How to get an accurate result
Under the age of 40, the breast consists mainly of glandular tissue, which transmits ultrasonic waves well. With age, the structure of the gland is dominated by adipose and connective tissue, so ultrasound becomes an auxiliary method that is used after mammography. This is due to the low information content of ultrasound examination in older age.
Ultrasound examination does not require special preparation, but it is important on what day of the cycle to do the ultrasound. For women with continued menstruation, it is optimal to come for an appointment on days 5-10 of the cycle. During this period, progesterone synthesis is at a minimum level, so the mammary gland remains soft and does not swell. Its elements are clearly distinguishable. After the onset of menopause, a woman can come for an ultrasound scan any day.
Ultrasound examination is carried out using various types of sensors, which affects the diagnostic result. When using a 7.5 MHz sensor, ultrasound sensitivity is up to 90%, specificity is up to 86%. The use of color Doppler mapping can increase the efficiency of studying a hypoechoic process. But for the diagnosis of small hypoechoic carcinomas, the sensitivity of ultrasound decreases to 58%.
The use of sensors with a frequency of 10-13 MHz allows you to get better results. In this case, small hypoechoic neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature are detected in 78% of cases.
Related article: Ultrasound of the mammary glands
What a formation with low echogenicity may be
Most often, hypoechoic formations that appear in the ovaries are cystic tumors with thin walls and clearly visible fluid inside. During an ultrasound examination, the doctor must indicate the size of the tumor, its shape and contours. Round type neoplasms can be:
- follicles;
- cysts;
- some types of tumors.
If the found hypoechoic area has uneven contours, it is most likely a fibroma, malignant tumor or cyst. In the ovaries, follicles, vascular tissue, the corpus luteum, and any type of cystic formation are characterized by low echogenicity. Only in rare cases does low echogenicity turn out to be a cancerous body. In reproductive age, heterogeneity of the ovary on ultrasound is considered normal. During menopause, when the appendages lose their functionality, the ovaries of a healthy woman should have a uniform structure.
Many patients are interested in the question of why doctors do not write the type of tumor in the diagnosis, but only mention the hypoechoic inclusion. The fact is that an accurate diagnosis can be made only after a more thorough examination and passing the necessary tests. Ultrasound examination gives only indirect results. Additional manipulations to confirm the diagnosis may include methods such as cystoscopy, biopsy or laparoscopy.
We recommend you learn: What is ovarian fibroid?
Normal and age-related changes in the mammary gland determined by ultrasound
Ultrasound examination using echo signs allows you to determine:
- stromal-glandular complex;
- condition of the ducts;
- volumetric formations;
- nature of blood flow;
- condition of the lymph nodes.
In women of reproductive age, the concept of normal is vague and depends on the presence of a period of lactation in the anamnesis and its duration. In most cases, the stromal-glandular complex is represented by a mesh structure with small hypoechoic cells up to 0.1 cm in diameter. If ultrasound is performed during the secretion phase, the stroma becomes swollen, loosened, and the cells may expand. That is why, to identify hypoechoic neoplasms, it is necessary to conduct a study no later than 10 days after the start of menstruation.
In patients aged 40-50 years, there is a significant increase in adipose tissue, the glandular component decreases, and the number of visible lobules decreases. Hypoechoic areas become invisible against the background of adipose tissue.
The structure of the mammary gland is influenced by the duration of the lactation period. In thin people who breastfed for a year or more, the mesh structure of the gland remains longer in the late reproductive period. This is not considered hyperplasia of glandular tissue, but is defined as a delay in age-related involution.
At 50-60 years of age, the bulk of the gland is adipose tissue, which contains a large number of hyperechoic connective tissue strands. The ducts may be moderately dilated and contain fluid, so they appear hypoechoic.
In postmenopause, due to suppression of ovarian function, various types of echo signs are observed within one mammary gland. Morphologically, the number of collagen fibers in the breast decreases, and the volume of connective tissue decreases. Therefore, when examining, noticeable:
- normal lobules;
- intralobular hyperplasia;
- hypoechoic cysts;
- areas of fibrosis.
During the postmenopausal period, dilated ducts and hypoechoic cysts with a diameter of up to 0.5 cm are classified as physiological age-related changes.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture varies depending on the underlying cause and location of the deviation. The main danger signs include:
- difficulty swallowing and eating;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- pain and discomfort at or near the site of hypoechogenicity;
- hoarseness and hoarseness in the voice;
- unreasonable decrease or increase in body weight;
- improper functioning of the digestive organs;
- constant drowsiness and feeling of fatigue;
- sudden mood swings;
- change in body temperature;
- dullness of hair;
- brittleness of the nail plate.
Patients often complain of drowsiness and fatigue
All symptoms are common. The patient may have several symptoms or all at once. It all depends on the factor that provoked the decrease in density.
In the presence of serious illnesses, the patient’s well-being rapidly decreases. Every day a person has less and less strength. Usual things become a real test. The skin becomes drier.
Signs of general intoxication of the body appear. Aggression may occur without obvious reasons. High risk of underweight.
Echogenicity and features of hypoechoic formations
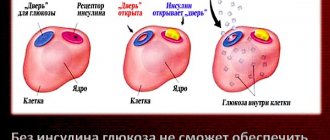
Ultrasound diagnostics is based on the principle of echolocation. The image on the monitor depends on the ability of the fabric to reflect waves. Different structures of the body have different abilities to transmit, reflect or absorb ultrasound. When a wave reaches the boundary of two media, part of it is reflected and goes back to the sensor, the rest of the beam follows further. The strength of reflection depends on the difference in acoustic density of the two media. The larger it is, the stronger the waves repel; the maximum indicator is observed when moving into a cavity with air. A large number of reflected waves creates a bright light image on the screen, or a hyperechoic zone.
Options for echographic imaging of breast cysts
A hypoechoic tumor means that most of the ultrasound waves are absorbed. Therefore, dark areas appear on the monitor. Anechoicity is manifested by the complete absence of wave reflection and appears as a black spot.
Hypoechoic formations can appear at different age periods. These are not always malignant tumors; a benign process may also have a similar ability to transmit ultrasound waves.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Diagnostic measures can be carried out in different ways, however, first of all, palpation is carried out. Thus, it is possible to identify the size and level of density of the formation, the location of the nodes, and the degree of their mobility. Then you need to start an ultrasound, this way you can clarify the results, which provides the necessary information for treatment.
When an ultrasound examination is carried out, data is obtained on the level of density, location of dislocation, volume and depth of the tumor formation. If the boundaries are as clear as possible, then we are talking about a focal process. If a change in the entire echo structure is observed, then the process is diffuse in nature.
Objects of the hypoechoic type have the appearance of white spots, the density of the structure is increased, so that ultrasound cannot pass through them. An isochogenic type node has the same density as the tissue when it is healthy. If you look at the screen, it is light gray in color, the degree of permeability is average. If they are very dark, then the density is low. It is noteworthy that using ultrasound it is not always possible to identify signs of cancer, so additional research is definitely needed.
It is necessary to do a biopsy and a cytological examination. The following methods are also used in diagnosis:
- laryngoscopy;
- MRI;
- hormonal blood tests.
Laryngoscopy is used if there is pressure on the larynx and trachea, and with the help of MRI it is possible to determine the smallest nodes and identify metastases. Hormonal tests will show how low or high their levels are; this always affects the functioning of the thyroid gland. Only after the results of all tests have been received, a specialist can prescribe a specific treatment method. It is not uncommon for a doctor to recommend taking preventive measures in cases where neoplasms in the thyroid gland do not harm health. However, at some time everything may become worse and then full treatment will be necessary.
Ultrasound assessment using the BI-RADS scale
The American College of Radiology (ACR) has developed a scale for studying mammography data, which is also used to standardize ultrasound data. It determines the risk level of malignant tumors. Using the data from the BI-RADS scale, the doctor can develop patient management tactics and determine the necessary treatment when diagnosing hypoechoic nodes.
To correctly assess hypoechoic neoplasms based on ultrasound results, the following requirements are imposed on it:
- period of manipulation - 5-10 days of the cycle, in women 40 years and older - only after preliminary mammography;
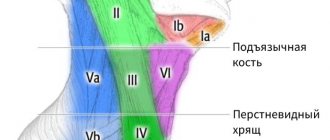
- the scanning area is the chest, which is viewed in quadrants, after which they proceed to ultrasound of the axillary lymph nodes, if there are pathological hypoechoic formations, the condition of the parasternal, intermuscular subclavian lymph nodes is assessed;
- position of the woman on the couch - sitting, lying on her back and sideways;
- equipment requirements - linear sensor with a frequency of at least 9 MHz, supplementation of the study with Doppler ultrasound.
When assessing a breast formation using the BI-RADS scale, the following signs are indicated:
- shape of formation - round, oval or irregular;
- location in space - vertical, horizontal, or indefinite with a spherical shape;
- the nature of the contours - smooth or uneven (radiant, wavy, star-shaped);
- boundaries – clear or fuzzy;
- echogenicity – iso-, anechoic, homogeneous and heterogeneous hypoechoic, hyperechoic;
- structure – homogeneous and heterogeneous due to inclusions;
- acoustic effects – dorsal signal amplification, lateral shadows;
- characteristics of the tissues around the formation - thickening of fiber, skin, violation of the integrity of the fascia.
The BI-RADS category is assigned depending on the type of education and its characteristics.
Treatment of isoechoic formations
As already noted, in most cases, isoechoic formations do not cause any harm to the patient. The doctor’s task after the first detection of such a formation is additional diagnostics - taking and analyzing a biopsy of tissue from the node
An isoechoic formation of the thyroid gland with some probability may be carcinoma, so it is important to exclude the presence of a cancerous tumor in the patient
If the node turns out to be benign, then further monitoring of the patient should be carried out. Every 6 months the patient must donate blood to study hormone levels, do an ultrasound and, if necessary, repeat a biopsy
It is important to track the dynamics of the disease - are the hormonal levels normal, is there any growth of the node
Treatment of nodes involves their removal. It is carried out if the node has reached a significant size, is somehow felt by the patient or visible to the naked eye. In this case, removal, depending on the location, size of the node, and other factors, can be done in various ways:
- The first, most obvious way is surgical removal. The surgeon makes an incision to expose the thyroid gland and removes the nodule or affected lobe. This method is simple and practiced everywhere, but has significant disadvantages. First of all, anesthesia negatively affects the patient’s condition. In addition, open surgery always carries an increased risk of infection and slows down the patient's recovery. Usually, after surgery, an unaesthetic scar is left on the patient’s neck.
- Other methods of removing nodes are non-invasive. Among those used in domestic medicine are destruction with ethyl alcohol and laser removal.
- When treating with ethyl alcohol, it is injected with a needle directly into the node under the control of an ultrasound machine. The substance destroys the tissue of the formation, and after several procedures the node disappears by itself, and with the help of the introduction of an adhesive composition, its capsule contracts and scars.
Laser removal is carried out by inserting a needle into the site, through which a laser emitter beam acts. Treatment with this method also requires several sessions, it requires quite a long time, and the procedure itself is relatively expensive.
Thus, an isoechoic formation does not always pose a threat to the patient’s health and does not require removal without disrupting the functions of the thyroid gland. Treatment of an isoechoic node consists of its removal, which can be done in various ways, including those that are non-traumatic for the patient.
How to identify a benign hypoechoic process
The formation of a homogeneous structure in the mammary gland can be benign. Most often, fibroadenoma manifests itself this way. With an oval shape, it can be located horizontally in space. Hypoechoic fibroadenoma has smooth contours with high clarity due to the existing thin pseudocapsule. The content is homogeneous, homogeneous. Behind the fibroadenoma, lateral shadows may be detected. Calcifications create acoustic shadows.
Ultrasound in color Doppler mapping mode shows that nodes up to 1.5-2 cm are without blood flow, no vessels have formed inside the hypoechoic structure and around it. Adjacent tissues are not changed and have a healthy vascular pattern.
If a fibroadenoma reaches a diameter of more than 1.5-2 cm, it is visible on the monitor as a hypoechoic formation of irregular shape, the contour becomes uneven, and the internal part becomes heterogeneous due to calcifications, areas of fibrosis, or cavities with fluid. At this stage, the vessels inside and outside the node are already identified. But the surrounding tissues are not changed. The blood flow in the vessels is minimal, no more than 0.2-0.22 m/s.
Options for echographic imaging of breast fibroadenoma
Signs of atypia may appear with fibroadenoma larger than 3 cm. At this stage, it is a hypoechoic heterogeneous formation with a large number of vessels. The speed of blood flow in them increases. Changes are an indication for a puncture biopsy.
Unlike breast fibroadenoma, the cyst always has a hyperechoic capsule and anechoic contents. The shape of the cysts is round or oval, with clear contours, the blood flow in them is not determined. Signs of an atypical cyst are:
- size more than 2 cm;
- border arteries around the cyst;
- internal partitions;
- internal tissue structures.
Any hypoechoic neoplasm of the mammary gland requires periodic observation in order to notice its growth and changes towards atypia. For women approaching menopause, surgical treatment is not recommended if several small hypoechoic structures are detected; only if they are atypical and rapidly progressing, a biopsy is necessary to choose a tactic.
What does an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland study?
This study is prescribed for all patients with the presence of nodes in the gland or changes in its volume. It can detect formations starting from 1mm. In this case, the number, size and localization of formations are determined.
The condition of the gland itself is also determined. When conducting research, the main thing for a doctor is to refute or confirm the oncological nature of the formation. A final diagnosis cannot be made on the basis of ultrasound alone; a histological examination of the biopsy specimen is required. But a full ultrasound examination will definitely be required, i.e. this serves as a starting point.
In addition, lymph nodes are examined during ultrasound. The lymphatic system receives all pathogens, atypical cells, it is always a refuge for metastases. With any pathology, the lymph nodes always become denser and enlarged. Therefore, their study plays a huge role in identifying pathology.
What else can an ultrasound reveal? The condition of the gland as a whole, its shape, the size of the capsule, the location of the gland, the homogeneity and condition of the parenchyma are determined, and suspicious areas with a heterogeneous structure are examined. When a large tumor is identified, it is necessary to evaluate tissue quality, pathological neoplasms, calcifications and the presence of pathological blood flow. Its presence will indicate tissue decay.
Ultrasound signs of malignant tumors of hypoechoic structure
Breast cancer ranks first among cancer pathologies among women and is the leading cause of death due to late detection. Its signs can be noticed during self-examination of the mammary glands, which is recommended for women every month. Sonographic signs of cancer are:
- vertical or uncertain spatial orientation, horizontal – very rare;
- the contours are fuzzy and uneven, may resemble rays or a star;
- hypoechoic heterogeneous internal structure;
- absence of lateral shadows behind the tumor;
- Acoustic shadow may be present.
Mucous tumors, as well as those with areas of hemorrhage and erosion, may resemble a breast cyst in structure.
Doppler examination of a hypoechoic node shows a large number of vessels inside. They can be hyper-tortuous, located radially or penetrate the thickness of the tumor. Blood flow in a hypoechoic formation of malignant origin can be retrograde, the minimum speed is 0.23-0.25 m/s. Late diastolic flow is not recorded in the tumor, which is how it differs from a benign process.
The echo structure of the diffuse form of cancer is different; sometimes it can resemble inflammatory processes in the breast. The skin and subcutaneous tissue also swell and thicken, and lymphatic vessels are identified. In the center of the malignant formation, a hypoechoic core is determined, which does not have clear contours and is heterogeneous in structure. Internally, vascularization is enhanced, and at the periphery, the vascular pattern is enhanced.
What to do after the examination?
If deviations (darkening or black areas) are detected during the examination, the patient is sent for additional examination. MRI, mammography, CT, radiography may be prescribed. If necessary, material is taken for a biopsy and blood for a general analysis. Drug treatment or surgery may be required.
To prevent hypoechoic formation in the chest, it is necessary to lead an active lifestyle, not abuse alcohol, and stop smoking. Diet also plays an important role in health. Ultrasound helps detect hypoechoic areas and their growth.
Tactics when detecting a hypoechoic node
After a detailed ultrasound, a score from 0 to 6 is assigned on the BI-RADS scale. It determines the doctor’s further tactics and the prognosis for the patient.
If the score is 0, further examination is necessary, which means there is not enough information to choose treatment tactics. This occurs when there is a chest injury, when conducting a detailed ultrasound is physically impossible. This assessment is given to women who underwent only echography without prior mammography during menopause.
Category 1 is safe. It means that a woman’s breast structure corresponds to age standards and only requires a routine annual examination.
If category 2 is set, this means that a benign formation has been detected in the breast. Its structure can be hypoechoic or anechoic, more often it is a fibroadenoma. This category includes:
- scarring;
- lipomas;
- simple cysts;
- slightly enlarged lymph nodes.
A similar category is assigned to women who have undergone breast replacement. These conditions do not require constant monitoring; a routine examination once a year is sufficient.
In category 3, benign hypoechoic processes are determined, which require dynamic monitoring every 3-6 months. It can be:
- small atypical cysts;
- inflamed cysts;
- hypoechoic fibroadenomas, which were identified for the first time.
Sometimes hypoechoic formations represent a delimited area of the gland that resembles adenosis, but does not have an enhanced vascular pattern. These conditions require close monitoring and treatment.
If there is no result of therapy, the formation is assigned category 4. These are all pathological formations that are most likely breast cancer. For them, a puncture biopsy is mandatory. Category 4 includes:
- hypoechoic atypical fibroadenomas;
- hypoechoic nodes larger than 3 cm;
- atypical cysts;
- chronic breast abscesses;
- mastitis that cannot be treated;
- hypoechoic nodes with hypervascularization;
- tumor growth by 5 mm or more in six months;
- delimited hypoechoic areas of the gland.
Category 5 is characterized by all ultrasound signs of breast cancer. But a biopsy is required to confirm the diagnosis. If the test does not reveal atypical cells confirming cancer, a repeat test is necessary.
The final category 6 is confirmed cancer, which must be treated comprehensively.
Causes and risk factors
There is a fairly large list of factors that can provoke the development of the formation of reduced echogenicity of the mammary gland. The most common is an increase in the amount of fluid in the chest. Other causes of the pathological condition:
- hereditary (genetic) predisposition to the development of mastopathy;
- late or first pregnancy, as well as abortions and miscarriages;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs, including oral contraceptives;
- refusal of breastfeeding, lactostasis or mastitis;
- psycho-emotional disorders, constant stress;
- menstrual irregularities, as well as early maturation of young girls and menopause;
- developmental pathologies or diseases of the endocrine structure;
- autoimmune diseases, including diabetes;
- obesity.
In order for the doctor to develop an effective therapeutic course, it is necessary to correctly identify the provoking factor.
Treatment methods for hypoechoic nodes
Hypoechoic avascular breast lesions of benign origin do not always need to be removed. If it is small in size, there is no progression, limited to annual observation. Women at risk need observation every 6 months. Drug therapy for the hypoechoic process with the herbal preparation Mastodinon is possible.
Hormonal contraceptives are not recommended if a hypoechoic formation is detected. But due to the connection between the formation and progesterone deficiency, the doctor may prescribe gestagenic drugs. Progesterone in tablet form is not justified in the treatment of hypoechoic formations. Its concentration in the mammary gland is 10 times greater than in the blood. Therefore, it is recommended to use local products in the form of a cream or gel (Progestogel). The course of therapy is 3 months.
Vitamin therapy and sedatives are used as auxiliary methods. If there is severe swelling of the breasts, diuretics may be prescribed in the second phase of the cycle.
Surgical treatment is used for nodular hypoechoic formations that do not respond to conservative therapy or are actively growing. Sectoral resection of the mammary gland is performed.
For confirmed breast cancer of a hypoechoic structure, complex treatment is carried out. Radiation therapy can be used after removal of the tumor, but no later than 6 months.
For breast carcinoma, one of the following types of surgery is performed:
- radical mastectomy;
- areola-preserving followed by plastic surgery;
- tumorectomy followed by radiation, used for intraductal cancer.
Chemotherapy is necessary for tumor metastases, in young women under 35 years of age, large tumor size, and stage 2-4 cancer. The choice of drug depends on the type of tumor, its sensitivity to hormones and other indicators.
Making a diagnosis based on the echogenicity of the thyroid gland
The hypoechoic structure of the gland most often indicates a malignant process, or the formation of vascular elements, fluid structures and nodular changes in the organ.
Thus, reduced echo signs of an enlarged gland can be observed if cystic inclusions or nodes are formed in it. Of course, after identifying hypoechoic zones, the patient is prescribed a fine-needle biopsy if the size of the tumors exceeds 1 cm.
This diagnostic procedure resolves the issue of the qualitative composition of the cellular structures of the gland, including the malignancy of the process.
If the echogenicity of the enlarged gland is reduced, laboratory blood tests are prescribed to determine the level of thyroid-stimulating hormones, T3, T4 and antibodies to thyroid tissue.