Indications and contraindications for MRI
As a result of scanning, tomograms are obtained - a whole complex of sequential images with stepped sections. They reflect vertical and horizontal surfaces and form a three-dimensional image. If necessary, the desired area of the image can always be enlarged. Indications for MRI are:
- skull injuries, brain disorders;
- constant headaches;
- frequent causeless fainting, dizziness;
- sudden loss of vision or hearing;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- numbness of the limbs;
- suspicion of fluid accumulation, neoplasms;
- degenerative and demyelinating pathologies of brain tissue;
- assessment of the condition before and after stroke, heart attack;
- control after surgical interventions.
Contrast is used to improve image clarity. It fills tissues and vessels, accumulating in pathological areas, which helps to make a more accurate diagnosis.
MRI has almost no contraindications. The examination is not carried out for patients whose weight is over 150 kg, if they are allergic to contrast, or if they have permanent metal implants in the body. Diagnosis is not recommended if the patient has serious mental disorders, makes convulsive movements or suffers from claustrophobia. However, if tomography is necessary, the patient can be placed in medicated sleep.
The principle of decoding images
Deciphering an MRI of the brain begins with taking many images. They are made in four projections. The film is then mounted on a backlit table or stand. This allows you to detect the smallest pathological abnormalities. During decoding, sections are compared with normal images.
On tomograms, the bones are indicated darker than the nerve areas, and the white medulla is indicated by light spots. For an accurate assessment, it is important to know the anatomy of the brain and its structures. Even if small deviations from the norm are detected, this does not always indicate pathology. Several procedures may be required to confirm the diagnosis.
This is often required to determine the dynamics of the development of the disease and the rate of spread of the pathological process. For example, this is required when a benign neoplasm is detected. Then it is important to track the growth and direction of spread of the tumor and detect the transformation into malignant in time. Also, using MRI, vessels, veins, arteries, and their blood supply are assessed.
To obtain a more accurate picture, a contrast-enhanced tomography is performed. Then the pathological areas are visible more clearly. For example, this makes it possible to detect the development of ischemic stroke. The walls of the vessels are clearly visible - aneurysms, hematomas, blockage of lumens, etc. are visible.
What changes are observed in various pathologies?
The table below shows the changes that are detected using images during the development of various diseases.
| Pathology | Changes in the resulting image |
| Multiple sclerosis. | There are light zones in the place where the white matter is located. There may be only one such spot, but sometimes there are several dozen of them. When interpreting the image, the doctor must differentiate autoimmune pathology from cancer. |
| Huntington's disease. | Foci of depletion of the caudate nuclei (a paired structure that is part of the striatum) are found in the structures of the brain. |
| Gliosis. | Focal formations are present in the white matter area. |
| Vascular aneurysm. | Thinned vascular walls are visible. |
| Tumor. | Space-occupying formations (one or several) that displace normal brain structures are clearly distinguishable. A benign tumor has clear boundaries; malignant tumors do not have such contours. |
| Stroke. | With this violation, a light spot is visible in the image. And in the case of a procedure with the introduction of contrast, a reduced blood supply is noted. With a hemorrhagic stroke, vascular ruptures are detected, which appear as dark cavities. Ring-shaped stripes are visible along their perimeter. |
The doctor can detect Alzheimer's syndrome, pathologies of the cerebral cortex, injuries, bruises and circulatory disorders.
What indicators are taken into account when decoding?
MRI is not a basic diagnostic method. The patient is sent for a tomography after an initial examination, which shows abnormalities or there are suspicions of certain diseases. This is first done using ultrasound, then the patient is checked on a tomograph.
What follows is a sequential transcript of the MRI of the brain. First, the shape of the organ, the symmetry of its halves, the presence or absence of indentations and protrusions are determined. Then the thickness of the medulla in the space between the cortex and the ventricles, as well as the white and gray substance, is assessed. Typically, scanning is done with contrast, which allows you to examine the vascular system, detect tumors in the first stages, metastasis and its spread.
Modern tomographs make it possible to obtain MRI images of the brain with small sections, which increases the accuracy of diagnosis. When comparing results, it is important to take into account the state of the central nervous system, external influences (state of the membranes, canals - auditory and visual, cranial bones, peripheral nerves). They can significantly affect the diagnostic results.
Contraindications
Any hardware diagnostic method, even the most modern and safe one, including magnetic resonance imaging with decoding, has its limitations. Contraindications for MRI of the brain:
Absolute restrictions:
- metal implant in the head area, braces;
- pacemaker;
- tattoos on the body containing a metal component;
- for women – pregnancy at any stage;
- individual intolerance to contrast solutions;
- severe course of kidney diseases, as well as cardiovascular diseases.
Relative contraindications:
- fear of closed spaces;
- the patient's childhood age is up to 5-7 years;
- diseases that do not allow a person to remain in one position for a long time, often of a psychiatric nature.
Before an MRI examination with its transcript, specialists must conduct a personal interview and questionnaire in order to identify possible contraindications to the examination in a person. This allows you to avoid various complications and undesirable consequences in the future.
How is a healthy brain shown on tomograms?
The examination produces images with dark and light areas. MRI of the brain is normal:
- tissues are visualized gray, cerebral fluid is slightly lighter, internal sinuses are completely black;
- with proper brain development, the signals from the apparatus are the same;
- the ventricles are of normal size, even their slight increase or decrease is considered a deviation;
- subarachnoid and perivascular cavities – no changes;
- clear, without inclusions, grooves, convolutions;
- the brain must be in a certain position, without displacement;
- eye sockets, sinuses, auditory canals - correspond to certain values;
- there can be no pathological changes in the tissues.
If an MRI is done with contrast, it should be distributed evenly throughout the vessels and tissues and not concentrated in single areas.
Decoding deviations
When interpreting, tomograms are compared with normal images. Next, the location of the brain, its size and other parts are determined. Digital parameters are evaluated. Brain MRI results show:
- Neoplasms of nervous tissue are shown as light lesions. They are asymmetrical and have uneven contours. They can be single or multiple, put pressure on nearby tissues, and “bite” into the ventricles. Occasionally, other types of neoplasms (for example, hematological malignancies) are detected in the brain. Tomography helps to clearly visualize tumor neoplasia.
- Intracranial pressure. It can be caused by neoplasms. The pressure inside the skull increases when the outflow of fluid from the skull is disrupted (if venous, this is due to compression of the external veins or muscles). This is not visible in the photographs. Intracranial pressure is determined indirectly by the distension of the ventricles and the volume of cerebrospinal fluid.
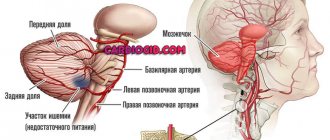
- Cerebrovascular pathologies. To identify them, the diagnostician evaluates the arteries - their thickness, the presence of blood clots or aneurysms in them, as well as fiber disintegration of the walls. If a stroke is suspected, the examination is carried out urgently. During ischemia, areas of softening are determined. They are blurred, have an irregular shape, are darkened, and are located only on one side. With a hemorrhagic stroke, more intense darkened areas appear, and the shape in the area of the supply of the vessel is disrupted. There is a displacement of brain tissue, which may be located behind the nerve tissue, in the area of the ventricles. After a stroke, a pseudocyst with cerebrospinal fluid is visualized. Adjacent tissues are displaced and deformed.
- Multiple sclerosis. It is characterized by the appearance of many light areas in the white matter. At the beginning of the development of pathology there are only one or two such areas, after progression there are dozens. If the examination is performed with contrast, the lesions will be of different colors, since the chemicals accumulate in different quantities.
- Alzheimer's disease. At the same time, tomograms show thickening of small vessels, which provokes chronic cerebral ischemia. Nerve tissues atrophy, the organ appears dry - with deep grooves.
- Parasitic pathologies. Using tomography, cysticercosis is diagnosed, in which one or more darkened, rounded areas are visualized. With echinococcosis and alveococcosis, such areas appear in the nervous tissue, while it is severely compressed. Toxoplasmosis is characterized by foci of petrification. They are denser and darker than the cranial bones.
- Traumatic brain injuries. In this case, bone fragments and hematomas may be visible.
- Vascular atherosclerosis. Such diagnostics are carried out only with contrast. Tomograms clearly show reduced vascular lumens and atherosclerotic accumulations.
- Aneurysms. Thinned and dilated walls of blood vessels are visible.
- Hypertensive angiopathy. The image shows small round lesions located very close to the vessels.
- Hydrocephalus. In this case, the ventricular cavities are greatly expanded, and the subarachnoid and perivascular areas are changed.
- Malformation. The image visualizes radially located vessels connecting in the center.
- Huntington's disease. Atrophied areas of the caudate nuclei are visible.
To determine the nature of the tumor, contrast is required. As the tumor grows, many new vessels appear. Contrast accumulates in them. Its accumulation in certain areas indicates cancerous growth. With the help of contrast, the boundaries of the tumor are clearly visible, and in the presence of metastases, their spread and germination into other tissues.
Interpretation of the results of an MRI study of the brain
MRI is a progressive diagnostic method. With its help, you can even identify anomalies that are not visible with other examination methods. Interpreting an MRI of the brain is a complex process. It can only be performed by a specialist with sufficient experience. Correct interpretation of the results will help make the correct diagnosis and develop a treatment program.
What diseases can be seen on MRI images?
Such an examination helps to identify all abnormalities of the brain and blood vessels. The procedure is prescribed for the following diseases:
- Malformations of the brain.
- Visual or hearing impairment.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms.
- Infectious diseases, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Hematomas after injury.
- Stroke.
- Epilepsy.
- Multiple sclerosis and some other diseases of the nervous system.
- Aneurysm, venous thrombosis and other vascular disorders.
- Dementia.
For these diseases, MRI will become the only reliable diagnostic method.
How are the results deciphered?
After the picture is taken, the doctor immediately begins to examine it. At the very end, he draws up a paper conclusion with all the results of his research and gives it to the patient. If desired, the examination result can be recorded on any electronic medium. This will help the patient show the pictures to various doctors and get a more accurate diagnosis.
Interpretation of brain MRI results consists of the following steps:
- The magnetic resonance tomograph transmits the examination results to a special computer. They are displayed as pictures of the brain. Ideally, there should be 4 projections: front, top, left and right.
- All photographs are printed on film.
- The specialist places all the images on a table with internal lighting.
- Consistently, without missing a single detail, the doctor examines all images. It determines normal values and the presence of abnormalities.
- The doctor draws up all his findings in the form of a written report and gives it to the patient.
The results of MRI of the brain in the form of a conclusion contain information about the shape and condition of all tissues examined. A conclusion is made about whether there are deviations from the norm.
The radiologist does not have the right to make an accurate diagnosis and develop a treatment program. This can only be done by the specialist who issued the referral for examination.
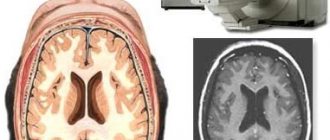
What does a healthy person's brain look like in an image?
MRI of the head helps to obtain images in which tissues are indicated by darkening and clearing. Brain tissue is gray in color. Leaking cerebral fluid appears as light gray streams. The black cavities in the image are intracerebral sinuses.
If all areas of the brain are developed correctly, then the intensity of the signal received from the tomograph will be the same. In a healthy person, the ventricular system should have normal dimensions. Any expansion or decrease is considered a deviation. Normally, there should be both perivascular and subarachnoid spaces. Pay attention to the condition of the grooves and convolutions. There should be no deviations in them.
The structure of the brain itself should also be within normal limits. It should not be displaced. The eye sockets, ear canals and sinuses should be of normal size. No diffuse or focal changes should be observed in the brain tissue.
During the procedure with contrast, you can carefully examine the condition of the vessels. They must be properly developed. The contrast agent should fill all vessels evenly.
If the MRI of the brain turns out to be inaccurate, that is, the image does not have sufficient clarity, the doctor decides to repeat the study. People may move during the procedure, which makes the picture blurry.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes a procedure with contrast. In this case, a special chemical is injected into the patient’s blood. Thanks to it you can get a clear, high-quality image. In this case, it is much easier to decipher the MRI of the brain.
The types of brain MRI results and the norm are prescribed in medical reference books. To identify abnormalities, the specialist always compares the patient’s images with samples from a healthy person.
What do the diseases look like in the pictures?
Deciphering an MRI of the brain is a complex and lengthy process. Even the patient himself can identify some serious diseases in the images. They are clearly visible in the image. These include:
Stroke
This disease is accompanied by cerebral oxygen starvation. The area where hypoxia is particularly severe is indicated by a light spot on the image. If the procedure was carried out with contrast, you can notice how reduced the blood supply is in this area.
Vascular ruptures help decipher the presence of a hemorrhagic stroke. Such places are displayed as dark cavities, which will have ring-shaped stripes along the periphery. Over time, the thickness of such rings will decrease, therefore, the sooner the patient is examined, the more accurately the diagnosis will be made.
Multiple sclerosis
This disease is accompanied by the appearance of nerve fibers that have lost their myelin layer. Such anomalies will be visible on the image as focal formations. During a procedure with contrast, they will have different shades, since they accumulate chemicals in different quantities.
Such lesions can be located in various areas of the white matter. At the initial stage of the disease, as a rule, one or two lesions are detected. As the disease progresses, the number of lesions can number in the dozens.
Neoplasms
When describing MRI of the brain, it is easiest to detect the presence of tumors. They look like light spots that have an asymmetrical shape and uneven edges.
The neoplasm can impair the functioning of surrounding tissues. If the tumor grows quickly enough, the formation of new blood vessels is observed in this area. If cancer is suspected, experts recommend conducting a contrast study. This will help more accurately identify the location of the tumor and the possibility of surgical removal.
Other pathologies
- Vascular atherosclerosis. Determination of diseases of the vascular system is carried out only during studies with contrast. With atherosclerosis, the images will clearly show a decrease in the lumen of blood vessels and the presence of atherosclerotic plaques.
- Aneurysm. The image will show that the walls of the vessels have become thin and expanded.
- Hypertensive angiopathy. The images will show small round cavities located in close proximity to the vessels.
- Malformation. An MRI will show radially arranged vessels that connect closer to the center.
- Hydrocephalus. The ventricular cavities are significantly expanded. The perivascular and subarachnoid spaces are changed.
- Congenital anomalies. Determined by comparing patient images with reference images. If the detected anomalies do not pose a threat to human health, then treatment will not be required.
Deviations from the norm in photographs may appear differently in different people. Therefore, deciphering the results should be trusted only to a practicing specialist with extensive experience.
What can make deciphering an MRI difficult?
The results of MRI of the brain in most cases are accurate and reliable. The contrast procedure always helps to get a clear picture. Therefore, in the absence of any contraindications, it is better to carry it out.
A deteriorated image is obtained in patients with endoprostheses. The presence of metal in them distorts the image. In addition, any metal object left in a pocket may invalidate the test results. Therefore, before the procedure, it is extremely important to remove all jewelry and check the contents of your pockets.
Metal particles may be contained in the ink used to apply tattoos. Therefore, the presence of drawings on the body becomes a contraindication to MRI. They not only worsen the results, but also cause pain during the examination.
The presence of braces can also ruin the picture. In this regard, it is imperative to notify the radiologist about them. If possible, it is better to remove them during the study.
Is it possible to interpret MRI results yourself?
The conclusion of MRI of the brain should be made only by a specialist with extensive experience. In order to correctly determine the presence of anomalies, it is not enough to have samples; it is necessary to have an excellent understanding of the anatomy of the human body. In addition, the doctor must not only analyze the images themselves, but also correlate them with the results of the preliminary examination and tests performed. This is the only way to get a complete picture of the disease and subsequently develop the correct treatment method.
If the deciphered MRI of the brain gives you doubts, you can always get the pictures in hand. The radiologist will give them to you in printed form and record them on any electronic media. You can then ask another specialist to analyze them.
Today it is possible to receive online consultations with specialists. All you have to do is post your photos on a specialized resource. You will receive not only a transcript of the results, but also an explanation of them in simple accessible language. But such consultations should not be taken as final. It is necessary to gather all opinions and consult a doctor you trust.
Remember that you need to do an MRI of the brain and get a transcript only from a specialist with extensive experience in practice.
Syrchin Vladislav Leonidovich Doctor Radiologist of the Highest category Experience - 16 years
Fadeev Stanislav Viktorovich Doctor Radiologist Candidate of Medical Sciences Experience - 15 years.
Factors that complicate decoding
In general, MRI images are clear, especially when contrast is injected. A blurred image may occur if the patient moves during the scan. Also, poor pictures are typical for people who have endoprostheses inserted. Any metal objects distort the image.
Therefore, before scanning, the patient takes them off. There may also be metal particles in tattoo ink. In this case, the patient may feel slight pain during the examination. Also, the picture is distorted by braces; they must be removed during scanning.
Self-decoding
MRI interpretation is a complex procedure that requires special knowledge and especially brain anatomy. To draw correct conclusions, you need to have normal images, a table of indicators, and be able to correlate detected deviations with them. In addition, many other factors that could have a negative impact play an important role.
MRI images are given to the patient and, if desired, you can try to understand them yourself. This can be done through online consultations. You can use the following short diagram:
- the cerebral cortex, temporal regions and the back of the head are determined;
- black spots on the images indicate spread of cerebral fluid, white spots indicate tumors;
- the brain should have smooth edges and a uniform structure;
- bright gaps indicate existing pathologies.
However, in any case, independent decoding cannot be taken as a final diagnosis. To do this, ordinary people who do not have a medical education do not have enough experience and practice. An MRI of the brain can only be concluded by a specialist.
Magnetic resonance imaging is the best diagnostic method, although it is very expensive, so it is not used as an initial method. The magnetic field allows you to evaluate different structures and identify pathological foci. Brain examinations are carried out mainly on high-field tomographs with high power, which expands diagnostic capabilities and increases information. As a result, many pathologies are detected in the early stages, which allows timely treatment to be prescribed.
- What diseases does MRI of cerebral vessels detect?
- CT scan of the brain
- CT and MRI - what's the difference?
- Ultrasound of neck vessels
- Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI
Survey histories
Svetlana: MRI did not confirm pituitary adenoma
December 2020
For a long time my husband and I tried to get pregnant. The attending physician prescribed examinations that would help determine the cause of infertility. One of them was a hormone test. As a result, it turned out that the prolactin content was greatly increased.
The gynecologist sent me to an endocrinologist, who told me to go for an MRI of the brain. The doctor noted that a pituitary adenoma may have developed, causing the hormone levels to become high.
Nothing to do. I had to go for the procedure. I was very afraid of the scan, because they complained on the forums that they found all sorts of abnormalities.
Moreover, it is not very pleasant to be in a closed device, and I am afraid of confined spaces. In fact, everything went well. It was uncomfortable, but tolerable. And the staff showed a truly humane attitude.
The conclusion states: no MRI evidence was found for the presence of focal or diffuse changes in the brain substance. The doctor said that I do not have any adenoma. Well, that's one less problem. Now we need to look for another cause of infertility. I hope that we will still become parents.
Anastasia: they did a brain scan on the child
March 2020
My son is 12 years old. He is quite a smart and active boy. He often hit his head. Recently he began to complain of pain in the forehead. We contacted a neurologist at our place of residence, who referred me for various studies, including MRI.
The procedure went well. All this time I sat next to my child and read aloud so that he would not be afraid of the closed tomograph.
Having received the conclusion, I learned that in the white matter of the right frontal lobe there are single small foci of irregular round shape with clear contours. Their size does not exceed 0.25 cm.
The formations are more likely of dystrophic origin. Fortunately, no other pathology was detected. The specialist indicated that these are foci of the above-mentioned formation.
Of course, I was seriously scared and immediately consulted a doctor. She reassured me that such a condition does happen. Since the son has no additional complaints, dynamic observation was suggested. She prescribed maintenance treatment and told me to go for regular check-ups. I hope serious illnesses will pass us by.
Andrey: headaches were associated with osteochondrosis
March 2012
About 7 years ago I suffered a serious injury to the top of my head and spine due to an accident. Pain appeared in the first area, which went away only with analgin. I decided to see a traumatologist, who advised me to see a neurologist.
At the appointment, the doctor listened to the complaints, checked the reflexes and gave directions for examinations. I went for an MRI of my brain and cervical spine. The scan itself was quite tolerable. There is a large device with a special retractable couch where the patient is placed.
A device similar to a remote control is placed in your hand. It is necessary in case you feel unwell. But it wasn't useful to me.
The brain was filmed for about half an hour, and the cervical region for about 40 minutes. The scanner made a loud knocking and buzzing sound. It was impossible to move, so as not to “blur” the picture.
After the scan, the doctor describes the image for about an hour. When completed, it produces an image with a conclusion. It turned out that there were no focal or diffuse changes in my head, but protrusion of intervertebral discs was discovered in my neck.
I have never regretted the procedure or the amount spent (and it is not small!). Thanks to magnetic resonance imaging, he received adequate therapy.
Against this background, headaches no longer bother me. In order not to worsen the condition of my neck, I regularly undergo MRI and treatment. I wish you all good health! May there never be an indication for a scan.
Olga: MRI helped make an accurate diagnosis
October 2020
In September of this year, my dad had a blood pressure surge. The day before, he became seriously nervous, and his blood pressure soared to 200/160 mm Hg. My father felt unwell, his speech and coordination deteriorated. We immediately called an ambulance, because about 2 years ago he had already had a similar attack.
Dad was hospitalized and many tests were prescribed. Analyzes did not reveal any serious abnormalities, so they decided to treat him and send him home.
After 2 weeks, no improvement was observed. I asked the doctor to conduct additional examination methods. The specialist ordered an MRI of the head.
It turns out that 2 years ago dad suffered a mini-stroke! Our family was in shock. As we were told, the image showed areas of clearing and smoothness of the convolutions in this area.
Of course, his therapy was adjusted and completely different medications were prescribed. I hope they will give the desired effect.
As for the MRI itself, it gave us hope for my father’s speedy recovery. Dad says that the procedure is not at all scary and painless. If you have any problems and conventional tests do not help make an accurate diagnosis, do not be afraid to undergo a tomography. This is an opportunity to have a healthy life!