Indications for the study
The doctor prescribes the procedure for children if there are signs of certain diseases or disorders.
Ultrasound of the peritoneum is prescribed for the purpose of preventive examination, preparation for surgery, as well as for diabetes mellitus and the appearance of the following symptoms in children:
- sour or bitter taste in the mouth during belching;
- increased gas formation;
- clinical signs of jaundice;
- pain in the navel area;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- feeling of heaviness in the hypochondrium on the right;
- suspicion of appendicitis;
- changes in the shape and size of internal organs detected by palpation;
- diseases that cause an enlarged spleen;
- frequent regurgitation in babies;
- stopping weight gain or systematically losing it;
- suspicion of pylorospasm and pyloric stenosis;
- causeless loose stools;
- previous injuries or bruises in the peritoneal area.
The examination does not cause discomfort or pain. It is important for the doctor to know what an abdominal ultrasound shows in a child in order to make the correct diagnosis.
Indications
This issue deserves special attention. Usually, ultrasound of the abdominal organs is prescribed for children as planned. However, in some cases, the doctor may send you for additional examination after a simple examination. A pediatrician or gastroenterologist writes out a referral for an ultrasound scan. What are the main indications for conducting this type of examination?
It is worth highlighting the following:
- Routine examinations of babies under 1.5 months of age. This type of examination helps to exclude congenital developmental pathologies, as well as to identify many diseases at an early stage.
- Complaints of painful or unpleasant sensations on palpation.
- Increased gas formation.
- Pain in the back and abdomen of a pulling or cutting nature.
- Bitterness in the mouth.
- Nausea.
- Heaviness in the stomach.
- The appearance of yellowness on the whites of the eyes and skin.
- Constant disruption of normal bowel movements.
- Sudden change in body weight.
- The appearance of a rash on the skin.
Where can I get an abdominal ultrasound for my child? This procedure is performed both in public hospitals and clinics, and in private medical centers.
What is examined during an ultrasound
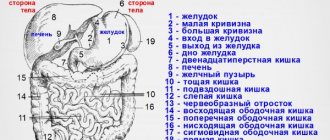
During the procedure, the following organs are examined:
- spleen - condition and size are determined;
- peritoneal lymph nodes - assess size;
- inferior vena cava;
- liver - the size, position relative to other organs, the presence of neoplasms, the condition of the bile ducts, walls and vessels are diagnosed;
- adrenal glands and kidneys - the relative position, formations, sizes are established;
- pancreas – condition is assessed;
- intestines and stomach – identify polyps and neoplasms;
- abdominal aorta - the condition of the vascular wall and blood flow are examined;
- bladder and ureters - assess contents, size and shape;
- gallbladder - the presence of foreign inclusions, polyps, and patency of the ducts is determined.
After the pediatrician receives the examination conclusion, based on the established age standards, he can already draw conclusions about whether there are disturbances in the functioning of the organs, and about the presence of a specific disease.
What is visible
Based on what is seen on an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, the child is diagnosed or additional tests are prescribed.
Based on the results, the doctor can draw the following conclusions:
- enlarged spleen – the presence of infectious inflammation, injury or heart attack;
- the presence of cysts on the liver or neoplasms - appropriate treatment or surgery will be prescribed;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- unsatisfactory condition of the gallbladder, thickening of the walls, expansion of the ducts, constrictions and kinks - may indicate cholecystitis, stones, congenital anomalies and other diseases;
- disturbance of blood flow in the vessels;
- the presence of congenital organ pathologies;
- peritoneal injuries;
- the presence of hyperplasia and hepatitis;
- disruption of the digestive tract;
- inflamed pancreas – development of reactive pancreatitis.
In young patients, a special form of pancreatitis is often detected, the treatment of which must be started immediately, otherwise a rapid transition to a chronic disease is possible.
After the ultrasound, the doctor writes down the results and gives the adult representative a conclusion, with which they should then go to the pediatrician.
What can be revealed through an examination?
An abdominal ultrasound in a child is usually done to examine the liver, spleen, gallbladder or pancreas. The doctor performing the procedure will definitely interpret the results, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body and normal indicators. In some cases, an ultrasound examination of the kidneys may be performed separately.
In addition to congenital anomalies, ultrasound helps determine pathological changes in the abdominal organs.
These include:
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- internal bleeding;
- blood diseases.
Disorders of this type may be indicated by enlarged internal organs, neoplasms, cysts and abscesses. Ultrasound also helps to detect the presence of harmful microorganisms in the liver tissue. An ultrasound examination can help diagnose pancreatic disease such as reactive pancreatitis. It usually appears in infants.
Using an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, it is possible to determine abnormalities in the motility of the gallbladder, cholecystitis, pyelonephritis, cysts and other formations. Most paid clinics today offer an ultrasound procedure of internal organs using Doppler. This examination can detect congenital kidney defects.
Ultrasound results
Based on the results of an ultrasound of the child’s abdominal cavity, the doctor can make a diagnosis and determine treatment.
The results of the study may reflect the following:
- presence of acute or chronic hepatitis;
- blood stagnation in the child’s liver;
- the presence of tumors on the liver;
- oncopathology;
- hard formations (stones) in the gall bladder, their size and location;
- narrowing or congenital abnormalities of the bile ducts;
- abscesses;
- the presence of free fluid in the peritoneum;
- enlarged size of the spleen, the result of injury or infarction of this organ;
- abnormal enlargement of retroperitoneal lymph nodes;
- hematomas;
- circulatory disorders in the branches of the abdominal aorta.
Ultrasound examination gives the doctor the opportunity to observe the process of development, course and treatment of the disease. Ultrasound can be repeated several times at the frequency prescribed by the doctor.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder in a child.
The gallbladder is a reservoir for the accumulation of bile. It has the shape of a “drop” or “pear”, and is filled with olive-colored bile; the gallbladder is located at the bottom of the liver. Bile takes part in digestion, namely in the digestion of fats, stimulates the intestines to work well, serves for the so-called “hygiene” of the intestines, both to suppress putrefactive processes and to fight protozoa and worms. Therefore, any dysfunction of this organ disrupts the digestive processes. As you know, ultrasound is the most effective and safe examination method. It is necessary to do an ultrasound of the child’s gallbladder if:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Suspicion of inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis).
- Abdominal injuries.
- Presence of bitterness in the mouth.
- Feeling of constant nausea or nausea with vomiting, especially bile.
The preparation is the same as for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity of a child: foods that cause gas formation (brown bread, peas, beans, cabbage, soda, cakes), spicy, salty, smoked foods are excluded. For better visibility on the device screen, you can take enzymes (Festal, Mezim-Forte, Creon) and carminatives (Espumizan, Dill water).
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach, dinner the day before no later than 19:00, which should be light; In the morning, before the examination, you should not drink water. As for infants, it is better for them to be examined before the next feeding. And for older children, you can take food with you. If there is a suspicion of the presence of stones or acute pain appears, in this case no special preparation is carried out.
A diagnostician conducting an ultrasound examination of a child’s gallbladder evaluates the shape, wall thickness, size and volume of the gallbladder. The size of the gallbladder in children depends on its age:
From 2-5 years, length 30-50 mm, width 13-24 mm;
6-8 years, length 45-75, width 10-20;
9-11 years, length 35-64, width 11-30;
12-16 years, length 40-80, width 12-27;
If the gallbladder has a drop-shaped shape, the walls are not enlarged, there is no stagnation of bile, there are no kinks, sand, and especially stones, then this is a normal variant.
- The diagnosis of Discension can be made if there are such deviations in the bladder: there is stagnation of bile, that is, the motility (work) of the gallbladder is disrupted and the tone of the bladder itself and the bile ducts is reduced, the neck of the gallbladder is bent, the walls of the bladder are thickened.
- The diagnosis of Cholelithiasis (Cholelithiasis) is made when there are stones in the cavity and bile ducts and a change in the position of the body of the organ; they move noticeably inside the gallbladder and give an acoustic shadow, in this case the boundaries of the organ become uneven, and thickening of the walls is diagnosed.
- Diagnosis Polyps, they are on the walls of the organ and have a round shape; do not give an acoustic shadow and are detected by chance, since they do not manifest themselves in any way.
Preparing a child: what not to do
To conduct an accurate study and obtain the most reliable results, it is necessary to properly prepare the child for an abdominal ultrasound. This is more difficult to do with young children, since they do not understand why they cannot eat this or that product. Parents should ensure that the recommendations for preparing for the procedure are fully followed.
Three days before the ultrasound, foods that lead to increased gas formation are excluded from the diet:
- milk and dairy products (porridge is cooked in water);
- legumes;
- flour and butter;
- sweets;
- cabbage;
- fresh or black bread;
- raw vegetables (due to long digestion);
- carbonated drinks, kvass;
- fresh fruits that directly affect intestinal function.
The first examination of the baby is carried out a few weeks after birth to obtain information about the condition of its organs. Next, parents have to give the child ultrasounds of the abdominal cavity and other organs up to three times during the first twelve months of life.
Preparation rules
Preparing your child for an abdominal ultrasound is important to obtain accurate results that will allow you to make the correct diagnosis. It begins 3 days before the scheduled examination. The most important thing is to obtain ultrasound accessibility of the area being examined. To do this, the child’s abdominal cavity must be free of food residues, gases, and air.
If the digestion process has not yet ended, then the gastrointestinal tract organs also function intensively. For example, in this case there is an active contraction of the gallbladder, the pancreas is slightly enlarged. During diagnosis, the doctor will not be able to obtain information about the accuracy of the size of the organ and its condition. Many parents are perplexed about how to prepare their child for an ultrasound.
To do this, the following simple recommendations are given:
- If a newborn is being examined, then before diagnosis you should stop feeding 3 hours before the scheduled procedure. That is, it is important to determine the time of the study immediately before the next feeding. When the baby is breastfed, then after eating you should wait 3 hours, if he eats formula - 3.5.
- When the examination is carried out on children from one to 3 years old, they should skip one meal. 3 hours should pass after the last feeding. If your baby asks for food, you can give him a small amount of sugar-sweetened water.
- When the diagnosis is carried out for children over 3 years old, they are able to endure a minor hunger strike. For them, ultrasound is best scheduled early. If the study is scheduled for the day, then at least 6 hours should pass after eating.
- If a child suffers from increased gas formation, then he can take Activated Charcoal or Espumisan for three days. It is important that the intestines are not full. If necessary, on the eve of the study, cleansing with an enema can be performed.
Preparing for an ultrasound: what is possible, regimen
The following dishes are allowed to remain on the menu:
- barley, buckwheat and oatmeal porridge in water;
- chicken and beef;
- boiled or steamed lean fish;
- one chicken egg per day;
- low-fat cheese or cottage cheese.
The total amount of food should be distributed over four to five meals per day. A light dinner is recommended the evening before the procedure. It is better if it is stewed vegetable puree. The time from the last meal to the examination should be more than six hours for children from three to six years old.
During preparation for an abdominal ultrasound, infants and very young children are fed in the evening, and in the morning before the procedure, feeding is skipped - the time from the last feeding to the examination should be at least four hours. Infants are also not given water one hour before the procedure to prevent the pancreas from producing enzymes.
Three days before the test, children are given medications that reduce gas formation. There is also a condition for nursing mothers - not to eat food that leads to the accumulation of gases.
How to prepare a child for an abdominal ultrasound
In order for the study to be as accurate as possible, it is necessary to prepare before it. With children, everything is much more complicated, since the child does not always understand why he cannot eat, for example, candy. One of the main features of preparing for an abdominal ultrasound is following a special diet. For about three days, you need to eliminate the following foods from your diet:
- Milk, even if the child eats cereal. In this case, you need to cook them in water for several days, since milk in some cases can cause increased gas formation
- Legumes. Quite often, children are given beans and peas, since these are the foods they love. But it’s best to exclude them for a couple of days
- Sweets, namely buns, as they contain yeast and sugar, which cause the formation of gases
- Cabbage
- Raw vegetables, as they take a long time to digest
- Fresh fruits that have a direct effect on the intestines
If a child often has constipation or, conversely, diarrhea, then it is best to give some enzyme preparations, for example, Festal, for a couple of days.
When preparing a child for an abdominal ultrasound, the following may be included in the diet:
- Porridges not cooked with milk and made from barley, buckwheat or oatmeal
- Chicken and beef, as they have the least impact on the intestines and stomach
- Fish, namely lean and cooked either in a double boiler, or simply boiled
- An egg, no more than one per day
- Low-fat cheese, which can be purchased in large hypermarkets
Ultrasound can answer many questions
At the same time, it is best to feed the child not three times a day, but five, to ease the work of the stomach. In the evening, before the ultrasound, it is not recommended to feed your baby a hearty dinner. It is best to prepare some kind of puree that will be quickly absorbed. In the case of small children, it is unlikely that you will be able to follow the above recommendations, and therefore you just need to not feed them in the morning (if possible) or take food with you to the clinic.
Read: MRI of the gastrointestinal tract: indications, process and evaluation of results
As for infants, it is better to skip the last feeding before the ultrasound so that the time interval is 3-4 hours. Also, there is no need to give your baby water an hour before the test, since even when drinking water, the pancreas begins to produce enzymes. It is also better for babies to start giving Espumisan, Bobotik or another medicine that will remove accumulated gases a few days in advance.
Children aged from one to three years are not recommended to eat 4 hours before the test. This is why many parents sign up for an ultrasound around lunchtime in order to feed their child breakfast. Children over 3 years of age should not eat 6 hours before the procedure. The ideal option would be to have an ultrasound scan on an empty stomach.
The reliability of the results obtained depends on how correctly the child was prepared for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Some parents neglect the requirements and get poor results for only one reason: they fed the baby before the ultrasound.
Recommendations for parents
Before the procedure, in order to reassure the babies for the first time, mothers should talk about how children are given an abdominal ultrasound, about the safety and painlessness of the examination. Usually, children do not like the cold gel that is applied to the stomach.
The following recommendations should be followed:
- if the examination takes place in cold weather and the ultrasound room is cool, then you need to take an additional diaper with you, which is placed on top of the hospital disposable one;
- the child should be dressed so that the abdominal area can be cleared for examination quickly and easily - a jacket with buttons or a zipper is suitable;
- To distract the kids, you need to grab toys;
- Mom needs to take cookies or chocolate with her in case she needs to examine the function of bile duct contractility.
It is advisable to undergo an ultrasound scan of the peritoneal organs annually.
What is a pediatric abdominal ultrasound?
The ultrasound examination method is based on the ability of different tissues of the human body to transmit vibrations of supersonic waves differently. Special equipment directs a high-frequency sound wave into the cavity of the patient being examined, and when reflected from the organ being examined, it creates an echo that is picked up by the scanning sensor. After special processing, the organ being examined is reflected on the device’s monitor in the form of a graphic image.
Using ultrasound, it is possible to study the features of the anatomical structure and functional activity of the digestive organs without damaging the integrity of the skin. According to qualified specialists, this diagnostic method is the most effective, painless and safe. Performing abdominal ultrasound for children is actively used in neonatology, surgery, oncology, gastroenterology and endocrinology:
- to determine the size, shape and location of any of the abdominal organs;
- studying the homogeneity and structure of their tissues;
- identifying existing developmental anomalies, injuries, inflammatory processes and tumor formations;
- assessing the possibility of complications of diagnosed pathologies.
Caring parents always ask the question: “Is it possible to examine the abdominal organs of a newborn child using ultrasound?” - you should not refuse the offer of your local pediatrician - the procedure will not have a negative effect on the baby’s body and will not cause him pain
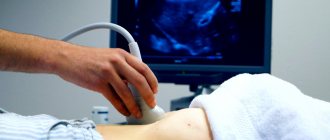
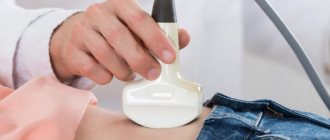
How is ultrasound performed?
An ultrasound of the abdominal organs for children is performed for ten to fifteen minutes, depending on each specific case, in the presence of an adult relative:
- The small patient is placed on the couch, the abdominal area is freed from clothing.
- The doctor applies a special product - a gel - to the middle of the abdomen, along which he moves the sensor from side to side, examining the insides. The product is colorless and odorless and does not cause allergic reactions.
- During the procedure, you may need to hold your breath or turn on your side for better authenticity.
- After finishing the examination, the doctor will wipe the gel off your tummy.
What is considered normal?
This is a condition when all organs have normal sizes and shapes, without the proliferation of tissues and stones, cysts, neoplasms and fluids. The diameter of all vessels should also remain within normal limits. The specialist must also check the condition of the bile ducts and the outflow of urine. Doctors do not recommend that parents try to decipher an ultrasound examination on their own. The problem is that in normal conditions, ultrasound readings of the abdominal organs in children and adults can vary greatly. And in young patients, indicators can vary depending on age. What is considered normal for an infant will be considered pathological in an older child.
An ultrasound examination can often diagnose abnormalities in the development of organs, which can return to normal with age. In addition, non-standard forms of internal organs are an individual feature of the child’s body and do not in any way prevent him from leading a normal life.
Study safety
Without such an examination, it is impossible to fully study the functions of the systems and organs of the child’s body. Any hospital has special rooms where you can give your child an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and other organs.
The ultrasound research method is based on the properties of ultrashort waves that penetrate tissues and organs with varying degrees of reflection. The device sends waves, then the sensor receives the return (reflected) signal and generates a black and white image showing the condition of the organs.
For more than twenty years, ultrasound has been widely used in pediatrics. During the examination, doctors clearly see the picture and assess the condition and location of various organs. The procedure differs from X-rays and CT scans in that the child is not exposed to radiation.
Data from numerous scientific tests and experiments have proven that ultrasound is absolutely safe and harmless to the child’s body. Proper preparation of the child for ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and other body systems is important.
The waves emitted by an ultrasound machine do not cause radiation exposure to the body, and also do not correspond in characteristics and nature to radioactive waves. They have a characteristic range that the human body does not perceive or feel.
Many natural phenomena produce similar ultrasonic vibrations, such as the sound of the sea surf or the blowing of the wind. Some animals are capable of emitting these waves, such as dolphins and bats.
Norm
In accordance with the age characteristics, the doctor will make a conclusion about the ultrasound of the child’s abdominal cavity.
A good result of the study is the following characteristics:
- the size of the organs corresponds to age standards;
- no stones were found in the gall bladder;
- organs have the correct shape and location;
- the thickness of the walls and the outlines of the organs correspond to the norm;
- no formation of cysts, tumors or tissue proliferation was detected;
- the vessels are of normal size.
When not to perform an ultrasound
To safely carry out the procedure, you need to know not only how to prepare a child for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, but also when such a procedure is not recommended.
The following restrictions apply:
- after fluoroscopy using contrast agents (irrigoscopy, gastrography), a delay of at least two days is required;
- two days later, an ultrasound examination can be performed after endoscopic surgery (colonoscopy, fibrogastroduodenoscopy) on the organs of the digestive tract;
- a delay before ultrasound of three to five days is required after pneumoperitoneum and laparoscopy.
Ultrasound examination is a safe and informative diagnostic method. It allows you to detect the disease in a timely manner and monitor the dynamics during treatment.