Infertility is a serious challenge for a woman. The world's leading experts are fighting the threat to motherhood. Special techniques have been developed to identify the causes of infertility and eliminate them. When hysteroscopy and laparoscopy are performed simultaneously. Why are both methods combined, how do they differ and what results do they lead to?
What is hysteroscopy?
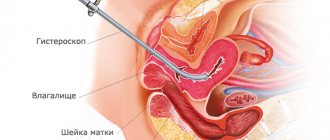
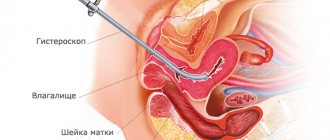
Hysteroscopy is an operation that is a minimally invasive intervention. It is carried out among women who are sexually active. The manipulation is carried out using a special device - a hysteroscope. During the study, the woman is in a state of sleep. Local anesthesia is used less frequently. In this case, the patient hears, sees, but does not feel everything.
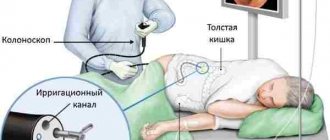
Hysteroscopy is an operation that is performed exclusively within the walls of a hospital. During the procedure, the woman is on a gynecological chair. A dilator and a special tube with a sensor, at the end of which there is a microcamera, are inserted into the cavity of the cervical canal. Using this equipment, the doctor can control the processes occurring inside the reproductive organ. Under pressure, the uterus expands, and the specialist can examine every centimeter of it. If necessary, during diagnosis, doctors can take a small piece of tissue for a more thorough examination. Also, if a polyp is detected, it can be removed immediately. The procedure allows you to eliminate some abnormalities in the development of the uterus, for example, synechiae.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a method of performing diagnostic and surgical operations on internal organs by introducing a miniature video camera and instruments through small incisions in the abdominal cavity.
This diagnostic method is widely used in gynecology:
- treatment of infertility with an unknown cause and in the absence of a positive response to hormonal therapy;
- operations on the ovaries in case of their degeneration or the presence of neoplasms;
- suspicion of growth of the endometrium beyond its layer or the formation of connective tissue cords in the pelvic organs;
- endometrioid disease;
- myomatous lesions of the uterus;
- blockage, ligation, or cutting of the fallopian tubes;
- internal bleeding due to ovarian rupture.
When performing diagnostic laparoscopy, a small incision (5-7 mm) is made in the navel area or slightly lower with an offset. If it is necessary to perform surgery on the tubes or ovaries, then 1-2 additional incisions of 5-7 mm are made, usually on the right and left in the lower abdomen.
In addition to traditional complications, such as bleeding and secondary infection, laparoscopy has unique complications:
- Blockage of blood vessels by gas bubbles. This condition can be caused by direct ingress of carbon dioxide into the vascular bed from the needle of a special surgical instrument. In addition, gas embolism can also develop if the walls of large veins are ruptured during laparoscopy, since the pressure in the abdominal cavity is higher than in the veins.
- Damage to a vessel in the abdominal wall. Injury to deep vessels usually results in rapid and significant blood loss. And if the superficial vessels are damaged, a thin stream of blood appears after the surgical instrument is removed.
- Traumatization of the gastrointestinal tract. The Veress needle has a tip shaped in such a way that it is almost impossible to damage the free moving loops of the intestine. However, it is difficult to protect adjacent intestines or intestines with limited mobility from damage due to their normal anatomical attachment.
- Damage to the bladder or ureter. This injury can be suspected by heavy bleeding from the port installed in the suprapubic region. Further detection of blood in the urine may indicate deep damage.
- Damage to the nerves of the pelvis. This may be due to the position of the patient on the operating table or to errors in determining the point of trocar insertion through the anterior abdominal wall and subsequent suturing of laparoscopic approaches.
Hysteroscopy examines and treats intrauterine problems, while laparoscopy examines and treats the uterus, tubes, and abdominal appendages.
Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are effective in solving many gynecological problems
Indications for hysteroscopy
The described procedure has its own indications. There are two types of manipulation: diagnostic hysteroscopy, during which the reproductive organ is examined from the inside, and operational. In the second case, during the manipulation the doctor performs surgical treatment. Most often, minimally invasive intervention is necessary for the following indications:
- abnormalities in the development of the uterus (formation of synechiae, septum);
- neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ (polyp, fibroids);
- endometrial hyperplasia and adenomyosis;
- remnants of the fertilized egg in the cavity of the muscular organ or incomplete abortion;
- heavy bleeding or breakthrough menstruation;
- infertility or frequent miscarriages;
- several unsuccessful attempts at in vitro fertilization;
- increase in the size of the uterus for unknown reasons.
Before the procedure, a woman must undergo tests. This includes a smear to check the purity of the flora and an analysis for infections, a blood test for the presence of hepatitis, syphilis and HIV. Additional diagnostics necessary before using anesthesia are also carried out.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a method of examining the uterine cavity using an optical instrument inserted into the uterus through the cervical canal. Initially, this endoscopic method was used only for diagnostic purposes, but in modern medical practice it is used for intrauterine surgical manipulations.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is indicated in the following cases:
- identification of neoplasms of various nature;
- the appearance of spotting after menopause;
- persistent menstrual irregularities in women of childbearing age;
- the fertilized egg is not visible on ultrasound;
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy up to 37 completed weeks;
- diagnosis of hydatidiform mole, a malignant tumor formed from epithelial cells of the chorion;
- with hormone replacement therapy to assess its effectiveness;
- control of the location of the intrauterine device.
Surgical procedures during hysteroscopy can be performed for the following purposes:
- intrauterine polypectomy;
- removal of the intrauterine contraceptive and other foreign bodies;
- dissection of the intrauterine septum or adhesions;
- narrowing of the mouth of the fallopian tubes;
- treatment of submucous uterine fibroids.
Despite the fact that hysteroscopy is considered a fairly safe procedure, in rare cases the following complications may occur:
- Trauma (perforation, perforation) of the uterus or cervical canal.
- Infection of the internal genital organs or exacerbation of infectious diseases that were not identified at the stage of preparation for the procedure.
- When carbon dioxide is introduced into the uterine cavity, changes in cardiac activity, an increase in the acidity of the body, blockage of blood vessels with gas bubbles, and mechanical trauma to tissues may occur.
- Damage to large vessels of the mucous layer of the uterine body, leading to severe bleeding.
- Reaction to anesthesia.
Previously, hysteroscopy was considered the prerogative of large medical institutions, but now it is used everywhere in gynecological hospitals and clinics.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy can be performed in a gynecological office without dilatation of the cervical canal of the cervix
Consequences of using a hysteroscope
What feedback has there been about the study? This manipulation quickly became so popular that diagnostic intervention is now performed on almost every fourth representative of the fairer sex of reproductive age. After the procedure, the woman must remain under the supervision of doctors for some time. If necessary, she is administered antibacterial drugs and anesthetics. If there is no surgery, the patient can go home within a few hours. However, if the doctor carried out the treatment, then everything will depend on the individual characteristics of the body and the course of the procedure.
Patients say that for several days after hysteroscopy, slight bleeding from the genital tract may be observed. They usually end on their own and do not require the use of additional medications. Also, some patients feel discomfort and minor pain. Doctors do not recommend having sexual intercourse for two weeks after the procedure.
The advantage of hysteroscopy is that after it is performed, the doctor can determine the cause of the problem with maximum accuracy and prescribe the correct treatment.
Fallopian tube laparoscopy
One of the most important organs of a woman's reproductive system is the fallopian tubes. Their main function is to connect the ovaries to the uterus. There are a number of diseases of this organ for which laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is indicated. These are, first of all, obstruction and adhesions of the tubes , as well as ectopic pregnancy .
Tubal ligation for sterilization is also performed using laparoscopic instruments. This surgical intervention prevents conception.
In the process of treating fallopian tube obstruction, which often becomes the cause leading to infertility in women, an accurate diagnosis is initially established. After this, the obstruction is treated directly. The elimination of adhesions of the fallopian tubes occurs in a similar way. Adhesions mainly occur as a consequence of inflammation. Using special instruments during laparoscopy, dissection and subsequent removal of adhesions are performed.
If a woman develops an ectopic pregnancy, then most often the attachment of the fertilized egg occurs in the fallopian tubes. If the embryo continues to grow during pregnancy, then eventually the woman is at risk of rupture of the fallopian tube. If pregnancy develops in the fallopian tube, the use of laparoscopy is advisable both to establish the correct diagnosis and to remove the fertilized egg if the fallopian tubes rupture. In the latter case, surgical emergency laparoscopy is practiced. Diagnosis using the laparoscopic method makes it possible to determine whether the fertilized egg is actually located in the fallopian tubes. Emergency laparoscopy allows you to restore the tube after a rupture has occurred. Thus, an operation using this method, unlike conventional surgery, helps preserve not only the fallopian tube, but also its functions.
Fallopian tube laparoscopy is also practiced in women diagnosed with hydrosalpinx . With this disease, a certain amount of fluid accumulates in the fallopian tubes. This occurs either due to inflammation of the tubes or due to impaired blood flow. The disease poses a particular danger to women, as the fluid-filled fallopian tubes can become twisted. With the help of laparoscopy, with this diagnosis, the fallopian tube is completely removed.
What is laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy of the uterus is an examination that is performed through the abdominal cavity. Manipulation is always carried out using anesthesia and a ventilator. Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy differ in that in the first case we can talk about surgical intervention, while the study described above is minimally invasive.
During laparoscopy, a special, complex device called a laparoscope is used. Using small incisions, the surgeon inserts instruments into the woman's abdomen. A camera is inserted in the navel area. It is she who transmits to the screen everything that happens in the patient’s stomach. Also, before inserting the instruments, the abdominal cavity is filled with a special gas. The woman's belly inflates, raising the upper wall. This is necessary so that the overview is maximum and there is no danger of damaging neighboring organs. Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy differ not only in the technique of intervention, but also in the duration of the operation. So, laparoscopy requires from 30 minutes to several hours. It all depends on the complexity of the operation. Hysteroscopy can be performed in 10-20 minutes.
Differences between methods
Hysteroscopy differs from laparoscopy in its technique. The hysteroscope is inserted into the uterus through the vagina. Laparoscopy is an invasive method of examining the uterine cavity and neighboring organs by puncturing the abdominal wall. Laparoscopy is always performed under general anesthesia, and hysteroscopy under local anesthesia.
Hysteroscopy is an internal examination of the organ; laparoscopy allows you to examine the outer surface of the uterus and adjacent organs.
Note! Hysteroscopy is performed without incisions or punctures of organs.
In what cases are internal and external examinations of the uterus performed?
Hysteroscopy (internal diagnostics) is prescribed for:
- detection of papillomas and growths on the mucous membrane;
- identifying the causes of irregularities in the menstrual cycle;
- removing the old coil and mucous residues after cleaning;
- identifying the cause of miscarriages;
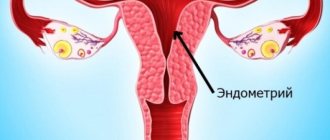
- endometrial studies;
- complications of pregnancy;
- research into the causes of other pathologies.
Diagnostics are also prescribed after an unsuccessful IVF protocol, periodic uterine bleeding, and congenital anomalies of the reproductive organs.
Laparoscopy is prescribed for:
- diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy;
- research into the causes of ovarian pathology;
- studies of neoplasms on the outer shell of the organ;
- performing organ perforation;
- other gynecological problems.
After the operation is completed, the puncture area is sutured; the stitches must be removed after 12-14 days in the hospital. Both procedures are carried out after examination of the tests in the laboratory. Since laparoscopy involves the introduction of anesthesia, preliminary preparation is necessary - refusal of food on the eve of diagnosis.
Contraindications to laparoscopy and hysteroscopy:
- malignant neoplasms;
- severe obesity;
- adhesions after previous abdominal operations;
- hernia.
Is there a risk of complications after surgery? Complications can appear after any surgical manipulation of internal organs, it depends on the severity of the existing pathology and the characteristics of the woman’s body. However, the statistics of complications is small.
In order not to provoke trouble after both procedures, you should not use tampons during menstruation, take hot baths or steam in a sauna. Douching and any manipulation of the genitals without the approval of a gynecologist are prohibited. These restrictions must be adhered to until your health is fully restored.
Indications for laparoscopy
The manipulation can be planned or emergency. Laparoscopy can also be therapeutic or diagnostic. It is worth noting that in any case it is necessary to pre-examine the woman. To do this, blood and urine tests are taken, an ultrasound of the genital organs is performed, and a consultation with a therapist and cardiologist is obtained. Of course, if we are talking about the patient’s life, then all these studies fade into the background. Doctors take all tests whenever possible. Indications for the study will be the following situations:
- infertility and ectopic pregnancy;
- disruption of ovarian function (polycystic disease);
- dense ovarian capsule;
- endometriosis and suspicion of it;
- neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature;
- adhesions in the abdominal cavity or fallopian tubes;
- fibroids of the outer lining of the uterus;
- perforation of the uterus and so on.
Infertility
Is laparoscopy and hysteroscopy performed for infertility? Is there a chance to restore reproductive function using these techniques? The causes of infertility can be very diverse. For example, adhesions in the tubes prevent sperm from moving into the ovaries. With the help of hysteroscopy, adhesions can be removed, which will clear the way for sperm.
Hysteroscopy allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis, on the basis of which the gynecologist prescribes a course of therapeutic manipulations corresponding to the clinical picture. Hysteroscopy also helps to get rid of many pathologies that impede successful fertilization:
- ovarian cysts;
- adhesive obstruction;
- tumors, cysts, polyps;
- endometriosis.
Conception after laparoscopy
Patients are interested in the question of the timing of possible pregnancy after surgical procedures. The chance of getting pregnant depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, the severity of the existing pathology and the complexity of the surgery performed. Age, existing chronic inflammatory processes of the reproductive organs and complications after surgery also contribute.
Premature pregnancy after laparoscopy always ends with undesirable consequences. The time of conception must be agreed upon with the local gynecologist.
When is it advisable to plan a pregnancy? For the body to fully recover after surgical procedures, three months or six months must pass. After a thorough examination of the patient, the gynecologist makes a conclusion about the possibility/impossibility of conceiving a child. Ovarian cyst surgery delays the time of planned fertilization by six months instead of three months.
Removal of polycystic ovary syndrome does not require a long recovery period, so after 28-30 days you can think about conceiving a child. Restoring women's health after an ectopic pregnancy requires a long period of rehabilitation - at least six months. Doctors are cautious about planning conception after an ectopic pregnancy and recommend giving the body rest for about a year.
How is childbirth after laparoscopy? This operation does not leave any scars on the body of the uterus, so the woman can give birth naturally. If doctors deem it necessary, the patient will undergo a caesarean section. One should not think that weak labor is caused by a previous operation before the birth - it depends on the characteristics of the female body.
Pregnancy after hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is divided into two types - diagnostic and surgical. After diagnostic procedures there are no obstacles to conception. Surgical procedures establish their own rules: the body needs a recovery period. Rehabilitation depends entirely on the severity of the pathological process and the surgery performed.
As a rule, six months is enough for the body to recover after the intervention. After surgery, intrauterine infection may develop, so premature pregnancy may result in miscarriage or premature birth.
A sluggish infectious process in the uterus can also provoke fetal hypoxia, polyhydramnios, abnormal fetal position and fetoplacental insufficiency. Therefore, it is not recommended to rush with fertilization. Before conception, the gynecologist will conduct a thorough examination using instrumental and laboratory diagnostics - ultrasound, culture of vaginal flora, blood and urine tests.
To maintain the pregnancy, synthetic hormonal drugs are used (for example, Duphaston), which promote reliable fixation of the embryo to the wall of the uterus. This drug also stimulates the endometrium, prepares the uterine cavity for gestation and eliminates contraction of muscle fibers. Duphaston is prescribed in the first trimester of pregnancy.
After laparoscopic surgery
According to women, after the operation the recovery process takes a long time. First, the patient recovers from anesthesia within a few hours. After this, the woman can stand up with the doctor's permission. However, this is very difficult to do. The possibility of leaving the medical facility on the same day is out of the question. Usually hospitalization lasts from 3 to 7 days. It all depends on the speed of recovery of the body.
After the procedure, the woman needs to have her stitches removed. This must be done after 2 weeks. You also need to care for scars and treat them with an antiseptic. You can return to your normal life and exercise no earlier than in a month.
Complications after laparoscopic examination
According to reviews from patients who have undergone laparoscopy, they note that after it the inflammation goes away for a very long time. Immediately after the operation, the woman recovers from anesthesia for several hours, she is allowed to go home only after a few days, and after 14 days she will need to have her stitches removed. Scars need to be well looked after so that infection does not enter the peritoneum through them and cause serious harm to health. But what is the difference between these two procedures, can one replace the other?
Hysteroscopy or laparoscopy: which is better?
This question often arises among representatives of the fairer sex. However, doctors cannot answer it unequivocally. Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are two completely different procedures. One can never replace the other. For example, during hysteroscopy, the doctor can take a piece of the endometrium for analysis or remove the remains of the fertilized egg from the uterus. With laparoscopy, such actions cannot be carried out, since the instruments are located in the peritoneum and do not enter the reproductive organ.
During laparoscopic surgery, it becomes possible to dissect adhesions, remove a cyst from the ovary, and excise an ectopic pregnancy. All these pathologies cannot be eliminated with the help of a hysteroscope alone. That is why it is not possible to say for sure which study is better. Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are often performed at the same time. In this case, it is not necessary to use anesthesia several times, and the doctor has many opportunities to thoroughly study the problem and eliminate it.
Bottom line
Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are modern methods of combating infertility. Both methods have differences in technical terms and subject of research. It is impossible to replace one procedure with another - they are used separately, one after another or together. Simultaneous laparoscopy and hysteroscopy provide a comprehensive clinical picture, saving doctors’ time and the patient’s energy.
Can hysteroscopy or laparoscopy help with infertility? Most patients gained a chance of successful conception after surgery. However, fertilization depends not only on treatment procedures, but also on the age of the patient and the severity of the disease. In any case, you need to use the chance to heal and believe in success.
Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy: patient reviews
Women say that when they turn to paid medical doctors, performing these procedures simultaneously is much cheaper. If we are talking about government institutions, then here too there are a lot of advantages of one-time hysteroscopy and laparoscopy.
- You can get all the tests done right away and not have to go to the doctor several times. After all, most conclusions are valid for a month.
- Possibility of using one anesthesia. It is worth noting that the anesthetics used have a negative impact on the health of the fairer sex.
- When all problems are eliminated at once, the woman receives a more effective result from the treatment.
Representatives of the fairer sex say that when carrying out the procedures described above (according to indications) and supplementing them with conservative treatment, the effect is noticeable almost immediately. The cycle is restored, disturbing symptoms disappear. Women wishing to give birth, if the outcome of the operation is good, can begin planning pregnancy for the next cycle.
Ovarian laparoscopy
In modern medicine, ovarian laparoscopy is practiced in the treatment of ovarian cysts . With the development of this disease, a cyst forms on the ovary - this is a cavity in which fluid is located. Such a formation can be either small or quite impressive in size. If multiple cysts develop on the ovary, the woman is diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome . With this disease, the patient often suffers from menstrual irregularities; polycystic disease can also cause infertility.
Laparoscopy of ovarian cysts is performed using general anesthesia . To avoid severe bleeding during surgery, blood vessels are coagulated. Those areas of the ovary that have been damaged are either sprayed with a laser or destroyed in other ways during the operation. Sometimes during this procedure, the doctor takes a tissue sample to perform a biopsy . This type of surgery is sometimes also practiced for endometriosis , adenomyosis , and uterine fibroids .
In case of ovarian disease, laparoscopy is one of the fastest and safest ways to cure the disease. It allows you to avoid injuries, significantly reduce the period of postoperative recovery and, accordingly, hospital treatment. During surgery, a woman loses a relatively small amount of blood: if we compare such blood loss with a conventional operation, then here the patient experiences bleeding with blood loss ten times less than during surgery. Another undoubted advantage is the possibility of using an optical device and, accordingly, significant magnification to ensure the accuracy of the operation.
Preparation for laparoscopy
Preparation for laparoscopy is the most important stage, on which the accuracy and safety of the upcoming examination directly depends. Your attending physician will help you prepare for the examination, who will explain the purpose of the examination, describe each stage in detail and tell you what measures you need to take on your own.
- Eliminate various painkillers and other medications that your doctor has told you to avoid.
- A week before surgery, strictly follow the necessary diet: exclude from your diet fruits, vegetables, especially legumes, brown bread and other foods that your doctor considers undesirable; eat low-fat broths, fish and meat, cottage cheese, porridge, kefir
- During the day of surgery, eat only liquid foods.
- 8 hours before laparoscopy, refrain from eating at all.
- Before the operation, a complete cleansing of the intestines is also recommended: the method of cleansing that is suitable for you will be determined by the attending physician
- Before the procedure, take a shower and shave the hair on your stomach and pubic area.
- To relieve anxiety, take the sedatives recommended by your doctor a few days before laparoscopy.
Pregnancy after laparoscopy
It is often very important for women who have undergone laparoscopic surgery to know when they can plan a pregnancy after laparoscopy. First of all, you should take into account the fact that laparoscopy in gynecology is performed quite often due to infertility. During the treatment process, the woman's adhesions are dissected, tube patency is restored, cysts are removed, and other necessary manipulations are performed. During treatment using laparoscopy, the patient’s ovulation processes are restored, obstacles to the movement of the egg are eliminated, so conception can occur after successful completion of treatment.
Thus, a woman should take into account that pregnancy after laparoscopy is possible in the near future. However, when pregnancy occurs, it is important for such patients to be constantly monitored by a gynecologist and undergo a comprehensive examination. Sometimes it is necessary to take medications for the normal course of pregnancy after laparoscopy. In this case, medications are prescribed to maintain normal hormonal levels.
Sometimes, if there is no pregnancy after laparoscopic intervention, the doctor may prescribe this procedure again.
Laparoscopy in urology
Laparoscopy in urology helps to diagnose and treat diseases such as:
- Kidney neoplasms (benign and malignant up to stage 2)
- Kidney cysts
- Hydronephrosis stage I-II
- Secondary wrinkled bud
- Tumors of the ureter
- Kidney stones
- Ureteral stones
- Kidney prolapse
- Localized prostate cancer
- Localized bladder cancer
- Varicocele
- Prolapse of the uterus, bladder, rectum
- Stress urinary incontinence in women