An objective examination of the patient should be carried out in a warm, dry room with good lighting. The patient should lie on his back, in a comfortable position, without tension. You should place a small pillow under your head.
The doctor sits on the patient's right side. It is best to examine a completely undressed patient, covered with a sheet. You can limit yourself to exposing the abdomen from the nipples to the upper third of the thighs.
Patient's history
When clarifying complaints and life history, you need to ask whether the patient has suffered from any chronic diseases of the abdominal organs, infectious diseases, diseases of the cardiovascular system, whether there have been any operations, and, of course, whether there have been hernias of the abdominal wall.
If you follow a certain order during the interview, you can collect a good and complete history; it does not take much time, but in many ways it helps to quickly establish the correct diagnosis. Still, it is impossible to rely only on anamnesis data, even when it would seem that the diagnosis is already clear. It is always necessary to perform a complete examination of the patient.
What is CT
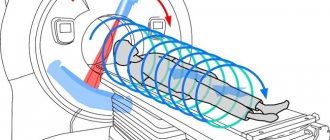
CT is a modern diagnostic method. The method is non-invasive because it does not require penetration into the body's structures. The skin remains intact. The examination makes it possible to study the internal organs of interest.
Computed tomography can detect diseases even in the initial stages of their course. This is possible even in the absence of external signs indicating the development of a pathological process. If necessary, the condition of the entire organism can be studied.
Computed tomography is highly detailed. This makes it possible to detect even minor pathological processes. When scanning, you can obtain an accurate three-dimensional image of the area being studied.
CT is often used when a tumor-like disease is suspected. The localization of the pathological process and the nature of the deviation are determined. If necessary, a biopsy is performed.
It is important to have a CT scan before surgery. This allows doctors to determine the progress of the operation. Diagnostics are also prescribed to monitor the effectiveness of the selected treatment. Tomography is also used to locate cystic formations in the body.
CT allows you to diagnose pathologies at the earliest stages before the first symptoms appear
The method was first used in the 70s of the last century. During this time, diagnostics have been improved and become completely safe for the human body. However, the method is not included in the list of mandatory annual tests. You need to resort to examination only as prescribed by a doctor, which means you need to undergo an initial examination in advance.
Diagnostics does not take much time. No surgical intervention or damage to the skin is required. After the manipulation, you can return to your normal lifestyle.
The examination is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor.
Facial expression, skin and lip color
The examination begins with a statement of facial expression, skin color and lips. In some acute diseases of the abdominal organs, for example, in advanced peritonitis, acute intestinal obstruction, the face takes on a specific expression called the Hippocratic face .
The color of the patient’s skin and lips is of great importance - the usual color, pale, bluish, gray-sallow, etc. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity and the conjunctiva of the eyes must be examined. Yellowness is often detected , which is an important symptom indicating an increase in bilirubin in the blood.
Damage to abdominal organs
With penetrating wounds, surgical disease of the abdominal cavity almost always occurs. If the spleen or liver is damaged, intra-abdominal bleeding is usually observed. A wounded person experiences decreased blood pressure and diffuse pain throughout the abdomen. If hollow organs, intestines or stomach are damaged, symptoms characteristic of inflammation of the peritoneum are observed.
If we are talking about a minor injury, then conservative treatment can be used; in more severe cases, surgical treatment cannot be avoided.
Pulse and increased body temperature
The pulse is counted for a minute. In a shorter time, rhythm disturbances, rare extrasystoles, etc. may not be detected. Pay special attention to the pulse rate. The correspondence of pulse rate to body temperature has great diagnostic value. Normally, for every 1 °C increase in body temperature, the pulse increases by 8-10 beats/min. The discrepancy between the pulse rate (its excess) and body temperature is an important symptom that indicates serious disorders in the body.
Measuring body temperature, in addition to the armpit, should also be performed in the rectum, where normally the temperature is 0.5–0.7 °C higher than in the armpit. During acute inflammatory processes in the pelvic cavity, near the rectum, the temperature in its lumen becomes 1-2 °C higher than in the armpit.
Decoding
Based on the images obtained, the radiologist enters into the examination protocol information about the size, shape, structure and relative position of organs, notes congenital anomalies and detected disorders. Enters his observations into a research protocol, which, together with the images, is transferred to the attending physician or given to the patient. Many diagnostic clinics can record the results on a computer disk, flash card, or send them by email. It is worth considering that the final diagnosis is made by a doctor of the appropriate profile based on the results obtained.
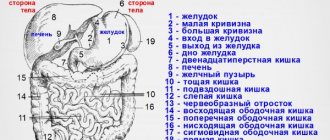
Abdominal examination
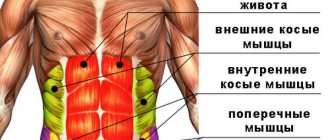
When examining the abdomen, pay attention to postoperative scars, making sure to specify what kind of surgery was performed and when. If you have a certificate from a medical institution, you must look at it and take it with you during hospitalization. The shape of the abdomen is of great importance for diagnosis: bloated, not bloated, evenly or more in any part; on the contrary, it is retracted or there is a so-called “frog belly”.
When a large amount of fluid accumulates in the abdomen, the abdomen is evenly enlarged in size and seems to be flattened, its lateral sections seem to “hang down.” Places of possible hernias must be examined - the inguinal and femoral areas, the area of the umbilical ring.
Attention is drawn to the participation of the anterior abdominal wall in breathing ; this symptom is very important, since with peritonitis the abdominal wall is motionless or its movements are extremely limited. To clarify this, you need to ask the patient to first inflate his stomach as much as possible, and then retract it. Patients with peritonitis, as a rule, cannot do this due to severe pain. If there is an acute inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity, movements of the anterior abdominal wall are accompanied by the occurrence of pain at some localized point, and the patient can quite accurately indicate with his finger the place of greatest pain.
The location of independent pain is specified, for which the patient is asked to show the place of greatest pain with one finger. Then the patient is asked to cough, and pain appears or intensifies at the site of the pathological process. Another similar method is when the patient is asked to strongly inflate or retract the abdomen; the pain, as a rule, intensifies in the area of the pathological focus.
Palpation of the abdomen
When palpating the abdomen, you need to follow some rules and techniques, without which the results will be very doubtful. First of all, it is necessary to place the patient in a horizontal position, so that he can lie comfortably. The doctor's hands should be warm and dry.
Palpation begins far from the location of pain. Sitting to the patient's right, the doctor places his right hand on the stomach, gently palpates the abdominal wall with his palm and fingertips (superficial palpation). Usually, beginners make a serious mistake: they hold their hand up and roughly feel the stomach, as if “poking” it with their fingers. Superficial palpation reveals the area of maximum pain and tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
Deep palpation of the abdomen
A continuation of superficial palpation is deep palpation of the abdomen, the purpose of which, in addition to clarifying the area of pain, is to identify pathological formations in the abdominal cavity and palpation of individual organs. During deep palpation, the doctor also holds his hand with an open palm on the patient’s stomach, but instead of “stroking” palpation, in time with the respiratory movements, he plunges his fingers deep into the abdomen. This movement should be soft, not intrusive and not rough, so as not to cause pain to the patient.
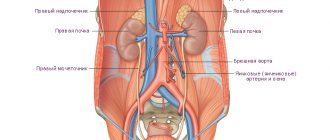
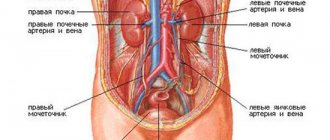
The liver can be felt in the right hypochondrium. Normally, its edge is smooth, soft, painless and may slightly protrude from under the costal arch. In the right iliac region, the dome of the cecum can be felt in the form of a doughy roll, sometimes rumbling upon palpation. In the left iliac region, the sigmoid colon is palpated, also painless. The spleen is not normally detectable; Only with a significant enlargement of the spleen, which often happens with the development of portal hypertension, does it become accessible to palpation.
Percussion of the abdomen
Percussion of the abdomen determines the boundaries and presence of hepatic dullness. If you receive a box sound in the right hypochondrium, i.e., the absence of hepatic dullness, one can think about the presence of free gas in the abdominal cavity, i.e., suspect perforation of a hollow organ.
Percussion determines the presence of fluid in sloping areas of the abdomen. To do this, percussion is first performed lying on the back and the border of dullness of the percussion sound is marked, then the patient is turned on his side and percussed again where there was dullness. If there is fluid in the abdomen, it flows down and the dullness disappears.
Auscultation of the abdomen
After palpation and percussion, they proceed to auscultation of the abdomen and determine a number of symptoms that occur in many acute surgical diseases of the abdominal organs (they are described below in the relevant sections).
The abdomen is auscultated using a phonendoscope, or, if it is not available, with the ear. Normally, irregular bowel sounds of varying intensity are heard. The complete absence of peristaltic noise - “ deathly silence ” - along with other symptoms is an important sign of an inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity.
The examination of the patient is completed with a rectal and vaginal examination.
Contraindications
Limitations in the use of CT are associated with the effect of ionizing radiation on the patient’s body. This study is contraindicated in pregnant women. It is not advisable to prescribe it to women who are breastfeeding. Due to the technical capabilities of the device, it is not performed on patients weighing more than 150 kg.
Enhanced CT has additional contraindications:
- impaired liver and kidney function;
- allergy to contrast;
- serious condition of the patient (coma, shock of various nature);
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
Although MRI is considered a safer study, it also has its contraindications:
- metal objects in the human body (foreign bodies, fragments);
- ferromagnetic implants (dentures on metal pins, pacemakers, artificial joints, heart valves, automatic medication dispensers, metal osteosynthesis devices, clamps and clips on blood vessels after surgery, hearing aids).
Under the influence of a magnetic field, they can change their temperature, move when heated and damage surrounding tissue.
Carrying out MRI in patients with fear of closed spaces causes certain difficulties. In this category of people, the study can be performed provided that open-type tomographs are used.
It is difficult for young children, restless patients, and those with neurological pathologies to remain motionless for some time, which is necessary to obtain a clear image. In such cases, they resort to short-term anesthesia (medical sleep).