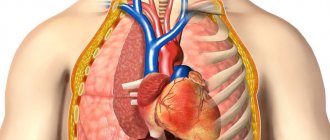
Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck usually occur as a result of contact with bacteria and viruses. If the enlargement is caused by infection, it is called lymphadenitis. Less commonly, cancer may be the cause.
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in keeping our body alive and is a major component of our immunity. Lymph nodes can be felt in the neck, chin, armpits and groin. In some cases, no action is required for treatment and a warm compress is sufficient. Treatment depends on the cause.
When is computer diagnostics necessary?
The largest accumulations of lymph nodes are located: in the occipital, behind the ear, parotid, submandibular regions, as well as on the surface of the neck. There are many inguinal lymph nodes and armpits.
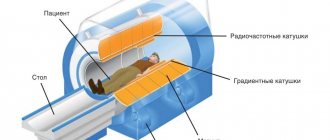
The norm is considered to be round formations with a diameter of no more than 8 mm in the neck and armpits, 1 - 1.5 cm are the optimal sizes of the inguinal and submandibular lymph nodes. In a healthy person, it is impossible to see their contours. However, upon palpation, you can find single nodes or entire groups of them. Lymph nodes located deep in the human body cannot be assessed in this way. In this case, only instrumental research methods (CT, MRI) will help.
You can check the neck area yourself. If the nodes are soft to the touch, mobile, not attached to each other and to the surrounding tissues, and painless, then there is no need to worry. If you notice enlarged and painful lumps, you should definitely contact one of the following specialists:
- infectious disease specialist;
- hematologist;
- surgeon or
- oncologist.
Having assessed the size, location, color and condition of the skin over the lymph nodes (presence of swelling, fistulas or scars), the doctor decides whether a computed tomography or MRI is needed.
Location of lymph nodes in the neck
According to the existing classification, in medicine there are 6 levels, and the same number of sublevels of cervical lymph nodes.
Level I: submental (IA), submandibular (IB)
The location of lymph nodes in the neck of sublevel IA is under the lower jaw, between the anterior parts of the digastric muscles and above the hyoid bone. This group includes the mental lymph nodes, consisting of the mental, sublingual, suprahyoid and thyroglossal-facial protective organ.
Sublevel IB is located under the mandible and above the body of the hyoid bone, between the anterior part of the digastric muscle and the stylohyoid muscle. This group includes submandibular lymph nodes, consisting of preglandular, postglandular, retrovascular and postvascular organs.
Level II: upper jugular
This level includes all lymph nodes located in the lateral triangle of the neck. They are also divided into 2 sublevels. Group II A is located at the base of the skull, above the conventionally designated horizontal line along the lower edge of the hyoid bone. Between the stylohyoid muscle and the posterior edge of the accessory nerve.
This sublevel consists of the retropharyngeal, tonsillar and jugular-digastric lymph node.
Lymph nodes in the neck have different locations.
The photo shows what they are called. Sublevel IIB is located under the base of the skull, above the level of the lower edge of the hyoid bone, between the accessory nerve and the posterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It consists of superficial cervical lymph nodes.
Level III: middle jugular
This level is located below the inferior line of the hyoid bone and above the inferior line of the cricoid cartilage. Between the anterior and posterior regions of the sensory branch of the cervical plexus. The middle jugular lymph nodes will include the superior thyroid and deep lateral.
Level V: rear nodes
This level consists of two sublevels. The VA group of lymph nodes is located at the angle of intersection of the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles, but above the lower edge of the cricoid cartilage. Between the posterior region of the sensory branch and the trapezius muscle. The VA sublevel consists of the intercalary and posterior cervical lateral types of nodes.
Lymph nodes in the neck, the location of which is indicated by sublevel V B, are located under the lower edge of the cricoid cartilage, but above the clavicle. Between the trapezius muscle and the posterior region of the sensory branch. This subgroup consists of transverse cervical, supraclavicular (without Virchow) and lower deep lateral lymph nodes.
Level VI: anterior nodes
This level is located under the hyoid bone, but above the jugular notch of the sternum. Between the carotid arteries on both sides. This group consists of pre- and paratracheal, precricoid and perithyroid types of lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes not included in the classification
In addition to the listed types of cervical nodes, there is a separate category that is not included in the general classification.
It includes the following organs of the immune system:
- behind the ear;
- suboccipital;
- parotid (near and inside the parotid salivary gland);
- retropharyngeal;
- facial;
- superior mediastinal.
How to prepare for a CT scan?
Tomography of the inguinal lymph nodes and in the neck area does not require special preparation. However, it is important for the patient to warn the doctor about the tendency to allergic reactions, if any. Especially if computer diagnostics are carried out with contrast.
The last meal should be no later than 4–5 hours before the CT scan. This requirement is also relevant when considering the possibility of performing CT scans using contrast agents.
Before a CT scan, you need to remove all metal jewelry from your neck and warn your doctor about the presence of prostheses and implants containing metal. Their depiction in photographs may lead to an incorrect diagnosis.
Contraindications to CT and MRI may include:
- severe kidney disease;
- high blood sugar;
- pregnancy;
- the patient is overweight - more than 120 kg (excessive fat deposits make it impossible to obtain a clear image of the lymph nodes, which are located deep).
For young children and patients with mental pathologies, to ensure their immobility, the procedure is performed in the presence of loved ones or, according to the doctor’s decision, under anesthesia.
Characteristic
Lymph nodes belong to the organs of the protective system. These are some kind of filters. Their function is to retain pathogenic substances circulating in the blood. Such “pests” include bacteria, cancer cells, various viruses, and toxic substances. Any change in the functioning of the lymph nodes causes their transformation, which is manifested by an increased size, compaction, irregular shape, excessive mobility, and a malfunction in the tissue ratio.
Moreover, the changes do not have an equal relationship with the degree of the disease. This allows you to do an ultrasound of the lymph nodes of the neck earlier. This makes it possible to identify pathology at an early stage. Ultrasound diagnostics during the procedure records the acoustic resistance of tissues. Due to the fact that different types of cells block ultrasonic propagation to different degrees. Next, the differences are transferred to the device monitor.
This allows you to record the changed parameters of the lymph nodes:
- shape;
- size;
- length;
- width;
- echogenic character.
Ultrasound of the cervical lymph nodes does not require special preparation. To carry out the procedure, the patient must lie on the couch. Next, the doctor treats the area to be examined with gel and presses the sensor tightly to the neck area. The ultrasound machine monitor projects the image.
The only condition for diagnosis is the patient's calm state. Because of this, he should avoid stressful situations before the procedure. The session is not performed if the skin of the neck is damaged. You also do not need to wear high-collared clothing for the examination. For women, it is better to put their hair in a ponytail and remove the chains from the neck area.
Each of the presented lymph nodes can be involved in the pathological process
What can a CT scan show?
Visualization using computed tomography allows you to: obtain a complete picture of the condition of the tissues of individual organs, carry out accurate diagnosis, save and compare study results. Lymph nodes, the cross section of which measures 10 mm or more, are considered pathological.
Images of lymph nodes (in the neck, armpits, in the groin folds), which are reproduced by computed tomography or MRI, make it possible to identify metastases, establish the stage of the disease and decide on the methods of treating the patient. Unfortunately, none of these technologies makes it possible to differentiate tumors or notice metastases in the early stages, if the lymph nodes have not yet changed significantly in size. A clearer picture is obtained when using CT with contrast injected into a vein and delivered with blood to the lymphatic system.
It should be remembered that enlarged lymph nodes do not necessarily indicate the presence of a tumor. Especially when it comes to the lymph nodes of the neck and submandibular. Much more often the cause is infection or inflammatory processes. Diagnosis always involves a comprehensive study of pathology. Therefore, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis only after a comprehensive study of the problem and analysis of the results of clinical and biochemical blood tests.
When a person’s lymph nodes in the root of the lung become inflamed, it means that inflammatory processes are occurring in the body. The reaction from these organs indicates infections, as well as tumors in which lymph collects. If there is inflammation of the lymph nodes in the lungs, or in the mediastinal complex, then the person has a disorder in the thoracic region. The sooner a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed, the greater the chance of a complete recovery without the slightest consequences. The normal size of a lymph node in humans is no more than 1 cm.
Lymphadenopathy – enlarged lymph nodes
Mediastinal lymphadenopathy has unclear symptoms. When it is discovered that a patient has enlarged lymph nodes, this fact causes anxiety and concern in the patient. An increase in the early stage is recognized by the following indicators: anxiety for two weeks without the appearance of other symptoms. This type of pathology is not dangerous and does not cause discomfort.
Lymph node examination
The clinical picture of lymphadenopathy is varied and is determined by etiological factors. Characteristic features of the general condition:
- discomfort in the chest area;
- night sweats;
- tachycardia;
- headache;
- unexplained fever greater than 38 degrees Celsius;
- unreasonable weight loss of the patient over the past 6 months;
- hoarseness of voice;
- cough;
- weakness.
Important! Enlarged lymph nodes are not a separate diagnosis. The reason that contributes to the increase lies in various pathologies.
Large nodes compress nearby structures. Symptoms become characteristic of a compressed organ. For example, disruption of the movement of food into the stomach (dysphagia) occurs due to mechanical action. The cause of characteristic shortness of breath may be tracheal obstruction.
The causes of enlarged lymph nodes are: tuberculosis, lymphoma, sarcoidosis, infectious mononucleosis, respiratory diseases. Enlarged breast lymph nodes are the first sign of tuberculosis. Lymphadenopathy in some cases is a complication of acute respiratory viral infections, pneumonia and influenza with complications in the bronchi. Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease in which inflammatory cells accumulate. The lungs are most often affected. The disease is accompanied by an increase in the norm of mediastinal lymph nodes. Lack of appropriate treatment will cause respiratory failure. Mononucleosis is a disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. This infection is also accompanied by mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
Lymphoma on the scalp
Lymphoma is a group of hematological diseases of the lymphatic system - cancer of the lymph nodes. It can cause enlargement of the mediastinal lymph nodes. When the sources of size changes become clear, then measures to treat the disease begin.
There is no prevention of mediastinal lymphadenopathy. Experts recommend leading a healthy lifestyle, paying attention to sports and proper nutrition, and giving up destructive habits.
Epidemiology
At the moment, it is impossible to say how often a problem with lymph nodes occurs in lung pathology, since there are no statistical data. However, in childhood this problem occurs in almost 40% of cases. In pediatrics, this problem is one of the most common.
If we talk about malignant causes, then with age the risk of such a problem occurring is quite large. By the age of 18-35, the problem is diagnosed in 20% of patients. Enlarged nodes in the chest due to tumors occur in 30% of cases, and in other diseases - about 25%. Next, let's look at why the lymph nodes in the lungs become inflamed.
Causes of inflammation
Lymphatic capillaries accumulate tissue fluid, as well as those substances that remain after metabolism in cells. This is how lymph is formed. The outflow is carried out using vessels that pass through the described nodes. Thanks to their existence, foreign particles are “filtered” in the body and subsequently removed from the body.
Lymph nodes become inflamed for some reasons, which we will describe below:
- Lymphadenitis. It is an inflammation of a bacterial, viral or aseptic nature. If there is any infectious process in the pulmonary system, then the lymph nodes in the lungs will certainly become inflamed. When viruses and bacteria enter the bronchi or mucous membrane, the mediators located on the surface become inflamed. As a result, blood flow increases, and the lymph nodes accordingly increase in size.
- Lymphadenopathy. We are talking about non-inflammatory problems. Often, the problem with enlarged lymph nodes in the lungs begins when there are various types of tumors in the body and with metastatic lesions. The nodes become inflamed due to the spread of lymphoid tissue of an atypical nature.
Drug treatment
Pathological damage detected after infection of blood vessels is bilateral, symmetrically located relative to each other. After diagnosis and observation of the dynamics of growth or decline of the pathology, treatment is prescribed. Non-steroidal drugs are used:
- Nimesil; Diclofenac; Ketorolac; Ibuprofen (used internally, ointments used externally).
- Epheralgon; Panadol; Nurofen; Ibuprom (prescribed to children in the form of syrups);
If affected by lymphedema: Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone.
Ointments and gels are successfully used in physiotherapy procedures. The main source of infection are viruses and bacteria. To combat them, doctors recommend antiviral drugs and antibiotics. Medicines with immunomodulating effects are in demand.
- Remantadine, Cycloferon, Amiksin, Arbidol (will help cope with viruses),
- Groprinosin, Isoprinosine (help strengthen immunity).
It is advisable to take antibiotics after a compatibility test. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of doctors. Self-medication is fraught with serious complications.
Lymphoma
This name hides several cancers that affect the lymphatic system as a whole. During the disease, one large tumor forms, and its metastases spread throughout the body. Symptoms include pain in the head, muscles and joints, and the temperature may also rise. Metastases reach the lungs and lymph nodes. As a result, a dry cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath appear. Over time, if treatment is not started and the symptoms are not stopped, the patient will develop heart pain. The prognosis is unfavorable. Even with timely treatment after diagnosis, patients rarely survive more than five years.
The structure and structure of the lymphatic system in the human body
The structure of the multi-level and complex mechanism includes lymphatic vessels - these are cylindrical cavities through which lymph flows, lymph nodes (small accumulations of lymphatic tissue located in different places throughout the body), lymphatic organs - the thymus, tonsils and spleen.
Content:
- The structure and structure of the lymphatic system in the human body
- What are lymph nodes in the neck
- Inflammation of the cervical nodes: characteristics of the concept
- Causes of inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes
- Symptoms of inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes
- Treatment of inflammation of the lymph nodes of the neck
In addition, two ducts participate in the system - the left and the thoracic, flowing into the right and left subclavian veins, respectively. All these elements are united by a liquid that circulates throughout all cavities - lymph.
The capillaries of the lymphatic system are tubes closed on one side, which together form a network in the tissues and organs of the human body. Capillaries have very thin walls, through which proteins, liquid and large particles freely enter the cavities. Due to the structural features of the walls of blood vessels, these elements are not able to penetrate into the vascular cavities through them, and they enter the blood precisely through the capillaries of the lymphatic system.
In turn, lymphatic vessels are a collection and fusion of small capillaries. In fact, they resemble veins in their structure, but have thinner walls. In addition, they have a large number of valves that regulate the outflow of lymph.
Each vessel passes through its corresponding lymph node. All nodes are combined into several groups located along the vessels. The mechanism of lymph movement looks like this: a large number of small capillaries carry lymph into the node, and from it it leaves through several efferent vessels.
The nodes themselves look like tissue formations, shaped like ellipses or beans, less often ribbon-shaped, up to 2 centimeters long. In these “beans”, lymph is filtered, during which various foreign inclusions are separated and destroyed. They also produce lymphocytes - cells that form part of the body's immune system. The vessels leaving the nodes unite into trunks that form the thoracic and right lymphatic ducts.
Through the right duct, lymph passes from the right arm, right half of the head and chest into the right subclavian vein. The thoracic duct moves fluid from the left upper half of the body to the left subclavian vein. In this way, lymph moves from the interstitial spaces into the blood.
Lymphocytic leukemia
Previously, this disease was most often found in children, since according to statistics, lymphocytic leukemia was diagnosed in children 2-4 years old. However, today the situation has changed, and adults also suffer from this disease. A person's appetite decreases, weakness and pain in the lungs appear. Over time, anemia appears, breathing problems arise and the heart hurts. Without treatment, the patient is unlikely to live more than three years; with treatment, stable remission can be achieved, lasting more than 10 years. It should be noted that cancer of the lymph nodes of the lungs is a common cause of their inflammation.
Symptoms of inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes
The most important manifestation is the appearance of some compactions and swelling at the sites of the nodes. When pressed, a person may feel pain.
With the progressive development of the disease, the patient develops:
- general weakness and malaise;
- loss of appetite;
- headache;
- elevated temperature.
Children often develop intoxication due to the inflammatory process.
Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes can be chronic or acute.
Chronic lymphadenitis
A condition characteristic of people with severely reduced immunity as soon as they develop any kind of disease, even a mild form of a cold. At the same time, the inflamed nodes are painless both during remission and during exacerbation of the chronic form. In rare cases, suppuration occurs. Chronic enlargement of the lymph nodes in the neck can accompany the development of tuberculosis at different stages - such lymphadenitis usually passes without fever, or with slight fluctuations to subfebrile values.
Acute form
It is a complication of a specific disease, accompanied by purulent processes in the lymph nodes, a sharp increase in temperature to 38-39 degrees. In this case, the skin over the node acquires a red tint, similar in shape and appearance to a boil. The further the disease progresses, the larger the size of the lymph node becomes, and its contours lose clarity.
Without medical help, such a condition becomes the cause of the development of sepsis or adenoma.
Unilateral enlargement of the lymph nodes of the neck
Cervical or submandibular nodes, enlarged on one side, signal the possible development of lymphoma or a tumor process of a non-lymphoid nature in the neck or head. It can be combined with unilateral inflammation of the supraclavicular lymph nodes, as well as those located in the area of the scalenus muscle, if, for example, metastases begin to spread from the tumor into the chest cavity or gastrointestinal tract.
Virchow's node is a unilateral enlargement of the supraclavicular node in metastases of gastric cancer.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in a child
The main reason is the presence of some infectious process and its effect on the body. In approximately 80% of cases of disease, node enlargement does not occur. However, if the child has a weak immune system, his painful condition will most likely cause lymphadenitis. For example, inflammation of the lymph nodes can occur due to mumps, tonsillitis or laryngitis.
The development mechanism looks like this: after bacteria enter the lymphatic channels, they are transferred to the lymph nodes. In the lymph nodes, after pathogenic microorganisms enter, the process of producing special cells to fight infection begins. For the most intense release of lymphocytes (protective cells), the size of the lymph node increases.
Severe inflammation occurs because the body is unable to cope with the bacterial load. The process may even lead to the formation of pus in the cavity of the node. The skin in the area where lymphadenitis develops becomes hyperemic and swollen.
The illness in a child begins with general malaise. The child becomes lethargic and capricious, and loses his appetite. Inflammation of the lymph nodes may be accompanied by fever and signs of intoxication.
It is very easy to determine the location of the lesion by touch; in acute cases it becomes visually noticeable. On palpation it gives off pain; the tissues above the node feel swollen and stretched. The condition may be accompanied by headache, chills, and weakness.
A slight enlargement of one lymph node, especially in an infant, may indicate that it simply began to work a little more actively than others, against the background of mild forms of illness, or after recovery.
Gradually it regresses and acquires normal size.
The baby’s occipital lymph nodes may become enlarged:
- due to measles;
- with rubella;
- with mononucleosis;
- with chickenpox;
- against the background of toxoplasmosis.
It is precisely such diseases that can often provoke inflammation of the nodes on the back of the head in a child. In severe cases, their increase can be noticed. The baby's face takes on a puffy expression.
In addition, the lymph nodes in the neck increase in size with cat scratches. This syndrome is relevant for children who have pets and who are often in contact with felines. Cat saliva contains a large variety of microorganisms. They can easily enter a child’s body if an animal bites or scratches him. Lymphadenitis can be observed within 2-3 days after receiving the wound.
Colds provoke inflammation of the lymph nodes in children, to which various diseases literally “stick”. In the presence of infectious diseases, lymphadenitis develops most quickly in the place closest to the entrance gate of the infection, so an inflamed cervical lymph node may indicate the development of diseases of the upper respiratory tract, throat, and head.
Lymphadenopathy in adults
The development of pathology in adults is most often caused by infectious factors, for example, diphtheria, tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis, rubella viruses, herpes, measles, fungal infections (actinomycosis, histoplasmosis), chlamydia and mononucleosis.
The problem may also be damage to the oral cavity by bacteria or viral microorganisms, but this condition is more common in children.
About 5% of cases of lymphadenopathy in men and women are associated with non-infectious factors, including the development of oncological processes - lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma.
Nonspecific infection is a condition that is quite rare in people with a low level of immunity. This type of pathological process develops due to opportunistic microflora, which normally lives constantly in the human body. While a person is healthy, the immune system is able to suppress its activity, keeping it at a safe background level. If favorable conditions appear for the activation of the flora (injuries, stress, illness, hypothermia), the immune system is no longer able to restrain its intense vital activity, and the person falls ill.
The first, most characteristic symptom is an enlargement of the lymph nodes to a size of more than 1 centimeter (inguinal - more than 2 centimeters). Depending on the etiological factor, the further course of the disease may be different.
Pain during inflammation of the lymph nodes is a sure sign of an inflammatory process.
Pain without enlargement at the site of the lymph node
Pain in the lymph nodes is not always accompanied by their enlargement. If the affected person has pain in the lymph nodes, but they are not enlarged or inflamed to the touch, this may indicate the presence of residual effects of a sore throat, ARVI, or some other respiratory infections. Doctors say that the duration of the painful syndrome after recovery can be used to judge how well a person’s immune system works: the longer the nodes hurt, the weaker the immune response.
In addition, the cause of pain in nodes without enlargement may be local infection, which does not affect general well-being.
Inflammation in oncology
The anatomical features of the neck structure cause frequent inflammation and the development of metastases in the cervical lymph nodes - this is due to the large number of lymphatic and blood vessels, as well as nerve fibers in this part of the body.
For cancer of various localizations, cervical nodes are indicated by protruding round formations with relatively clear contours. On palpation, they are characterized by painlessness, dense and elastic texture, and slight mobility.
Metastases appear in the nodes of the neck due to cancerous tumors in the following organs:
- in the larynx;
- in the lips and tongue;
- in the thyroid gland;
- in the stomach;
- in the skin of the neck and head.
Inflammation of the deep lymph nodes cannot always be felt, but some asymmetry is noticeable in the appearance of the neck.
Malignant cells in lung or esophageal cancer can enter the right supraclavicular node, and if the patient has complaints of inflammation of the left node, this may be a consequence of the spread of malignant tumors in the liver, stomach, colon or rectum.
Condition of the lymph nodes after chemotherapy
In some cases, during radiation treatment and chemotherapy for oncology, lymph nodes, including those in the neck, may become inflamed in patients. This happens due to the high sensitivity of lymph node follicles to cytostatic toxins. The development of lymphadenopathy after chemotherapy is caused by damage to lymph node cells, a decrease in the number of lymphocytes and leukocytes in the blood, as well as a specific reaction of the body to infection.
Diseases as a cause of enlarged nodes
Enlarged lymph nodes are most often a symptom of a disease. This is considered a normal protective reaction by the immune system. Let's look at the most popular reasons.
- Pleurisy. Characterized by inflammation of the pleura, this is the serous membrane. It is located in the chest cavity. If the disease is not treated in time, abscesses may develop.
- Pulmonary tuberculosis. As a rule, the disease is characterized by inflammation of the lymphatic vessels and, accordingly, nodes.
- Pneumonia. A disease in which the lungs become inflamed. Depending on where the source of inflammation is located, certain groups of lymph nodes are affected.
- Bronchitis. As a rule, the lymph nodes in the lungs become inflamed in both acute and chronic cases.
- Neoplasms of a malignant nature. When cancer cells enter the lymph nodes through blood vessels, inflammation occurs.
- Lymphogranulomatosis. This pathology is of an oncological nature. Primarily affects the lymph nodes. This problem is characterized by inflammation of all groups of nodes in the body.
- Viral hepatitis. When hepatitis C develops, a person begins to experience severe symptoms. The inflammatory process affects the entire body. In addition to enlarged lymph nodes, the patient experiences weakness and a headache.
- Sarcoidosis. Granulomas form in the lungs, these are foci of inflammation. At the first stage, there is only one manifestation: enlarged lymph nodes. As it progresses, fever (up to 37.5 degrees), cough, chest pain, lack of appetite and headache are added.
- AIDS virus. Enlarged lymph nodes in the lungs are one of the manifestations that occurs in every second HIV patient.
Specific lymphadenitis
Inflammatory processes in the lymph node system caused by specific infections, such as syphilis, whooping cough, tuberculosis, diphtheria, are called specific lymphadenitis. This condition is accompanied by high fever, as well as skin rash, headache, and fever.
Thus, the lymph node system acts as a protector of the body from various infections and cancers, so they often “take the hit” on themselves. Pathogenic organisms settle in the lymphatic tissue and are neutralized. If the lymph nodes enlarged for a while, but then returned to normal, it means that they have overcome the pathogen and everything is calm in the body again. But if the inflammation, as mentioned above, lasts for some time and does not go away, causes pain, begins to spread to the lymph nodes in other parts of the body, this serves as an alarm signal and indicates that it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor to determine the exact causes of the enlarged lymph nodes and making the correct diagnosis, on which the health, and sometimes the life, of the patient depends.
And finally - 2 videos “Causes of enlarged lymph nodes” and “Lymph nodes - invisible self-defense”:
Medicinal reasons
Pulmonary lymphadenopathy can also occur when taking drugs that affect the state of the lymphatic system as a whole. Among such means the following should be noted:
- Antibiotics. Most drugs cause enlargement of the lymph nodes, so they should be prescribed with caution, especially if the person has a weakened immune system.
- Antihypertensive drugs. Such drugs are necessary to lower blood pressure. Their side effect is the described symptom.
- Antimetabolites. These drugs are necessary to stop biochemical processes in the body. They are especially often prescribed if the patient has a malignant tumor at an early stage.
Duration of lymph node enlargement
Typically, with a bacterial or viral infection in the first stage, enlargement of the lymph nodes in the neck is accompanied by an increase in temperature. When palpated, they become painful; with prolonged swelling, additional signs appear: loss of appetite, general malaise of the body. When the disease is treated with antibiotics or other targeted agents, the swelling in the lymph node subsides and the pain goes away.
If the enlarged lymph nodes in the neck last for several months, this may indicate a tumor, and the symptoms cannot be treated with antibiotics.
With tumor lymphangitis, the nearest lymph nodes gradually enlarge, which can be located not only in the neck.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor can do an ultrasound and palpate the lymph nodes to determine their exact characteristics.
Symptoms
If a person has a pathology associated with the lungs, then with inflammation of the lymph nodes the following symptoms appear.
- The temperature rises to 40 degrees with infectious diseases, and up to 37.5 with chronic inflammation and tumors.
- The appearance of chest pain. This is due to the fact that the nerve endings begin to be compressed. Also, the reason for this effect may be the disintegration of the tissue of the node in the presence of a tumor, or stretching of the capsule. Exactly where the pain will be located and how severe it will be depends entirely on the location.
- Breathing problems, development of dyspnea. If a lymph node in the chest increases in size, the patient always complains of difficulty in inhaling or exhaling, and there may be a feeling of lack of air and squeezing.
- Problems with swallowing, so-called dysphagia. It occurs only when a person’s lymph nodes in the lungs are too greatly enlarged. In this case, they compress the esophagus, making it difficult for a person to swallow.
- Pulsation of the veins in the neck is one of the symptoms. It is characteristic of the stage of the disease when the great vessels are already involved in the inflammatory process. This symptom occurs when the outflow of blood is disrupted.
Alarming symptoms
The slightest changes in the size of the mediastinal lymph nodes are dangerous to health. This group of nodes reacts only to serious unnatural processes occurring in nearby organs. Pathologies - hyperplasia, changes in lymph outflow, inflammation - dictate an urgent clarification of the basis of the development problem. The thoracic nodes respond precisely to the developing pathology occurring in neighboring organs.
The enlargement of the mediastinal lymph nodes is characterized by the following processes:
- the body's response to chronic inflammation;
- hyperplasia - cell division in oncology;
- infections in the body provoke changes in lymph outflow.
If you experience symptoms of pain in the chest area, difficulty breathing, or night sweats, you should immediately consult a doctor. An increase in liver and spleen parameters may occur. Changing their size also requires increased attention. Symptoms of inflammation or enlargement of nodes have unclear boundaries and unclear manifestation. This fact makes it difficult to seek help on time and complicates the diagnosis of the disease.
According to the time course of the disease, there are three stages of the diagnosis: acute, chronic, recurrent. The third is associated with a repeated attack of the disease.
Diagnostics
If a person develops symptoms of varying nature and intensity, then differential diagnosis should be carried out. This is done in order to understand how serious the situation is and how many body structures are involved in the process. Let us next consider all possible diagnostic measures.
- General blood analysis. It is done to detect an increased level of white blood cells as well as the rate of red blood cells. These indicators can make it clear whether there is inflammation in the body.
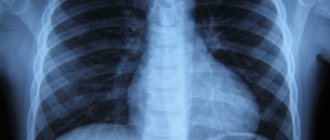
- Chest X-ray. It is done in two projections: direct and lateral. Thanks to this diagnostic measure, you can see the presence of pathological changes, as well as how strongly the lymph nodes in the lungs are involved in the process.
- Computed tomography allows us to understand the exact location and size of damage, especially when it comes to the mediastinum.
- Needle biopsy. It is carried out if the diagnostic methods described above have not brought any results. Most often it is done when there is a suspicion of cancer.
Diagnostic methods
The first sign of the development of lymphadenitis is an increase in lymph nodes by 1.5 or 2 times. This occurs as a result of an increase in the supply of tissue fluid in the parenchyma of the organ and an increase in the concentration of white blood cells, due to the body’s protective reaction to the invasion of infection.
This sign is fundamental in diagnosing the disease. Combining it with a medical history, additional pathological symptoms and bacteriological studies allows the doctor to accurately establish a diagnosis.
Main types of diagnostic tests and studies:
- general blood test - to determine the number of leukocytes in the plasma and identify the causative agent of the pathology;
- bacterial culture - to confirm or refute the presence of streptococci and staphylococci;
- Ultrasound;
- biopsy - to identify rare types of infections and atypical cancer cells.
Which doctor should I contact?
Please keep in mind:
- If a person has bronchitis, pleurisy and other mild pulmonary diseases, then the treatment will be carried out by a therapist and a pulmonologist. Conservative therapy. For these diseases and enlarged lymph nodes in the lungs, treatment is easy.
- Pneumonia or pleurisy with complications is treated by a surgeon. You should also contact him for purulent lymphadenitis.
- An oncologist should treat lymphomas, lymphogranulomatosis and other oncological problems.
- If problems with the lymph nodes appear due to tuberculosis, then you should contact a phthisiatrician.
Principles of treatment of lymphadenitis and lymphadenopathy
Treatment for enlarged lymph nodes depends entirely on the cause of the problem. Let's consider treatment methods for any primary diseases:
- For bronchitis and pneumonia, antibacterial therapy is carried out. Antitussives, expectorants and antipyretics are prescribed, if necessary.
- During the development of tuberculosis, the doctor prescribes a long course of treatment with antimycobacterial agents.
- For lymphogranulomatosis, chemotherapy is prescribed to reduce pressure on the lymph nodes of the mediastinum of the lung.
- If the patient has tumors, they are first removed, followed by chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Treatment of problems with tumors
If the enlargement of nodes is caused by tumors, then the following treatment methods should be used:
- Immunotherapy. Thanks to it, the body’s protective functions increase, and it begins to intensively fight the disease.
- Radiation therapy. This method allows you to destroy all cancer cells through radiation. This therapy is carried out with caution, as it has consequences for the entire body as a whole.
- Operation. If indicated, the tumor and all affected parts can be removed.
- Symptomatic measures. This therapy is carried out in order to get rid of the manifestations.
It is important to remember that as the cancer begins to recede, the lymph nodes in the lungs will return to normal.
Anatomy and physiology
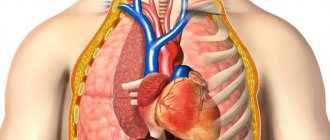
In an important area of the mediastinum there are a large number of lymph nodes. The superior mediastinal lymph nodes are located on both sides of the trachea. Lower mediastinal - next to the esophagus. The aortic ones are located between the pulmonary trunk and the aorta. The root lymph nodes include the nodes of the root of the lung. Lymph nodes, including the mediastinum, cleanse nearby organs of infections and toxins.
Inflammation or enlargement of nodes is a reaction to a malfunction of the body. They take on the role of a filter for infectious spreads. The heart, lungs, bronchi, and trachea are released through lymphatic drainage through the vessels to the nearest nodes. In this way, the pericardium, pleura, and esophagus are cleansed.
The growth of mediastinal lymph nodes is promoted by smoking, taking chemicals and medications for a long time; environmental hazardous effects of dirty air, gases and harmful vapors. Systematic hypothermia reduces human immunity. Various viral diseases with numerous complications appear.
Complications and consequences
As a rule, all resulting complications are associated in most cases with the underlying disease. Among these, abscess and phlegmon, fistulas and so on should be noted.
If the lymph nodes in the lungs and in the mediastinum are enlarged, then obstructions of various types, impaired blood flow and problems with the esophagus may occur. Sometimes the pathology leads to pulmonary dysfunction, as well as heart failure. When a tumor process becomes the cause of node enlargement, metabolic complications arise. Problems with the kidneys, blood and electrolyte balance begin.
Classification of cervical lymphadenitis
In medicine, there are several classifications of inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes (lymphadenitis). The data indicated in them is used to determine the diagnosis.
Depending on the duration of the transition period of lymphadenitis from the latent state to the active phase:
- Spicy . It is characterized by vivid clinical symptoms and lasts about 15 days. This form often develops when wounds become infected and as a result of postoperative complications.
- Chronic . Duration is about 1 month or more. This form is characteristic of protracted infectious pathologies, as well as autoimmune disorders and cancer.
- Recurrent . This type is characterized by periodic episodes of exacerbations and periods of relief of the same lymph nodes, but inflammation can switch to nearby organs.
Depending on the etiology of the pathological process:
- nonspecific form - the causative agent is a conditionally pathogenic microflora, which, under favorable conditions, develops into a pathogenic state that can be quickly cured;
- specific form - develops when exposed to pathogens of a certain type, as a result of which lymphadenitis acts as a symptom of the underlying disease.
According to the nature of the pathological process, lymphadenitis occurs:
- serous - characteristic of viral and oncological etiology;
- purulent - develops in the chronic form of a bacterial disease.