious illness due to increased fatigue. Against the background of stress and deviations in the daily routine, the overall resistance of the body decreases.
The key role in recovery belongs to the correct organization of sleep and wakefulness, chronic fatigue should be avoided, and promptly consult a doctor for medical help.
Low hemoglobin in childhood
A decrease in hemoglobin to dangerous levels is observed in adolescence due to hormonal changes. The second place among the causes of anemia is nutritional disorders. The child’s diet must contain meat, vitamin-rich vegetables and cereals to normalize intestinal motility.
Newborns often have low hemoglobin levels if they did not receive enough nutrients in the womb. If there is no threat to the life of the baby, the amount of the substance increases to normal levels by correcting the nutrition of the mother and child.
By correcting the diet, hemoglobin levels are stabilized in children and adults
Prevention of anemia
If you have one or more symptoms, you should consult a physician. It is necessary to monitor your health status once every six months. If the likelihood of illness is high, the doctor will prescribe therapy with iron supplements. The dose and duration of the course are determined individually. For better absorption of iron, a table without flour, fatty and dairy products is prescribed.
If a lethal level of hemoglobin is detected, the patient is prescribed a transfusion of red blood cells in an inpatient setting. Do not underestimate the seriousness of the pathology by postponing a visit to the doctor. Only a specialist will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe individual treatment.
Low hemoglobin in women causes and symptomatic treatment
It all depends on what caused the iron deficiency.
In case of bleeding, all efforts are directed towards stopping it; in case of exacerbation of diseases, the main symptoms of the disease must be eliminated; in case of chronic primary anemia, replacement therapy is prescribed. But there are general principles for correcting hemoglobin levels:
- Oral medications (containing divalent heme iron) are prescribed, the best of which is Hemobin. In addition to iron, they contain B12, ascorbic and folic acids.
- Means are used to accelerate the absorption of iron from the digestive tract. They are taken in courses of two months, until a detailed blood test shows an acceptable level of protein. Low hemoglobin in a woman (84 - 92 g/l), the cause of which may be hidden, for example, in chronic inflammation, requires treatment by intravenous administration of drugs. This is regarded as an acute anemic condition, since the generally accepted norm for a healthy middle-aged woman is 120-150 g/l.
- Intravenous medications are prescribed for diagnosed dystrophy of intestinal tissue and for gastric bleeding that complicates the absorption process. This category of products includes “Venofer”, “Ektofer”, “Ferrum”.
If low hemoglobin is diagnosed in women and its causes are atypical, then treatment with folk remedies can do little to help.
You should not even try to eliminate the state of iron deficiency on your own, since the complex of provoking factors is individual in each case, and all folk recipes are based on the same components. In addition, only a doctor can calculate the correct dosage for replacement therapy. An excess of iron will affect the body no less severely than anemia itself. Attempts at self-treatment can blur the clinical picture of the disease, which will make it very difficult to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate drug treatment.
If there is a suspicion of low hemoglobin, the causes and consequences (possibility of chronicity of the process) in women are established through laboratory tests
However, the easiest way is to take care of your own health and pay attention to the prevention of anemia. Almost all causes of low hemoglobin in women are easily eliminated at the initial stage, but the chronic form of the disease is difficult to correct and requires a long course of treatment
Hematologists have identified several risk groups: pregnant women, women who have undergone abdominal surgery, those with diabetes, and organ failure. They are recommended to take blood biochemistry tests at least once every three months, as well as undergo preventive and precautionary courses of treatment, which include iron supplements, multivitamin complexes and dietary nutrition.
Prevention and prognosis
You can avoid the development of a situation such as low hemoglobin by following simple rules. Prevention of this condition includes:
- maintaining a healthy and moderately active lifestyle;
- complete and balanced nutrition;
- prevention of stressful situations;
- absence of any injuries or wounds;
- control over hormonal levels;
- Regularly undergoing a complete preventive examination at a medical institution.
The causes and consequences of low hemoglobin dictate the prognosis of the pathology. In the absence of therapy, there is a worsening of the underlying problem, frequent relapses of symptoms, and the possibility of death due to complications cannot be ruled out.
The norm of hemoglobin in the blood of women
The number showing the hemoglobin level is determined by the attending physician from a general blood test. For a healthy adult woman, this figure should be in the range from 120 g/l to 140 g/l. For women who are professionally involved in sports, pregnant women and smokers, the norm of hemoglobin in the blood may differ slightly from this figure.
Table of normal indicators for women of different ages
How the norm for blood tests changes with age can be seen in the table:
| Age group | Hemoglobin, g/l |
| 15-18 | 115-153 |
| 18-65 | 120-155 |
| More than 65 | 120-157 |
The older a woman is, the more reasons there are for a decrease in hemoglobin. After 40 years, rapid changes in hormone production and the onset of menopause contribute to fluctuations in blood composition. And after a woman reaches 50 years of age, the most common cause of hemoglobin deficiency is a lack of folic acid and B vitamins in the diet.
Normal hemoglobin levels during pregnancy
A sharp decrease in the level of red cells in the blood in pregnant women is very common
It is important to monitor it and remember that a significant deviation from the norm threatens the baby with pathologies and entails a danger to the health of the expectant mother. Possible complications:
- Uterine hypotension is a condition that entails a decrease in muscle contractions;
- Hypoxia is a state of lack of oxygen for the fetus;
- Delay and even arrest of fetal growth and development;
- Child's body weight deficiency at birth;
- Pathologies of the nervous and respiratory systems.
During pregnancy, a woman needs to carefully monitor her hemoglobin level: many doctors are confident in the connection between this indicator in the expectant mother and the subsequent health of the child. Children who suffer from iron deficiency before birth do not learn well, get tired quickly and often suffer from colds and viral diseases.
The table shows the normal indicators for women at different stages of pregnancy:
| Gestational age | Hemoglobin, g/l |
| Pregnant women, I and III trimester | 110 |
| Pregnant women, 2nd trimester | 105 |
Causes of low hemoglobin
Low hemoglobin in women: causes and consequences are clearly interrelated. There are 3 main reasons for lack of hemoglobin. First of all, there is a deficiency of iron in the body. After all, it is this microelement that is actively consumed during the synthesis of hemoglobin.
Low hemoglobin in women: causes and consequences
The second serious reason is bleeding. They can be large, during operations, injuries, childbirth, etc. So insignificant, hidden. For example, small but constant blood loss due to a stomach ulcer.
The third reason is when the body is unable to absorb iron from food. This happens when there is a lack of hemoglobin catalyst substances in the diet, these are vitamins B, PP and C.
Iron deficiency
Iron deficiency in the body is fraught with a wide variety of diseases. After all, this is a metabolic and immune disorder. Unfavorable changes occur in the mucous membranes, their barrier function is disrupted. As a result, infection easily penetrates the body, causing all kinds of disorders.
Therefore, a person suffering from iron deficiency most often falls ill with the flu, acute respiratory infections, which lead to serious complications - sinusitis, rhinitis. Diseases of internal organs, for example, various types of gastritis, can also occur. There is also a disturbance in cardiovascular activity - shortness of breath and tachycardia occur. Blood pressure decreases.
Functions of iron in the body
Problems are also detected on the part of the liver; it cannot fully perform its functions. Therefore, there is a decrease in blood glucose, albumin and prothrombin.
Iron deficiency is especially dangerous for pregnant women , because it causes placental insufficiency. The production of necessary hormones decreases, which negatively affects the formation and gestation of the fetus.
Blood loss
The reasons for low hemoglobin levels in the blood of women may be blood loss as a consequence of surgery, chronic diseases, etc. There are both extensive and very small, but chronic blood losses.
Rapid blood loss in large quantities provokes the occurrence of posthemorrhagic anemia. This can be various injuries and internal bleeding, for example, kidney, uterine, pulmonary, etc.
In this case, after 2 days, the blood volume in the body is restored, however, the number of leukocytes and hemoglobin is significantly reduced. After 4 days, the number of leukocytes and hemoglobin begins to increase, but at a slow pace. Therefore, during this period it is very important to support the body, give it the necessary amount of nutrients, and above all, iron.
Chronic anemia
Low hemoglobin content in the blood can occur in women due to constantly recurring small blood losses, which is fraught with serious consequences. For example, nosebleeds, heavy menstrual bleeding, stomach ulcers or hemorrhoids and other reasons. The result is a significant decrease in the level of iron and, accordingly, hemoglobin.
Erythropoiesis disorders
Erythropoiesis is the process of hematopoiesis. The consequence of impaired erythropoiesis is oxygen starvation of the body tissues, since it is distributed throughout the body in insufficient quantities. This leads to various kinds of diseases. This situation can arise as a result of chronic infectious processes, poisoning and intoxication, and malignant tumors.
The main cause of erythropoiesis is a deficiency of proteins, vitamin B12, folic acid and iron.
Accordingly, one of the consequences of this disorder is a decrease in hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells in the blood of women.
Increased destruction of red blood cells
Rapid destruction of red blood cells can occur as a result of poisoning, sepsis, and various serious infectious diseases such as malaria. The cause may also be skin lesions, burns and blood transfusion if it was of the wrong type.
In this case, red blood cells are destroyed faster than new ones can mature. This disease is called hemolytic anemia. There are two main types - intravascular and when the breakdown of red blood cells occurs outside the vascular system, in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, liver or spleen.
Lack of red blood cells in the blood causes anemia
With hemolytic anemia, the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin decreases, but iron increases. At the same time, active hematopoiesis continues in the bone marrow.
In some cases, in order to save a person from this problem, they even resort to surgery, removing the spleen.