Ultrasound of the brain in an infant is the most common way to examine parts of the central nervous system, their blood vessels and surrounding tissues. Due to the speed, high accuracy and painlessness of the procedure, this method allows you to quickly diagnose serious organ pathologies at an early stage of development, which is extremely important at this age, since the life of a small patient often depends on how quickly the final diagnosis is made.
Indications for testing in newborns
The diagnostic procedure for examining the structures of the central nervous system in an infant using ultrasound equipment is called neurosonography. It is performed through an open large fontanelle and shows the physiological state of the newborn’s nervous tissue at the current moment.
A routine brain ultrasound is prescribed to all children at the age of 1 month to identify hidden developmental anomalies of this organ.
However, there are a number of cases when an ultrasound of the brain is performed on a newborn to assess the state of brain structures in the first hours of life. These include the following situations:
- severe pregnancy;
- rapid or prolonged labor;
- multiple pathologies of the development of internal organs in a newborn;
- long waterless period;
- if the fetus was extracted using a vacuum;
- if the newborn was born earlier or later than the established deadlines;
- low birth weight (less than 2800 g);
- low levels of general condition, that is, below 7/7 on the Apgar scale;
- external developmental anomalies;
- convex fontanel;
- lack of crying in the first minutes of life after birth;
- receiving birth injuries of varying complexity;
- the presence of convulsive syndrome in the mother;
- incompatibility of the Rh factor of the blood of the mother and newborn;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus.
Repeated ultrasound of the brain substance is required at 1 month if the newborn has the following pathologies:
- uneven skull;
- a disorder of muscle tone, which is expressed in torticollis, paralysis and strabismus;
- excessive and repeated regurgitation after eating;
- if the newborn was born by caesarean section.
Also, using ultrasound of brain structures in infants, the effectiveness of prescribed treatment after head injuries, infections and neurological diseases is monitored.
What is it: the essence of the study
Neurosonography is a diagnostic test performed using ultrasound waves and allows one to study certain parameters of the brain.
The essence of the method is that an ultrasound sensor, which is both its source and recorder, is installed in the skull area and affects the brain. Important to remember! Neurosonography (NSG) is a method, the full implementation of which is possible only until that period of the child’s life while the large fontanelle remains open!
Is ultrasound of the brain harmful for children under one year old?
Parents are often concerned about how harmful it is for young children to undergo a brain ultrasound. However, they do not need to worry - neurosonography is an absolutely painless procedure, during which the condition of the nervous tissue is assessed by exposing the area under examination to ultrasound waves of a certain frequency. It is performed non-invasively, in real time and without the use of anesthesia. In addition, ultrasound does not require special preparation and can be performed repeatedly in a short period of time.
The advantage of using brain ultrasound over other methods of examination is obvious even to a person ignorant of medicine: firstly, it does not require large financial costs to examine the internal state of this organ of a newborn and is available free of charge with a referral from a specialist under the compulsory medical insurance policy. Secondly, it does not require special preparation and administration of medications the day before.
One of the advantages of brain ultrasound in children under one year of age is the immediate receipt of examination results, while the decrypted data contains all the information necessary to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
However, despite all the advantages, modern ultrasound equipment does not allow a full assessment of the internal state of brain tissue, therefore, if a serious illness is detected, the baby may be referred for additional examination.
Ultrasound characteristics
Ultrasound of the newborn's head is performed using neurosonography. It can be used to diagnose newborn babies and babies up to one year old. In rare cases, if his fontanel is not overgrown, it is carried out for up to one and a half years inclusive. Using high-frequency waves, an image is formed on the screen. Ultrasound of the brain of newborns is painless and safe.
This quality allows research to be carried out as needed to monitor treatment. In addition, this procedure does not require anesthesia. The baby may sleep or even cry. This will not affect the result in any way. Ultrasound studies of the brain study the structure of tissues, blood vessels, and the degree of blood supply to the organ. During diagnosis, the doctor analyzes the processes of the brain and their dynamics.
How to do an ultrasound of the brain in a newborn
Immediately after birth, the bones of the newborn’s skull are movably connected, and there are no sutures between them. At the same time, in the areas of connection of the main bones, 6 fontanelles or non-ossified areas of the cranial vault can be distinguished, filled with dense and fairly flexible connective tissue.
All of them are overgrown during the first year of life, with the last one to close is the large fontanelle, which is of interest from a research point of view. Because of this, the brain is examined using ultrasound equipment until it ossifies.
During an ultrasound, the newborn may be dozing or awake, as any of these conditions does not interfere with obtaining reliable indicators. However, if the specialist is faced with the task of examining the vessels, then it is not recommended to feed the newborn 1-1.5 hours before the event.
The procedure for performing an ultrasound scan of the brain is no different from performing an ultrasound scan of any other organ: the specialist applies a high-viscosity gel to the area of the child’s head being examined, which is usually the large or anterior fontanel. Then he places a sensor against it - a black and white image is displayed on the equipment screen, from which the state of the brain parts is determined. Next, measurements are made of internal structures: hemispheres, ventricles, subarachnoid space, etc. If necessary, if other fontanelles are not overgrown, then the manipulations are repeated.
The data obtained in this way is carefully recorded on a special form for further decoding. If there are pathologies, the specialist can also select one frame and print it on special paper. This is done so that the attending physician can subsequently personally examine the identified pathology.
As mentioned earlier, the ultrasound procedure has no restrictions, therefore, if necessary, it is performed on all children without exception, including premature ones, which greatly facilitates the diagnosis of brain disease.
When is neurosonography prescribed?
Neurosonography is advisable in cases where medical indications arise in the form of complaints or certain symptoms indicating brain damage. Due to its safety and high diagnostic value, neurosonography (NSG) has begun to be widely used for screening studies of all newborns at risk for the development of pathology of the central nervous system (primarily the brain).
Ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography) is prescribed for newborns according to indications and for all infants at the age of one month. Neurosonography is included in the list of studies during preventive medical examinations of minors.
Neurosonography of the newborn’s brain is performed once every 1 month of life, but can be carried out until the child’s fontanelle closes and as long as necessary (according to indications and to assess the effectiveness of treatment).
The sutures and fontanelles of a newborn’s skull are capable of transmitting ultrasound, so while the fontanelles have not closed, it is possible to conduct neurosonography. The sutures of the child’s skull close soon after birth, and the large fontanelle usually closes by the end of the first year of life (from 9 months to 1.5 years).
Neurosonography of a newborn: Ultrasound of the infant's brain
Norms and parameters
The diagnostician deciphers the data, so there is no point in parents trying to understand what is written on the issued diagnostic sheet.
The condition of the structures is assessed by a specialist based on the physiological state of the newborn at the time of the examination: date of birth, weight, age and conditions under which the baby was born (caesarean section or natural birth). It follows from this that for each category of infants there are certain norms of brain development, by which its neurological health is determined.
During an ultrasound, the following indicators are assessed:
- condition of the main departments;
- trunk symmetry;
- relief of the bark;
- homogeneity of ventricular tissue;
- echogenicity of the basal ganglia;
- hyperechogenicity of the choroid plexus.
The results of an ultrasound scan of the newborn’s brain are normal: the sections are symmetrical and homogeneous in composition, the grooves and convolutions of the cortex have a clear pattern, the interhemispheric fissure is no more than 3 mm, there are no seals, cysts or neoplasms, the membranes are not transformed.
For ease of interpretation, all norms are summarized in a special table of brain ultrasound indicators from 0 to 3 months:
| Brain structure | Newborn, normal in mm. | 3 months, normal in mm. |
| Lateral ventricles | Anterior horns – 2-4 Occipital horns – 10-15 Body – up to 4 | Anterior horns – up to 4 Occipital horns – up to 15 Body – 2-4 |
| III ventricle | 3-5 | Up to 5 |
| IV ventricle | Up to 4 | Up to 4 |
| Interhemispheric fissure | 3-4 | 3-4 |
| Large tank | To 10 | Until 6 |
| Subarachnoid space | Until 3 | Until 3 |
Thus, it turns out that the result of an ultrasound examination of parts of the brain at 1 month differs slightly from the data of an ultrasound examination of a newborn and does not exceed these indicators of the norm for a child at 3 months. As you grow further, all indicators change accordingly.
Description of the method
NSG of the brain of newborns: norm and interpretation
NSG of the brain of newborns is an ultrasound procedure that allows you to assess the condition and location of the structures of the central nervous system. The method is used until the fontanelles on the skull close, i.e. up to 1.5-2 years. Neurosonography is included in the standard examination of children aged 1 and 3 months.
The procedure is safe for the child, since ultrasonic waves do not affect the functioning of nervous tissue and other organs. The principle of operation of the NSG is simple - the device sends ultrasound deep into the skull. Individual waves are reflected from brain structures and return back. The sensor captures them and converts them into an image, which is assessed by the attending physician.
We recommend reading: Mydocalm and alcohol: compatibility, consequences, how long after you can drink
Pathologies detected on ultrasound, interpretation of results
The discrepancy between the obtained indicators and accepted standards usually indicates the presence of brain pathology. Let's consider some types of pathology separately.
Accumulations of cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space
The volume of the ventricles is individual for each age, but their size should not exceed a certain value. If such an anomaly was detected on an ultrasound, then we can talk about such a serious pathology as hydrocephalus or cerebral hydrocephalus, during which the size of the ventricles increases due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in them and the subarachnoid space.
Of course, a final diagnosis can be made only after undergoing a series of additional studies, but in such a child the disease is often visible to the naked eye: a wide forehead, a large head, and protruding fontanelles are clearly visible.
This disease usually occurs during the perinatal period when the fetus is infected with cytomegalovirus or toxoplasmosis, as well as against the background of other developmental pathologies. Dropsy, of course, is not a fatal disease, but it can bring a lot of suffering to a newborn: he often has a headache, he gets tired quickly and is delayed in development.
Slight enlargement of the ventricular cavity
A slight increase in the ventricular cavity is also observed in children with impaired absorption of calcium, which gives the specialist reason to assume the presence of rickets.
Choroid plexus cysts
Often, against the background of prematurity and the pathological course of labor, choroid plexus cysts form in the newborn. They are small neoplasms consisting of cells in the inner layer of the ventricles, which are filled with cerebrospinal fluid. This anomaly is not considered dangerous, but requires careful monitoring by specialists.
Arachnoid cysts
Arachnoid cysts. They are located in the arachnoid membrane and look like a small neoplasm filled with fluid. They grow quickly and can put pressure on the functional centers of the central nervous system, which leads to the appearance of various neurological abnormalities. For this reason, arachnoid cysts must be treated.
Ischemic disease
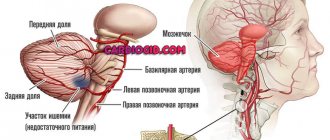
Ischemic disease. It develops against the background of insufficient supply of the brain with nutrients and oxygen, due to which the nerve tissues are partially destroyed and die. This manifests itself in a slowdown and reversal of the development of the newborn. The impetus for the development of this pathology is stenosis of the walls of blood vessels.
Neurosonography is required to determine the location of the hemorrhage after head injuries, as well as to assess the state of the circulatory system of the brain of premature infants.
Of course, with the help of ultrasound it is impossible to determine the location of the tumor in the brain, but if the screen reveals a shift in the location of the main parts or their enlargement, then this gives rise to a more detailed study of the parts of the central nervous system using other neuroimaging methods.
Let's summarize: Ultrasound of the newborn's brain is a fast and safe diagnostic method that allows you to detect the pathology of this organ of the newborn at the initial stage of formation.
What does the study show?
NSG (neurosonography) allows you to visualize the following brain structures in a newborn:
- The ventricles of the brain and indicators of the main structures through which the brain fluid (CSF) circulates;
- The severity and nature of the convolutions of the brain, as well as the furrows between them;
- Plexus of intracranial vessels and their characteristics (if the study is supplemented by transcranial Dopplerography);
- Dense processes of the dura mater of the brain, dividing it into anatomical sections (falciform process and tentorium cerebellum);
- The gap between the hemispheres of newborns;
- The nature of the midline structures of the brain and the symmetry of the formations located on either side of them;
- Characteristics of the space located under the arachnoid membrane of the brain (subarachnoid space);
- Identification of additional formations in the cranial cavity that should not be normal (anomalies and malformations, cystic cavities, vascular growths and angiodysplasia, softening of certain areas of the brain (leukomalacia).
This is the main method for detecting structural pathology of the brain in newborns. The main indication for diagnosis is a deviation in the infant’s neurological status coupled with a violation of a number of laboratory parameters.
The method is invaluable if the child’s condition is severe and it is not possible to transport him to the functional diagnostics department for an MRI.
Neurosurgical operations carry a high risk, since orientation in the cranial cavity and brain structures is difficult.
Ultrasonography can help the surgeon ensure that the surgical instrument hits the target as quickly and accurately as possible, using a minimum of technical means.
Ultrasound helps determine the location, depth, size of the surgical target, and select the optimal access with a minimal operating window.
It is carried out if the pediatrician or neonatologist suspects or has diagnosed the following conditions:
- intrauterine infection;
- prematurity;
- history of hypoxia (during pregnancy or childbirth);
- abnormalities in the development of organs or systems;
- anomalies in the development of the bones of the facial and cerebral parts of the skull;
- infectious diseases have been detected in the mother or child.
Children under one year old
In older children, the study helps to track the timeliness of brain development and identify the cause of neurological symptoms (convulsions, pain, etc.).
It is worth remembering when conducting NSG that the older the child, the smaller the fontanel and the narrower the acoustic window. Consequently, a smaller viewing angle for the sensor.
For children up to one year old, the method of ultrasonography is available - visualization of the structures of the spinal cord. Spinal ultrasonography is used before lumbar punctures, as a screening method for diagnosing spinal canal pathology.
Rarely, but it happens. In adults, the bones of the skull are connected by sutures, the fontanelles are closed, and there is no cartilage between the bones of the cerebral part of the skull. Ultrasound cannot penetrate the cranial cavity, which makes research impossible (in the traditional sense - research through the fontanelles).
In adults, transcranial ultrasonography is possible. It is possible to diagnose cerebral edema, dislocation, and enlargement of the third ventricle. But in some cases, in adults, the brain is not accessible for research due to a narrow “acoustic window.”
The use of ultrasonography results and interpretation of the clinical picture makes it effective to diagnose intracranial hematomas, which are often present in adult patients with cerebrovascular accidents.
But the main method of neuroimaging in adults and older children is CT and MRI.
Pediatric neurosonography is an informative diagnostic method. This diagnostic method allows you to obtain information:
- About the sizes, contours, shapes, area of the ventricles of the organ.
- About the state of blood vessels in the cerebral cortex, their structure, wall thickness.
- About the presence of anomalies in the form of aneurysms, cysts - cavities with fluid, as well as hypoxia, cerebral ischemia.
The study allows you to identify foci of hemorrhage - this is indicated by the contours of the ventricles. Expanded sizes may be a consequence of developing rickets, hydrocephalus - diseases that affect mental development. Disturbances in the structure of the walls - aneurysms - threaten circulatory disorders. Cysts cause epilepsy.
Methodology
The standard protocol involves placing an ultrasound probe on the large fontanel. As a rule, it ossifies up to 24 months, but can persist for up to 3 years. The optimal position for a child is lying on his back. However, in some cases, diagnosticians use non-standard positions for neurosonography. The most common of them are presented in the table:
| Baby's position | Where is the ultrasonic sensor placed? | Which structures are best visible? |
| On the side | Temporal bone scales | Parietal lobes of the brain. It is mandatory for children who have suffered a head injury. |
| Lateral fontanelles (anterior and posterior) | Parts of the brain located in the posterior fossa of the skull are assessed. | |
| On the stomach | · Foramen magnum; · Occipital (small) fontanel. | The optimal position for studying the posterior cranial fossa. |
In addition to brain tissue, doctors can additionally examine the condition of two vessels that are accessible with the standard position of the sensor. These are the vein of Galen (one of the largest venous vessels inside the skull) and the anterior cerebral artery. To assess the presence/absence of pathology and interpret the results, you need to know the norms of this study.
The standard protocol involves placing an ultrasound probe on the large fontanel. As a rule, it ossifies up to 24 months, but can persist for up to 3 years. The optimal position for a child is lying on his back. However, in some cases, diagnosticians use non-standard positions for neurosonography. The most common of them are presented in the table:
Get a free doctor's consultation
It is recommended to do the first ultrasound of a newly born child when he is exactly one month old. Ultrasound for newborns (normal) can be a unique way to detect hidden pathologies of internal organs. If any are detected, the child can be cured, since the time required for this therapy will not be lost.
How is NSG performed?
Neurosonography of the brain: how and when is it performed?
Neurosonography in newborns is performed like any ultrasound procedure. The child is placed on a couch, previously covered with a diaper. Body position: lying on your back. One of the parents is next to the newborn, calming him down.
Acoustic gel is applied to the fontanel area, ensuring high conductivity of ultrasound. The sensor of the device is applied to it and a study is carried out. The procedure lasts 5–10 minutes depending on the scope of the examination. There is NSG with Dopplerography. In this case, the attending physician has the opportunity to assess blood flow in the cerebral vessels and identify its disturbances.
Preparing the child
Special procedures, such as prescribing pharmacological drugs before the study, are not indicated. It is recommended to feed and change the baby 30-40 minutes before neurosonography so that nothing bothers him during the diagnosis. If he falls asleep, you should not wake him up, since in this case it will be much easier to perform an ultrasound.
For children who are placed in life support machines (“incubators”), the ultrasound machine is transported directly to the neonatal intensive care unit. The examination is not hampered by any catheters, probes, pulse oximeter, etc. This is another advantage of neurosonography.
Almost the only instrumental way to assess the state of the central nervous system at an early age is neurosonography. This is an ultrasound of the brain of a newborn or a child up to 36 months, which is performed through the fontanelles and other structures of the skull that are passable for the ultrasound signal. Why is it made? The method is used both as a screening and for examining young children with nervous diseases.
It should be noted that ultrasound is safe and does not have any side effects on body tissue, so it can be prescribed an unlimited number of times. There are also no contraindications for neurosonography - it can be done on children of any weight and severity of the condition. If necessary, the ultrasound machine is transported to the “incubators” and the procedure is performed “on site”.