MRI of the throat is relevant when other research methods turn out to be uninformative. Basically, the indication for its implementation is a suspicion of cancer. The reasons for performing the procedure may be:
- anatomical abnormalities of the throat structure;
- voice change;
- the need to visualize a foreign object;
- problems with food passing into the stomach;
- regular headaches, dizziness (may indicate disorders in the cervical vessels);
- "lump in the throat;
- periodic attacks of suffocation;
- difficulty breathing and swallowing;
- injuries to the mucous membranes of the throat;
- pronounced asymmetry, swelling of the soft tissues of the neck area;
- the need to evaluate the results of ongoing antitumor therapy;
- preparation for surgery and assessment of the results of surgical treatment.
Photo: MRI of the larynx and neck
MRI of the throat and larynx: what diagnostics show
MRI of the larynx includes a detailed examination of the larynx, salivary glands and thyroid gland. An MRI of the throat can be done if there are suspicions of inflammatory diseases, neoplasms, or infectious processes. To undergo an examination, one or more of the following symptoms is sufficient:
- the appearance of laryngeal edema;
- breathing problems;
- change in the size of the thyroid gland (increase in size);
- copious mucous and purulent discharge from the respiratory tract;
- a feeling of sore throat occurring simultaneously with an increase in temperature.
Regardless of what an MRI of the throat and larynx shows, a scan is performed either to confirm or exclude the suspected diagnosis. In some cases, diagnostics are prescribed to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for diseases of the ENT organs.
MRI of the larynx is prescribed for:
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- injuries to the throat and larynx;
- the presence of neoplasms and metastases;
- diseases of the salivary glands, lymph nodes;
- osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia.
MRI of the throat and larynx shows a huge number of different diseases and pathological conditions. It is also important to remember that if the patient has a high risk of developing certain diseases, an MRI of the throat should be done for preventive purposes at least once a year.
Photo
| Carcinoma-oropharynx-PET-and-MRI |
| Laryngeal cancer on MRI |
| Laryngeal cancer |
| Thyroid cancer |
| Thyroid cancer |
Contraindications for MRI of the larynx
Despite its high accuracy and safety, MRI of the throat has some contraindications:
- Patient's age. Thus, it is not possible to do an MRI of the throat for children under the age of 7 years, since they cannot comply with the main condition - to ensure complete immobility during the examination.
- Obesity. Magnetic resonance imaging is not performed on patients whose weight exceeds 120 kg for the reason that the diagnostic table is not designed for large body weights.
- Patients with metal objects in the body. These can be any implants and stimulators that may begin to move or cause a burn during an MRI of the trachea.
- Patients with uncontrollable tremors of the limbs. There is no point in having tomography performed on such patients because the images will be inaccurate.
- Patients with claustrophobia. Finding a patient inside a scanner can cause a panic attack, so for safety reasons, it is advisable for such people to undergo magnetic resonance imaging only in a state of medicated sleep.
In exceptional cases, an MRI of the larynx can be performed on a pregnant woman if there are compelling indications. However, scanning with contrast will be strictly contraindicated, since contrast has a toxic effect on the body of the developing fetus, which can lead to irreparable consequences.
How is the procedure performed?
Having a tomography scan of the throat is a fairly simple procedure that does not cause any discomfort. Algorithm for the procedure:
Linear X-ray tomography
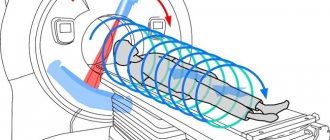
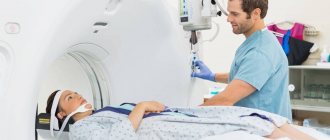
- During the examination, the patient lies down on the table, then he is secured using belts and bolsters.
- Afterwards, the table moves into the machine, where it remains for the entire duration of the procedure. Typically the examination time varies from 20 to 40 minutes. There are different models of devices, in some the body is inside the tomograph, in others it is outside.
- An important condition is to ensure immobility during the entire study.
- To ensure the safety of the patient, the tomograph is equipped with ventilation, lighting, and supports the communications necessary for contact with operators and doctors.
- If tomography is done with contrast, then food intake is allowed 6 hours before diagnosis, fluid intake is allowed 1 hour.
- You should not bring things into the equipment room that cause a reaction in the tomograph. It is necessary to leave all metal utensils, cell phones, and jewelry in the locker room.
Braces should be removed before the examination.
How to properly prepare for magnetic resonance imaging
MRI of the throat and larynx shows a variety of diseases, even though the larynx is one of the most difficult areas to examine. The patient does not need to follow any strict preparatory measures before the scan, which is a huge plus for patients. It is only important to adopt some recommendations that may be useful during an MRI of the trachea:
- For 3-5 days, you should eliminate fatty and spicy foods from your diet, and also give up any foods that can cause increased gas formation and discomfort in the intestines. This recommendation should be given special attention if the diagnosis will be carried out using a contrast agent.
- 5 hours before the start of the examination, you should refuse any food, as food can cause discomfort at the most inopportune moment.
- Before scanning, you need to remove all metal objects, including dentures and hearing aids. You can also change into hospital clothes, as they are more comfortable. During the examination, the patient should experience maximum comfort.
- If you have a tendency to have panic attacks, it is better to drink any sedative. You can ask your doctor to prescribe the most effective and appropriate one.
Laryngeal cancer - symptoms and manifestations in men and women
Patients with laryngeal tumors may present with the following complaints:
If the tumor is located above the vocal folds:
- Sensation of a foreign body in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing solid food (dysphagia)
- Pain when swallowing food (odynophagia), radiating to the ear
Tumor of the vocal folds:
- Hoarseness is the first sign of a throat tumor in women and men
- Lack of voice (aphonia)
Tumor of the subglottic region of the larynx:
- Breathing difficulties due to laryngeal stenosis
- Minimal or no hoarseness
Progress of the survey
Before undergoing an MRI of the throat, the patient must submit all documents to the radiologist (results of previous studies, an extract from the outpatient card, personal medical record), and also inform about potential contraindications and the presence of chronic diseases.
Even seemingly insignificant diseases can act as strict contraindications to undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. The radiologist must be aware of everything. The examination will be carried out in several stages:
- If an MRI of the larynx is performed using a contrast agent, then before the examination begins, a special drug will be administered intravenously to the patient. As a rule, an allergy test is performed before its administration. If its results did not reveal the presence of intolerance, then there will be no contraindications to this method of examination.
- The patient will be asked to go to a special room where the tomograph is located. To ensure complete immobility and eliminate any involuntary movements of the limbs, the body will be secured with special straps. The patient should not be frightened by such a need, because this is done in his interests.
- After this, the retractable table is rolled into the tomograph and the device begins its work. Medical personnel leave the room and monitor the progress of the MRI of the trachea from the next room through a special window.
- The examination continues for 20-30 minutes. During operation of the scanner, specific noises are produced. This is normal and you should not be afraid of these sounds.
As soon as the scanning is completed, the patient can immediately leave the office, change into personal clothes and go to wait to receive a report from the doctor. If a person does not have enough time, the survey results can be sent to him by email. In any case, as soon as the conclusion is received, it should be taken to the specialist who has written a referral for an MRI of the throat and larynx.
Price
The price for an MRI is from 3,000 to 7,500 rubles. Depends on the clinic, the type of tomograph, and the qualifications of the doctor who performs the diagnosis and interprets the results.
MRI is a safe, non-toxic, non-invasive procedure that determines the early stages of the development of pathological conditions of the throat, larynx, and thyroid gland.
The earlier therapy begins, the better the prognosis. Suitable for patients of all age groups, including newborns.
The introduction of contrast agents expands diagnostic capabilities and increases image clarity.
Decoding the results
The images obtained by MRI of the larynx can be printed or recorded on any digital media. This opportunity allows the patient to show the results of the examination to absolutely any specialist, regardless of where exactly he goes.
Interpretation of the results obtained should be carried out exclusively by a competent specialist with extensive experience, because only in this case can the patient fully rely on the professionalism of the doctor.
The radiologist will compare the obtained images with samples without pathology and determine the presence of abnormalities, if any. After this, the specialist prepares a conclusion, on the basis of which further therapeutic tactics are made.
If necessary, the scan can be rescheduled, and even frequent scanning will not have a negative impact on the patient’s health due to the absolute harmlessness of the diagnosis.
What diseases does a CT scan of the throat show?
The neck area contains vital organs located in close proximity to each other. A CT scan of the throat will help determine which structures are affected and cause clinical symptoms in the patient.
A CT scan of the larynx is performed to diagnose the following diseases:
- consequences of injuries, damage, foreign bodies;
- inflammatory diseases – laryngitis, laryngotracheitis;
- diverticula of the larynx, esophagus (protrusions of the walls of the organ) and their inflammation;
- complications of inflammatory processes - abscesses, phlegmon;
- developmental anomalies – laryngocele, stridor;
- tumor-like formations - cysts, song nodules, polyps;
- benign tumors - fibromas, papillomas, adenomas;
- cancer (the vast majority of cases are squamous cell carcinoma);
- metastases to the larynx and nearby lymph nodes;
- vascular diseases.
A CT scan of the throat allows you to assess the condition of all tissues of the neck, identify organ diseases, and differentiate them from pathology of the cervical spine and vascular diseases.
Developmental anomalies
Organ defects that occur during intrauterine development are caused by exposure to unfavorable external factors (physical, chemical) or are of a genetic nature.
The main malformations of the neck organs, which can be detected using a CT scan of the throat:
- Cysts and fistulas are the most common developmental anomaly. Cysts form from the thyroglossal duct, which normally should disappear. The cyst is located on the front or side surface of the neck and is represented by a dense elastic formation that is not fused to the surrounding tissues. The inside of the cyst is filled with fluid. With inflammation and suppuration of the cyst, the formation of a fistula is possible - a duct connecting the cavity of the cyst with the surface of the skin.
- Laryngocele is the formation of a cyst-shaped cavity filled with air in the ventricle of the larynx. If this pathology is detected, surgical treatment is necessary to avoid complications (infection, obstruction of the airway).
- Torticollis is a pathological shortening of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, causing a constant tilt and rotation of the head to one side. Diagnosis of the disease should be carried out in infancy, when surgical treatment will be effective. If left untreated, complications appear - facial asymmetry, flattening of one side of the head.
- Accessory ribs – normally there are no ribs in the cervical spine. Additional ribs compress the muscles, blood vessels and nerves of the neck, causing pain and causing neurological disorders.
- Klippel-Feil syndrome - shortening of the neck occurs, CT scan shows fusion of 4-6 cervical vertebrae into a single mass, a decrease in the number of cervical vertebrae. The disease includes multiple developmental defects - dental anomalies, microcephaly, spina bifida, renal hypoplasia, and deafness.
Tumors
Laryngeal cancer is the most common malignant cancer of the head and neck. The disease occurs gradually under the influence of a complex of unfavorable factors:
- smoking – almost all cancer patients smoke, passive smoking is especially dangerous;
- regular alcohol consumption;
- chronic exposure to toxic components of inhaled air (exhaust gases, gasoline, vapors of acids, alkalis, mineral oils, welding aerosol, asbestos dust);
- the presence of chronic inflammatory processes, papillomas, cysts, benign tumors, which, with prolonged existence, can become malignant.
Carrying out a CT scan if you suspect the development of cancer allows you to assess the depth, size and stage of the tumor, and determine the presence of metastases in the lymph nodes of the neck. Based on the images, the oncologist makes a conclusion about the advisability of a particular method of therapy, and the surgeon has the opportunity to plan the operation. After treatment, control photographs are taken.
Inflammatory diseases
Inflammation of the neck organs occurs when infection penetrates or the mucous membrane is injured.
Inflammatory processes that are diagnosed using CT:
- Diverticulitis is an inflammation of a pathological protrusion of the wall of the esophagus or pharynx, caused by the accumulation of pieces of food in the diverticulum cavity. The pharyngoesophageal diverticulum is located on the left at the level of the cricoid cartilage of the larynx. If left untreated, the presence of a diverticulum can be complicated by impaired swallowing, the formation of a malignant tumor, and bleeding.
- An abscess is a complication of infectious diseases of the pharynx, which forms when the infection moves from the mucous membrane to the deeper layers of tissue. The abscess is localized in the peripharyngeal space, represented by a cavity containing pus and surrounded by a capsule. Lack of treatment leads to a breakthrough of the capsule and release of purulent contents into the surrounding tissues and blood (sepsis).
- Cellulitis is a diffuse purulent inflammation of tissues without a clear boundary, resulting from trauma, tissue damage, as a complication of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the throat. Cellulitis creates a risk of developing tissue necrosis and sepsis.
Advantages of MRI of the larynx over other diagnostic methods
Various methods can be used to identify diseases of the pharynx. Most often, patients are referred for a computed tomography scan, ultrasound diagnostics or endoscopy. However, MRI of the trachea has a number of advantages over other diagnostic methods.
First of all, this list includes complete harmlessness to the patient’s body. To date, no harmful effects of the magnetic field on the body of the subject have been identified. The only exception is pregnant women. The magnetic field can have a negative effect on the developing fetus, so tomography is not prescribed to expectant mothers in the early stages of pregnancy.
Another undoubted advantage is non-invasiveness, which is why magnetic resonance imaging is very popular among patients. It is impossible not to mention the high information content - tomography allows you to obtain highly accurate images, and if necessary, the finished images can be viewed in a volumetric projection.
MRI of the throat and larynx also provides the opportunity to detect the presence of even the most minor neoplasms, regardless of their nature: benign or malignant.
Despite the many advantages, tomography also has some disadvantages. For example, if during an MRI of the trachea one can learn about disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland, then a more specific study of this organ should be carried out separately.
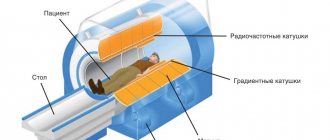
Classification of tomographs
A technical device for magnetic resonance imaging of the body is called a tomograph. The device has many technical characteristics, among which the most important are:
- External design features
- Magnetic field voltage
- Projection resolution
- Duration of scanning one zone
- Maximum load capacity of the extendable table.
The main criterion for classifying tomographs - design features - divides the devices into two types:
Closed tomograph
– a complex device consisting of a retractable table for transporting the patient and a cylindrical capsule for scanning, software and control system.
This type of device has the following advantages:
- Increased magnetic field voltage from 1.5 to 3 Tesla allows for high-quality scanning with maximum detail of projections.
- Diagnosis of minor organic and functional disorders.
- High research speed.
Weaknesses of the tomograph:
- Discomfort for patients with anxiety-phobic disorders.
- Impossibility of examining overweight and large body size patients.
Open tomograph
– the working magnet is located above and below the retractable platform.
Advantages of open type devices:
- The absence of closed circuits reduces anxiety and creates comfortable conditions for children and people with claustrophobia.
- Possibility to conduct examinations for overweight and large body size patients.
The downsides of open hardware are:
- Low magnetic field voltage makes it difficult to diagnose mild pathologies.
| Open MR tomograph | Closed-type MR tomograph |
The resolution of the images and the speed of the study are directly influenced by the magnetic field voltage of the tomograph.
The following classes of devices are distinguished:
- Low-field tomographs in which the magnetic field strength does not exceed 0.5 Tesla. The devices make it possible to recognize objects from 5-7 mm, that is, a pronounced pathology.
- Mid-field tomographs with intensities up to 1 Tesla are not much more informative than the capabilities of first-class equipment.
- High-field tomographs with a working magnetic field voltage of 1.5 Tesla are a common class of equipment. The devices recognize minor defects and tumors up to 1 mm.
- Ultra-high-field tomographs with a magnetic field voltage level of 3 Tesla allow high-quality research to be carried out in a short period of time.
The capabilities of tomographs are constantly being improved. At the moment, devices with a voltage of 1.5 Tesla are sufficient for effective examination.
| Image quality depending on equipment power |
Indications and contraindications
The CT method of the neck and larynx is based on the work of X-rays, with the help of which a computer builds layer-by-layer images of the larynx and simulates a three-dimensional image for a full analysis of all structures of the neck.
This type of hardware research is carried out:
- to identify the degree of injury to the trachea and associated tissues;
- in the diagnosis of various formations of the larynx and diseases of the thyroid gland (tumors, cysts);
- to assess the condition of the vascular system of the neck;
- to determine the focus of inflammatory processes.
Although the method is based on the work of X-rays, the radiation dose is minimal, so CT is considered a safe research method.
There are several contraindications for which a specialist will select a different diagnostic method. This includes the period of bearing and feeding a child, childhood (up to 15 years), and the presence of implants with metal elements. If the patient is prescribed the use of contrast during the procedure, the list of contraindications and adverse reactions expands - contrast is not administered to patients with renal failure.
Alternative diagnostic methods
Alternative diagnostic methods include ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. However, CT of the throat has a clear advantage - this method is the most informative and fastest. In addition, it allows you to identify even minor pathological processes and evaluate the structures of internal organs.
If we talk about which type of diagnosis is better: MRI or CT, then it will be quite difficult to answer this question unambiguously. Both research methods serve completely different purposes, although many of the data obtained may be duplicated.
A CT scan of the throat is performed using X-rays, so it allows you to examine dense formations and hollow organs. Magnetic resonance imaging is the best way to identify soft tissue conditions and is widely used to evaluate injuries to the neck and ligaments.
If there is a need to scan patients in an emergency situation, the choice of one or more examination methods is at the discretion of the doctors, based on the nature of the pathological condition.
About the method
A study using computed tomography is a basic type of hardware diagnostics, which helps a specialist create a description of the structure of soft and hard tissues, allows them to be visualized without violating the integrity of the patient’s skin.
This type of research has the following advantages:
- high efficiency;
- almost complete safety;
- high speed of conduction.
Using tomography, a 3D model of the patient’s larynx anatomy is created, which allows the doctor to identify the source of destructive processes and make the correct diagnosis with concomitant treatment.
What preparation is required
Examination of the throat using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner does not require any preparation from the patient. The main condition for a successful examination is the patient’s immobility during a fairly long scan.
After the procedure, specialists will see high-quality images of the upper respiratory tract on the screen in several projections:
- axial;
- frontal;
- sagittal.
If necessary, an MRI examination is carried out with the introduction of a contrast agent into the venous system, which makes it possible to determine the clear boundaries of the tumor formation, establish the nature and boundaries of the spread of the pathology. The results of antitumor therapy are clearly visible in comparison with previous images.
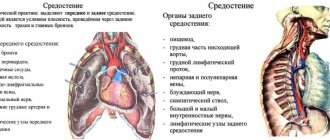
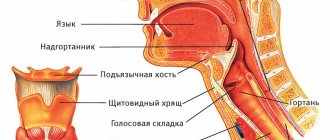
A little anatomy: the structure of the larynx
Before answering the question of what can be seen on the results of an MRI of the larynx, it is necessary to become familiar with the anatomical features of the pharynx. The larynx is the upper part of the respiratory system, located between the trachea and pharynx. The organ is divided into several sections:
- supraglottic – vocal and vestibular folds;
- subglottic - a section located under the vocal folds;
- fold section - vocal muscles and folds, ventricles of the larynx.
The laryngeal framework is a cartilaginous skeleton, the basis of which is the cricoid cartilage. In this case, this cartilage connects to the arytenoid and thyroid cartilage. The frame also includes other cartilages - epiglottis, wedge-shaped, cornicular.