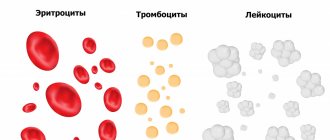
What is a biopsy
The invasive intervention is a simple gynecological operation performed on an outpatient or inpatient basis. The purpose of a biopsy is to collect cells and pieces of tissue intravitally for microscopic examination to determine the nature of the pathology.
Such a surgical intervention does not exclude the occurrence of various complications after the procedure. Before the analysis, the woman should be informed in detail about all possible consequences. Discharge after a cervical biopsy and slight bleeding in the first days should not disturb the patient. These symptoms are always present after such a diagnosis.
Pregnancy after cervical biopsy
Features of pregnancy after biopsy:
- After simple biopsy methods, you can become pregnant when the body’s rehabilitation is complete. This information can be clarified with your doctor after the procedure.
- If a large area of tissue was taken for analysis, pregnancy planning should be discussed with your doctor. He may advise you to delay conception and sexual activity until your cervix is completely healed. The recovery period will increase and additional examinations - ultrasound - will be required.
- During recovery, the uterus is most often incapable of fertilization. But if the patient becomes pregnant after the biopsy, there will be a risk of premature birth. Doctors put additional stitches on the wound to increase the chances of carrying a child.
- For nulliparous girls, the most gentle analysis methods are now used. If the procedure and recovery went without complications, you can become pregnant.
First, before conception, you need to consult a gynecologist.
Features of the procedure
Of course, every woman before a biopsy worries about possible complications. A competent doctor should explain the reasons for the invasive intervention, talk about the course of the operation and the resulting consequences. Brown discharge after a cervical biopsy may persist for several days.
Immediately after completion of medical procedures, the patient is given recommendations to help quickly recover from the diagnosis.
Puncture and conchotomy therapy
This type is used much more often than others and is carried out with a special needle. This operation is quite simple. There is no need to use anesthesia during this procedure, as it only lasts a few minutes.
This biopsy is named after the instrument used during the work - a conchotome (scissors with special sharp ends). During the procedure, local anesthesia is used. The discharge of bloody contents continues for about the next five days.
Indications for the procedure
The main task of a biopsy is to identify the presence of atypical pathological cells in the tissues of an organ. The following deviations may be the reason for ordering an analysis:
- dysplasia or ectopia of the cervix;
- oncology;
- precancerous conditions;
- infertility;
- papilloma virus;
- polyps or condylomas of the cervix.
An invasive diagnostic method is carried out in the first period of the cycle, 3-6 days after the end of menstruation. It is forbidden to do a biopsy at the time of maturation of the corpus luteum. In this case, the woman’s body will not have time to recover by the beginning of the next cycle.
The gynecological procedure itself lasts no more than half an hour under general or local anesthesia. Most often it is done on an outpatient basis. After the procedure, the patient needs to rest for 20–40 minutes, then she can go home.
In some cases, when it is necessary to take a large piece of tissue for analysis, the woman may be asked to go to the hospital for several days.
If the patient has had a cervical biopsy in the past and is planning a pregnancy, it is necessary to warn her doctor about this.
Reasons and features of a biopsy
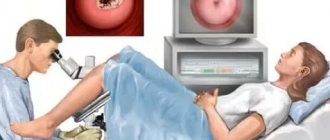
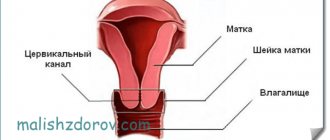
The procedure is a surgical intervention that results in the removal of a small piece of cervical tissue. A biopsy is performed at the very beginning of the menstrual cycle, when better cell regeneration is observed. Before performing the procedure, the patient must undergo examination to exclude the presence of infections. If they are detected, it is necessary to carry out appropriate therapy and only then prescribe tissue sampling.
There are several types of this procedure depending on the technique, instruments used, medications, etc. Regardless of the type, a woman is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse for several days before the procedure, and not to eat or drink anything for 12 hours.
Read more How to do biometrics of the cervix during pregnancy
A biopsy of the cervix is performed to identify abnormal cells. It is prescribed when the patient has been diagnosed with erosion, human papillomavirus, cervical dysplasia, oncological or precancerous condition of the cervix, polyps, and infertility.
Before prescribing the procedure, the doctor must check the woman for contraindications. These include:
- infectious diseases - until complete recovery;
- chronic diseases of the pelvic organs;
- poor blood clotting;
- hormonal disorders;
- pregnancy.
This gynecological procedure is usually performed on an outpatient basis. After it, it is recommended to rest for several hours in a medical facility and only then return home. If a large area was taken, the woman is usually placed in a hospital for two to three days.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that a biopsy is a simple and fairly quick procedure that does not require extensive invasive intervention, there are some contraindications to its implementation:
- Chronic inflammatory process of the pelvic organs.
- Violation of the hemocoagulation system.
- Pregnancy period.
- Various infectious diseases that can significantly distort the analysis results.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Weakened immunity.
Before performing a biopsy, the doctor must prescribe preliminary blood tests. When various pathologies are identified, their treatment will first be required. Invasive diagnosis is possible only after some time.
Failure to comply with these requirements can lead to the fact that the discharge after cervical invasion becomes intense and various complications develop. The woman will need medical attention.
Discharge after biopsy: norm and pathology
Normal consequences of the procedure
Cervical biopsy, as already noted, is traumatic. After the procedure, slight bleeding is considered quite normal. The degree, nature and duration of this phenomenon directly depend on the type of procedure and the amount of tissue taken for examination:
puncture
This is the most common biopsy and uses a special needle. The operation lasts about 10 minutes. No anesthesia is used. The procedure itself is not painful; the woman feels only a slight short-term tingling sensation. After it, light bleeding is considered normal.
Pink Bloody
Conchotomnaya
This is a procedure performed using scissors with pointed ends. During this procedure, local anesthesia is used in the area of the cervix. A natural consequence is considered to be pink discharge in women with drops of blood throughout the week.
Discharge with a drop of blood
Radio wave
The most gentle type of biopsy, which is often prescribed to women who have not given birth. After this least traumatic procedure, scant bleeding in a woman for three days is considered normal. You may also experience slight watery discharge on the first day after the procedure.
Light spotting
Laser
This is also not a very traumatic manipulation, however, the technique for performing it requires general anesthesia for the patient. Natural consequences of the procedure include white, pinkish or brown discharge throughout the week.
Pinkish Smearing cream
Loop
A type of biopsy that is performed with a special power tool. It is performed under local anesthesia. Over the next three weeks, discharge mixed with blood is observed.
Bloody Mixed with blood
Wedge-shaped
Wedge-shaped - used when a large area of tissue is removed. It is performed using a surgical scalpel and only under general anesthesia or epidural anesthesia (for the lower part of the body). After this procedure, the woman experiences severe pain and observes heavy discharge. The latter worry for up to two weeks.
Circular
This is also a large area biopsy. It is done using general anesthesia. Discharge and pain are present for up to four weeks. After this procedure, the patient is often prescribed pain medications.
After the biopsy, greenish or brown discharge may also appear.
Yellow-green Brownish
They will be considered normal if before the procedure the tissue collection site was treated with any medical solutions (for example, during colposcopy).
Pathologically dangerous discharge
As mentioned above, discharge after a cervical biopsy is a completely normal phenomenon. However, there are situations when such consequences become pathological and indicate the emergence of complications. So, you need to see a doctor if the discharge:
- acquired a bright scarlet or dark color;
- turned yellow two weeks after the procedure;
- have an unpleasant odor;
- come out in copious blood clots;
- are purulent in nature;
- observed for more than three weeks.
It is necessary to seek help, and urgently, when bleeding appears, as during menstruation.
A large amount of blood released may indicate poor clotting or non-compliance with the basic rules of the recovery period, which we will discuss below.
Among the main reasons for the appearance of bleeding or other dangerous discharge after this procedure, in addition to neglecting the basic recommendations of the doctor, are:
- Damage to the uterine walls during tissue sampling.
- Seam rupture.
- The beginning of the inflammatory process.
- Infection.
- Premature onset of menstruation due to hormonal or cyclic imbalance.
- Slow healing.
- Insufficient qualifications of the doctor who performed the biopsy.
Complications may occur if the patient has not been fully examined for various gynecological ailments. This is why initial tests are of great importance for the successful completion of a biopsy.
Consequences of the procedure
Typically, patients notice discharge after a cervical biopsy. Is this the norm? As a rule, this is a fairly common phenomenon and should be treated not as a pathology, but as a healing process.
The discharge may vary in color and intensity and continue until the next menstruation. There is no need to worry too much about this.
Usually after a cervical biopsy the discharge is bloody. In this case, the patient notes a slight nagging painful sensation in the lower abdomen. According to doctors, this can last 5-10 days. As the tissues heal, the discharge becomes more scanty. After menstruation, the cervix is completely cleared and bleeding stops.
It is not uncommon for a patient to notice yellow discharge after a cervical biopsy. This is also normal and does not require seeing a doctor.
If the bleeding becomes profuse and becomes threatening, we can talk about the development of a complication such as bleeding. It is necessary to immediately contact a gynecologist if you have the following ailments:
- The discharge is not very intense, but lasts more than 3 weeks.
- Severe bleeding of a bright color appeared.
- The temperature rose to 38 °C.
- The discharge has acquired a foul odor.
Such symptoms indicate the development of an infection and require immediate medical attention. The doctor must identify the cause of the complication and prescribe treatment.
How does the intensity of discharge depend on the type of biopsy?
The days of the menstrual cycle on which the procedure is performed affect the amount of discharge. In the first half of the menstrual cycle, it is safer to perform the procedure, and the cervix will recover faster.
Discharge after a cervical biopsy can be of different volumes and colors. This depends on the instruments used to perform the operation and the type of biopsy.
puncture
- a frequently used procedure that feels painless, so anesthesia is not needed;
- A sample of the material is taken from the patient using a special needle;
- a small wound remains that bleeds for 2 to 4 days.
- small bloody spots;
- scanty bleeding.
Conchotomnaya
The manipulation has a number of nuances:
- a painful procedure that takes place under local anesthesia using special scissors;
- After the manipulation, a small wound remains, which bleeds for about 7 days.
Features of discharge: pink, pink-red discharge during healing time.
Radio wave
- prescribed to nulliparous and pregnant women;
- The basis of this painless procedure is electric current;
- After taking a sample of the cervix, the device seals the wound site.
- watery;
- less often - scanty bleeding for 3 days.
Laser
- a painful procedure, performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia;
- a non-traumatic type of biopsy: the wound obtained during the process is immediately sealed with a laser.
- white, brown discharge for 7 days;
- sometimes bloody discharge for 2-3 days.
Loop
- carried out with a special tool in the form of a loop;
- the procedure is painful, so local anesthesia is given;
- Due to the use of electric current, the manipulation leaves a scar on the cervix.
- bleeding 1-3 weeks;
- pink and brown discharge.
Wedge-shaped
A wedge biopsy is performed as follows:
- the procedure is performed under general, epidural or spinal anesthesia;
- the sample is taken with a scalpel;
- After the manipulation, a large triangular wound remains.
- heavy bleeding for 2 weeks;
- discharge is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen.
Circular
The manipulation has the following specifics:
- According to reviews, this is a very painful procedure;
- during the process, spinal, general anesthesia, and epidural anesthesia are used;
- pain relief is given for several days after the biopsy;
- During the procedure, a large area of tissue is cut out.
- heavy bleeding for 2-4 weeks;
- Severe pain is also observed.
Curettage (scraping)
The manipulation is carried out in this way:
- due to severe pain, intravenous anesthesia is performed;
- They expand the cervical canal and take scrapings from the mucous tissue of the cervix.
- scanty discharge for 5-10 days;
- may smear as during menstruation.
Read more Synechiae of the vulva according to ICD 10
The complete absence of discharge after curettage is a pathology in which it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Why does bleeding occur?
There are many reasons for the appearance of heavy discharge after a biopsy procedure. Among them are the following:
- premature onset of menstruation due to cycle failure due to stress;
- poor healing of biopsy lesions;
- possible rupture of sutures as a result of non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations;
- infection of the uterus during invasive intervention;
- complete disregard for doctor's instructions during the recovery period.
In addition, the cause of spotting after a cervical biopsy may also be insufficient qualifications of the doctor. If the physician has not made sure that there are no contraindications to the biopsy, has not identified low-grade inflammatory processes in time, or has performed a traumatic invasive intervention, bleeding may become the main complication in the postoperative phase.
How many days does it bleed
Discharge that continues for 10-14 days is considered normal. They are dim and have a smearing character. Gradually their number decreases, and the condition returns to normal. If you bleed for more than 3 weeks, this may indicate a health problem.
The following manifestations indicate the development of a dangerous pathology:
- bright scarlet color of discharge;
- the presence of clots in the blood;
- intense bleeding;
- prolonged increase in body temperature;
- the appearance of an unpleasant purulent odor of discharge;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen, often cramping in nature;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- yellow-green color of discharge, indicating the presence of an inflammatory process or infection;
- low blood pressure;
- headaches and dizziness;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- development of weakness and fatigue.
Recovery period
After the procedure, the woman is strictly prohibited from lifting weights, going to the pool or swimming in the sea. It is necessary to completely avoid sexual relations and not be excessively physically active.
To minimize the risk of complications after the biopsy procedure, a woman should strictly follow all recommendations prescribed by her doctor. They include:
- You cannot take a bath, visit a bathhouse or sauna. For personal hygiene, it is recommended to use only the shower.
- Do not use medications that thin the blood.
- Do not use intravaginal suppositories or syringes.
- Completely abandon tampons and introduce sanitary pads.
If all recommendations are strictly followed, the discharge after a cervical biopsy will stop in a week, the state of health will return to normal, and the woman will continue her normal life.
The duration of the recovery period is individual for each patient and depends on strict compliance with all the gynecologist’s instructions.
Radio wave, loop and laser
Radio wave biopsy is performed with a special device. It is considered less traumatic, therefore it is allowed for nulliparous girls. There is almost no discharge after the procedure. Blood may begin to flow only after several days and in very small quantities.
Laser biopsy is performed using general anesthesia. This procedure is not traumatic, therefore it is considered relatively safe for the woman’s body. The bleeding process continues for five days. In this case, the blood does not flow, but comes out with a smearing consistency; the color of the discharge can vary from pink to brown.
Loop biopsy is also called electrosurgical because an electrical device is used to collect biological material. The biopsy is performed under local anesthesia. After the procedure, bleeding is characterized by a particular duration (about two weeks), as well as profuseness.
What should you be wary of?
If, after a cervical biopsy, the yellow discharge turns red-brown and continues for more than 2 weeks, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
In addition, general malaise, fever, migraine, lightheadedness and intense pain in the pubic area should alert you. You need to clearly know that if after the biopsy heavy bleeding begins, the discharge acquires a foul odor, or changes in consistency, you need to urgently visit a gynecologist. Typically, this clinical picture is characteristic of an associated infection.
Only timely contact with a specialist will help avoid further development of pathology and prevent complications.