Cerebral structures are extremely complex. The brain is responsible for the normal activity of the body, all functions: both voluntary and those that are not comprehended by a person. Millions of transactions take place here.
The possibility of life activity as such is determined by the electrical activity of the nervous system, the transmission of impulses along certain circuits and neural structures. All deviations from the norm are explainable from the point of view of dysfunction, disturbances in the movement of impulses along nerve fibers.
EEG of the brain is a sensitive method for assessing the functional state of cerebral structures using a special apparatus that monitors the electrical activity of the brain as a whole and individual structural components of the nervous system.
There are several modifications of the technique. In particular, there are complex diagnostic methods that reveal clinical issues in different aspects.
The study is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist, as prescribed by him. If there is a reason for it.
The abbreviation EEG stands for encephalography. This is an informative technique, but it alone is not enough. As a rule, a group of studies is carried out: including MRI, skull x-ray, and other diagnostic procedures. Based on the results, conclusions can be drawn.
The essence of the study and what it shows
Diagnostics is based on the registration of special signals from cerebral structures, which precisely indicate certain pathological processes and changes. To better understand what's what, let's turn to the anatomical certificate.
Normally, the human brain works due to spontaneous excitation, the generation of an electrical impulse and its transmission through neurons, the construction of specialized circuits and networks.
This activity causes cerebral structures to vibrate at specific frequencies. Based on this characteristic, experts identify rhythms of different intensities.
For example:
- Alpha waves, which correspond to a state of complete relaxation, half-asleep.
- Beta - during moderate concentration.
- Gamma impulses are associated with increased stress on the psyche and intellectual pursuits.
- And so on, the list goes on.
Special equipment can detect and record such electrical signals and vibrations. In a convenient form, the specialist receives information about the peculiarities of the brain.
Based on the correlation of certain cerebral impulses, the doctor can draw conclusions about the nature of the nervous system and pathological processes. Although the exact data still depends on the results of several procedures.
What can be tracked based on the results of such instrumental diagnostics:
- Brain rhythms, features of electrical activity. In general, regardless of possible pathological processes.
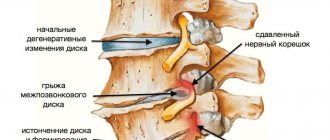
- The emergence of foci of increased excitation. Similar anomalies occur against the background of epilepsy, after injuries and injuries.
- Decrease or increase in the activity of certain areas of cerebral structures.
Thus, the EEG shows inflammatory, destructive, tumor, neurological disorders or indirectly indicates them.
The technique is universal in its way, but does not provide 100% data. Additional measures are needed: MRI, computed tomography, skull x-ray, ultrasound of cerebral vessels.
The encephalography technique itself is heterogeneous. There are several modifications of the diagnostic method. Including EEG, MEG, PEG and others. We will talk about them further.
EEG monitoring
EEG monitoring is carried out to record and recognize brain activity during an epileptic attack.
The patient is hospitalized in a hospital for several days, and all anticonvulsants are discontinued for provocation. Monitoring is carried out with parallel audio and video recording for a day or more.
The method is more effective than conventional EEG for localizing areas of increased seizure activity, as well as for prescribing and monitoring the effectiveness of drug therapy.
What diseases can be detected
The instrumental method is nonspecific. This means that it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on the results alone.
There will remain room for doubts and questions until additional clarifying procedures are carried out.
Still, the method may prompt some thoughts. What diagnoses can be suspected based on the results of encephalography:
Epilepsy
The disease is complex and multifaceted. Contrary to popular belief, it does not always manifest itself “in all its glory”: foam at the mouth, spasms and convulsions, loss of consciousness and falling.
Insidious, silent variants of the pathological process are also possible. When the disease is discovered by chance and as a result of diagnosis for other disorders.
The diagnosis of epilepsy can be made based on the results of encephalography. As a rule, the technique is used several times. To finally verify the essence of the deviation.
Organic and other psychoses
That is, those disorders that directly disrupt the normal biochemistry of cerebral structures. For example, schizophrenia, the consequences of consuming drugs, alcohol, and certain drugs.
An imbalance in brain rhythms is detected as a result of insufficient or excessive signal movement along neurons.
Of course, it is impossible to establish the origin of the violation. To do this, you need to collect anamnesis and monitor the patient for at least several weeks.
Insomnia
As an independent disease or syndrome against the background of one or another pathological process.
The EEG technique is used for routine assessment of the situation, and to obtain more data, doctors resort to studying the circadian rhythm of the brain. This is much more difficult in terms of conducting and deciphering the results.
Psychosomatic disorders
For example, the notorious vegetative-vascular dystonia, which, in fact, is not an independent diagnosis at all. Here again problems of interpretation arise. To understand the essence of the violation, you need to know the context of the situation - it will help you draw conclusions and make an accurate diagnosis.
An EEG is an examination that allows you to identify inflammatory, degenerative, intoxicating, and tumor processes, but only halfway, since a lot of questions remain.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor either puts forward a hypothesis regarding the situation or verifies a previously defined pathological process. Depends on the order of examinations.
In what cases is EEG prescribed?
After a conversation with the patient and studying the medical history, the specialist decides to prescribe encephalography. Typically, indications for an EEG are frequent headaches, sleep problems, fainting, fatigue and chronic fatigue.
Deterioration in well-being may be a sign of disorders in the functioning of the brain. The above ailments often arise due to:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head;
- inflammatory processes in meningitis and encephalitis;
- endocrine disorders;
- malignant or benign neoplasms.
For patients suffering from epilepsy who have undergone neurosurgical interventions and head injuries, EEG monitoring is mandatory.
Indications
The reasons for a brain encephalogram are inflammatory, tumor, neurological diseases and individual symptoms that, theoretically, may indicate a problem.
Specific indications include:
- Insomnia. Various types. Some patients cannot enter a state of rest at all. Others quickly “pass out”, but just as quickly jump up and remain awake all night. And so on.
Insomnia is often associated with neurological problems. Therefore, encephalography is one of the first to be performed to exclude functional disorders.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system. Hormonal imbalances have the potential to alter normal brain function. An encephalogram is used to study the extent to which certain abnormalities affect the activity of cerebral structures.
First, the level of hormones as a whole is measured, and expanded data on the diseased organ is obtained (thyroid, pituitary gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, reproductive structures).
- Dizziness. Disturbances in normal coordination of movements. Movement disorders. What they are connected with, what caused the symptoms, is another question. We'll have to look into it separately and factually.
- Fainting. Impaired consciousness. Syncope is usually caused by disorders of cerebral blood flow and ischemia of brain tissue. There are options. Encephalography will just help to understand the situation.
- Suffered a stroke. Acute disturbance of blood flow in the brain. Affects the nature of the work of cerebral structures, the speed and quality of transmission of nerve impulses. A break in some of the established neural circuits cannot be avoided.
An encephalogram of the head provides an opportunity to assess the nature of the problems, their degree, and the exact location of the disorder.
In addition, tomography is performed to study anatomical and structural disorders in addition to functional ones.
- TBI, neck injuries. Because they rarely go away without consequences.
- Headache. Any location and intensity. The origin again remains a mystery for the time being. Until a full and comprehensive diagnosis is carried out.
- Nausea, vomiting for no apparent reason. Especially if they are repeated on a regular basis.
- Seizures similar to epileptic.
- Convulsions of unknown origin. May be associated with disorders of the central nervous system.
- Previous or suspected inflammation of the brain. Encephalitis, meningitis. The point is to study how much cerebral structures are affected. Also, in this way it is possible to study the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Coma. As part of monitoring the electrical activity of nerve tissue. As soon as the rhythms begin to fade, this is an unfavorable sign. It is corrected in the format of maintaining basic body functions.
- Suspected brain tumors, neoplastic processes.
- Mental development disorders. Usually we are talking about younger patients. Special stimulant drugs are prescribed as needed.
- Mental disorders. Oddly enough, in this way it is possible to study the effectiveness of medications, antipsychotics and others. Based on the results, one can judge the restoration or, on the contrary, regression of brain functions and the quality of therapy.
- Preoperative preparation. Encephalography is mandatory.
- Study of the patient's condition after surgery.
These are the key indications.
Electroencephalography is well tolerated, can be repeated several times, does not create a harmful load on the body and is recommended for patients of all ages; contraindications include acute conditions and pathologies that preclude adequacy.
Types of Stimulating Signals
An encephalogram of the brain is taken according to certain rules: in a state of wakefulness and sleep (infants, complex epileptiform conditions, etc.), under the influence of several types of basic stimuli.
Main incentives:
- periodic photo flashes of bright light with closed eyelids;
- increasing the depth of breathing (hyperventilation) for five minutes;
- blinking movements of the eyelids.
If necessary, a neurologist may prescribe additional elements of stimulation (psychological testing, medications, staying in a dark room for forty minutes, sleeping for 6-8 hours (night sleep), clenching hands into fists, deprivation).
Contraindications
Here are some reasons for refusing the examination:
- Extensive wounds after surgery. Because the affected area simply cannot be disturbed. Infectious problems, suture dehiscence and other pathological consequences are possible.
- Acute psychoses. Because the patient simply cannot sit through the entire procedure calmly and without moving. This eliminates the physical possibility of conducting research.
- Untreated injuries, wounds in the head area. Which is due to the same reasons: you can get an infection or harm a person even more.
- Septic diseases, processes. Up to the banal ARVI, which is associated with obvious distortions of brain rhythms. We need to wait for the right moment.
The list of contraindications is minimal. These are relative options. Once the base is gone, exploration can be done.
Possibilities of electroencephalography of the brain
An electrocyfogram of the brain, through the use of electrical impulses, allows one to assess the state of some problem areas of the brain, the dynamics of bioelectrical activity, and predict the development of some serious diseases.
Sometimes electroencephalography, on the contrary, poses even more questions to specialists than before the procedure, so the patient should not be surprised if, after one procedure, he is suddenly scheduled for another, for example, angiography or MRI. Sometimes a body of research is very useful.
So, EEG research has the following capabilities:
- search for areas of the brain where the onset of epileptic seizures is clearly manifested;
- determining the causes of panic attacks and unexplained anxiety;
- tracking impulses during the period of normal state (without headaches, convulsions);
- determination of the nature of brain pathology. This leads to a disadvantage of electroencephalography - it can only determine the degree of development of the disease and its possible cause. It is, of course, impossible to see the location of the pathology using electrical impulses. For example, in case of a head injury, the EEG procedure does not give an exact indication of the area in which the mechanical impact was most clearly manifested; it does not see damage to the skull bones or cracks, but by tracking electrical dynamics it can predict the appearance of any disease;
- assessment of brain function during sleep and wakefulness. Sometimes this requires the patient to try to relax and fall asleep. The two states of sleep and wakefulness manifest themselves differently in the brain. Under certain circumstances, the doctor needs to see exactly this difference.
The electroencephalogram is usually deciphered by a neurologist, who, accordingly, makes a diagnosis. In the practice of a neurologist, the EEG procedure is a very popular phenomenon.
Types of EEG and their differences
There are 5 modifications of the method.
- The classic method is electroencephalography - a non-invasive diagnosis that is based on measuring the electrical potentials of the brain and the total activity of cerebral structures. This is the most accurate way to study the condition of nerve tissue.
On the other hand, he is very sensitive. An awkward micro-movement is enough to blur the results.
At the same time, the results are affected by stress factors and the patient’s tension. And decoding is very difficult when the doctor is not experienced enough. There is a high risk of error.
- If classical EEG examines the electrical activity of the brain, rheoencephalography (abbreviated REG) focuses on the state of blood vessels. The essence of the technique is the effect on cerebral structures of a low-power current.
Based on the response, the doctor draws conclusions about the condition of the vascular walls, their conductivity and other characteristics. This is a very specific examination method.
- Echoencephalography (EchoEG) is used to assess the anatomical state of the brain. The technique is based on the reflective ability of the tissues of cerebral structures and the density of the substance.
Using echoEG, you can diagnose tumors and other space-occupying formations, and displacement of brain tissue. Which is very important in the early stages, because later treatment becomes unlikely.
- Pneumoencephalography (PEG) is extremely specific. The technique is based on filling the drainage system of the brain with air. It is injected in small quantities through a puncture in the lumbar region.
The technique allows you to measure pressure in the conduction system, assess the likelihood of ventricular dislocation and intracranial hypertension. These are indirect signs of several possible pathologies.
- Finally, magnetoencephalography (MEG), a visual method for assessing the electrical activity of the brain. Using special sensors, the desired indicator is recorded, after which, in visual form, the doctor receives a full-format picture of the distribution of impulses.
This is very convenient, since both foci of increased activity and shifts relative to the norm are visible. The method is used both in medicine and in theoretical scientific research.
As can be judged from the descriptions, none of the methods practically overlaps with the other. They face completely different goals and objectives.
Therefore, these methods can be prescribed in a system determined by a doctor.
Examination stages
An EEG is performed on a child in several stages, during which practically nothing is required from parents. The entire procedure is supervised by a medical specialist, who will tell the child what needs to be done. To better understand the survey, it is useful to consider what steps it contains.
Procedure:
- The child will be taken to a specialized soundproof room where equipment and a couch are located.
- The minor will be asked to sit or lie down and then have a helmet with electrodes attached to their head. It comes in different types, most often resembling a fabric cap or rubber mesh.
- Before connecting the sensors, the scalp will be lubricated with a special gel; in rare cases, the epithelium will also be wiped with alcohol. Clips will be attached to the baby's ears that will not conduct current.
- Further actions depend on the patient's age. The babies are placed on the table or left in the mother's arms. You need to make him fall asleep, otherwise you won’t be able to get accurate results. The examination itself takes about 20 minutes.
- For older children, the procedure is performed a little differently. They need to sit on the couch and take a reclining position. The patient will need to relax and not turn his head, and there is no need to bend over. Such actions can significantly distort the result.
- Next, the specialist will record a background curve that records the state of the brain during calm and inactivity.
- After this, the child will need to open and close his eyes according to the doctor's command. Thanks to these actions, it will be possible to assess the processes of inhibition, as well as excitation.
- If the baby is already three years old, then the doctor will ask him to take a deep breath and exhale, or vice versa, breathe quickly. This test will help identify the presence of a tumor, epilepsy and other hidden disorders.
- At the last stage, the child undergoes photostimulation during an EEG. To do this, the baby will need to close his eyes, after which the doctor will present a light bulb to his head. It will light up and go out at a certain interval, and this test will be useful in identifying problems with the mental and mental development of the child.
The procedure is standard and usually does not cause any difficulties. In most cases it takes about 20 minutes, in extreme cases 30 minutes.
As an exception, the doctor can conduct special tests, for example, to check the reaction to sound, to record the functioning of the brain during deep sleep. The specialist may also ask the child to clench and unclench his fist, or take a light psychological test.
Much depends on the child’s condition, as well as what abnormalities he has or is suspected of having. The obtained indicators will help to understand whether everything is in order with the minor’s central nervous system, as well as whether therapy is helping. In some cases, the analysis is carried out not just once, but several times, if the situation requires it.
All decisions regarding the examination should be made by the attending physician, and parents will only have to listen to his recommendations.
Preparation
No special events needed. All you have to do is come to the clinic. The only exception is pneumoencephalography, but this is a very specific technique that is rarely used due to its invasiveness and a lot of discomfort for the patient.
During the examination, the person must sit or lie still. The fewer voluntary movements, the higher the information content of the technique.
You also need to maintain maximum peace. If there is such a need, it is permissible to use sedatives several hours before the test.
Standard herbal remedies such as chamomile, motherwort or valerian will do. The main thing is not with alcohol. Decoctions and infusions are allowed.
It is highly advisable to follow these basic rules the day before the examination:
- No smoking.
- Do not drink alcohol, coffee, tea.
- You need to remove metal jewelry right in the office.
Preparation for an EEG of the brain means abstaining from psychotropic substances, stimulants, including those of natural origin, and also following all instructions from the doctor’s assistant or the specialist himself.
Progress of the procedure
It all depends on the specific technique and its modifications. In general, the algorithm will be like this:
- The patient lies down on a couch or sits on a chair. It is important to relax as much as possible and suppress the feeling of internal tension.
- The doctor or his assistant lubricates the areas where the sensors are applied with a special gel. This is necessary in order to facilitate the conduction of the signal and its registration.
- A special network of sensors (cap) is placed on the head, which will record brain activity.
- The next step is to check the operation of the device.
- The encephalograph records the diagnostic results, builds a special graph and displays the information on the monitor or in printed form (depending on how old the device is in a particular institution).
If necessary, special functional tests are carried out. They do not pose any particular difficulty for the patient. The doctor gives instructions.
Among them:
- Close/open your eyes.
- Make a fist, relax your hand.
- Breathe hard, quickly and often.
- Noise and light stimuli are also used. This is somewhat uncomfortable, but quite tolerable.
The readings are then recorded again. The sensors are removed from the patient. A person receives the result in their hands after 10-20 minutes or at any other time by agreement.
An EEG with stress tests shows the brain’s reaction to a stress factor, a voluntary motor act, and describes the adaptive abilities of the nervous system. This is significant.
There are other options. For example, when conducting 24-hour encephalography, rhythms are recorded longer, and so on.
Methodology
The EEG technique is as follows:
- Electrodes are connected to the electroencephalograph, which are placed in the form of a cap on the surface of the subject’s head. The standard scheme provides for the installation of 21 electrodes. These sensors are designed to capture potential differences between electrodes in different leads and transmit information about them to the main equipment (device, computer) for automatic processing and analysis. They record at a certain frequency - 5-10 pulses per second.
- The encephalograph processes the received signals, amplifies them and records them on paper in the form of a broken line, very reminiscent of an ECG. During recording, the patient is asked not to move and lie with his eyes closed.
- After a resting EEG, stress tests are performed to assess the brain's response to stress.
- A neurologist or neurophysiologist must interpret the results and issue a conclusion.
The study is carried out in a specially equipped room, protected from noise and light.
How long does the procedure take?
The EEG time depends on the type of study:
| Type of study | Routine EEG | EEG with deprivation | EEG of daytime sleep | Night sleep EEG | EEG monitoring |
| Time | 15–20 minutes | 20 minutes | 1–3 hours | 10–12 hours | from 12 hours to several days |
Decoding the results
Interpretations should be carried out by specialists. Because it’s not easy to figure it out on your own.
Here is a specific example of a diagnostician’s conclusion based on a patient’s EEG:
If translated from medical into Russian, these are minor disorders of the brain. Let's figure it out in order.
- Alpha rhythms are predominantly recorded during diagnosis, since they are responsible for the patient’s state during relaxation. The normal frequency is 8-13 Hz (we have 6-7).
- As for microvolts, the indicator is no more than 100. There are mild deviations from the adequate limit.
- Disorganization can be either an acceptable option (with fatigue, stress), or the result of pathology against the background of blood flow disorders.
- RFS is rhythmic photostimulation. Special diodes are placed in front of the patient's eyes, irritating cerebral structures. In our case, the indicators increased slightly, within normal limits. This rules out epilepsy (which is the first thing they look for).
The reaction in the occipital leads is within the desirable range, since this is where the visual cortex, the final segment of the visual analyzer, is located.
- HV is hyperventilation. That is another functional test. The replacement of the alpha rhythm is due to the gradual relaxation of blood vessels, which is also explainable from an anatomical point of view by the saturation of the body with oxygen and changes in blood acidity.
In any case, deciphering EEG indicators falls on the shoulders of the doctor and is based on the study of rhythms of different types, their frequency and intensity, and the results of functional tests.
Taking an encephalogram for the traffic police, reasons and necessity
According to the rules, obtaining and replacing rights since 2014 is accompanied, in addition to passing a standard medical examination, by taking an electroencephalogram. And by providing the traffic police with a certificate with a link to the EEG.
An encephalogram of the brain allows you to assess the functional state of brain structures. It is capable of identifying a number of pathologies of the brain and central nervous system, those conditions in which a person, while driving a vehicle, can be dangerous to himself and others (epilepsy, neoplasms, anxiety-depressive disorders, etc.).