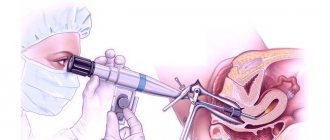
Hysteroscopy is a low-traumatic method for diagnosing and treating gynecological diseases. Even a visual intervention, not to mention therapeutic manipulations, provokes the release of mucus and a small amount of bloody streaks from the genital tract.
Few women know what discharge should be like normally after hysteroscopy. Information about the duration of smearing and its nature, how much blood should come out after the procedure, will help patients monitor their condition and consult a doctor in time if there are complications.
Bloody issues
If the patient has undergone diagnostic hysteroscopy, then the menstrual cycle is not disrupted. If the procedure involved curettage, then spotting is allowed on the same day. In addition, as with laparoscopy, the day of therapeutic hysteroscopy will be considered the first day of the cycle. If heavy bleeding continues for more than 2 days after the procedure, this is a serious reason to seek help from a specialist.
Bleeding after hysteroscopy can occur for the following reasons:
- Rupture of the uterine wall. This usually happens as a result of strong pressure on the dilator or probe, especially against the background of severe dilatation of the cervix. Or if this reproductive organ has become loose. In most cases, this pathology is iatrogenic (caused by medical personnel) in nature.
- Excessive cleaning of the endometrium. If scraping is too thorough, the mucous membrane suffers and is damaged, and there is even a threat of complete damage to the germ layer.
- Inflammation of the uterus. This pathology could already be present, but after the manipulation it made itself felt. In addition, a secondary infection may occur due to the fault of unscrupulous medical personnel who do not follow basic asepsis rules. Or the patient did not adhere to postoperative recommendations and did not take antibacterial drugs.
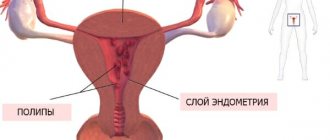
The opposite of bleeding can be another complication - hematometra. This is an accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity caused by a violation of its outflow. This happens as a result of insufficient contraction of the uterus, blocking of the cervical canal by a polyp, blood clots or elements of a disintegrating tumor.
If the patient finds a small amount of scarlet blood discharged, then she has no serious cause for concern, since this is quite natural after hysteroscopy.
In addition to discharge, after hysteroscopy the patient may be bothered by nagging pain in the lower abdomen
Possible causes of bleeding
Hysteroscopy is required to treat various diseases and may be accompanied by heavy bleeding. This occurs especially after surgery or curettage. A woman should not be afraid or worry too much, but if the amount of blood does not decrease within several days, she still needs to see a doctor.
Cause of heavy bleeding during menstruation after hysteroscopy:
- the doctor touching the organs of the reproductive system (in the case of cutting out tumors, polyps, removing the endometrial ball, biopsy);
- performing an abortion or curettage of a cavity;
- inaccurate implementation of this procedure and, as a result, severe complications.
If bleeding does not go away within five to seven days and is very heavy, you should definitely consult a doctor. He prescribes special restorative therapy that will help get rid of complications.
Cycle after curettage
After polyp removal
The presence of polyps in the uterus causes women many problems and is characterized by the appearance of bloody discharge between menstruation, pain in the lower abdomen at rest and during sexual intercourse. Endoscopic methods are used to diagnose and treat this disease. After removal of a polyp during hysteroscopy, the following discharge may be observed.
Physiological discharge is within normal limits. If the removal of the polyp was less traumatic, then the discharge may be completely absent or it may not last more than 2 days. If the uterus has been cleaned, a copious secretion may be released or it may smear for up to two weeks.
Discharge of blood from the uterus. Blood flows against the background of damage to the vessels of the uterine wall. It is normal if there is little of it and it is scarlet in color. If the blood mass is dark or coagulated, then this is not necessarily an indicator of bleeding. Blood that has accumulated in the uterine cavity during surgical procedures may be released in the form of dark clots for some time.
Pain after hysteroscopy
Purulent discharge - they may indicate a secondary bacterial infection. Usually the causative agents are staphylococci or streptococci. Vaginal secretions do not become more transparent over time, but, on the contrary, cloudy yellow discharge with a greenish tint appears.
Putrefactive discharge - they appear against the background of clostridia, a special type of microorganisms living in an airless environment, entering the uterine cavity. The discharge is viscous, mucous with a strong unpleasant odor.
If the discharge after hysteroscopy is dark, brown with black streaks, then this is a serious cause for concern. So, the body may react to inappropriate hormonal therapy, or this may be the result of curettage - remnants of the endometrium come out. But in any case, this is a reason to go for a consultation with your gynecologist.
Transparent, reddish, sticky (ichor) discharge is considered normal after hysteroscopy. Their volume should not exceed 50 ml per day. As the wound heals, their volume should decrease. And by 3–5 days after the manipulation, the discharge should completely disappear.
After polyp removal, many women experience leucorrhoea mixed with blood, which may be a variant of the normal immune response
Endometrial hysteroresectoscopy - what is it?
The content of the article:
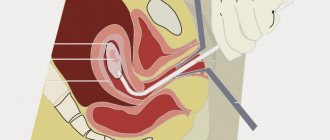
Hysteroresectoscopy is an examination of the uterus using an optical instrument. It is administered through the cervical canal, after which the doctor carries out the necessary manipulations.
Since this manipulation is a kind of mini-operation, the patient will have to undergo a fairly lengthy examination. In general, the procedure does not require special preparation, but in some cases hormonal therapy may be recommended. It is needed when removing fibroids, dissecting intrauterine septa or fusions, and checking the mucous membrane.
The method can be prescribed at different times of the cycle. In its first phase, it is carried out if there is a suspicion of fibroids or endometriosis, since during this period the endometrium has a thin layer and is well cut off. It should be noted that minor discharge may be observed during hysteroscopy of an endometrial polyp, which is considered normal.
Within normal limits
Slight bleeding or mucus mixed with blood on the first day and spotting that lasts for the next week is normal and should not cause much concern to the patient.
If hysteroscopy was performed for therapeutic purposes, then the bloody mass of discharge resembles menstruation in volume and can last up to 2 weeks. Moreover, the intensity and nature of the secretion may change day by day. The patient may notice brown spotting. The alarm should only be sounded if the smear has an atypical consistency with a dark brown color and a pungent odor.
In addition, it also happens that discharge after hysteroscopy is completely absent. This may be due to the high degree of qualification of the doctor, who was able to carry out the manipulation very carefully and did not significantly damage the vessels of the uterine wall. However, other causes associated with certain pathologies cannot be excluded.
Contraindications to the procedure
The study has contraindications. These include:
- active inflammatory process in the pelvic organs;
- oncological pathology of the cervix;
- pregnancy period (with the exception of a pathological course requiring emergency intervention);
- violation of the blood clotting process;
- severe somatic diseases in the stage of decompensation;
- infectious diseases in the acute period;
- cervical stenosis.
In the above cases, hysteroscopy is not performed, as it may be complicated by adverse consequences.
Recovery period
As a rule, recovery after hysteroscopy does not take much time and occurs relatively easily, without much effort on the part of the woman. And yet, since the patient may experience watery or bloody discharge from the genital tract for 2–4 weeks after the procedure, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Every day a woman should perform thorough hygiene of the external genitalia and also use sanitary pads.
- During this period, nothing should be inserted into the vagina. This includes not only hygiene items, but also medications or medical procedures (tampons, suppositories, douching).
- Until vaginal discharge stops, a woman should abstain from intimacy with her sexual partner.
- Thermal procedures (bath, sauna, solarium), swimming in open bodies of water (river, pond, lake) and taking baths should be avoided. Of the water procedures, only washing in the shower is allowed.
Only a doctor can say with certainty how serious a deviation from the norm some discharge is. Of course, there is no need to panic out of the blue. But if all patients went to see a gynecologist on time, then many serious complications could be avoided.
Additional nuances of scraping
Preparation
Since the curettage procedure is an operation, the preparation for it will be appropriate.
Analyzes:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Fluorography.
- Smear.
- Biochemical blood test (HIV, syphilis, blood group).
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the pelvic organs.
- Cardiogram.
Immediately before the operation it is recommended to eat and drink; the procedure must be carried out on an empty stomach.
In the morning before the procedure, you should take a shower, remove hair from the perineal area, and put on clean underwear.
You should also be prepared for the fact that you will have to spend several days in the hospital. Therefore, take with you a robe, slippers, a change of underwear, pajamas and other necessary accessories.
Procedure
The procedure itself takes place in several stages and lasts from 15 to 30 minutes.
Stages:
- Anesthesia. Before this, the anesthesiologist asks the patient about her state of health, previous diseases, and the presence of allergic reactions.
- After the patient has fallen asleep, the gynecologist inserts a speculum into the vagina and exposes the cervix.
- The uterus is secured with special forceps to ensure immobility during the procedure.
- The doctor then measures the length of the uterus using a special probe.
- The next stage is dilation of the cervix; for this, the gynecologist uses special dilator sticks, which are alternately inserted into the uterine os, expanding it.
- The scraping itself. To do this, use an instrument resembling a spoon with a sharp edge (curette). At this stage, the doctor uses a curette to remove the upper functional layer of the endometrium (the upper layer of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity).
- If the patient has any tumors, they are removed immediately.
- At the end of the procedure, the doctor removes the fixing forceps, treats the uterus with antiseptic solutions, and puts ice on the patient’s stomach.
- The operation is completed, the woman goes to the ward.
How the scraping procedure is performed is described in the video:
If you want a child, then you will have to wait a little, since you can plan a pregnancy no earlier than 3-6 months after the procedure. This is exactly how long it takes for the endometrium to recover.
In case of violations of the endocrine system, it will take 2-3 years to restore it. If you suffer from autoimmune diseases, be prepared for complications during pregnancy.
You may have to bear your baby under the strict supervision of doctors.
Gynecological curettage is a complex procedure that is very stressful for the female body. It is carried out after a miscarriage, abortion, frozen pregnancy and in the presence of certain other medical indications. A woman should know how much blood flows after cleaning the uterus. Although this is normal, bleeding that lasts too long may indicate a pathology.
It is important to detect the problem in time
Is it possible to do hysteroscopy?
There are many opinions on this question. Normally, this procedure is not recommended for young girls, especially under 25 years of age. But, if the case is serious enough and you can’t do without it, then the doctor prescribes it anyway. It is also not recommended to do hysteroscopy for women after childbirth for six months. This is explained by the fact that all the functionality of the genital organs must be fully restored. But again, it is worth noting that in particularly urgent situations such a procedure may be prescribed. In particular, we are talking about heavy bleeding after childbirth.
Hysteroscopy can be prescribed by a doctor in different situations, based on tests. If the patient’s painful picture requires this, then there can be no talk of any prohibitions. In such cases, the main thing is to undergo all the necessary tests and find out that a woman is allowed to undergo just such a procedure. The blood clotting indicator plays a particularly important role in the tests. Low coagulation levels can be a serious threat to a woman's life.
- Author: Boris
How did I become a doctor? Quite a difficult question... If you think about it, there was no choice. I was born into the family of a resuscitation doctor, and every day at dinner I heard my father’s story about how his day went. As a child, this all seemed fantastic, beyond reality. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Share with your friends!