What it is
MSCT is a multilayer computed tomography (angiography), which is a more modern type of CT. Sometimes it is called multi-slice, multi-spiral. During a session, you can do MSCT of the brain and skull bones. This allows you to quickly get a complete picture of the patient’s condition, which is important when minutes count.
The method is based on the ability of X-rays to pass through tissues of varying densities, moving in a spiral . As a result of the study, an accurate image of the brain is obtained on the monitor. With the help of the first devices, doctors could obtain 2 slice images per session.
Now the technology is more advanced and 320 images can be taken in one procedure. This significantly improves the effect of multi-slice tomography. New capabilities allow you not only to see the image, but also to monitor the processes occurring in the brain in real time.
Most often, MSCT is prescribed for scanning skull bones, since the device is good at examining hard structures. After the session, a three-dimensional image is obtained in which all the details are clearly visible. The method is used for injuries to determine the extent of damage and prescribe the correct course of treatment.
Advantages of MSC brain tomography
The session is a kind of CT scan. Scanning is carried out using the latest generation equipment. The device settings have been improved; they help change the scanning mode at the doctor’s discretion and help differentiate each desired area. With MSCT angiography of cerebral vessels, the parts of the examined organ are displayed on a panoramic image in the smallest detail.
To perform MSCT of the head, a device with great functionality is used. The use of equipment significantly reduces the load from x-rays. This minimum dose cannot be achieved with standard tomography. Also, the use of the latest generation equipment allows us to reduce research time.
Modern devices reduce the number of contraindications. It becomes possible to perform MSCT of the head region for obese people weighing over 120 kg, as well as for patients with fixed dentures or a pacemaker.
The process of using a contrast agent looks different. The drug is used in a minimal amount; it is administered with a compact injector built into a special device. The injector operates automatically. The method is called bolus contrast; it allows you to control the dosage of the dye as accurately as possible. This measure reduces the load on the kidneys several times when contrast is used.
What is MSCT of the brain? This is scanning the desired areas. To perform a full session, only one revolution of the device capsule is enough. Some tests take about a minute. Multilayer MSCT of the head is the performance of several images of an organ in a section. As a result, scanning allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image of the organ. Using this method, early stages of cancer are detected.
Benefits of the procedure:
Possibility of diagnosing patients suffering from claustrophobia. Open types of tomograph are suitable for children and elderly patients, people who experience fear in closed spaces. The devices allow diagnostics for sedentary people, as well as patients with psychosomatic and mental disorders.
MSCT devices operate silently and do not create psychological discomfort for the person being examined. Spiral devices work well - MSCT of brain vessels with contrast is more informative.
The required cut parameter is set by a specialist, which is very convenient for scanning. The doctor sets a minimum cut of a millimeter. This allows pathology to be detected at a very early stage.
Special devices record all layer-by-layer scanning signals received from the sensors. The computer processes the information and transforms it into an overall picture. In the image, the doctor perfectly visualizes the details of the brain. X-ray is a less informative diagnostic method. However, its cost is accessible to all social strata.
Comparison with MRI and CT
What MSCT and MRI have in common is layer-by-layer scanning of tissues. But, unlike MRI, the multispiral method does not use a magnetic field. In addition, MSCT is often used to examine hard tissues - bones, cartilage, etc., while MRI is effective only for soft structures. It does not use X-rays, which makes magnetic resonance imaging acceptable during pregnancy.
MRI is not performed if the patient has metal implants. Another difference is that MSCT is used not only for examining the brain, but also for other organs. MRI is performed only to diagnose head structures.
Unlike classical CT:
- MSCT of the head is performed faster (session time reduced to 5 minutes). This allows the method to be used by people suffering from claustrophobia, the seriously ill, connected to life support systems and children.
The method is used in emergency situations, since thanks to the high scanning speed, people can be quickly examined.
- The examination result is more accurate, since the doctor sets the necessary settings to obtain the required image.
- The patient is not exposed to much radiation.
- The procedure is performed quietly, which ensures patient comfort.
- If there is a need for a contrast scan, the patient is injected with less colored liquid than with other diagnostic methods.
- The patient is injected with contrast using an injector located in the device body. The procedure is performed automatically and is called bolus contrast. The amount of fluid administered is controlled by the device. The patient can also be given a contrast agent using a dropper.
- The information content of the procedure increases, since data from different planes is used to obtain an image.
Alternative research methods
In addition to MSC scans of the brain, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), which is also carried out using a special tomograph, is considered an informative and reliable method of examination. What it is? Thanks to MRI, it is possible to obtain layer-by-layer clear images of internal organs in the desired projection. Both methods are good and give really accurate results, but differences still exist, namely:
- MSCT perfectly visualizes the ventricular system of the brain and pathological changes in the bones of the skull.
- MRI diagnostics are quite good at recognizing abnormalities in gray and white matter tissue.
MSCT results on a computer screen
You can undergo an MSCT examination yourself, without a doctor’s prescription, but despite this, before scanning it is recommended to visit a doctor who will determine whether there are contraindications to such a procedure. You can undergo diagnostics at a medical center, which is equipped with a working and modern tomograph. Medical center specialists must have skills and experience working with such equipment.
Worth remembering! The results obtained do not constitute a medical opinion or an accurate diagnosis!
Indications for use
Most often, MSCT of the head is prescribed:
- for traumatic brain injuries;
- for the diagnosis of primary and secondary brain tumors;
- for tumors of the meninges;
- inflammation in the middle ear;
- leakage of cerebrospinal fluid due to injuries of the base of the skull;
- hematomas, brain cysts;
- hemorrhagic strokes;
- vascular aneurysms.
The method makes it possible to conduct a comprehensive examination of the skull bones and soft tissues of the brain in one session. During an examination of the head, MSCT gives the image:
- cranial vault;
- temporal bones;
- paranasal sinuses;
- skull base;
- vascular system of the brain;
- cavity structures.
The manipulation is carried out before brain surgery in order to study the condition of the tissues and perform surgery as quickly and successfully as possible. Multi-slice diagnostics are carried out in cases of impaired consciousness of the patient, paralysis/numbness of the facial muscles, decreased vision, headaches/dizziness.
In the postoperative period, MSCT allows you to monitor the recovery process and determine the effectiveness of the chosen treatment. The method helps diagnose pathologies of the temporal bones that lead to hearing loss.
Indications
MSCT of all cerebral vessels is a procedure necessary to identify the condition after a stroke and for a number of other ailments. An examination of the organ should be performed if it is necessary to identify the causes of confusion and numbness. The study is necessary to undergo in case of injury, constant dizziness and fainting.
The diagnostic method is prescribed by doctors:
- to detect vascular pathology;
- for diagnosing arterial hypertension;
- to localize a cyst or tumor;
- before surgery;
- for diagnosing hearing loss;
- to determine the causes of dizziness and fainting.
The procedure is necessary for cancer therapy. It allows you to clearly monitor the condition of the affected areas and see the results of the prescribed drug therapy. Tomography has been used by doctors for a very long time. When performing a scan, all the nuances of the pathology are revealed. Preparing and conducting the session does not have any difficulties.
How is the examination carried out?
To perform MSCT of the head, the patient sits on a couch. The upper body is placed in the apparatus. Sensors rotate around a person's head to scan the tissue being examined. The movement occurs in a spiral (hence the name of the procedure). If the area being examined is small, one revolution of the device is sufficient. A full brain scan will require a lot of effort. The procedure is usually performed without contrast.
Tissue scanning is carried out in 1 mm increments. This image allows you to see foci of the disease of minimal size.
For high-quality scanning, detectors (sensors) are installed in a row in the device body. The most accurate result of MSCT of the head is obtained in machines with 64 detectors. But there are devices with a smaller number of sensors: 2, 4, 16, 32.
The speed of passage of the substance through the vessels is high. This and high resolution makes the picture clear and detailed. Such technical characteristics allow you to create a 3-dimensional image of tissue on the screen.
Despite the fact that radiation is used for the study, it is so small that the patient does not feel a headache after the procedure.
What is a CT scan of the brain?
Despite the fact that CT is a radiological research method, the data obtained during a CT scan is an order of magnitude more informative than the results of classical radiography, and what a CT scan of the brain determines is of great importance in an accurate and timely diagnosis.
During computed tomography, a series of black and white images are obtained in three planes:
- frontal, which is carried out along the base of the zygomatic arches through the external auditory canals;
- axial, carried out through the external auditory canals along the lower edge of the orbits and in this projection the temporal bones, jugular foramen, cranial fossae and foramen magnum are clearly visualized;
- sagittal, which divides the study area into left and right symmetrical halves.
A series of images obtained can be reconstructed into a three-dimensional picture of the brain, which makes it possible to judge the spatial location of its structures and the relationship of pathology with unchanged tissues.
CT image acquisition is based on the different densities of different tissues and structures of the brain. Therefore, pathological disorders can manifest themselves either as darkened “dense” areas, for example, in the case of a tumor, or as “clearing” areas, as in the case of cysts, or their alternation.
Some pathologies may not be accompanied by a significant change in X-ray density compared to unchanged tissue, but are manifested by a change in the size of the head structure, deformation, dilation or narrowing of blood vessels, etc.
With intravenous contrast, pathological lesions are stained more intensely than healthy areas, which helps to increase the resolution of CT.
Contrast study
To obtain a clearer image, in some cases, the patient is injected with a colored liquid. Vascular examination is carried out only with contrast. The liquid entering the vessels stains them and on the monitor the doctor clearly sees the state of the vascular system.
Examination of brain tissue can be carried out either with or without a colored substance. For a complete examination of the brain, the patient may be injected with a contrast agent. The decision about the need for such a step is made by the attending physician and the radiation therapy doctor.
The colored substance is a nonionic composition with iodine. In addition to examining blood vessels, it is usually used to detect brain tumors. MSCT with contrast makes it possible to see malignant tumors - to determine the boundaries of neoplasms, the stage of development of the pathology, and the presence of damage to parenchymal tissues.
The contrast agent is excreted from the body within 24 hours by the kidneys. After administering the liquid, a person may experience a metallic taste in the mouth and a sensation of heat spreading throughout the body.
MSCT of the head: what is it, indications, preparation - MEDSI
Table of contents
- What is MSCT for brain research?
- Indications for prescribing the MSCT procedure of the head
- How is MSCT performed?
- Differences between MSCT and MRI
- Contraindications and risks
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
MSCT (OR SCT)
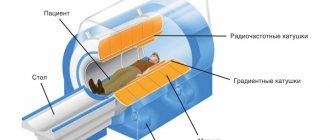
– multislice (also multislice) computed tomography. A radiation diagnostic method that allows you to achieve highly detailed images of an organ. It differs from conventional CT by the arrangement of sensors that move around the patient in a spiral (hence the name), thus increasing the scanning field and reducing procedure time.
What is MSCT for brain research?
MSCT of the brain is a multi-slice scan of brain structures. Depending on the settings of the tomograph, it can record both soft tissues of different densities (vessels, glands, brain tissue and meninges) and bone structures of the skull. The procedure lasts up to 20 minutes, depending on the purpose and scope of the study.
MSCT of the brain is prescribed:
- If a stroke is suspected - in order to clarify the focus and extent of the lesion (ischemia, bleeding, hematoma)
- For the diagnosis of neoplasms (cysts, tumors, infiltrates), their location and size
- For obsessive headaches, dizziness, double vision and other meningeal symptoms of unknown origin - in order to clarify the diagnosis
- If you have symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
- When performing a biopsy of neoplasms of brain structures - for the purpose of better visualization for greater accuracy of the procedure
- After a head injury to assess the degree of damage to the brain and membranes, the presence of bleeding, foreign bodies
- To assess the condition of blood vessels and the level of blood supply to the brain (for atherosclerosis, ischemia, aneurysm)
To study the condition of the vessels, a radiopaque substance is used, which makes it possible to trace the vessel along its entire length: to assess its integrity, filling, and patency. With the blood flow, it passes through the vessels, highlighting them in the picture. CT uses iodine preparations, which are then excreted from the body by the kidneys.
Contraindications for the use of contrast:
- Kidney failure
- Regular use of Metmorphine (for diabetics)
- Intolerance to iodine-containing drugs
- History of hypersensitivity reactions (anaphylactic shock, angioedema), asthma
MSCT devices administer a contrast agent as a bolus - automatically, in a strictly dosed mode. This method allows you to reduce the dose of the drug.
Indications for prescribing the MSCT procedure of the head
- Examination of the bone structures of the skull in cases of suspected microdamage, structural changes, metastases
- Examination of the temporal bones in the presence of pathologies of the auditory or vestibular apparatus
- Oncological search (determining the localization of a tumor in an organ if its presence is suspected) and diagnosis of small focal neoplasms up to 1 mm in size
- Control of antitumor therapy
- Determining the causes of impairment or lack of consciousness
- Suspicion of stroke, cerebral edema, intracranial bleeding, hematoma or hemorrhage
- Assessment of the state of the hypothalamic-pituitary system
- Diagnosis of vascular disorders
- Preparing for surgery
- Clarifying the indications of conventional CT or MRI
How is MSCT performed?
- The device is adjusted to the desired structure depending on its density
- The patient changes into loose clothing without metal parts (usually a light disposable gown)
- All jewelry, watches, and dentures are removed during the procedure.
- The examinee is comfortably placed on a flat movable couch and fixed on it
Further movements will be performed only by the device:
- The couch progressively moves into the device as the desired area of the body is scanned, and the sensors rotate around it, illuminating the selected structures
- The patient does not experience any sensations during the procedure
- When a contrast agent is injected, a slight metallic taste in the mouth and a feeling of spreading warmth may occur, but this quickly passes
Differences between MSCT and MRI
- Visualization method: in MSCT - these are x-rays, in MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) - magnetic waves that are reflected from tissues
- Accuracy: MSCT is more accurate than MRI
- Oncological diagnostics: MSCT is preferable
- Indications: MSCT is the method of choice for visualizing bone structures, MRI for soft organs and tissues
- Contrast agent: in MSCT – iodine preparation, in MRI – gadolinium (less allergic than iodine)
- Frequency: MSCT – no more than 3 times a year, MRI – without restrictions
- The presence of metal and electronic implants in the body, tattoos with metal-based paint: MSCT - with caution, MRI - contraindicated
- Children's age, pregnancy: MSCT is contraindicated, MRI is allowed from the 12th week of pregnancy (children under 7 years old are performed under anesthesia)
- Duration of the procedure: MSCT – 15–20 minutes, MRI – up to 40
Contraindications and risks
An absolute contraindication to SCT is some types of oncological pathologies. The main restrictions relate to the use of contrast media.
But there are some risks that the patient should be aware of:
- Frequent CT scans at a young age increases the risk of development, worsening or recurrence of cancer
- Research may lead to malfunctions of electronic implants
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- The availability of new generation MSCT devices allows the procedure to be carried out as quickly as possible and the radiation dose to be minimized
- High accuracy and detail of images allows early diagnosis of pathology, which improves the prognosis of the disease
- Research is carried out by qualified and experienced doctors who constantly improve their knowledge and skills in radiological diagnostics.
- The service includes more than 25 types of research
- A wide network of clinics makes the MSCT procedure accessible to residents of any district of Moscow
Make an appointment by calling 24/7 8 (495) 7-800-500.
Do not delay treatment, consult a doctor now:
- MSCT (multi-slice spiral computed tomography)
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- Express diagnosis of the causes of headaches
What does a study using MSCT give?
A computer examination of the brain allows one to determine not only structural, but also qualitative changes in the condition of tissues.
When examining the head, MSCT helps to identify:
- the amount of cerebral edema;
- displacement of structures;
- state of the subarachnoid space;
- small focal hemorrhages;
- hematomas and their outer and inner layers;
- inflammatory processes resulting from traumatic brain injury;
- the presence of pus in the subdural and epidural space;
- vascular condition;
- hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension;
- tumors and cysts of soft tissues, cartilage, bones.
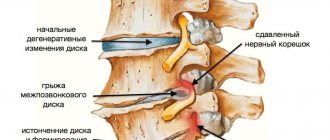
The procedure detects the onset of degenerative changes in brain tissue. This makes it possible to stop the process at an early stage.
What does it show
An informative method helps the doctor recognize any brain pathology. The session allows you to identify:
- brain diseases;
- stroke;
- hemorrhage;
- fractures of the cranial bones;
- aneurysm;
- bleeding;
- hematoma spot;
- cyst;
- tumors;
- inflammation.
Using a tomograph, the structures of the cerebellum, pons, hypothalamus, and thalamus are visualized. Both hemispheres of the brain are thoroughly examined.
The brain is the main element of the entire central nervous system. Its structures contain a huge number of neurons that create certain electrical impulses. Special connections are formed in the brain; the organ exercises control over all systems of the body. It controls the functions of all internal organs, ensures the necessary reactions and the formation of connections.
When the disease occurs, natural control and communication mechanisms are disrupted. A detailed examination using MSCT helps to identify the causes of disorders and the development of pathology. Some pathologies are congenital. The procedure shows the localization and parameters of the pathological focus, all the smallest changes in nearby tissues.
It is especially important to perform a session after a stroke. The results of the procedure will help the doctor prescribe the correct therapy to restore vital functions. The image clearly shows all pathological changes in organic structures and in the walls of blood vessels.
Contraindications to the procedure
MSCT of the brain is a fairly safe procedure. It does not cause any particular harm to human health. But there are a number of contraindications: asthma, pregnancy, kidney pathologies, heart failure, allergies to contrast agents, multiple myeloma, diabetes.
The last contraindication is not absolute. The procedure is not used for people taking metformin. If a day before the procedure a person does not take the drug, MSCT is still performed.
Multi-brain scans are not usually performed on children. But in extreme cases, they weigh the pros and cons and make a final decision on the advisability of carrying out the procedure on the child.
Contraindications
A CT scan of the brain can be performed using special contrast agents, so it is not recommended for use if you are prone to allergic reactions, especially if you are hypersensitive to iodine-containing drugs. Also, computed tomography is not performed if the level of creatinine in the blood serum is elevated, severe bronchial asthma or in the presence of hypothyroidism.
Pregnant women are advised to use alternative testing methods due to the risk of exposure of the fetus to radiation. Young children also have a higher sensitivity to radiation, so they undergo CT scans of the brain only when strictly indicated. It is worth noting that X-ray radiation increases the risk of cancer, so unnecessary CT scanning is unacceptable.
In addition, very obese patients may not fit into the tomograph opening, or their weight may become an obstacle to moving the special table on which the patient should be placed during the examination.
An important disadvantage of brain CT is that it cannot detect the inflammatory process in the meninges.
Possible risks and complications
Modern diagnostic devices emit a minimal dose of radiation. They usually do not cause discomfort or complications. Side effects from MSCT of the head are rare, but they do occur.
Complications may appear in the following cases:
- Repeated manipulation can lead to the development of cancer.
- If the patient has electronic stimulators, under the influence of radiation, malfunctions of the devices may occur.
- A person may be allergic to contrast.
The greatest disadvantage of MSCT is the high cost of the procedure. But, in comparison with the result that is achieved during multiscanning, this question is removed. Another problem is that angiography machines are still very rare.
Indications for CT scan of the head and neck
Computed tomography of the head carries a certain radiation load on the body, so scanning is recommended no more than 3 times a year for emergency indications.
The interval between studies should not be less than 4 weeks. For preventive purposes, experts do not recommend undergoing examination, as the X-ray load on the body increases. The main indications for CT of the head and neck are:
- dizziness and tinnitus, the causes of which have not been established;
- anomalies in the development of bone structures of the head, blood vessels;
- suspicion of the development of a hernia in the cervical spine;
- neck and head injuries;
- suspected tumors of the head and neck;
- headache;
- identifying dilation of blood vessels in the neck and head;
- signs of cerebrovascular insufficiency.
When contacting specialists at the Yusupov Hospital with these signs, patients receive advice on the scope of diagnostic measures to identify the causes of the pathology, after which they are sent for diagnosis.
Make an appointment
Preparation for MSCT
Before the procedure, the patient must tell the doctor whether he is allergic to iodine and what medications he is taking. If there is an allergy to iodine, the person is given steroids. A multispiral examination of the head will be successful if you follow the rules:
- do not eat 4 hours before the procedure;
- do not drink tea, coffee or smoke before the session;
- show the doctor the results of previous studies, if any;
- undergo an examination to clarify whether the patient has contraindications to MSCT;
- Tell your doctor about previous illnesses.
If contrast manipulation is performed during lactation, after MSCT you should not breastfeed the baby for several days. This allows the contrast liquid to be completely removed from the mother’s body and makes the milk safe.
To undergo the procedure, wear loose clothing that does not restrict movement and does not pinch blood vessels and muscles. Before the session, the person is advised to remove metal objects, including jewelry.
MSCT is performed not only to examine the brain, but also other organs. The method allows you to diagnose diseases more accurately, quickly, without significant damage to human health. The decision to use MSCT of the head is made only by the doctor.
MSCT with contrast
Contrasting involves intravenous injection of a dye into the venous bloodstream. An iodide preparation is used, after administration it stains the walls of blood vessels. In the photographs, the areas stained with the product are clearly visible, tumors and cysts are clearly visualized, which makes it possible to identify the features and nature of the neoplasms.
Before the session begins, the patient undergoes a mandatory allergy test. A small amount of contrast is injected into the patient's body. Doctors are monitoring the person. In the absence of allergies, the contrast is completely introduced into the body. If you are allergic to iodine, the test is not performed. Before the session, doctors identify the patient’s characteristics and the body’s needs. If there are contraindications, scanning is not performed.
What does MSCT of the brain determine?
In addition to the main aspects of the purpose of CT, multispiral examination, due to its diagnostic depth, is indicated to identify the causes of:
- pain in the middle ear;
- manifestations of subatrophy (the initial stage of neuron death);
- vascular malformations (pathological connections);
- changes in the cavities of the brain (hydrocephalus, intracranial hypertension).
Angiography is often used when performing a biopsy of a region of the brain to control the manipulation. The procedure is periodically prescribed to patients after brain surgery to evaluate the rehabilitation process, as well as to check the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy.
Congenital anomalies - indications for research
The latest capabilities of CT scans of brain vessels
Nothing stands still, and even relatively new computer diagnostics, such as brain tomography, have been replaced by an even more modern technique - MSCT (multispiral computed tomography). What is it and what does this examination show? This is an analogue of CT, which has higher diagnostic capabilities. Multislice computed tomography of the brain creates such a high-resolution image that the diagnostician notices even the smallest changes in tissue structures.
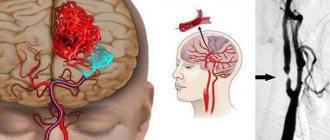
What is cerebral angiography?
With such an examination it is almost impossible to miss the initial stages of pathological processes. This type of diagnostics appeared in the late 90s of the last century, and continues to develop in various directions in the study of the human body. One of the important and indispensable examinations developed on the basis of the multispiral method is MSCT angiography - visualization of cerebral vessels.
As you know, vessels are hollow organs, so angiography is performed with the introduction of a magnetic contrast agent, which fills the vascular space, making it visible to X-rays. Contrast is injected intravenously at certain time intervals during the procedure, and as a result, the doctor receives images of the vessels at different phases of the drug. This examination allows you to take pictures of the vessels of the head with an interval of less than 1 mm, which allows the specialist to carefully examine even the smallest disorders and tissue changes.
With this method, small neoplasms, minor developmental anomalies and degenerative lesions as a result of injuries, ischemia and other pathological processes are not ignored. The speed of creating images with MSCT is very high. A large number of them are performed in a short time, which makes it possible to simulate the three-dimensional structure of the vessels, in contrast to the two-dimensional one with conventional CT. In addition, such reconstructions can be obtained in any necessary plane, and MSCT requires much less irradiation of the body.
Is it harmful to do
Is CT harmful to health: computed tomography is a radiation exposure. The annual permissible dose of radiation exposure per year is 150 mSv. If you receive a smaller dose, the body is not damaged; if it is more, the likelihood of mutations and the development of radiation sickness increases. One CT scan of the brain is equal to 2 mSv. That is, the harm of CT scans to the body from radiation exposure tends to zero, since this value does not reach 150 mSv.
Is CT scanning with contrast harmful? Pharmacological drugs consist of chemical compounds to which, when administered, the body can respond with an allergic reaction. They come in 3 types:
- Subtle side effects. They develop in 5 out of 100 patients. These are dizziness, nausea, sometimes vomiting, headache, burning sensation, flush of heat, pain at the site of needle insertion. These side effects are normal and go away on their own.
- Moderate side effects. Basically these are massive swelling of the face, difficulty breathing, lack of air. This condition requires immediate emergency care.
- Severe side effects. This includes cardiovascular failure and fainting. This occurs more often in people who have a history of allergies to other substances. Resuscitation measures are used here.
To prevent side effects, allergy tests are usually carried out: a light wound is made on the subject, where small doses of the allergen are applied, after which this area is studied to see how the skin reacted. Also, to reduce reactions, antihistamines that have an antiallergic effect are administered before the procedure. Is it harmful to do a CT scan? Computed tomography itself is harmless, but contrast agents can cause damage.