For diseases of the stomach and small intestine, computed tomography (CT) is an effective, painless method of diagnosing the body. Thanks to CT, the doctor can detect defects and pathologies that are not visible with other studies. The tomograph analyzes the received data and generates a three-dimensional image, where you can see not only pathological changes, but also their location and size.
The 3D visualization in the form of a snapshot shows clear intestinal reliefs, thickness and structural changes of the mucous epithelium. CT is prescribed for visual visualization of affected organs, identification of foci of inflammation, tumors and other neoplasms in the stomach and small intestine.
Do they do a CT scan of the stomach?
Examination for diseases of the gastrointestinal system includes clinical, histological and endoscopic techniques. However, in some situations, traditional directions do not provide complete information. Therefore, to clarify the pathological condition, a CT scan of the stomach and other parts of the digestive tract is done. This is a more acceptable diagnostic method for the patient, given that it is performed without swallowing a light bulb (endoscopy). The study allows us to determine the type, location and extent of the pathological process.
Indications
The diagnostic procedure with layer-by-layer sections is a high-precision technique. Specialists most often resort to such an examination when a large process is suspected in a patient. Computed tomography shows: the thickness of the walls of organs, their structure, location, changes in surrounding tissues. Research is used in the following situations:
- Clarification of the stage of the malignant process, the degree of tumor infiltration in the wall of the organ and beyond.
- To detect cancer recurrence.
- To monitor the result of the therapy.
- Determining the cause of displacement of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum or other parts of the digestive tract.
- Detailing the type of volumetric formation when alternative methods do not provide sufficient data.
- Differential diagnosis of cysts, ulcerative defects, infiltrative malignant pathology.
- Determination of probable metastatic foci in parenchymal organs, lymph nodes, bone tissue.
- To reduce the number of unnecessary surgical interventions for inoperable tumors.
Nuances of intestinal examination
Modern techniques used to diagnose diseases of the rectum and duodenum make it possible to identify the cause of pain in the intestinal area, providing doctors with sufficient information, which makes it possible to prescribe the correct treatment.
CT and MRI are designed to examine the small and large intestines. Despite the high level of information content, none of the presented options can act as a separate technique on the basis of which the final diagnosis will be made.
Bowel examination using MRI or CT has the following advantages:
- Reliable and clear visualization of soft tissues. Thanks to the possibility of using special contrast agents, it is possible to assess the intensity of blood supply processes in different areas of the gastrointestinal tract.
- No need for complex preparation. It is enough to remove metal products from the body and you can begin the procedure.
- Painless and absolutely safe. Magnetic resonance imaging does not have any negative effects on the body. CT scanning is not recommended for frequent use. MRI will allow you to obtain images of individual tissues in the format needed to identify the diagnosed pathology.
Examination of the intestine using magnetic resonance imaging does not make it possible to determine functional disorders of the digestive system, as well as to identify autoimmune diseases. Using this technique, only tumors and ulcers can be detected, as well as the condition of the intestinal ducts.
What is a CT scan of the stomach
Computed tomography is the process of obtaining information about an organ through computer processing of X-ray radiation. Refers to complex diagnostic methods. As a result of irradiation of tissues of different densities, sections with images of organs appear on digital media.
CT scan of the stomach is a study that requires special preparation. This is due to anatomical and functional features, given the hollow nature of this section of the digestive system. The examination is performed using a spiral tomograph. The MSCT procedure takes from 20 to 60 minutes.
The fundamental difference between magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography
What are the differences between MRI and CT when examining the intestine? These diagnostic measures make it possible to determine the condition of internal organs without causing discomfort during the examination. In the first and second cases, it is possible to obtain clear images.
A method such as CT is carried out using a tomograph using x-rays. MRI produces a powerful magnetic field on the body, which causes changes in hydrogen atoms in the body. That is why this technique has limitations in use.
Table. Difference between computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging:
| Research methodology | Advantages | Risks and Disadvantages |
| MRI | 1. Assess the degree of transmural and parietal lesions; 2. Allows you to determine the area of tumor localization on the intestinal walls and outside, identifying fistulas. | 1. Insufficient accuracy of imaging of inflamed areas of the mucous membrane or lack of visualization of existing disorders. |
| CT | 1. Detects lesions of the mucous membrane and polyps. 2. It is highly effective in diagnosing large formations and allows visualization of abnormalities occurring outside the intestine. 3. Makes it possible to identify oncological processes at the initial stages of development. | 1. Risks of radiation exposure. 2. Presence of contraindications (pregnancy, obesity, acute pain and severe inflammation). |
What does a CT scan of the stomach with contrast show?
To achieve good visualization, the technique is combined with the administration of special drugs intravenously and orally (by mouth). A CT scan of the stomach with contrast shows the organ more clearly and reveals minimal changes in its structure. The patient undergoes preliminary preparation, which is agreed upon by a radiologist. The optimal route of administration and type of medicinal substance are determined based on the data obtained about the patient and the expected pathology.
Computed tomography is an expensive examination. Therefore, the equipment is installed in large treatment centers or private structures. The price of diagnostics depends on the number of sections, the type and route of contrast administration, and the quality of the equipment. The cost may also vary in different regions and ranges from $45 to $350.
Preparing for the examination
To obtain high-quality information, a person is prepared for research. Before the procedure, the doctor specifies the following information:
- medical history;
- allergic reactions to drugs, especially iodine-containing ones;
- a list of tests performed over the past year;
- results of previous gastric CT studies;
- X-ray load data for 5 years.
Important!
Diagnosis is always carried out on an empty stomach. This means that the last meal should be no later than 6 hours before the procedure.
There are several ways to contrast the abdominal organs. The choice of method is determined by the doctor after assessing the situation in each specific case. They resort to the options presented in the table.
Table 1. Types of computed tomography
| Type of CT examination | Rules of application |
| Using a contrast agent | Within 45 minutes before the procedure, oral administration of Trazograph or Urografin is prescribed. 1 ampoule with a volume of 20 ml is diluted in 600 ml of water and given to drink in small sips |
| With water without contrast | Within 2 hours before the examination, take 1.5 liters of still water, drink 250 ml immediately before the procedure |
Attention! If the patient has not previously experienced intolerance to iodine or drugs that contain it, but symptoms of intolerance are observed while taking contrast, further administration of the substance should be immediately stopped and immediate measures should be taken to prevent the development of an allergic condition.
To obtain high-precision images with highlighting of the tissue structures of the digestive tract, you can do a PET CT scan. This is a spiral tomography with intravenous administration of glucose labeled with a radioactive isotope, most often fluorine-18. The method allows you to diagnose cancer at different stages, including metastases to other organs.
CT scan of the esophagus: indications for the procedure, interpretation of its results and cost
Gastroenterological diseases have become widespread these days. Therefore, to identify them, the most modern diagnostic methods are needed, which include CT of the esophagus.
The procedure is a scan of organ tissue with a layer-by-layer analysis of their condition. Such a thorough examination makes it possible to detect diseases at the earliest stage of development, which makes it possible to carry out full treatment.
CT scan of the esophagus
Computed tomography is usually prescribed to the patient by the attending physician for specific indications. As a rule, it is used when gastroscopy, radiography or ultrasound scanning are not able to provide the specialist with a sufficient amount of information or have a large number of contraindications.
When a CT scan of the esophagus is performed, what the device shows is completely recorded. The display of tissue on the tomograph monitor is of the highest quality. During the study, the doctor takes a large number of images, which allows you to study the course of the pathology over time or monitor the progress of treatment.
Features of the procedure
A CT scan of the esophagus and larynx can be performed on almost any affected area. The study is highly informative because it uses a short step of the apparatus to obtain finer, layer-by-layer images. X-rays that illuminate the patient's body pass through any barriers, carefully recording every millimeter of the surface.
Often, a contrast agent, usually barium or iodine based, is used for better viewing. It is introduced, filling the lumen of the esophageal tube.
Typically, computed tomography lasts no more than thirty minutes, depending on the location of the pathological focus.
The research technique allows you to obtain a photo demonstrating the smallest details of the condition of the internal tissues.
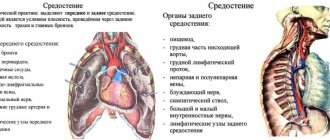
Esophagus, its functions and diseases
This part of the gastrointestinal tract is one of the most important and connects the pharynx to the stomach. Through it, food enters the underlying parts of the digestive tract.
It is necessary to dwell in detail on the anatomy of the esophagus. It is a hollow tube about thirty centimeters long and two wide, stretching quite freely when chewed food passes through.
The structure of the body includes departments:
- Abdominal.
- Chest.
- Cervical.
They are not equal in length and width. The trachea is located behind the esophagus, and its lower end is adjacent to the stomach.
With the help of the muscle layer, food is evacuated to the stomach, where it is digested. Such activity of the organ is designated as motor and becomes its main function. The passage of the lump is facilitated by mucus produced by special endocrine glands located inside the tube along its entire length.
Another goal is to prevent gastric contents from flowing back into the oral cavity. That is, thanks to the esophagus, the process of digesting food is reliably ensured. Due to vigorous activity, the organ is susceptible to a variety of diseases.
The most common pathologies of the esophagus fall into the category:
- inflammation;
- hernias;
- diverticulum;
- cardiospasm;
- reflux;
- neoplasms;
- tumors;
- injuries;
- erosions;
- cancer;
- tissue sclerosis.
Without urgent diagnosis and treatment, they can lead to dire consequences.
For what diseases of the esophagus are CT data important?
Indications for computed tomography are various dysfunctions of its functions, severe belching, the development of tumors of a benign nature, the ingress of foreign objects, any pathologies of the stomach or esophagus.
As a rule, a CT scan of the esophagus is performed for symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases, which include pain, burning, difficulty swallowing food, heartburn, a feeling that something is bothering you inside, nausea, etc.
A similar clinical picture often accompanies inflammatory or infectious diseases, as well as various neoplasms, benign (adenomas, lipomas or papillomas, found in every twentieth patient) or malignant (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, which make up most of the pathologies of the esophagus).
Contraindications for CT
CT of the esophagus and stomach is not recommended if the following restrictions exist:
- bearing a child;
- the presence of large metal implants;
- wearing a pacemaker;
- Cardiac bypass surgery or valve replacement;
- insulin pump;
- the need to use an internal hearing aid;
- neuromuscular conduction stimulator;
- tattoos made on the basis of metallic dye;
- installation of hemostatic clips;
- mental imbalance;
- severe heart disease.
Preparation and performance of CT
In order to get the most reliable results, you need to carefully prepare for the esophageal computed tomography procedure.
The device will make it possible to assess the condition of the organ from three projections. Therefore, you should come to a specialist strictly on an empty stomach, and the period of complete fasting should not be less than five hours.
A few days before the study, it is necessary to exclude liver, dairy or meat products, vegetables, baked goods, fruits, coffee, lemonade, and tea from the diet. It is better to give preference to a slag-free diet.
It is necessary to take Activated carbon and enzymes in advance.
If you have severe nervousness, you need to take sedatives, because the procedure requires complete immobility of the patient. At the reception, you should remove jewelry, watches, items made of iron or other metals. If a CT scan of the esophagus is performed with contrast, then preparation should include allergy tests for the substance used.
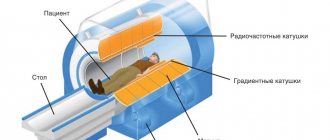
The study is carried out using a special device called a computed tomograph.
- The patient is placed in a supine position on a special table, which is moved for a few seconds into the main chamber, where photographs of the organ being studied are taken.
- The esophagus is scanned using X-ray equipment. A beam of rays wraps around the patient and records all pathological changes.
- It is captured by circular sensors, which convert it into electrical energy, which is transmitted to the computer.
- The signals are amplified and then recorded into its memory using digital information. If there is insufficient data, a command is issued to change the projection, after which the procedure is repeated again.
- The emitter stops when it receives enough data after about three seconds.
Important information about this highly effective examination method is provided in this video.
What does a CT scan of the esophagus show: interpretation of the results
The study protocol indicates:
- location of the pathological focus;
- its nature;
- view;
- various seals;
- tumor volume;
- threat of malignancy;
- risk of perforation of the inner wall;
- condition of neighboring organs;
- degree of neglect of the disease;
- tissue structure;
- ulcerative process;
- presence of metastases;
- their number.
Computed tomography of the esophagus is performed in many medical institutions in Moscow or other cities that have modern equipment.
It is carried out under a compulsory medical insurance policy in public hospitals or for a certain cost in private clinics. The price of the procedure starts from three thousand rubles.
Source: https://GastrituNet.online/bolezni-pishhevoda/diagnostika/kt-pishhevoda.html
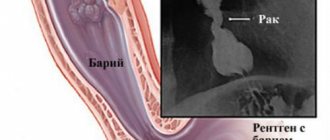
CT scan of the stomach with barium
For many years, barium has been used to contrast the stomach and intestines during X-ray examinations. The method is cheap, so it is still used today. Such diagnostics are not always informative, especially for cancer of the digestive tract. In addition, barium suspension can be retained in various parts, disrupting the motor function of the gastrointestinal system. The solution requires special preparation before use.
When examined layer by layer, the mixture may produce additional shadows and images may be misinterpreted. Therefore, a barium CT scan of the stomach is not performed.
Important! If an X-ray examination with barium sulfate was performed, it is recommended to postpone the CT diagnosis for a week so that the substance is completely removed from the body.
How to do an MRI of the intestines
Before starting the procedure, the patient must take off his clothes and all metal objects: earrings, chains, watches. The tactics of magnetic resonance and computed tomography are different.
An hour before diagnosis, the patient drinks 1 liter of a special liquid (two-phase solution of a contrast agent). This helps to better visualize the contours of the intestine and stretch its walls, which makes it possible to examine darkened areas and bends.
Progress of the procedure:
- The patient lies down on a couch, which slides into a special device.
- The patient must remain motionless for an hour.
Nutrition before CT scan of the stomach
Additional preparation includes proper nutrition the day before the procedure. To obtain a high-quality diagnostic result, a diet is necessary before an abdominal CT scan. 2-3 days before the procedure, exclude foods that lead to bloating. These include:
- legumes;
- bread and pastry made from yeast dough;
- fat meat;
- carbonated drinks;
- raw vegetables and fruits.
You are allowed to eat porridge, lean meats and fish, and steamed vegetable dishes. On the day of the study, food intake is limited. CT scan is performed on an empty stomach. To reduce the manifestations of flatulence, defoamers and sorbents are prescribed for several days.
Contraindications
In most cases, adults tolerate the examination well. However, there are conditions in which X-ray diagnostics with layer-by-layer image acquisition are not performed. CT scanning of the stomach with contrast is contraindicated in the following situations:
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- severe diabetes mellitus, renal failure;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- multiple myeloma;
- with a body weight above 150 kg, taking into account the limitation on the technical characteristics of the device;
- some mental illnesses – schizophrenia, claustrophobia;
- if iodine intolerance is noted.
For young children, CT scans are performed under general anesthesia.
This is due to the need to remain motionless for a certain period of time. Radiation exposure is also taken into account before performing a CT scan.
Pros and cons of the method
When searching for a research technique to make a diagnosis, the choice in favor of tomography is made based on its advantages:
- provides high-quality and clear images of the structures being studied;
- has a high scanning and data acquisition speed;
- performs planar reconstruction of images;
- minimizes the number of artifacts in images caused by physiological movements;
- reveals the localization and identifies forms of inflammation;
- when examined, it covers all segments of the colon;
- does not violate the integrity of the skin;
- does not cause pain or discomfort during examination;
- slight dependence of the quality of diagnosis on the experience of the radiologist.
The disadvantages of CT include the negative impact of radiation exposure on the patient, the inability to collect material for morphological examination, and the risk of developing hypersensitivity reactions to the contrast agent.