What does research mean?
Representatives of the fairer sex should have a gynecological smear (for flora, for cleanliness) regularly. The analysis is a preventive one, prescribed during planning and to monitor the course of pregnancy and after childbirth. It must be carried out if the patient complains of:
- nagging, aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- burning and itching in intimate areas;
- pathological vaginal discharge (leucorrhoea, mixed with blood, pus);
- change in the consistency of the secretion;
- unpleasant odor;
- menstrual irregularities;
- problems with conception.
The results of the analysis are assessed collectively, determining the risk of the pathological process for the female reproductive system.
Table - Characteristics of the degrees of vaginal cleanliness by smear
| Purity level | Description |
| 1 (complete gynecological health, rare) | Acidic environment There are no pathogenic microbes No blood cells Lactobacilli and Dederline bacilli are detected |
| 2 (minor deviations, typical for most women) | Acidic environment Cocci are found in single quantities Up to 10 leukocytes, up to 5 epithelial cells |
| 3 (inflammatory process, often accompanied by unusual discharge or itching) | Alkaline environment Bacteria of the coccal group, fungi, and E. coli are detected The number of beneficial microorganisms is sharply reduced Moderately increased levels of leukocytes and key cells |
| 4 (there is an infectious disease) | Alkaline environment Microflora is represented by pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microbes Beneficial bacteria are not detected The number of leukocytes is sharply increased |
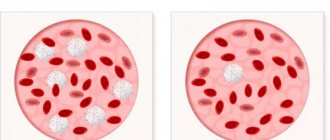
Leukocytes are protective blood cells. They provide systemic and local immunity, fight against agents foreign to the body (bacteria, viruses, toxins, allergens). The number of cells increases during inflammatory processes.
Under the influence of mediators, they are directed to the zones of invasion of pathological agents, enter the intercellular space, destroy and absorb the “killed enemy”. Thus, the number of leukocytes increases sharply at the site of inflammation. As cells are destroyed, they die and release mediators, causing infiltration, swelling, tissue irritation and thereby continuing the immune reaction.
In all environments of the body, a small number of leukocytes are always present. They protect them from pathogens. A sharp increase in concentration indicates an attack has taken place and the defense forces have been activated. An increase in the number of white cells in a smear indicates the development of an infectious or inflammatory process in the organs of the urogenital tract. The higher the concentration, the more intense the pathological changes.
White blood cell counts are important not only for healthy women, expectant and new mothers. Virgins may have deviations. They are caused by infections, allergic reactions, disturbances of the vaginal biocenosis and other factors.
Explanation of smear analysis
Data indicated in the smear analysis:
Leukocytes
The leukocyte rate depends on the location from which the smear was taken. Their content is normally small. In the urethra, the number of leukocytes is 0 – 5 – 10, in the vagina their concentration corresponds to 0 – 10 – 15, and in the cervical canal from 0 to 30.
During pregnancy, the content of leukocytes increases slightly and can range from 15 to 20 (in the vagina) in the field of view.
Flat epithelium
Flat epithelium lines the vagina, urethra and cervical canal. In normal smears, the number of epithelial cells ranges from 5 to 10. When the epithelium disappears (0 cells in the field of view), they speak of atrophy of the mucous membrane, and in the case of an increase in epithelial cells, inflammation.
Slime
The content of mucus in moderate quantities is considered normal in all three points, but it may be absent in the urethra.
Lactobacilli or Doderlein bacilli
Normal smears are characterized by a high content of them in the vagina, while they are absent in the cervix and urethra. When the number of lactic acid bacteria decreases, they speak of bacterial vaginosis.
Yeast
Fungi of the genus Candida are normally absent at all three points of smear collection, but their occasional presence in the vagina is allowed. An increase in yeast-like fungi indicates thrush.
"Key" cells
They are conglomerates of squamous epithelial cells and bacteria - gardnerella. Normally absent, the presence of such cells is a sign of gardnerellosis or bacterial vaginosis.
Leptothrix
Refers to anaerobic (living without air) gram-negative bacteria, often found in mixed infections, for example, thrush and bacterial vaginosis or trichomoniasis and chlamydia. If these bacteria are detected in a smear, an advanced analysis for sexually transmitted infections is indicated.
Others
- Mobiluncus - also refers to anaerobic microorganisms and is present in candidiasis or bacterial vaginosis.
- Trichomonas is a protozoan; normally they are absent from the smear.
- Gonococci - cause a sexually transmitted disease - gonorrhea, respectively, are normally absent.
- Escherichia coli - normally observed in single numbers in a vaginal smear. As the concentration of bacteria increases, bacterial vaginosis and neglect of personal hygiene are possible.
- Cocci - in gynecological smears are divided into gram-positive - colored blue and gram-negative - do not stain and remain pink. Gram-positive cocci include opportunistic bacteria: streptococci, staphylococci and enterococci, which are normally found in smears in single quantities. When their concentration increases, they speak of nonspecific vaginitis (colpitis).
Degrees of vaginal smear purity
When we talk about gynecological smears, we mean not only smears taken from the cervical canal, urethra and vagina, but also a separate type of smear that determines the degree of cleanliness of the vagina. The material is collected from the walls of the vagina and dried on a separate glass. There are 4 degrees of purity, but only degrees 1 and 2 are considered normal:
- 1st degree - leukocytes 0 - 5
It is considered an ideal option. The number of leukocytes is small, the microflora is mainly (up to 95%) represented by lactic acid bacteria, and there are only a few epithelial cells.
- 2nd degree - leukocytes 5 - 10
It is also normal, but opportunistic microorganisms (cocci or single yeast fungi) are detected in small quantities in the smear. Lactobacilli predominate, leukocytes and mucus are moderate, epithelial cells are normal.
- 3rd degree - more than 10 (up to 50)
The content of leukocytes increases, a lot of mucus and epithelium are detected. The concentration of Doderlein bacilli decreases due to an increase in opportunistic flora.
- 4th degree - leukocytes completely (cannot be counted)
Against the background of a huge number of leukocytes (the term “entirely” is indicated in the description of the smear), pathogenic microorganisms (gonococci, trichomonas) are determined. Doderlein's rods are not detectable, there is a lot of mucus and epithelial cells (a consequence of the inflammatory process).
If grade 3 and 4 purity of the vaginal smear is detected, it is necessary to establish the cause of inflammation and carry out treatment.
Norm
The average physiological indicator of leukocytes in a female flora smear is considered to be 15 units in the field of view of the microscope. However, for a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the urogenital tract, several samples of biomaterial are taken at once for research:
- from the inlet of the urethra (in the analysis indicated by the letter U);
- from the posterior wall of the vagina (V);
- from the cervical canal (C).
A vaginal smear may contain up to 15 leukocytes, a cervical smear - up to 10, and a urethral smear - up to 10 in the field of view. Depending on the degree of increase in the indicator, minor, moderate, and severe leukocytosis are distinguished.
An increase in the amount of up to 20 units is considered physiological during pregnancy, before the onset of menstruation, and for a certain period after childbirth. Such a deviation is not a sign of pathology if it is not combined with its other laboratory symptoms (abundance of mucus, phagocytosis, deviations of other parameters, abundance of epithelial and key cells).
Table - Norms of indicators in the analysis of gynecological smears
| Diagnostic criterion | V | C | U |
| Leukocytes | 0‒15 | 0‒10 | 0‒10 |
| Epithelium | less than 10 | less than 10 | less than 10 |
| Slime | no/moderate | no/moderate | No |
| Key cells | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| Gonococci | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| Trichomonas | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| Other flora | Gram-positive rods, lactobacilli | ‒ | ‒ |
| Candida | no or isolated | ‒ | ‒ |
As can be seen from the table, smear analysis reflects the presence of the most common sexually transmitted infections. However, negative results do not exclude the possibility of infection with other STIs. If, based on the study data, the gynecologist suspects sexually transmitted infections, additional tests will be required.
How to assess deviations from the norm
Blood donated for analysis contains a lot of information about what processes occur in the female body. As for the content of leukocytes in it, the following deviations from the norm may be observed:
- Leukocytosis - the number of leukocytes exceeds the established standard.
- Leukopenia – the content of white blood cells is less than normal.
- The structure of the leukocyte formula is disturbed - the ratio between the constituent leukocytes is incorrect.
- Excess immature blood cells.
Each of the identified violations should be examined by conducting additional tests. Only then can the doctor diagnose the disease and prescribe therapy.
Undesirable changes in the white blood cell count may include:
- Primary – caused by diseases of blood cells.
- Secondary – arising as a reaction of the female circulatory system to pathologies and damage to certain organs.
The causes of leukocytosis, if they are not related to the physiology of a woman, are as follows:
- injuries: bruises, dislocations, fractures, damage to internal organs;
- burns;
- bleeding;
- cardiac ischemia;
- anemia.
A decrease in the level of leukocytes compared to the norm is possible in the presence of infectious diseases, pathologies of the bone marrow and endocrine system, and problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
By the level of leukocytes, doctors judge how a woman’s recovery process is proceeding after undergoing chemotherapy due to a tumor of the breast or internal genital organs.
Leukopenia means a decrease in the body's resistance and requires adequate diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of leukocytosis
Disturbances in the composition of intimate microflora and an increase in the number of protective bodies can be suspected by symptoms. These include all signs of inflammatory changes in the pelvic organs and urinary system:
- burning, itching, increased sensitivity of mucous membranes;
- curdled, purulent, bloody discharge;
- bad smell of secretions;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- cycle disruptions (delays, premature and intermenstrual bleeding);
- failure to conceive within a year after stopping contraception;
- chronic cracks in intimate places;
- swelling and redness of the mucous membranes;
- rashes;
- urinary disorders (frequent urge, pain, impurities in urine).
Nonspecific symptoms of gynecological inflammation include fatigue, apathetic mood, and low-grade body temperature.
Why are leukocytes elevated?
Gynecologists recommend seeking help, undergoing examination and laboratory diagnostics for any symptoms of diseases of the female genital organs. In addition to physiological reasons, leukocytosis is caused by pathological ones. Remaining undiagnosed, they trigger acute and chronic inflammatory changes in the pelvis, which is fraught with purulent-necrotic and adhesive processes, leading to hormonal imbalances and infertility.
Infections
Pathogenic bacteria and viruses can enter a woman’s body through sexual contact, through blood, or if hygiene rules are violated. ( household) contact with carriers of STIs ( Sexually Transmitted Infections ) . Gynecological inflammation is caused by bacteria:
- gonococci (gonorrhea develops);
- Klebsiella (causes granuloma inguinale);
- pale spirochetes (syphilis);
- mycoplasma, ureaplasma (mycoureaplasmosis);
- chlamydia (chlamydia);
- Koch bacilli (tuberculosis);
- gardnerella (gardnerellosis, also known as bacterial vaginosis).
Approximately 60% of adult patients have a protozoal infection (trichomoniasis). Viruses (HIV, herpes, papillomavirus, cytomegalovirus) can provoke changes in indicators. The most common fungal infection is candidiasis, or thrush (caused by Candida albicans). Much less often, actinomycetes are the cause of inflammation.
Non-infectious provocateurs of leukocytosis
A shift in test results is not always a sign of a dangerous infection. Increased penetration of leukocytes into tissues can be caused by other factors:
- injuries to the mucous membranes (during sex, during and after childbirth, when performing hygiene procedures, other foreign objects);
- tumors (benign and malignant neoplasms change local immunity);
- kidney diseases (the source of leukocytes can be urine and the urological tract);
- diabetes mellitus, especially decompensated forms (acidity and blood circulation in the body changes, which entails microflora disturbances).
If there are deviations in the results of a gynecological smear examination, signs of nonspecific inflammation (caused by representatives of normal microflora) are often detected. The cause of the pathology is vaginal dysbiosis or another name - gardnerellosis (changes in the composition of the biocenosis in intimate areas). Normally, about 98% of all bacteria are lactobacilli. Up to 5% may be other microorganisms. Beneficial representatives of the flora inhibit their growth and prevent inflammatory diseases. The composition of the microflora changes and dysbiosis occurs against the background of:
- hormonal disorders, as well as when taking certain oral contraceptives;
- reduction of local and systemic immunity;
- hepatitis, kidney and intestinal pathologies;
- use of antibiotics;
- changes in the anatomical shape of the vagina (after trauma during childbirth, for example);
- radiation and chemotherapy;
- taking cytostatics, hormones, immunosuppressants;
- use of spermicides;
- oral, anal and other types of non-traditional sex;
- abuse or neglect of hygiene procedures;
- regular stress;
- allergies to hygiene products.
Usually the biocenosis is quickly restored. With significant violations, E. coli and other microorganisms multiply uncontrollably, causing tissue inflammation.
What diseases does leukocytosis indicate?
An increase in the level of protective bodies in smears may indicate inflammation of the pelvic organs of any localization. Deviations in analyzes accompany:
- colpitis (inflammatory changes in the vagina);
- endocervicitis and cervicitis (damage to the cervix);
- endometritis (mucous membranes of the uterus);
- adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages);
- urethritis, cystitis (damage to the bladder and urethral canal).
If there are no signs of the listed diseases, the doctor will suspect dysbiosis or tumors and prescribe additional examinations.
How to lower your white blood cell count
Sometimes an increase in leukocytes in a smear may not be associated with the woman’s health condition, but with a medical error or incorrect analysis.
That is why it is recommended to do not one, but two analyzes to eliminate error. Moreover, when their level is slightly increased, it is necessary to sanitize the vagina especially carefully, and only then do a secondary analysis. For such sanitation, decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, St. John's wort, aloe leaf juice, and oak bark are ideal.
If, after repeated analysis, leukocytes are again elevated, but only slightly, this is considered the first sign of vaginal or intestinal dysbiosis. Then you need to take a smear on the flora, which will clarify the picture. Only after repeated analysis and a smear on the flora, the doctor will be able to clearly determine the cause of their increase and the disease. And only then competent treatment of the problem will begin.
If the inflammatory process has not started, warm baths (at least 45 degrees) will help, which can stop the inflammation process by warming up. After them, it is very good to douche with a solution of chlorophyllipt or chamomile decoction. Before using any of these drugs, you should definitely consult your doctor.
There are vaginal suppositories that are designed specifically for such cases - to reduce the level of leukocytes. But they also must be strictly prescribed by a doctor.
Self-medication is not suitable here; the disease can be advanced in such a way that it will then require a lot of time and effort to treat it. Therefore, if there is an increase in leukocytes in the smear, it is best to undergo a full examination by a specialist.
Only after such a complete examination will the doctor be able to prescribe a treatment regimen for the problem that has arisen. The inflammatory process will not resolve on its own - this is not a simple runny nose that goes away in a week.
A woman’s internal genital organs have a number of features that make it difficult to quickly remove inflammation. And the more inflammation starts, the worse the consequences will be.
All organs of a woman, both reproductive and urinary and urine-forming, are closely connected. And inflammation of one organ without timely treatment can spread to neighboring organs.
This is why constant and regular testing for the content of leukocytes in a smear is so important - it can detect the onset of the disease at the earliest stages, when treatment can be quite simple. When such an increase in the level of white blood cells is observed in a pregnant woman, and she does not carry out the necessary treatment, the consequences can be very unfavorable
This includes early miscarriage, chronic miscarriage, and even infertility.
When such an increase in the level of white blood cells is observed in a pregnant woman, and she does not carry out the necessary treatment, the consequences can be very unfavorable. This includes early miscarriage, chronic miscarriage, and even infertility.
Any increase in the level of leukocytes, both in a pregnant woman and without pregnancy, is the body’s cry for help!
In order to prevent your body from “screaming” often, you need to carefully monitor the sanitization of your genitals, avoid hypothermia, intimate contacts with untested partners or frequent changes of sexual partners. And, most importantly, consult a gynecologist regularly, and also regularly have a smear test. Leukocytes in a smear in women should always be normal.
It is easier to “catch” a disease at the initial stage and treat it than to then spend a long time and persistently getting rid of the consequences and complications!
Increase in leukocytes during pregnancy
Expectant mothers undergo gynecological smears at least 3 times during pregnancy. This is necessary to monitor the state of women’s health and timely detection of infectious and inflammatory changes. An increase in indicators to 15–20 units is considered a physiological norm associated with the activation of local immunity due to hormonal changes.
If an increase in the number of cells above these values is detected, the doctor suspects infection. With a decrease in systemic immunity, an exacerbation of chronic inflammation or activation of latent microbial diseases is possible. The sooner they are detected, the sooner treatment will begin, and the mother and fetus will be out of danger.
In addition to the smear results, you will need to undergo PCR or ELISA tests for infections; if necessary, a culture of biomaterial will be carried out to determine the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics. If the examination does not yield results, the obstetrician-gynecologist will prescribe local treatment (with drugs with antiseptic properties in the form of suppositories). If deviations persist after a control analysis, broad-spectrum antibiotics will be selected (taking into account the timing of pregnancy).
Expectant mothers cannot ignore leukocytosis. STIs are dangerous due to complications of pregnancy, premature termination, intrauterine or intrapartum infection of the fetus.
Physiology of a woman and the norm of leukocytes
Natural physiological processes that constantly occur in the female body lead to excess leukocytes. These include:
- the period just before the start of menstruation;
- the onset of pregnancy;
- postpartum period.
Carrying a child and subsequent childbirth is a serious burden on the female body. Within it, restructuring and adaptation are carried out, requiring the use of additional resources and capabilities. The woman's immune system begins to function with increased productivity. A slightly larger number of leukocytes are produced.
From the twenty-eighth week (the beginning of the third trimester) of bearing a child, their content for the expectant mother can be 15 × 109. The norm is exceeded by more than one and a half times.
They are mainly concentrated in the area of the uterus, and their purpose is to stimulate its contraction, prevent infection and protect the baby.
With the onset of labor, the number of leukocytes again increases rapidly and can reach 30 × 109, which is three times the norm. This is how the body prepares for significant blood loss. And it is inevitable when a woman gives birth to a baby.
Over the course of several days after childbirth, the body gradually recovers. This is accompanied by increased production of leukocytes, which promotes the healing of damaged tissue. White blood cells return to normal on the third to fifth day after the baby is born.
If this does not happen, then postpartum complications are possible.
During menstruation or headaches, women often take painkillers. This may cause your white blood cell count to become lower than normal.
Antibiotics and drugs that help lower blood sugar have a similar effect. Taking hormonal contraceptives may affect changes in blood composition. All of these drugs should not be taken uncontrolled. Those medications that negatively affect the level of white blood cells should be excluded from your first aid kit.
Increased white blood cells in a smear after childbirth
When analyzing intimate flora in the postpartum period, deviations (up to 45 units) are physiological. They are caused by injuries and regeneration processes in the uterus and vagina. Changes in indicators can be traced until the lochia are completely discharged and normalize after 40–45 days. It is then that it is recommended to take the test in order to get the most reliable results. The smear is examined earlier if:
- before giving birth, the woman was diagnosed with and treated for an STD (to monitor the effectiveness of therapy);
- there are complaints indicating inflammation;
- symptoms of cystitis appeared.
The reasons for the increase in indicators are similar to those for healthy women and require the attention of a doctor.
Examination of the number of leukocytes in a vaginal smear
Errors begin with incorrect sampling of material for research, continue at the stage of analysis and calculations, and end at the decoding stage, since even medical workers incorrectly interpret what the norm of leukocytes is in the vaginal contents.
Smears are taken with disposable instruments, but a separate instrument is needed to collect material from each point.
If you need to examine the composition of a smear from the vagina, cervix and urethra, then it is unacceptable to do this with one instrument, there should be three.
The smear material for counting the number of leukocytes should be applied to the laboratory glass in as thin a layer as possible, performing as few smearing movements as possible, which destroy the epithelial cells.
Examination of a thick layer of vaginal contents under a microscope and smearing movements lead to many false-positive results.
Granulocytes are the main phagocytes of the uterus. Any medical textbook or article contains information that an increase in their number serves as an indicator of the inflammatory process.
Indeed, the increased content of granulocytes in a smear on the flora of vaginal discharge allows us to make an assumption about the focus of inflammation
To understand whether an inflammatory process is occurring, it is important to correctly count the number of granulocytes
In the post-Soviet space, the overwhelming majority of laboratories count the total number of leukocytes in the field of view, which leads to erroneous conclusions about the presence of an inflammatory process and the prescription of potent drugs, often even without any special symptoms or complaints from patients.
At the same time, doctors are interested in only one function of phagocytes - to absorb pathogens, and completely ignore another - to absorb and assimilate dead cells and tissues.
The massive death of cells in the uterine mucosa, combined with the presence of blood, becomes a favorable environment for the development of microorganisms that can penetrate the uterus from the vagina.
In this case, phagocytes play the role of orderlies - they clean the surface of the uterus after exfoliating excess cells so that viruses, bacteria or fungi cannot gain a foothold in these areas.
Video:
Agranulocytes, macrophages before menstruation, make up a fifth of all leukocytes in the uterus and vaginal secretions.
Their task is to use special enzymes to break down dead cells of the uterine mucosa and produce substances that promote rapid tissue restoration.
Having received alarming results of a smear on the vaginal flora, do not rush to panic, especially in the absence of serious symptoms and before consulting with a trustworthy specialist.
How to give a smear correctly
To get accurate results of a flora test, a woman must properly prepare for the test. It is better to go to the clinic in the middle of the cycle. 1–2 days before the test, you should not have sex, douche with any solutions, or use cosmetics and detergents with a spermicidal or antibacterial effect. Hygiene before the procedure consists of washing with warm water without soap the night before. It is advisable not to urinate 2 hours before sampling.
How the analysis is done
A doctor or laboratory technician takes a smear (usually in antenatal clinics). To do this, the woman should sit in the gynecological chair and relax. Biomaterial from different places is obtained using cytobrushes (most preferable), a Folkaman spoon, a bacteriological loop or an Eyre spatula. The procedure takes a few minutes and is usually painless. The material is placed on a glass slide, labeled, and sent to the laboratory. Here the laboratory assistant stains the samples and examines them under a microscope (counts the number of cells) and enters the information into the protocol.
Flora smear
A flora smear can be performed as one of the elements of a preventive examination, or prescribed if the presence of gynecological diseases is suspected. Indications for testing are:
- presence of pain in the lower abdomen;
- there are disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- a woman experiences discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- pathological vaginal discharge is observed;
- the woman is pregnant;
- there is itching and burning during urination;
- a woman is forced to take antibiotics, hormonal agents and other drugs for a long period of time.
Many pathologies are asymptomatic in the first stages. To detect them early, it is recommended to have a pap smear every three months. The material is collected from the walls of the vagina, cervix or urethra. To carry out the procedure, a disposable spatula is used. The process does not require much time. It is not associated with pain. Taking a smear causes discomfort only if the walls of the urethra are damaged. This is possible if there is an infection or inflammatory process.
It is necessary to prepare for taking a smear. It must be taken into account that a number of factors can lead to distortion of the results. Therefore, experts recommend abstaining from sexual intercourse 3 days before visiting the doctor. A week before the study, you must stop using any form of medication. 2 days before the test, soap and gel should not be used for hygiene of the external genitalia. Only warm water is allowed. The last cleansing of the external genitalia is carried out the evening before visiting the doctor. 3 hours before your visit to a specialist, you should not urinate.
A smear is not taken during menstruation. The exception is situations when urgent diagnostics are necessary. The best time is considered to be the first days after menstruation or shortly before its onset.
What are the deviations?
Sometimes a smear analysis shows not only leukocytosis, but also its causes:
- a low proportion of beneficial lactobacilli indicates dysbiosis;
- candida indicates a fungal infection;
- Trichomonas - about trichomoniasis;
- gonococci - about gonorrhea.
However, the smear is not tested for other STIs, but simply indicates that there is inflammation, but it is not known of what nature. Detecting them will require specific research. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) tests are carried out to detect HIV infection, herpes virus, and syphilis provocateur. PCR diagnostics involves studying the blood or secretions of the vagina, cervix for other pathogens (fungi, protozoa, ureaplasma, mycoplasma and others).
Comprehensive information about the state of the body is provided by blood and urine tests. The nature of tissue changes is learned from cytological and histological analyzes of smears. Ultrasound is prescribed to visualize the pelvic organs. By studying the results of all diagnostic procedures, the gynecologist makes a diagnosis and selects treatment.
Diagnostic methods
The first step is often a repeat smear to rule out improper preparation for the test or other physiological factors. If leukocytes are again far from normal, then the following diagnostic measures are justified:
- Smears for bacterial culture from the cervical canal and vagina - in order to identify the pathogen and the appropriate means of antibacterial therapy (specialized or broad-spectrum).
- Urogenital PCR smear - allows you to detect a viral or bacterial infection long before the first symptoms appear.
- A smear for cytology makes it possible to detect inflammatory or tumor processes in the cellular layer of the cervix.
- ELISA and PIF methods - as a supplement or replacement for PCR diagnostics.
- Blood test for the presence of antibodies using ELISA or PCR techniques.
- Ultrasound of the genital organs and biopsy - if tumor structures are detected.
- Colposcopy – to examine the cervix and/or take a biopsy.
You may also need examinations and consultations with specialized specialists - an endocrinologist, urologist or allergist.
How to eliminate deviations in the analysis of vaginal cleanliness
Therapy is not aimed at correcting leukocytosis (since this is only a diagnostic sign), but at eliminating its cause - an inflammatory or infectious process. For this purpose, drugs of local and systemic action are prescribed. The list of medications depends on the cause and essence of the pathological changes.
Douching
To cleanse intimate cavities, procedures with Chlorhexidine, potassium permanganate solution, Miramistin, and Yoddicerin are prescribed. The products not only disinfect mucous membranes, but also purely mechanically wash away bacteria and dead epithelial cells. Douching is carried out 1-2 times a day for 5-7 days in parallel with other methods of drug treatment. Intravaginal administration of antiseptics is contraindicated in pregnant women.
Candles
Suppositories are used to treat almost all gynecological disorders. Drugs are selected taking into account the nature of the pathogen or a broad-spectrum medication is prescribed.
Table - Popular suppositories for the treatment of gynecological inflammation
| Group of drugs | Name | Mode of application |
| Antifungal | Pimafucin | 1 candle per night, 6‒10 days |
| Livarol | 1 candle per night, 6–12 days | |
| Anti-inflammatory | Revmoxicam | 1 suppository 2 times, rectally, up to 5 days |
| Dicloberl | 1 piece each 1–2 times rectally, up to 5 days | |
| Antibacterial | Hexicon | 1-2 pcs. per day, up to 14 days |
| Betadine | 1 sup. per day 7 days | |
| Healing | Sea buckthorn oil | 1 candle per night, 7-10 days |
| Vagical | 1 sup. 2 times a day, up to 10 days | |
| Complex action | Terzhinan | 1 tablet intravaginally, 10–14 days |
| Polygynax | 1 capsule intravaginally, 10–14 days | |
| Antimicrobial | Flagyl | 1 suppository per day, 7‒10 days |
| Trichopolum | 1 tablet per day, 10 days |
Surface treatment products
If the inflammatory process or fungus spreads to the external genitalia, the doctor may prescribe irrigation with antiseptic agents (Chlorhexidine, aqueous solution of Furacilin, Betadine, Citeal). They are used upon completion of hygiene procedures. Unlike douching, irrigation of the external genitalia is allowed for pregnant women.
To treat candidiasis, ointments and creams with antimycotics are often prescribed. they are used in parallel with suppositories. Treatment of the external genitalia is carried out 2-3 times a day, after hygiene.
An alternative to suppositories are vaginal creams (Lomexin, Kolpotrofin, Dalatsin, Macmiror). They can be inserted into the vagina using a special applicator or used externally.
Other means
In complex therapy of gynecological diseases, antibiotics are prescribed taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen. Such therapy is necessary for myco- and ureoplasmosis, chlamydia, and other infectious diseases. The fact is that pathogenic microorganisms reside not only on the surface of the mucous membranes, but also in their depths, and are capable of persisting in the body. Local treatment in this case is not enough and systemic drugs cannot be avoided. They cannot be used independently due to the risk of developing microbial resistance and chronic pathology.
Table - The most popular antibiotics for use in gynecology
| Drug name | Mode of application |
| Doxycycline | 100 mg twice a day for 7 days |
| Roxithromycin | 150 mg twice a week |
| Josamycin | 500 mg 3 times a day for 10 days |
| Levofloxacin | 500 mg 10 days |
In difficult cases, therapy is supplemented with immune stimulants. They increase the body's support capacity and accelerate the suppression of bacterial or viral infections.
Table - Immunomodulators for gynecological diseases
| Drug name | Mode of application |
| Cycloferon tablets | 3-4 tablets per day according to the scheme |
| Viferon-feron 1‒3 million IU | 1 suppository 2 times a day, up to 10 days |
| Timalin Liof. for injection | 1 injection 1 time per day, 10 days |
Reduced values
If a woman’s blood test shows less than 4x109/l of leukocytes, this condition is considered leukopenia, and is always associated with a breakdown of the immune system.
It can be temporary if provoked by taking certain medications, such as analgin, and other painkillers, for migraines or painful periods. The level of leukocytes in the blood must be monitored. Deciphering the analysis with low values may indicate the presence of the following problems in the body:
- Malfunctions in the bone marrow, where white blood cells are formed and mature. Its functioning can be affected by physical injury, disease, and internal defects.
- Lack of certain components involved in the formation of leukocytes: folate, vit. B1, B12, copper and iron. At the same time, the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood decreases. After eliminating the causes of the deficiency of substances necessary for synthesis by adjusting the diet, the indicator returns to normal.
- Increased destruction of leukocytes under the influence of potent medications (antibiotics, antiepileptics, anticancer and anti-inflammatory drugs).
- For diseases caused by a bacterial or viral infection, which include measles, influenza, HIV, hepatitis, rubella.
- In case of starvation or severe exhaustion, depression, low blood pressure.
- With B12 deficiency anemia.
- In case of radiation sickness and in the first stages of leukemia.
- With an unfavorable hereditary predisposition.
- For autoimmune diseases.
Treatment of leukopenia is aimed at combating the underlying disease or the cause that caused it. Antihistamines or steroids are used to eliminate inflammation. If the drop in white blood cell levels is caused by cancer, chemotherapy is used.
In exceptional cases, they resort to the procedure of leukophoresis, in which excess leukocytes are removed from the blood.
Traditional methods of treatment
Inflammations in the field of gynecology, manifested by an increase in the level of leukocytes, are recommended to be eliminated using available means. Douching is considered the most effective:
- with herbs (sage, chamomile, eucalyptus, St. John's wort);
- whey (especially appropriate for candidiasis);
- a solution of iodine, salt and soda;
- infusion of garlic (5 cloves per liter of boiling water).
Tampons with a mixture of aloe and honey are recognized as a universal remedy against erosion, inflammation and infections. They are inserted into the vagina every day at night for 10–14 days.
Treatment recommendations
If the cause of abnormalities in the smear is an inflammatory disease, it is important to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions and undergo full treatment. Until recovery, you should stop using any medications (which the doctor does not know about), bad habits, and sexual intercourse. Traditional methods of therapy should be used only after the approval of a specialist.
In some cases, indicators do not return to normal even with treatment. Then the gynecologist suggests that the woman undergo a comprehensive examination (including hormones, tumor markers), normalize her work and rest schedule, and eliminate the influence of stress or excessive physical activity.
Prevention of violations
To prevent an increased white blood cell count as a result of a clean smear, all STI prevention measures and good hygiene should be followed:
- have sexual intercourse with one trusted partner;
- use condoms in dubious relationships;
- change your underwear regularly (preferring natural fabrics);
- use personal hygiene products only as directed;
- refuse self-medication;
- eat rationally;
- leave bad habits.
Neglect and excessive attention to hygiene are equally harmful for women. Deep washing and douching (without a doctor's prescription) can cause disturbances in the intimate microflora.
What to remember
The leukocyte count in a gynecological smear is an important laboratory sign that helps to identify many dangerous diseases. To eliminate errors and correctly understand the analysis information, you need to remember:
- the number of leukocytes increases before menstruation, during pregnancy, after childbirth, which is not considered a pathology;
- the average norm is 15 units in the field of view of the microscope;
- 2 days before the test you cannot take medications, have sex, douche, or use suppositories;
- a significant increase in level accompanies gynecological inflammation;
- the more serious the disease, the higher the number of protective cells;
- The gynecologist should evaluate the test results and prescribe treatment.
This is interesting!
A sharp increase in the number of white blood cells in a smear may indicate a sexually transmitted disease. The pathogen cannot always be identified based on the results of the analysis (after all, only the presence of the main pathogens is assessed). The woman being tested will be given other STI tests, but her partner will not. In this case, re-infection is possible. An increased number of leukocytes in a woman’s smear indicates the need to examine a man with whom the patient has sexual contact. For this it is better to use the PCR method. Read all about the polymerase chain reaction and its advantages over other studies in the article at the link.
Diagnosis and treatment
If a woman has an increase in the number of leukocytes in a smear, it is necessary to establish the cause that provoked this phenomenon. Typically, an increase in the number of white blood cells is accompanied by an increase in opportunistic microflora, which allows one to immediately suspect a particular disease. However, in practice, only leukocytes can increase, and specific pathogens are absent. In this situation, the gynecologist will direct the woman to take a smear test again, choosing the most successful day of the menstrual cycle and recommending that she properly prepare for the test. If an increase in the number of white blood cells is observed in a repeat smear, an extended examination is carried out. Can be done:
- PCR for sexually transmitted infections. The method allows you to identify hidden diseases that may not manifest themselves clinically, but can lead to infertility.
- Colposcopy. The study is an examination of the cervix under multiple magnification. The method allows you to detect leukoplakia, dysplasia or cancer at the initial stage.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Various tumor formations can provoke an increase in the number of leukocytes, which can be diagnosed using ultrasound.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor can refer the patient to related specialists. So, if a woman is overweight, has thyroid disease or diabetes, she will need to consult an endocrinologist. If diseases of the urinary system are detected, they are referred to a nephrologist. Consultation with an allergist is required if there is a suspicion of an increase in the number of leukocytes as a result of exposure to various irritating factors. If the reason for the deviation from the norm is neurosis, treatment is prescribed by a neurologist.
Therapy directly depends on the cause that provoked the increase in the number of leukocytes. Most often, their growth occurs as a result of inflammation. In this situation, local or general treatment can be carried out. The first category includes medicinal douching. The course is short. Its duration usually does not exceed 4-5 days. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe the use of suppositories. Then the normal vaginal microflora is restored. If the patient has infections or sexually transmitted diseases, antiviral drugs or antibacterial therapy are prescribed.